Catalog
Introduction to Nginx web Foundation
Two deployment modes:
1) yum installation
Change official source:
[root@web ~]# vim /etc/yum.repos.d/nginx.repo [nginx] name=nginx repo baseurl=http://nginx.org/packages/centos/7/$basearch/ gpgcheck=0 enabled=1
Install dependency packages
yum install -y gcc gcc-c++ autoconf pcre pcre-devel openssl-devel make automake
Install nginx-1.16.0
yum install -y nginx
Start nginx and set boot-up self-start
[root@web01 ~]# systemctl start nginx [root@web01 ~]# systemctl enable nginx
Start error:

Error Cause: 80 Ports Occupied
Solution: Whoever occupies and kills
systemctl stop httpd
Monitor whether nginx started successfully
#Method 1: Monitoring process
[root@web01 ~]# ps -ef|grep [n]ginx
root 12457 1 0 11:44 ? 00:00:00 nginx: master process /usr/sbin/nginx -c /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
nginx 12458 12457 0 11:44 ? 00:00:00 nginx: worker process
#Method 2: Monitoring Port
[root@web01 ~]# netstat -lntup|grep 80
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:80 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 12457/nginx: master
#Method 3: systemd
[root@web01 ~]# systemctl status nginx
● nginx.service - nginx - high performance web server
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/nginx.service; enabled; vendor preset: disabled)
Active: active (running) since Tue 2019-08-13 11:44:03 CST; 8min ago
Docs: http://nginx.org/en/docs/
Process: 12456 ExecStart=/usr/sbin/nginx -c /etc/nginx/nginx.conf (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Main PID: 12457 (nginx)
CGroup: /system.slice/nginx.service
├─12457 nginx: master process /usr/sbin/nginx -c /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
└─12458 nginx: worker process
#Method 4: Open browser access#Method 5: curl command [root@web01 ~]# curl 10.0.0.7 [root@web01 ~]# curl www.driverzeng.com
View the version of nginx
[root@web01 ~]# nginx -v nginx version: nginx/1.16.0
2) Source installation
decompression
tar xf nginx-1.16.0.tar.gz #Create a www user groupadd www -g 666 useradd www -u 666 -g 666 -s /sbin/nologin -M
generate
./configure --prefix=/usr/local/nginx-1.16.0 \ --user=www \ --group=www \ --with-http_ssl_module \ --with-http_stub_status_module \ --with-stream
Compile
make
install
make install
How to upgrade nginx or add functionality
ln -s /usr/local/nginx-1.16.0 /usr/local/nginx #Upgraded version ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/nginx-1.17.2 \ --user=www \ --group=www \ --with-http_ssl_module \ --with-http_stub_status_module \ --with-stream \ --with-http_mp4_module #Resoft Link rm -f /usr/local/nginx && ln -s /usr/local/nginx-1.17.2 /usr/local/nginx ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- #add module ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/nginx_new-1.16.0 \ --user=www \ --group=www \ --with-http_ssl_module \ --with-http_stub_status_module \ --with-stream \ --with-http_mp4_module #Resoft Link rm -f /usr/local/nginx && ln -s /usr/local/nginx_new-1.16.0 /usr/local/nginx
Ansible,SaltStack
First source code installation, then rpm package, put in yum warehouse, then yum installation
Managing nginx with system D
vim /usr/lib/systemd/system/nginx.service [Unit] Description=nginx - high performance web server Documentation=http://nginx.org/en/docs/ After=network-online.target remote-fs.target nss-lookup.target Wants=network-online.target [Service] Type=forking PIDFile=/usr/local/nginx/logs/nginx.pid ExecStart=/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx #Command Path -c /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf #Main Profile Path ExecReload=/bin/kill -s HUP $MAINPID ExecStop=/bin/kill -s TERM $MAINPID [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
nginx-related configuration files
1.Nginx main configuration file parameters
| Route | type | Effect |
|---|---|---|
| /etc/nginx/nginx.conf | configuration file | nginx master configuration file |
| /etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf | configuration file | Default Site Profile |
2.Nginx proxy related parameter files
| Route | type | Effect |
|---|---|---|
| /etc/nginx/fastcgi_params | configuration file | Fastcgi proxy profile |
| /etc/nginx/scgi_params | configuration file | scgi proxy profile |
| /etc/nginx/uwsgi_params | configuration file | uwsgi proxy profile |
3.Nginx encoding related configuration files
| Route | type | Effect |
|---|---|---|
| /etc/nginx/win-utf | configuration file | Nginx Coding Conversion Mapping File |
| /etc/nginx/koi-utf | configuration file | Nginx Coding Conversion Mapping File |
| /etc/nginx/koi-win | configuration file | Nginx Coding Conversion Mapping File |
| /etc/nginx/mime.types | configuration file | Content-Type and Extensions |
4.Nginx Manage Related Commands
| Route | type | Effect |
|---|---|---|
| /usr/sbin/nginx | command | Nginx command line management terminal tool |
| /usr/sbin/nginx-debug | command | Nginx Command Line and Terminal Debugging Tool |
4.Nginx log related directories and files
| Route | type | Effect |
|---|---|---|
| /var/log/nginx | Catalog | Nginx stores log directories by default |
| /etc/logrotate.d/nginx | configuration file | Nginx Default Log Cutting |
nginx configuration file details
The main configuration file of Nginx is divided into three parts to learn: CoreModule (core module), EventModule (event-driven module), HttpCoreModule(http core module).
