preface
This blog will introduce how to deploy and access an nginx service in a k8s cluster. This article is a brief introduction to the following five concepts. The details are in the subsequent blog posts of the column.
Namespace
introduce
Namespace is a very important resource in k8s system. Its main function is to realize resource isolation of multiple environments or multi tenant resources.
by default, all pods in the kubernetes cluster can access each other. However, in practice, you may not want two pods to access each other. At this time, you can divide the two pods into different namespaces. k8s by allocating resources in the cluster to different namespaces, a logical "group" can be formed to facilitate the isolated use and management of resources in different groups.
different namespace s can be managed by different tenants through the authorization mechanism of k8s, so as to realize the resource isolation of multiple tenants. At this time, the resource quota mechanism of kubernetes can be combined to limit the resources that can be occupied by different tenants, such as CPU usage, memory usage, etc., so as to realize the management of available resources of tenants.
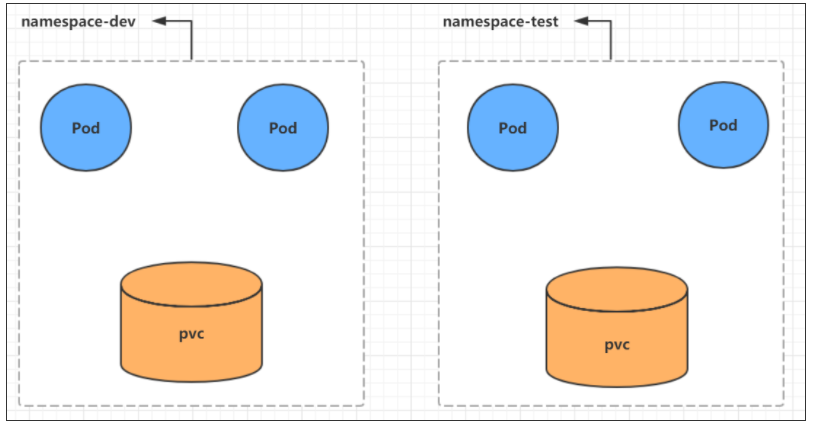
k8s after the cluster starts, several namespace s will be created by default
[root@master k8sYamlForCSDN]# kubectl get namespaces NAME STATUS AGE default Active 8h # All objects that do not specify a Namespace are assigned in the default Namespace kube-node-lease Active 8h # Heartbeat maintenance between cluster nodes, v1 13 start introduction kube-public Active 8h # Resources under this namespace can be accessed by everyone (including unauthenticated users) kube-system Active 8h # All resources created by the Kubernetes system are in this namespace
operation
see
# 1 view all ns commands: kubectl get ns
[root@master k8sYamlForCSDN]# kubectl get ns
NAME STATUS AGE
default Active 8h
kube-node-lease Active 8h
kube-public Active 8h
kube-system Active 8h
# 2 view the specified ns command: kubectl get ns name
[root@master k8sYamlForCSDN]# kubectl get ns default
NAME STATUS AGE
default Active 8h
# 3 specify output format command: kubectl get ns name - o format parameter
# kubernetes supports many formats, such as wide, json and yaml
[root@master k8sYamlForCSDN]# kubectl get ns default -o yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Namespace
metadata:
creationTimestamp: "2022-02-28T03:07:56Z"
labels:
kubernetes.io/metadata.name: default
name: default
resourceVersion: "205"
uid: 0ba523b8-7614-4681-9260-bf15f85c0524
spec:
finalizers:
- kubernetes
status:
phase: Active
# 4. View ns details command: kubectl describe ns name
[root@master k8sYamlForCSDN]# kubectl describe ns default
Name: default
Labels: kubernetes.io/metadata.name=default
Annotations: <none>
Status: Active # Active namespace in use Terminating deleting namespace
# Deleting a namespace will delete all the pod s in it, so it takes time. During this time, it is Terminating
establish
# Create namespace [root@master k8sYamlForCSDN]# kubectl create ns dev namespace/dev created
delete
# Delete namespace [root@master k8sYamlForCSDN]# kubectl delete ns dev namespace "dev" deleted
collocation method
# First, prepare a yaml file: ns-dev.yaml vi ns-dev.yaml
apiVersion: v1 kind: Namespace metadata: name: dev
# Then you can execute the corresponding create and delete commands: # Create: kubectl create - f ns dev.yaml [root@master k8sYamlForCSDN]# kubectl create -f ns-dev.yaml namespace/dev created # Delete: kubectl delete - f ns dev.yaml [root@master k8sYamlForCSDN]# kubectl delete -f ns-dev.yaml namespace "dev" deleted
Pod
introduce
pod is the smallest unit for k8s cluster management. To run, the program must be deployed in the container, and the container must exist in pod. Pod can be regarded as the package of container, and one or more containers can exist in a pod.
