1. Development process of mybatis
Mybatis official website: https://mybatis.org/mybatis-3/zh/index.html
- Introducing MyBatis dependency
- Create core profile
- Create entity
- Create Mapper mapping file
- Initialize SessionFactory
- Using SqlSession object to manipulate data
1.1 introduction of MyBatis dependency (Maven)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.java</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<dependencies>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.mybatis/mybatis -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis</artifactId>
<version>3.5.1</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/mysql/mysql-connector-java -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.47</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
1.2 create core profile
Create mybatis config. In the / src/resources / folder XML and configure it
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<settings>
<!-- goods_id -> goodsId Hump naming conversion-->
<setting name="mapUnderscoreToCamelCase" value="true"/>
</settings>
<!-- By switching default The database can be switched flexibly-->
<environments default="dev">
<environment id="dev"> //Environment configuration
<transactionManager type="JDBC"></transactionManager>//What transactions are used to manage the database
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/babytun?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="wwe61846"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
<environment id="prd">
<!-- use JDBC Database transactions commit/rollback -->
<transactionManager type="JDBC"></transactionManager>
<!-- The database is managed by connection pool -->
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://192.168.1.155:3306/babytun?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="wwe61846"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
</configuration>
When < environment id = "dev" > is changed to < environment id = "prd" > the environment with ID "prd" will be used and the database will be replaced.
1.5 initialize SessionFactory
SqlSessionFactory
- Create the core object of MyBatis
- Used to initialize MyBatis and create SqlSession object
- Ensure that SqlSessionFactory is globally unique in the application
SqlSession
- It is the core object of MyBatis operation database
- Use JDBC to interact with the database
- CRUD corresponding method is provided
@Test
public void testSqlSessionFactory() throws IOException {
// Use Reader to load mybatis config. Under classpath XML core configuration file
Reader reader = Resources.getResourceAsReader("mybatis-config.xml");
// Initialize SqlSessionFactory object and resolve mybatis config XML file
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(reader);
System.out.println("SessionFactory Loading succeeded");
SqlSession sqlSession = null;
try {
// Create a SqlSession object. SqlSession is an extended class of JDBC, which is used to interact with the database
sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
// Create a database connection (for testing). Normally, it is created by MyBatis. If you use MyBatis normally, you don't need other Java SQL package.
Connection conn = sqlSession.getConnection();
System.out.println(conn);
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
// If type = "POOLED", it means that the connection pool is used, and close means that the connection is recycled to the connection pool
// If type = "UNPOOLED", it represents direct connection, and close will call connection Close() method
sqlSession.close();
}
}
Initialize tool class MybatisUtils
At / SRC / main / Java / com pfeiking. mybatis. Create MyBatisUtils class under utils
package com.pfeiking.mybatis.utils;
import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.Reader;
public class MyBatisUtils {
// static is a class, not an object, and globally unique
private static SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = null;
// The static block is used to initialize static objects
static {
Reader reader = null;
try {
reader = Resources.getResourceAsReader("mybatis-config.xml");
sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(reader);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
throw new ExceptionInInitializerError(e);
}
}
public static SqlSession openSession(){
return sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
}
public static void closeSession(SqlSession sqlSession){
if (sqlSession != null){
sqlSession.close();
}
}
}
@Test
public void testMyBatisUtils() throws Exception {
SqlSession sqlSession = null;
try {
sqlSession = MyBatisUtils.openSession();
Connection conn = sqlSession.getConnection();
System.out.println(conn);
}catch (Exception e){
throw e;
}finally {
MyBatisUtils.closeSession(sqlSession);
}
}
2 data query
MyBatis query steps
- Create Entity
- Create Mapper
- Write SQL Tags
- Enable hump naming mapping
- newly added
- SqlSession executes a select statement
2.1 create entity