Nginx Master Profile/etc/nginx/nginx.conf It's a plain text file, and the entire configuration file is organized in blocks. Generally, each block is bracketed in a pair of braces{}To indicate the beginning and the end.
Nginx The main configuration file is divided into three parts for learning. CoreModule(Core module),EventModule(Event Driven Module),HttpCoreModule(http Kernel module)
CoreModule Core module
user www; #Users used by Nginx processes
worker_processes 1; #Number of work processes that Nginx runs (recommended to be consistent with CPU or auto)
error_log /log/nginx/error.log #Nginx error log storage path
pid /var/run/nginx.pid #pid process number generated after Nginx service runs
EventModule(Event Driven Module)
events {
worker_connections 25535; #Maximum number of connections supported by each worker process
use epoll; #Event-driven model, epoll default
}
HttpCoreModule(http Kernel module)
#http layer start
http {
#Contains resource type files
include /etc/nginx/mime.types;
#By default, the download mode is transmitted to the browser (provided that the resource is not found in mime.types)
default_type application/octet-stream;
#Log format
log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
'$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
'"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
#Access Log
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log main;
#Efficient File Transfer
sendfile on;
#Use with sendfile
#tcp_nopush on;
#Long connection timeout
keepalive_timeout 65;
#Whether to turn on compression or not
#gzip on;
#Using Server to configure a Web site, each Server {} represents a Web site (referred to as a virtual host)
'server' {
listen 80; #Listener port, default 80
server_name driverzeng.com; #Provided domain name
access_log access.log; #Visit log of the website
#Control website access path
'location' / {
root /usr/share/nginx/html; #Location of the source code of the website
index index.html index.htm; #Files returned to the Web site by default
}
}
...
#Second Virtual Host Configuration
'server' {
...
}
include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf; #Contains all files ending in. conf in / etc/nginx/conf.d / directory
} #http end layerLog format
log_format abd '$remote_addr - |$remote_user| [$time_local] "$request" '
'$status $body_bytes_sent $bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
'"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
$remote_addr # Record client IP address
$remote_user # Record client user name
$time_local # Record common local time
$time_iso8601 # Record local time in ISO8601 standard format
$request # Method of recording requests and http protocol of requests
$status # Record request status code (for locating error information)
$body_bytes_sent # Number of resource bytes sent to the client, excluding the size of the response header
$bytes_sent # The total number of bytes sent to the client
$msec # Log write time. In seconds, the accuracy is milliseconds.
$http_referer # Which page link is the record accessed from?
$http_user_agent # Record client browser related information
$http_x_forwarded_for #Record client IP address
$request_length # The length of the request (including the request line, the request header and the request body).
$request_time # Request time, in seconds, in milliseconds
# Note: If Nginx is located in the load balancer, after nginx reverse proxy, the web server can not get the real IP address of the client directly.
# The $remote_addr gets the IP address of the reverse proxy. The reverse proxy server is in the http header information forwarding the request.