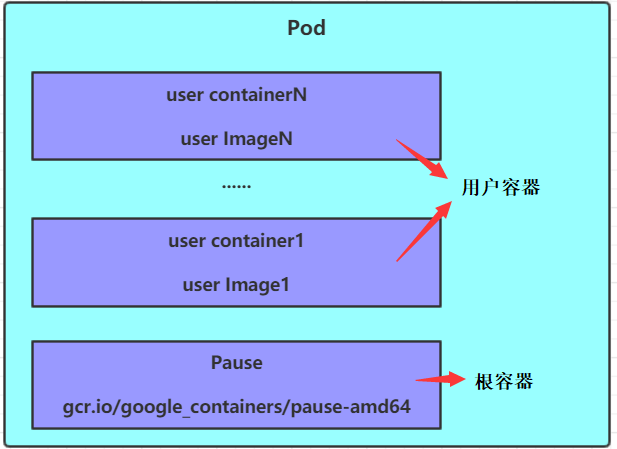
As for what is a user container and what is a root container, we will introduce it in detail in the next blog post of the column, so we won't repeat it here
k8s after the cluster is started, all components in the cluster run in Pod mode. You can view it with the following command:
[root@master k8sYamlForCSDN]# kubectl get pod -n kube-system NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE coredns-64897985d-4w7gt 0/1 ImagePullBackOff 0 8h coredns-64897985d-5jpxz 0/1 ImagePullBackOff 0 8h etcd-master 1/1 Running 0 8h kube-apiserver-master 1/1 Running 0 8h kube-controller-manager-master 1/1 Running 0 8h kube-flannel-ds-78vrj 1/1 Running 0 8h kube-flannel-ds-84dvq 1/1 Running 0 8h kube-flannel-ds-lv5jf 1/1 Running 0 8h kube-proxy-vxflz 1/1 Running 0 8h kube-proxy-w886d 1/1 Running 0 8h kube-proxy-xb7kp 1/1 Running 0 8h kube-scheduler-master 1/1 Running 0 8h
operation
Create and run
# kubernetes provides commands to run Pod separately, and others are implemented through Pod controller # If it is created by the pod controller, it will be automatically created when the specified pod is deleted # Run is a command to run pod separately and will not be created automatically # Command format: kubectl run (pod controller name) [parameter] # --Image specifies the image of the Pod # --Port specifies the port # --Namespace specifies the namespace [root@master k8sYamlForCSDN]# kubectl run pod-nginx --image=nginx --port=80 --namespace=dev pod/pod-nginx created
View pod information
# View basic information of Pod [root@master k8sYamlForCSDN]# kubectl get pods -n dev NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE pod-nginx 1/1 Running 0 18s # View Pod details [root@master k8sYamlForCSDN]# kubectl describe pods pod-nginx -n dev ... ...
Access Pod
# # Get podIP [root@master k8sYamlForCSDN]# kubectl get pods pod-nginx -n dev -o wide NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES pod-nginx 1/1 Running 0 77s 10.244.2.7 node2 <none> <none> # #Access POD [root@master k8sYamlForCSDN]# curl 10.244.2.7:80 <!DOCTYPE html> ... </html>
Delete specified Pod
# Delete specified Pod [root@master k8sYamlForCSDN]# kubectl delete pods pod-nginx -n dev pod "pod-nginx" deleted [root@master k8sYamlForCSDN]# kubectl get pods -n dev No resources found in dev namespace. # If the current Pod is created by the Pod controller, the controller will monitor the status of the Pod. Once the Pod is found dead, it will be rebuilt immediately # If you want to delete the pod, you must delete the pod controller. If you delete the pod controller, its corresponding pod will be deleted automatically # 1. First query the Pod controller in the current namespace [root@master ~]# kubectl get deploy -n dev [root@master k8sYamlForCSDN]# kubectl get deployments -n dev # No resources found in dev namespace. There is no controller at present, because it is the run command. The following is the assumption NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE nginx 1/1 1 1 9m7s # Next, delete this PodPod controller [root@master k8sYamlForCSDN]# kubectl delete deploy nginx -n dev deployment.apps "nginx" deleted # Wait a moment, then query the Pod and find that the Pod has been deleted [root@master k8sYamlForCSDN]#kubectl get pods -n dev No resources found in dev namespace.