package com.pfeiking.mybatis.entity;
public class Goods {
private Integer goodsId;
private String title;
private String subTitle;
private Float originalCost;
private Float currentPrice;
private Float discount;
private Integer isFreeDelivery;
private Integer categoryId;
public Integer getGoodsId() {
return goodsId;
}
public void setGoodsId(Integer goodsId) {
this.goodsId = goodsId;
}
public String getTitle() {
return title;
}
public void setTitle(String title) {
this.title = title;
}
public String getSubTitle() {
return subTitle;
}
public void setSubTitle(String subTitle) {
this.subTitle = subTitle;
}
public Float getOriginalCost() {
return originalCost;
}
public void setOriginalCost(Float originalCost) {
this.originalCost = originalCost;
}
public Float getCurrentPrice() {
return currentPrice;
}
public void setCurrentPrice(Float currentPrice) {
this.currentPrice = currentPrice;
}
public Float getDiscount() {
return discount;
}
public void setDiscount(Float discount) {
this.discount = discount;
}
public Integer getIsFreeDelivery() {
return isFreeDelivery;
}
public void setIsFreeDelivery(Integer isFreeDelivery) {
this.isFreeDelivery = isFreeDelivery;
}
public Integer getCategoryId() {
return categoryId;
}
public void setCategoryId(Integer categoryId) {
this.categoryId = categoryId;
}
}
2.2 create Mapper and write < Select > sql Tags
Map the fields and entities in the database one by one through Mapper. You need to create mappers / goods.com under / src/main/resources / XML.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="goods">
<!-- establish select label; id It's down there sql Alias of; resultType Object to put data back -->
<select id="selectAll" resultType="com.pfeiking.mybatis.entity.Goods">
select * from t_goods order by goods_id desc limit 10
</select>
</mapper>
@Test
public void testSelectAll() throws Exception {
SqlSession session = null;
try{
session = MyBatisUtils.openSession();
List<Goods> list = session.selectList("goods.selectAll");
for (Goods good: list){
System.out.println(good.getTitle());
}
}catch(Exception e){
throw e;
}finally{
MyBatisUtils.closeSession(session);
}
}
2.3 start hump naming mapping
For the goodId in the entity and the good in the database_ For ID correspondence, it needs to be in mybatis config Add a setting item to XML
<settings> <!-- goods_id -> goodsId Hump naming conversion--> <setting name="mapUnderscoreToCamelCase" value="true"/> </settings>
2.4 SQL transfer parameters
Query < Select >
Pass a single parameter in goods Add select statement to XML
<select id="selectById" parameterType="Integer" resultType="com.pfeiking.mybatis.entity.Goods">
select * from t_goods where goods_id = #{value}
</select>
@Test
public void testSelectById() throws Exception {
SqlSession session = null;
try{
session = MyBatisUtils.openSession();
Goods goods = session.selectOne("goods.selectById", 1602);
System.out.println(goods.getTitle());
}catch(Exception e){
throw e;
}finally{
MyBatisUtils.closeSession(session);
}
}
Pass multiple parameters
<select id="selectByPriceRange" parameterType="java.util.Map" resultType="com.pfeiking.mybatis.entity.Goods">
select * from t_goods
where
current_price between #{min} and #{max}
order by current_price
limit 0, #{limt}
</select>
@Test
public void testSelectByPriceRange() throws Exception {
SqlSession session = null;
try{
session = MyBatisUtils.openSession();
Map param = new LinkedHashMap();
param.put("min", 100);
param.put("max", 500);
param.put("limt", 10);
List<Goods> list = session.selectList("goods.selectByPriceRange", param);
for (Goods good: list){
System.out.println(good.getTitle()+" "+good.getCurrentPrice());
}
}catch(Exception e){
throw e;
}finally{
MyBatisUtils.closeSession(session);
}
}
Get multi table Association query results
- Using LinkedHashMap to save multi table union results
- MyBatis wraps each record as a LinkedHashMap object
- key is the field name and value is the value corresponding to the field name. The field type is automatically determined according to the table structure
- Advantages: easy to expand and use
- Disadvantages: too flexible for compile time checking
<select id="selectGoodsMap" resultType="java.util.LinkedHashMap">
select g.*, c.category_name ,'1' as test from t_goods g, t_category c
where g.category_id = c.category_id
</select>
@Test
public void testSelectGoodsmap() throws Exception {
SqlSession session = null;
try{
session = MyBatisUtils.openSession();
List<Map> list = session.selectList("goods.selectGoodsMap");
for (Map map: list){
System.out.println(map);
}
}catch(Exception e){
throw e;
}finally{
MyBatisUtils.closeSession(session);
}
}
2.5 ResultMap result mapping
- You can map query results to Java objects of complex types
- It is suitable for Java objects to save multi table association results
- Support advanced features such as object association query
Create com pfeiking. mybatis. DTO, DTO data transmission object, which expands the original object for data storage and expansion.