# Add X-Forwarded-For information to record the client IP address and the server address requested by the client.game Logging Actual Warfare
location /favicon.ico{
access_log off;
return 200;
}
location /js/common.js{
access_log /var/log/nginx/js.log main;
}Log Cutting
cat /etc/logrotate.d/nginx
/var/log/nginx/*.log {
daily # Cut logs every day
missingok # Log Loss Ignorance
rotate 52 # Log retention for 52 days
compress # Log file compression
delaycompress # Delayed Compression Log
notifempty # Do not cut empty files
create 640 nginx adm # Log file permissions
sharedscripts
postrotate # Commands to Cut Log Execution
if [ -f /var/run/nginx.pid ]; then #Determine whether there is a pid
kill -USR1 `cat /var/run/nginx.pid`#Reload
fi
endscript
}Handwritten Virtual Host
1. Edit the virtual host and create the query directory
[root@web01 conf.d]# vim game.conf
server {
#Listening port
listen 80;
#Domain name,; (to write ip) localhost;
server_name localhost;
#location matching rule
location / {
#Specify site directory
root /code/h5_games;
#Specify index page (default home page)
index index.html;
}
}
#Create Site Catalog
[root@web01 conf.d]# mkdir /code
#Authorize www users to give site directories
[root@web01 conf.d]# chown -R www.www /code
#Manual creation of index
[root@web01 code]# echo game > /code/index.html
-----------------------------Source Packet Writing-------------------------------------
//Be careful:
1.nginx -V Find out nginx The main configuration file, then write the virtual host, create the directory separately;
2.Annotate the main configuration file, except for calls include /etc/nginx/game.conf#Write absolute paths
3.nginx -t#inspect
4.restart
5.Other basic consistency2. Upload, check
[root@web01 code]# ll /code/ total 18860 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 19304923 Aug 14 11:36 h5_games.zip -rw-r--r-- 1 www www 5 Aug 14 11:51 index.html [root@web01 code]# pwd /code [root@web01 code]# unzip h5_games.zip
3. Check the grammar of nginx for errors
[root@web01 code]# nginx -t nginx: the configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf syntax is ok nginx: configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf test is successful
4. Overload Nginx [reload|restart]
[root@web01 code]# systemctl reload nginx
5. Setting up hosts (based on domain name)
MacBook-Pro:~ driverzeng$ sudo vim /etc/hosts#Windows also works 10.0.0.101 game.driverzeng.com
6. Check if the setup is successful
MacBook-Pro:~ driverzeng$ ping game.driverzeng.com PING game.driverzeng.com (10.0.0.101): 56 data bytes 64 bytes from 10.0.0.101: icmp_seq=0 ttl=64 time=0.267 ms 64 bytes from 10.0.0.101: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.450 ms 64 bytes from 10.0.0.101: icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=0.508 ms 64 bytes from 10.0.0.101: icmp_seq=3 ttl=64 time=0.464 ms
7. Browser Detection
Open browser access: http://game.driverzeng.com
 

Virtual Host
Usually there are many business systems in the enterprise, so how do many business services use Nginx configuration?