Configuration operation
create a pod nginx Yaml, as follows:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: pod-nginx
namespace: dev
spec:
containers:
- name: pod
image: nginx
ports:
- containerPort: 80
name: nginx-port
protocol: TCP
# Write yaml file [root@master k8sYamlForCSDN]# vi pod-nginx.yaml # establish [root@master k8sYamlForCSDN]# kubectl apply -f pod-nginx.yaml pod/pod-nginx created # query [root@master k8sYamlForCSDN]# kubectl get pods -n dev NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE pod-nginx 1/1 Running 0 11s # delete [root@master k8sYamlForCSDN]# kubectl delete -f pod-nginx.yaml pod "pod-nginx" deleted
Label
introduce
Label is an important concept in k8s system. Its function is to add identification on resources to distinguish and select them.
Features of Label:
- A Label will be attached to various objects in the form of key/value pairs, such as Node, Pod, Service, etc
- A resource object can define any number of labels, and the same Label can also be added to any number of resource objects
- The Label is usually determined when the resource object is defined. Of course, it can also be dynamically added or deleted after the object is created
Multi dimensional grouping of resources can be realized through Label, so that resource allocation, scheduling, configuration, deployment and other management can be carried out flexibly and conveniently.
Some common Label examples are as follows:
- Version label: "version": "release", "version": "stable"
- Environment label: "environment": "dev", "environment": "test", "environment": "pro"
- Schema label: "tier": "frontend", "tier": "backend"
After the label is defined, the selection of labels should also be considered, which requires the use of Label Selector, namely:
Label is used to define an identifier for a resource object
Label Selector is used to query and filter resource objects with certain labels
There are currently two types of label selectors:
- Equation based Label Selector
name = slave: select all objects containing key="name" and value="slave" in the Label
env != production: select all objects including key="env" in Label and whose value is not equal to "production"
- Collection based Label Selector
name in (master, slave): select all objects containing key="name" and value="master" or "slave" in the Label
name not in (frontend): select all objects that contain key="name" in Label and whose value is not equal to "frontend"
Multiple label selectors can be used to select labels. In this case, multiple label selectors can be combined and separated by comma "," and ". For example:
name=slave,env!=production name not in (frontend),env!=production
operation
Command mode
# Create a pod [root@master k8sYamlForCSDN]# kubectl create -f pod-nginx.yaml pod/pod-nginx created # View the label of pod [root@master k8sYamlForCSDN]# kubectl get pod -n dev --show-labels NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE LABELS pod-nginx 1/1 Running 0 17s <none> # Tag pod resources [root@master k8sYamlForCSDN]# kubectl label pods pod-nginx -n dev version=2.0 pod/pod-nginx labeled # View the label of pod [root@master k8sYamlForCSDN]# kubectl get pod -n dev --show-labels NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE LABELS pod-nginx 1/1 Running 0 59s version=2.0 # Update tag for pod [failed] [root@master k8sYamlForCSDN]# kubectl label pods pod-nginx -n dev version=3.0 error: 'version' already has a value (2.0), and --overwrite is false # Update tag for pod [succeeded] (overwrite) [root@master k8sYamlForCSDN]# kubectl label pods pod-nginx -n dev version=3.0 --overwrite pod/pod-nginx labeled # View the label of pod [root@master k8sYamlForCSDN]# kubectl get pod -n dev --show-labels NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE LABELS pod-nginx 1/1 Running 0 90s version=3.0 # Filter Tags [root@master k8sYamlForCSDN]# kubectl get pods -n dev -l version=1.0 --show-labels No resources found in dev namespace. # Filter Tags [root@master k8sYamlForCSDN]# kubectl get pods -n dev -l version!