1. Introduction
CGAN improves the quality of generated data by combining tag information and SGAN improves the quality of generated data by reconstructing tag information. So can we use both? The answer is obvious, because ACGAN does this. For more details, see the paper Conditional Image Synthesis with Auxiliary Classifier GANs
2. Model structure
The input of G is classified label and fixed distribution noise, and the output of D is true or false and classified label.
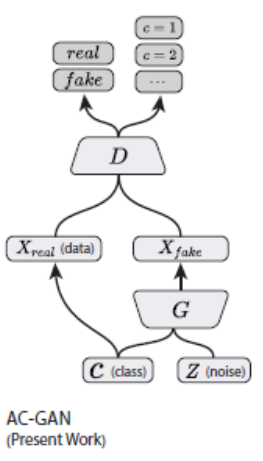
Ls is the loss of true or false judgement, Lc is the loss of classification, D is trained to maximize LS + LC while G is trained to maximize LC-LS.
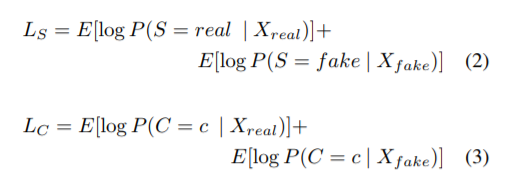
3. Model characteristics
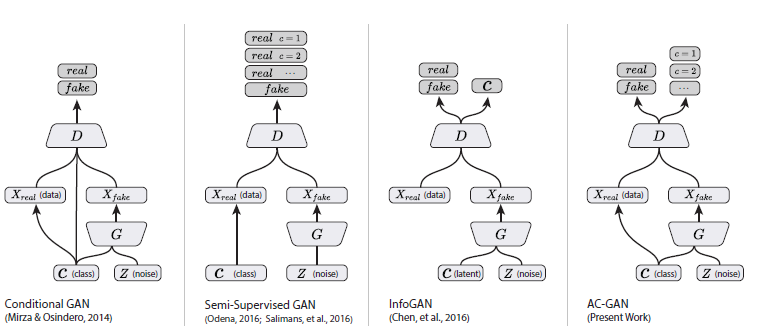
CGAN (see Introduction to CGAN and Code Practice (See also SGAN) SGAN Introduction and Code Practice InfoGAN (see InfoGAN Introduction and Code Practice ACGAN obviously combines these three characteristics.
4. Code implementation keras
class ACGAN():
def __init__(self):
# Input shape
self.img_rows = 28
self.img_cols = 28
self.channels = 1
self.img_shape = (self.img_rows, self.img_cols, self.channels)
self.num_classes = 10
self.latent_dim = 100
optimizer = Adam(0.0002, 0.5)
losses = ['binary_crossentropy', 'sparse_categorical_crossentropy']
# Build and compile the discriminator
self.discriminator = self.build_discriminator()
self.discriminator.compile(loss=losses,
optimizer=optimizer,
metrics=['accuracy'])
# Build the generator
self.generator = self.build_generator()
# The generator takes noise and the target label as input
# and generates the corresponding digit of that label
noise = Input(shape=(self.latent_dim,))
label = Input(shape=(1,))
img = self.generator([noise, label])
# For the combined model we will only train the generator
self.discriminator.trainable = False
# The discriminator takes generated image as input and determines validity
# and the label of that image
valid, target_label = self.discriminator(img)
# The combined model (stacked generator and discriminator)
# Trains the generator to fool the discriminator
self.combined = Model([noise, label], [valid, target_label])
self.combined.compile(loss=losses,
optimizer=optimizer)
def build_generator(self):
model = Sequential()
model.add(Dense(128 * 7 * 7, activation="relu", input_dim=self.latent_dim))
model.add(Reshape((7, 7, 128)))
model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8))
model.add(UpSampling2D())
model.add(Conv2D(128, kernel_size=3, padding="same"))
model.add(Activation("relu"))
model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8))
model.add(UpSampling2D())
model.add(Conv2D(64, kernel_size=3, padding="same"))
model.add(Activation("relu"))
model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8))
model.add(Conv2D(self.channels, kernel_size=3, padding='same'))
model.add(Activation("tanh"))
model.summary()
noise = Input(shape=(self.latent_dim,))
label = Input(shape=(1,), dtype='int32')
label_embedding = Flatten()(Embedding(self.num_classes, 100)(label))
model_input = multiply([noise, label_embedding])
img = model(model_input)
return Model([noise, label], img)
def build_discriminator(self):