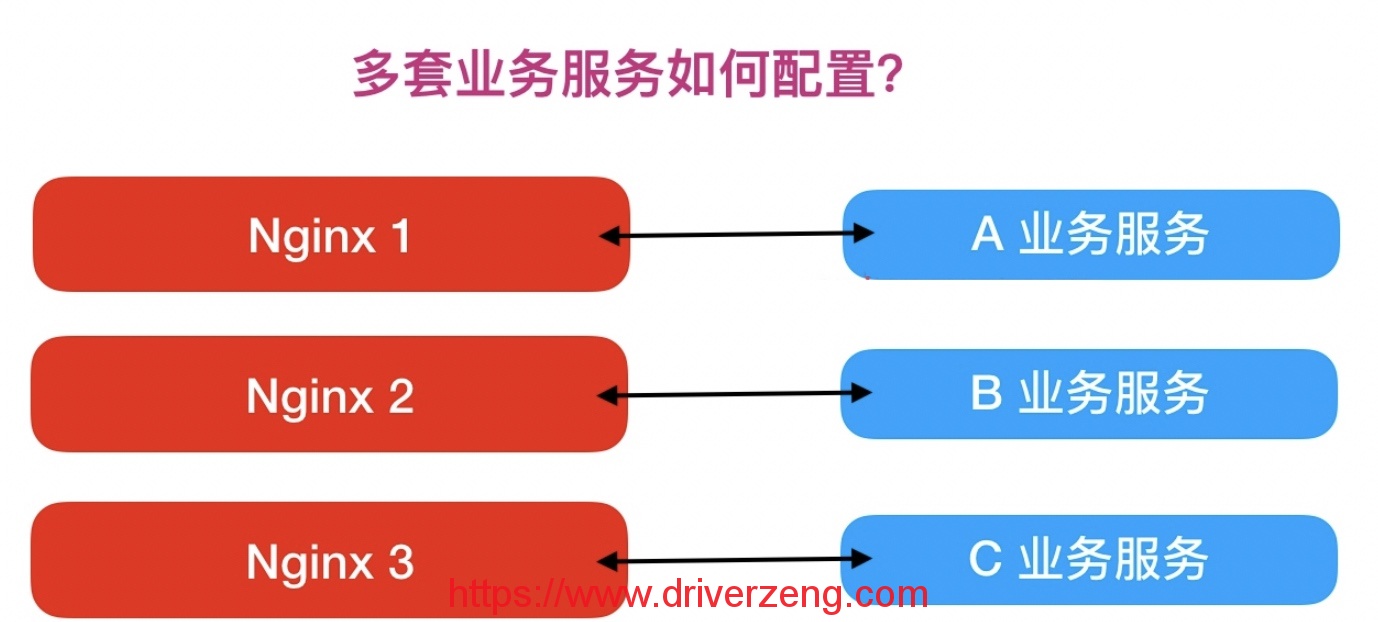 

If deployed in the above way, Nginx needs to be configured by multiple servers, but if deployed in the virtual host mode, multiple separate services will be run on the same Nginx, which are independent of each other. Simply put, seemingly multiple business systems can actually run on a single Nginx service
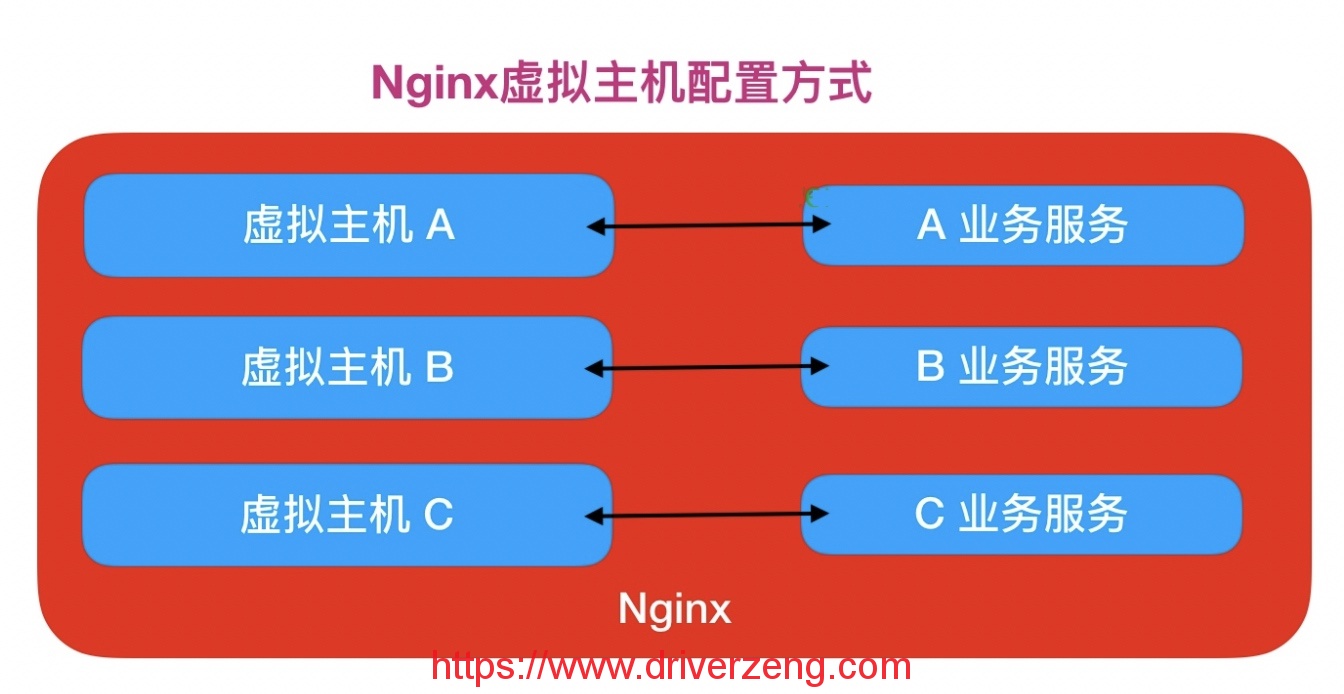 