=1.0 --show-labels NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE LABELS pod-nginx 1/1 Running 0 2m52s version=3.0 # To delete a tag is to follow the key with a minus sign, i.e. "-" [root@master k8sYamlForCSDN]# kubectl label pods pod-nginx -n dev version- pod/pod-nginx unlabeled # View the label of pod [root@master k8sYamlForCSDN]# kubectl get pod -n dev --show-labels NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE LABELS pod-nginx 1/1 Running 0 3m27s <none>
collocation method
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: pod-nginx
namespace: dev
labels:
version: "4.0"
env: "test"
created: "wxf"
spec:
containers:
- name: pod
image: nginx
ports:
- containerPort: 80
name: nginx-port
protocol: TCP
# establish [root@master k8sYamlForCSDN]# kubectl apply -f pod-nginx.yaml pod/pod-nginx created # View pod information [root@master k8sYamlForCSDN]# kubectl get pod -n dev --show-labels NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE LABELS pod-nginx 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 4s created=wxf,env=test,version=4.0
Deployment
introduce
in kubernetes, pod is the smallest control unit, but kubernetes rarely directly controls pod, which is generally completed through pod controller. The pod controller is used for pod management to ensure that the pod resources meet the expected state. When the pod resources fail, it will try to restart or rebuild the pod.
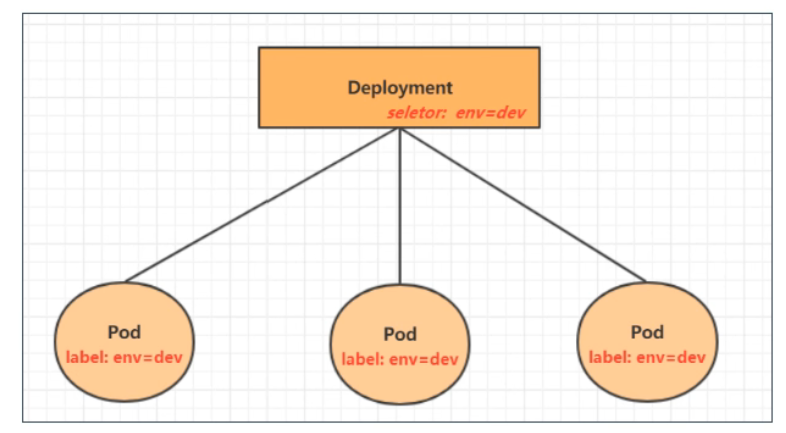
there are many types of pod controllers in kubernetes. This chapter only introduces one: Deployment. Other pod controllers are expected to be introduced in detail in the next blog post. The relationship between Deployment and pod is established through label, as shown in the following figure:
operation
Command operation
# Create deployment # Command format: kubectl create deployment name [parameter] # --Image specifies the image of the pod # --Port specifies the port # --replicas specifies the number of created pod s # --Namespace specifies the namespace [root@master k8sYamlForCSDN]# kubectl create deployment deploy-nginx --image=nginx --port=80 --replicas=3 --namespace=dev deployment.apps/deploy-nginx created # View the created Pod ```bash [root@master k8sYamlForCSDN]# kubectl get pods -n dev NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE deploy-nginx-fb669cc4f-5xd5j 1/1 Running 0 3m32s deploy-nginx-fb669cc4f-69pln 1/1 Running 0 3m32s deploy-nginx-fb669cc4f-tpfhp 1/1 Running 0 3m32s # View deployment information [root@master k8sYamlForCSDN]# kubectl get deployment -n dev NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE deploy-nginx 3/3 3 3 4m21s # UP-TO-DATE: number of copies successfully upgraded # AVAILABLE: number of AVAILABLE copies # View the details of deployment and pod [root@master k8sYamlForCSDN]# kubectl get deployment,pods -n dev --show-labels NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE LABELS deployment.apps/deploy-nginx 3/3 3 3 5m42s app=deploy-nginx NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE LABELS pod/deploy-nginx-fb669cc4f-5xd5j 1/1 Running 0 5m42s app=deploy-nginx,pod-template-hash=fb669cc4f pod/deploy-nginx-fb669cc4f-69pln 1/1 Running 0 5m42s app=deploy-nginx,pod-template-hash=fb669cc4f pod/deploy-nginx-fb669cc4f-tpfhp 1/1 Running 0 5m42s app=deploy-nginx,pod-template-hash=fb669cc4f [root@master k8sYamlForCSDN]# kubectl get deployment -n dev -o wide NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE CONTAINERS IMAGES SELECTOR deploy-nginx 3/3 3 3 5m58s nginx nginx app=deploy-nginx
# View details of deployment
[root@master k8sYamlForCSDN]# kubectl describe deployment -n dev