package com.pfeiking.mybatis.dto;
import com.pfeiking.mybatis.entity.Goods;
public class GoodsDTO {
private Goods goods = new Goods();
private String categoryName;
private String test;
public Goods getGoods() {
return goods;
}
public void setGoods(Goods goods) {
this.goods = goods;
}
public String getCategoryName() {
return categoryName;
}
public void setCategoryName(String categoryName) {
this.categoryName = categoryName;
}
public String getTest() {
return test;
}
public void setTest(String test) {
this.test = test;
}
}
<resultMap id="rmGoods" type="com.pfeiking.mybatis.dto.GoodsDTO"> <!-- Set primary key field and attribute mapping--> <id property="goods.goodsId" column="goods_id"></id> <!-- Set non primary key field attribute mapping--> <result property="goods.title" column="title"></result> <result property="goods.originalCost" column="origin_cost"></result> <result property="goods.currentPrice" column="current_price"></result> <result property="goods.discount" column="discount"></result> <result property="goods.isFreeDelivery" column="is_free_delivery"></result> <result property="goods.categoryId" column="category_id"></result> <!-- GoodsDTO Properties in--> <result property="categoryName" column="category_name"></result> <result property="test" column="test"></result> </resultMap> <select id="selectGoodsDTO" resultMap="rmGoods"> select g.*, c.category_name ,'1' as test from t_goods g, t_category c where g.category_id = c.category_id </select>
@Test
public void testSelectGoodsDTO() throws Exception {
SqlSession session = null;
try{
session = MyBatisUtils.openSession();
List<GoodsDTO> list = session.selectList("goods.selectGoodsDTO");
for (GoodsDTO g: list){
System.out.println(g.getGoods().getTitle());
}
}catch(Exception e){
throw e;
}finally{
MyBatisUtils.closeSession(session);
}
}
3 data writing
Write operations include the following three types
- Insert - < Insert >
- Update - < update >
- Delete - < delete >
3.1 database transactions
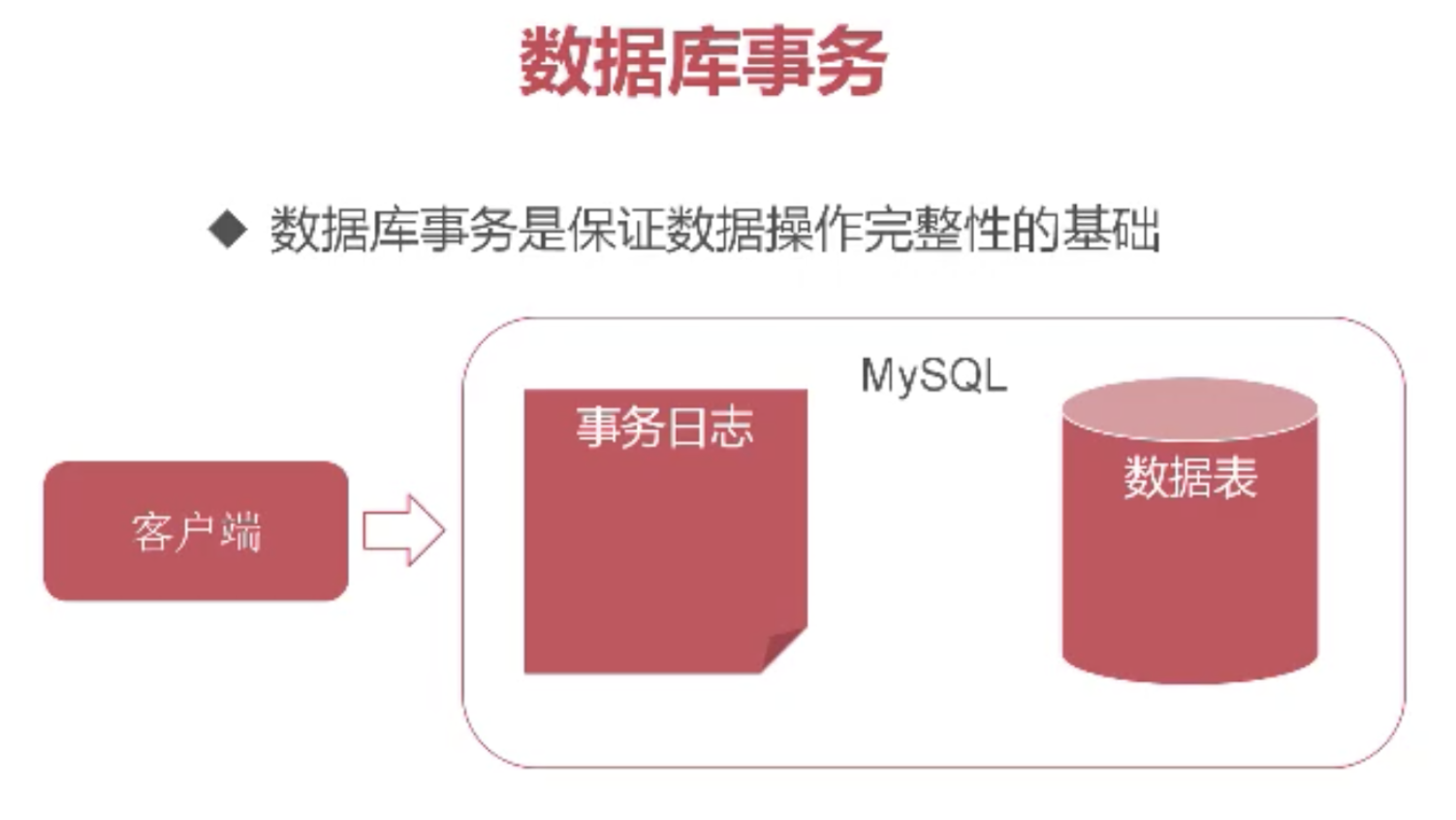
3.2 NEW
<insert id="insert" parameterType="com.pfeiking.mybatis.entity.Goods">
insert into t_goods(title, sub_title, original_cost, current_price, discount, is_free_delivery, category_id)