Nginx configures virtual hosts in three ways:
Mode 1. Host-based multi-IP mode
Mode 2. Port-based configuration
Mode 3: Based on multiple hosts name (multi-domain name)
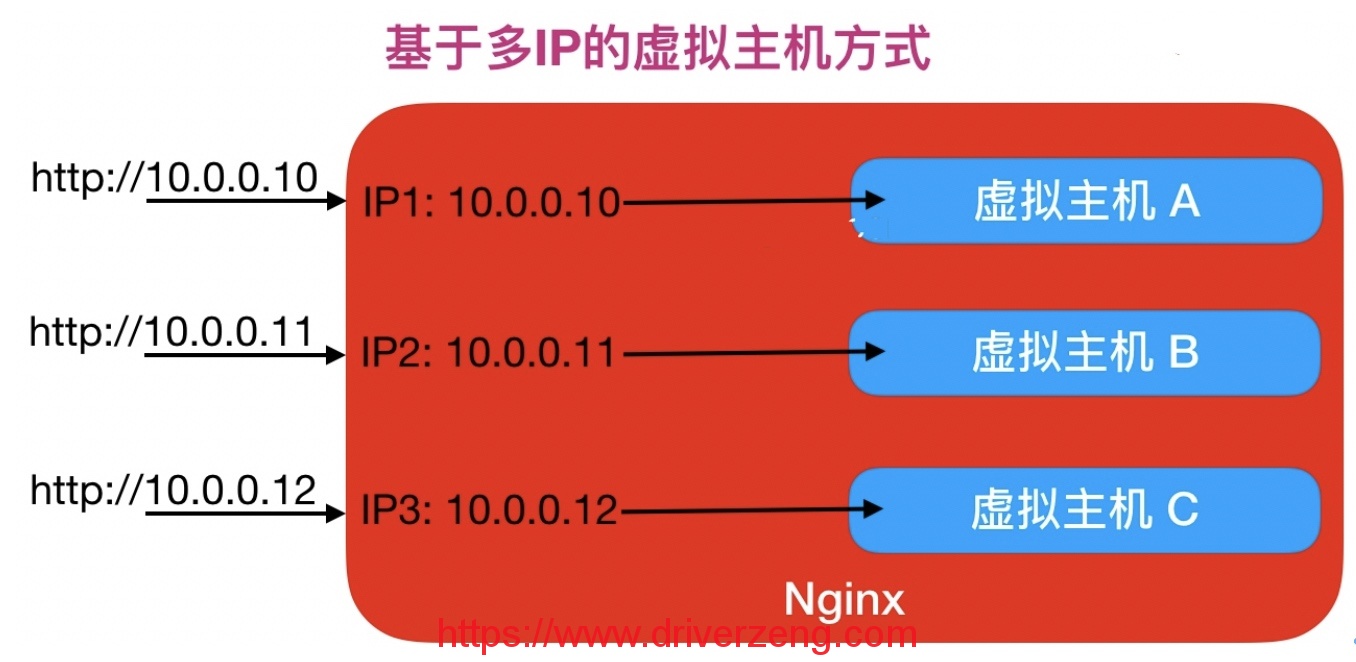 

- Then there are two ways based on multi-IP:
 

1. How to configure multi-network card and multi-IP
server {
...
listen 10.0.0.10:80;
...
}
server {
...
listen 10.0.0.11:80;
...