Name: deploy-nginx
Namespace: dev
CreationTimestamp: Mon, 28 Feb 2022 21:10:32 +0800
Labels: app=deploy-nginx
Annotations: deployment.kubernetes.io/revision: 1
Selector: app=deploy-nginx
Replicas: 3 desired | 3 updated | 3 total | 3 available | 0 unavailable
StrategyType: RollingUpdate
MinReadySeconds: 0
RollingUpdateStrategy: 25% max unavailable, 25% max surge
Pod Template:
Labels: app=deploy-nginx
Containers:
nginx:
Image: nginx
Port: 80/TCP
Host Port: 0/TCP
Environment: <none>
Mounts: <none>
Volumes: <none>
Conditions:
Type Status Reason
---- ------ ------
Available True MinimumReplicasAvailable
Progressing True NewReplicaSetAvailable
OldReplicaSets: <none>
NewReplicaSet: deploy-nginx-fb669cc4f (3/3 replicas created)
Events:
Type Reason Age From Message
---- ------ ---- ---- -------
Normal ScalingReplicaSet 6m29s deployment-controller Scaled up replica set deploy-nginx-fb669cc4f to 3
# # Delete the deployment Pod controller. If the deployment corresponding to the pod is deleted, the pod will also be deleted [root@master k8sYamlForCSDN]# kubectl delete deployments.apps deploy-nginx -n dev deployment.apps "deploy-nginx" deleted [root@master k8sYamlForCSDN]# kubectl get deployment,pods -n dev No resources found in dev namespace.
Configuration operation
# Create a deploy nginx yaml vi deploy-nginx.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: deploy-nginx
namespace: dev
spec:
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
run: "nginx"
template:
metadata:
labels:
run: "nginx"
spec:
containers:
- name: pod
image: nginx
ports:
- containerPort: 80
protocol: TCP
# establish [root@master k8sYamlForCSDN]# kubectl apply -f deploy-nginx.yaml deployment.apps/deploy-nginx created # see [root@master k8sYamlForCSDN]# kubectl get deployments.apps -n dev NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE deploy-nginx 0/3 3 0 11s [root@master k8sYamlForCSDN]# kubectl get deployments.apps,pods -n dev NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE deployment.apps/deploy-nginx 0/3 3 0 15s NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE pod/deploy-nginx-579f68df74-pn2c8 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 15s pod/deploy-nginx-579f68df74-sv9nz 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 15s pod/deploy-nginx-579f68df74-wpndc 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 15s # delete [root@master k8sYamlForCSDN]# kubectl delete -f deploy-nginx.yaml deployment.apps "deploy-nginx" deleted
Service
introduce
At present, Deployment can be used to create a group of pods to provide services with high availability.
Although each Pod will be assigned a separate Pod IP, there are two problems:
- Pod IP will change with the reconstruction of pod
- Pod IP is only the virtual IP visible in the cluster and cannot be accessed externally
This makes it difficult to access this Service. Therefore, kubernetes designed Service to solve this problem.
Service can be regarded as a group of external access interfaces of similar pods. With the help of service, applications can easily realize service discovery and load balancing.
