Reflection: the soul of frame design
- Framework: semi-finished software, which can be developed on the basis of framework and simplify code
- Reflection: encapsulates the components of a class as other objects, which is the reflection mechanism
- Benefits:
- These objects can be manipulated during program execution
- It can be decoupled to improve the scalability of the program
**Java code goes through three stages in the computer:
Source code stage, Class object stage, Runtime runtime stage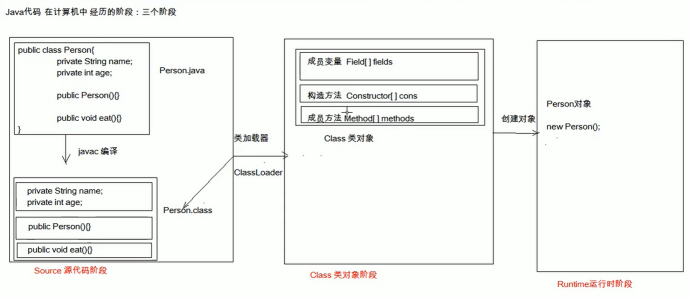
-
How to get the Class object:
- Class.forname: load the bytecode file into memory and return the class object
- Most of them are used for configuration files, and the class name is defined in the configuration file. Read file, load class
- Class name. Class: obtained by the attribute class of class name
- Mostly used for parameter passing
- Object. getClass(): the getClass() method defines the
- How to get bytecode for objects
-
Conclusion:
The same bytecode file (*. class) will only be loaded once during a program run, and the class object obtained in any way is the same. -
Class object function (get function):
- Get member variable
- Field[] getFields(): get all public decorated member variables
- Field getField(String name): gets the public decorated member variable of the specified name
- Field[] getDeclaredFields(): get all member variables without considering modifiers
- Field getDeclaredField(String name): gets the member variable with the specified name
- Get construction method
- Constructor<?>[] getConstructors()
- Constructor getconstructor (class <? > parameterTypes)
- Constructor<?>[] getDeclaredConstructors()
- Constructor getdeclaredconstructor (class <? > parameterTypes)
- Get member method
- Method[] getMethods()
- Method getmethod(String name, class <? > parameterTypes)
- Method[] getDeclaredMethods()
- Method getDeclaredmethod(String name, class <? > parameterTypes)
- Get class name
- String getName()
- Get member variable
-
Field: member variable
- Operation:
- Set value void set(Object obj,Object value)
- Get value get(Object obj)
- Ignore security check for access modifier
- setAccessible(true): violent reflection
-
Constructor: construction method
- Create object:
- T newInstance(Object... initargs)
- If you use the empty parameter construction method to create an object, the operation can be simplified:
newInstance of Class object
-
Method: Method Object
*Execution method:
*Object invoke(Object obj, Object... args) -
Get method name:
-
String getName: get method name
-
Case study:
- Requirement: write a "framework" that can help us create objects of any class and execute any methods of any class without changing any code of the class
- Realization:
- configuration file
- reflex
- Steps:
- Define the full class name of the object to be created and the method to be executed in the configuration file
- Load read profile in program
- Using reflection technology to load class files into memory
- create object
- Execution method
-
Case code (get Class object function):
- Create a class
package product; public class Person { public String name = "Zhang classmate"; public void eat(){ System.out.println("Person eating..."); } }
- Create a Class that can get the function of Class object
package product; import java.lang.reflect.Field; import java.lang.reflect.Method; public class ClassObject function { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { //Get the Class object of Person Class PersonClass = Person.class; Method[] b = PersonClass.getDeclaredMethods(); for (Method e:b) { System.out.println(e); } //Get the value of member variable name Field c = PersonClass.getField("name"); Person p = new Person(); Object d = c.get(p); System.out.println(d); } }
3. Test results: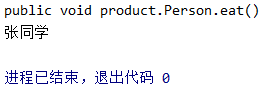
- Case code (Note: the profile must be at the same level as the package):
- Create a class to test
package product; public class Person { public void eat(){ System.out.println("Person eating..."); } }
- Create a configuration file (file suffix is. properties)
className = product.Person //Full class name of test class methodName = eat //Methods to be tested
3. Create a class that can load configuration files
package product; import java.io.InputStream; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import java.util.Properties; @SuppressWarnings("all") public class reflectTest { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { //1 load profile //1.1 create Properties object Properties pro = new Properties(); //1.2 loading configuration files, converting to a collection //1.2.1 get the configuration file under the class directory ClassLoader classLoader = reflectTest.class.getClassLoader() ; InputStream is = classLoader.getResourceAsStream("pro.properties"); pro.load(is); //2 get the data defined in the configuration file String className = pro.getProperty("className"); String methodName = pro.getProperty("methodName"); //3 load this class and enter memory Class cls = Class.forName(className); //4 creating objects Object obj = cls.newInstance(); //5 get method object Method method = cls.getMethod(methodName); //6 execution method method.invoke(obj); } }
- Test results:
Person eating...