}2. How to configure single network card with multiple IP
#Add an IP
[root@web01 ~]# ip addr add 10.0.0.11/24 dev eth0
# Virtual Machine Configuration Scheme
[root@web01 ~]# cat /etc/nginx/conf.d/addr1.conf
server {
...
listen 10.0.0.10:80;
...
}
[root@web01 ~]# cat /etc/nginx/conf.d/addr2.conf
server {
...
listen 10.0.0.11:80;
...
}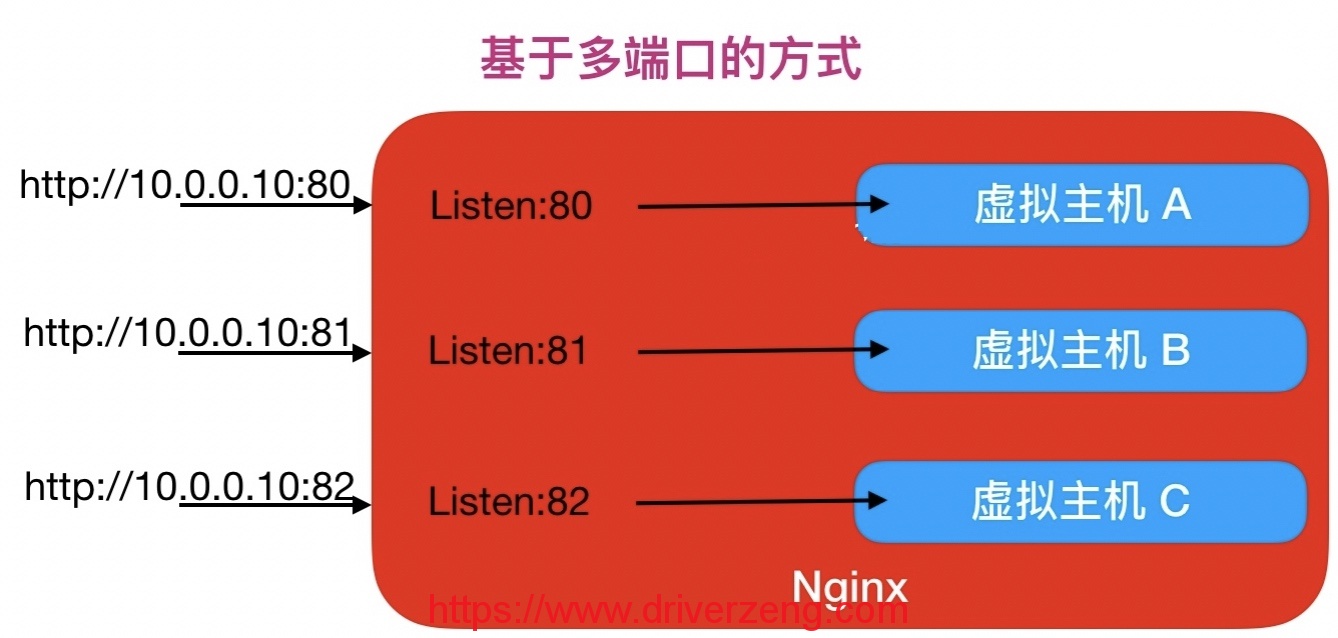 

Nginx multi-port virtual host mode, the specific configuration is as follows
#Simply modify the listen listening port, but do not conflict with the system port
[root@web01 ~]# cat /etc/nginx/conf.d/port1.conf
server {
...
listen 80;
...
}
[root@web01 ~]# cat /etc/nginx/conf.d/port2.conf
server {
...
listen 81;
...
}
[root@web01 ~]# cat /etc/nginx/conf.d/port3.conf
server {
...
listen 82;
...
} 

* 1. Create the corresponding ** web site directory and program code*
[root@web01 ~]# mkdir /soft/code/{server1,server2}
[root@web01 ~]# echo "server1" > /code/server1/index.html
[root@web01 ~]# echo "server2" > /code/server2/index.html2. Configuring Virtual Hosts with Different Domain Names
[root@web02 ~]# cat /etc/nginx/conf.d/server1.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name 1.oldboyedu.com;
root /code/server1;
index index.html;
...
}
[root@web01 ~]# cat /etc/nginx/conf.d/server2.conf
server {
...
listen 80;
server_name 2.oldboyedu.com;
root /code/server2;
index index.html;
}