values (#{title}, #{subTitle}, #{originalCost}, #{currentPrice}, #{discount}, #{isFreeDelivery}, #{categoryId})
</insert>
@Test
public void testInsert() throws Exception {
SqlSession session = null;
try{
session = MyBatisUtils.openSession();
Goods goods = new Goods();
goods.setTitle("Test goods");
goods.setSubTitle("Test subtitle");
goods.setOriginalCost(200f);
goods.setCurrentPrice(100f);
goods.setDiscount(0.5f);
goods.setIsFreeDelivery(1);
goods.setCategoryId(43);
// The return value is the total number of records successfully inserted this time
int num = session.insert("goods.insert", goods);
System.out.println(num);
session.commit();//Commit transaction data
}catch(Exception e){
throw e;
}finally{
MyBatisUtils.closeSession(session);
}
}
3.3 selectKey and useGeneratedKey
3.2.1 differences
-
selectKey obtains the primary key value of the newly added data and adds it to < Insert >. It is necessary to explicitly write an SQL statement to obtain the latest primary key
-
The useGeneratedKey property will automatically generate the corresponding SQL statement according to the driver
<insert id="insert" parameterType="com.pfeiking.mybatis.entity.Goods">
insert into t_goods(title, sub_title, original_cost, current_price, discount, is_free_delivery, category_id)
values (#{title}, #{subTitle}, #{originalCost}, #{currentPrice}, #{discount}, #{isFreeDelivery}, #{categoryId})
<selectKey resultType="Integer" keyProperty="goodsId" order="AFTER">
select last_insert_id()
</selectKey>
</insert>
<insert id="insert"
parameterType="com.pfeiking.mybatis.entity.Goods"
useGeneratedKeys="true"
keyProperty="goodsId"
keyColumn="goods_id">
insert into t_goods(title, sub_title, original_cost, current_price, discount, is_free_delivery, category_id)
values (#{title}, #{subTitle}, #{originalCost}, #{currentPrice}, #{discount}, #{isFreeDelivery}, #{categoryId})
</insert>
@Test
public void testInsert() throws Exception {
SqlSession session = null;
try{
session = MyBatisUtils.openSession();
Goods goods = new Goods();
goods.setTitle("Test goods");
goods.setSubTitle("Test subtitle");
goods.setOriginalCost(200f);
goods.setCurrentPrice(100f);
goods.setDiscount(0.5f);
goods.setIsFreeDelivery(1);
goods.setCategoryId(43);