model = Sequential()
model.add(Conv2D(16, kernel_size=3, strides=2, input_shape=self.img_shape, padding="same"))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(Dropout(0.25))
model.add(Conv2D(32, kernel_size=3, strides=2, padding="same"))
model.add(ZeroPadding2D(padding=((0,1),(0,1))))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(Dropout(0.25))
model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8))
model.add(Conv2D(64, kernel_size=3, strides=2, padding="same"))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(Dropout(0.25))
model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8))
model.add(Conv2D(128, kernel_size=3, strides=1, padding="same"))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(Dropout(0.25))
model.add(Flatten())
model.summary()
img = Input(shape=self.img_shape)
# Extract feature representation
features = model(img)
# Determine validity and label of the image
validity = Dense(1, activation="sigmoid")(features)
label = Dense(self.num_classes, activation="softmax")(features)
return Model(img, [validity, label])
def train(self, epochs, batch_size=128, sample_interval=50):
# Load the dataset
(X_train, y_train), (_, _) = mnist.load_data()
# Configure inputs
X_train = (X_train.astype(np.float32) - 127.5) / 127.5
X_train = np.expand_dims(X_train, axis=3)
y_train = y_train.reshape(-1, 1)
# Adversarial ground truths
valid = np.ones((batch_size, 1))
fake = np.zeros((batch_size, 1))
for epoch in range(epochs):
# ---------------------
# Train Discriminator
# ---------------------
# Select a random batch of images
idx = np.random.randint(0, X_train.shape[0], batch_size)
imgs = X_train[idx]
# Sample noise as generator input
noise = np.random.normal(0, 1, (batch_size, 100))
# The labels of the digits that the generator tries to create an
# image representation of
sampled_labels = np.random.randint(0, 10, (batch_size, 1))
# Generate a half batch of new images
gen_imgs = self.generator.predict([noise, sampled_labels])
# Image labels. 0-9
img_labels = y_train[idx]
# Train the discriminator
d_loss_real = self.discriminator.train_on_batch(imgs, [valid, img_labels])
d_loss_fake = self.discriminator.train_on_batch(gen_imgs, [fake, sampled_labels])
d_loss = 0.5 * np.add(d_loss_real, d_loss_fake)
# ---------------------
# Train Generator
# ---------------------
# Train the generator
g_loss = self.combined.train_on_batch([noise, sampled_labels], [valid, sampled_labels])
# Plot the progress
print ("%d [D loss: %f, acc.: %.2f%%, op_acc: %.2f%%] [G loss: %f]" % (epoch, d_loss[0], 100*d_loss[3], 100*d_loss[4], g_loss[0]))
# If at save interval => save generated image samples
if epoch % sample_interval == 0:
self.save_model()
self.sample_images(epoch)
def sample_images(self, epoch):
r, c = 10, 10
noise = np.random.normal(0, 1, (r * c, 100))
sampled_labels = np.array([num for _ in range(r) for num in range(c)])
gen_imgs = self.generator.predict([noise, sampled_labels])
# Rescale images 0 - 1
gen_imgs = 0.5 * gen_imgs + 0.5
fig, axs = plt.subplots(r, c)
cnt = 0
for i in range(r):
for j in range(c):
axs[i,j].imshow(gen_imgs[cnt,:,:,0], cmap='gray')
axs[i,j].axis('off')
cnt += 1
fig.savefig("images/%d.png" % epoch)
plt.close()