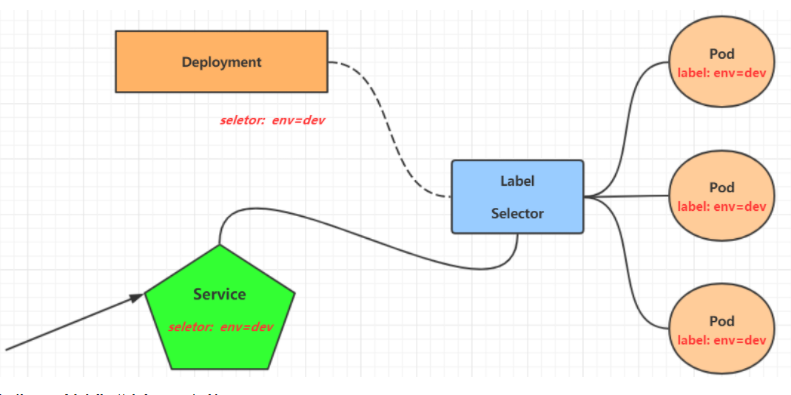
operation
Operation 1: create an accessible Service in the cluster
Here is a brief introduction – type=ClusterIP, which means that only the internal ip of the cluster can access this service
# Expose Service [root@master k8sYamlForCSDN]# kubectl expose deployment deploy-nginx -n dev \ --name=svc-deploy-nginx --type=ClusterIP --port=80 --target-port=80 service/svc-deploy-nginx exposed # View service [root@master k8sYamlForCSDN]# kubectl get service svc-deploy-nginx -n dev -o wide NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE SELECTOR svc-deploy-nginx ClusterIP 10.99.101.216 <none> 80/TCP 47s run=nginx # A CLUSTER-IP is generated here, which is the IP of the service. This address will not change during the service life cycle # You can access the POD corresponding to the current service through this IP [root@master k8sYamlForCSDN]# curl 10.99.101.216:80 <!DOCTYPE html> ... ... </html>
Operation 2: create a Service that can also be accessed outside the cluster
# The type of the Service created above is ClusterIP. This ip address is accessible only within the cluster # If you need to create a Service that can also be accessed externally, you need to modify the type to NodePort [root@master k8sYamlForCSDN]# kubectl expose deployment deploy-nginx -n dev \ > --name=svc-deploy-nginx --type=NodePort --port=80 --target-port=80 service/svc-deploy-nginx exposed # # At this time, you will find that a Service of NodePort type appears, and there is a pair of ports (80:31928/TC) [root@master k8sYamlForCSDN]# kubectl get service svc-deploy-nginx -n dev -o wide NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE SELECTOR svc-deploy-nginx NodePort 10.99.149.210 <none> 80:30945/TCP 10s run=nginx # Next, you can access the node IP:30945 to access the service through the host outside the cluster # For example, access the following address through the browser on the host computer http://192.168.109.100:30945/

Delete Service
[root@master k8sYamlForCSDN]# kubectl delete svc svc-deploy-nginx -n dev service "svc-deploy-nginx" deleted
collocation method
Whether it is ClusterIP or NodePort, the ClusterIP in yaml file: 10.109.68.72 can not be configured. If it is not configured, it will be automatically allocated
# Create an SVC nginx yaml vi svc-deploy-nginx.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: svc-deploy-nginx
namespace: dev
spec:
type: ClusterIP
clusterIP: 10.109.68.72
selector:
run: "nginx"
ports:
- port: 80
targetPort: 80
protocol: TCP
[root@master k8sYamlForCSDN]# kubectl apply -f svc-deploy-nginx.yaml service/svc-deploy-nginx created [root@master k8sYamlForCSDN]# kubectl get service svc-deploy-nginx -n dev -o wide NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE SELECTOR svc-deploy-nginx ClusterIP 10.109.68.72 <none> 80/TCP 10s run=nginx [root@master k8sYamlForCSDN]# kubectl delete -f svc-deploy-nginx.yaml service "svc-deploy-nginx" deleted
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: svc-deploy-nginx
namespace: dev
spec:
type: NodePort
clusterIP: 10.109.68.72
selector:
run: "nginx"
ports:
- port: 6872
targetPort: 80
protocol: TCP
[root@master k8sYamlForCSDN]# kubectl apply -f svc-deploy-nginx.yaml service/svc-deploy-nginx created [root@master k8sYamlForCSDN]# kubectl get service svc-deploy-nginx -n dev -o wide NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE SELECTOR svc-deploy-nginx NodePort 10.105.26.121 <none> 6872:31758/TCP 4s run=nginx [root@master k8sYamlForCSDN]# kubectl delete -f svc-deploy-nginx.yaml service "svc-deploy-nginx" deleted