// The return value is the total number of records successfully inserted this time
int num = session.insert("goods.insert", goods);
System.out.println(num);
session.commit();//Commit transaction data
System.out.println(goods.getGoodsId());
}catch(Exception e){
throw e;
}finally{
MyBatisUtils.closeSession(session);
}
}
3.3.2 application scenarios
- selectKey is used for shrinking relational databases
- useGenerateKeys only supports databases of type "self incrementing primary key"
3.4 update
<update id="update" parameterType="com.pfeiking.mybatis.entity.Goods">
update t_goods
set
title = #{title},
sub_title = #{subTitle},
original_cost = #{originalCost},
current_price = #{currentPrice},
discount = #{discount},
is_free_delivery = #{isFreeDelivery},
category_id = #{categoryId}
where
goods_id = #{goodsId}
</update>
@Test
public void testUpdate() throws Exception {
SqlSession session = null;
try{
session = MyBatisUtils.openSession();
Goods goods = session.selectOne("goods.selectById", 739);
goods.setTitle("Update test item");
int num = session.update("goods.update", goods);
System.out.println(num);
session.commit();
}catch(Exception e){
throw e;
}finally{
MyBatisUtils.closeSession(session);
}
}
3.5 deletion
<delete id="delete" parameterType="Integer">
delete from t_goods where goods_id = #{value}
</delete>
@Test
public void testDelete() throws Exception {
SqlSession session = null;
try{
session = MyBatisUtils.openSession();
int num = session.delete("goods.delete", 739);
System.out.println(num);
session.commit();
}catch(Exception e){
throw e;
}finally{
MyBatisUtils.closeSession(session);
}
}
3.6 SQL injection
Definition: an attacker uses SQL vulnerabilities to bypass system constraints and obtain data beyond his authority
Two value transfer methods of MyBatis:
- **${} * * text replacement, SQL text replacement without any processing
- **#{} * * precompiled value. Using precompiled value can prevent SQL injection, put parameters into SQL as strings, and the placeholder of SQL is also strings
${}
select * from t_goods where title = '' or 1 = 1 or title='xxxxxxxx'
#{}
select * from t_goods where title = "''or 1 = 1 or title='xxxxxxxx'"
When inserting sql clauses, use * * ${} * *.