Introduction to webrtc Chapter 4 data channel
1, Introduction
In the process of realizing end-to-end connection in webrtc, in addition to transmitting media stream, it can also transmit text, files, pictures and other data. It is also practical in IM scenarios, and does not need third-party message services, such as websocket, transparent message and so on.
The creation of data channel depends on the connection of RTCPeerConnection. The connection process can be viewed in Chapter 3. After the connection is established at both ends, data can be sent.
2, Practice
1. Data object RTCDataChannel
that.localConnection.createDataChannel('webrtc-datachannel')
Through RTCPeerConnection connection, you can create an RTCDataChannel object. When creating, you need to pass in the channel name
| Method name | parameter | explain | type |
|---|---|---|---|
| pc.createDataChannel() | Channel name | This method creates a channel to send any data | method |
| pc.ondatachannel() | It is rtcdatachannelevevent event, and the returned parameter is receiver data channel event Channel is the channel | event | |
| RTCDataChannel | Two way channel between two RTCPeerConnection connections | object | |
| RTCDataChannel.send() | Data sent by data | The data sending method and data parameters can be string,byte,ArrayBuffer,Blob, etc | method |
| RTCDataChannel.close() | Close channel | method | |
| RTCDataChannel.onmessage() | The callback function after the channel receives data, event Data is the received data | event |
2. Data sending process
The most basic reference scenario of data channel is text sending. Use the send method of RTCDataChannel to create a data sending channel. After the sender and receiver establish a connection, they can send data
1. Create local connection, remote connection, sendchannel and revicechannel
2. Send, create connection, initiate proposal negotiation and session. Refer to Chapter 3 here
3. Create a locally connected data channel
that.sendChannel = that.localConnection.createDataChannel('webrtc-datachannel')
4. Set the ondatachannel event of the remote connection. The channel in the event parameter is the remote data channel
receiveChannelCallBack: function (event) {
let that = this;
that.receiveChannel = event.channel
that.receiveChannel.onmessage = that.onReceiveMessageCallBack;
that.receiveChannel.onopen = that.onReceiveChannelStateChange;
console.log("Receive channel callback", that.receiveChannel)
},
that.remoteConnection.ondatachannel = that.receiveChannelCallBack;
5. Set the sending and receiving callback methods locally and remotely, and receive the event of the callback method Data is the data in the obtained pipeline
onReceiveMessageCallBack: function (event) {
console.log("Data received:" + event.data)
this.receiveData = event.data
},
3. Examples
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>RTCPeerConnection Connection test</title>
</head>
<body>
<div class="app">
<div>
<h3> send out </h3>
<div style="margin-left: 70px;margin-top: -39px;margin-bottom: 10px;">Status:{[sendChannelState]}
</div>
<div>
<textarea style="width: 400px;height:100px;" placeholder="Please enter the text to send...." v-model="sendData"></textarea>
</div>
</div>
<div>
<h3> receive</h3>
<div style=" margin-left: 70px;margin-top: -39px;margin-bottom: 10px;">Status:{[receiveChannelState]}</div>
<div>
<textarea style="width: 400px;height:100px;">{[receiveData]}</textarea>
</div>
</div>
<input type="button" title="call" value="call" v-on:click="call"/>
<input type="button" title="send out" value="send out" v-on:click="send"/>
<input type="button" title="Hang up" value="Hang up" v-on:click="stop"/>
<hr>
</div>
</body>
<script src="/static/js/Vue.2.5.3.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript">
navigator.getUserMedia = navigator.getUserMedia || navigator.webkitGetUserMedia || navigator.mozGetUserMedia || navigator.msGetUserMedia;
let vm = new Vue({
el: ".app",
delimiters: ['{[', ']}'],
data: {
// Local connection
localConnection: null,
// Remote video stream
remoteConnection: null,
// Local channel
sendChannel: null,
sendChannelState: "",
// Remote channel
receiveChannel: null,
receiveChannelState: "",
// Remote received data
receiveData: "",
// Send data locally
sendData: "",
// ICE service address
configuration: {
"iceServers": [
{
"urls": "stun:49.232.162.254:2478",
"username": "admin",
"credential": "admin"
}
]
},
},
methods: {
stop: function () {
let that = this
that.remoteConnection.close()
that.localConnection.close()
that.localConnection = null
that.remoteConnection = null
console.log("Close session")
}
,
send: async function () {
let that = this;
if (that.sendData == "") {
return
}
if (that.sendChannel == null) {
return
}
console.log(that.sendChannel.readyState)
that.sendChannel.send(that.sendData)
console.log("send data:", that.sendData)
}
,
call: async function () {
let that = this;
console.log("Start call")
// Listen and return icecandidate information
that.localConnection = new RTCPeerConnection()
that.localConnection.addEventListener("icecandidate", that.onIceCandidateA)
// Instantiate transmission channel
that.sendChannel = that.localConnection.createDataChannel('webrtc-datachannel')
that.sendChannel.onopen = that.onSendChannelStateChange
that.sendChannel.onclose = that.onSendChannelStateChange
that.remoteConnection = new RTCPeerConnection(that.configuration)
that.remoteConnection.addEventListener("icecandidate", that.onIceCandidateB)
// Remote data arrival listening event
that.remoteConnection.ondatachannel = that.receiveChannelCallBack;
// Monitor ICE status changes
that.localConnection.addEventListener("iceconnectionstatechange", that.onIceStateChangeA)
that.remoteConnection.addEventListener("iceconnectionstatechange", that.onIceStateChangeB)
// Create call offer
try {
console.log("localConnection establish offer Session start")
const offer = await that.localConnection.createOffer()
await that.onCreateOfferSuccess(offer)
} catch (e) {
console.log("Create session description SD Failed:", e.toString())
}
}
,
receiveChannelCallBack: function (event) {
let that = this;
that.receiveChannel = event.channel
that.receiveChannel.onmessage = that.onReceiveMessageCallBack;
that.receiveChannel.onopen = that.onReceiveChannelStateChange;
console.log("Receive channel callback", that.receiveChannel)
},
onReceiveChannelStateChange: function () {
this.receiveChannelState = this.receiveChannel.readyState
console.log("Accept channel status:" + this.receiveChannel.readyState)
},
onReceiveMessageCallBack: function (event) {
console.log("Data received:" + event.data)
this.receiveData = event.data
},
onSendChannelStateChange: function () {
this.sendChannelState = this.sendChannel.readyState
console.log("send channel state change", this.sendChannel.readyState)
},
// Proposal offer created successfully
onCreateOfferSuccess: async function (event) {
let that = this
// Set connection description
console.log("localConnection establish offer Return to SDP information", event.sdp)
console.log("set up localConnection Local description start...")
try {
await that.localConnection.setLocalDescription(event)
console.log("set up localConnection Local description succeeded")
} catch (e) {
console.log("set up localConnection Local description error:", e.toString())
}
console.log("set up remoteConnection Remote description start")
try {
await that.remoteConnection.setRemoteDescription(event)
console.log("set up remoteConnection The remote description is successful")
} catch (e) {
console.log("set up remoteConnection Remote description error:", e.toString())
}
// Start answering
console.log("remoteConnection Create reply answer start")
try {
const answer = await that.remoteConnection.createAnswer()
console.log("remoteConnection Successfully created reply")
await that.onCreateAnswerSuccess(answer)
} catch (e) {
console.log("remoteConnection Create reply error:", e.toString())
}
}
,
// answer response created successfully
onCreateAnswerSuccess: async function (answer) {
let that = this
console.log("remoteConnection Create reply answer Data:", answer)
console.log("localConnection And remoteConnection Exchange response answer information start")
try {
await that.remoteConnection.setLocalDescription(answer)
console.log("set up remoteConnection Get local answer Answer remote description succeeded")
} catch (e) {
console.log("set up remoteConnection Get local answer Response description error:", e.toString())
}
try {
await that.localConnection.setRemoteDescription(answer)
console.log("set up localConnection Far end answer Response description successful")
} catch (e) {
console.log("set up localConnection Far end answer Response description error:", e.toString())
}
}
,
// Callback method for monitoring ICE state change events
onIceStateChangeA: function (event) {
console.log("monitor localConnection ICE state", this.localConnection.iceConnectionState)
console.log(event)
}
,
// Callback method for monitoring ICE state change events
onIceStateChangeB: async function (event) {
console.log("monitor remoteConnection ICE state", this.remoteConnection.iceConnectionState)
console.log(event)
}
,
onIceCandidateA: async function (event) {
let that = this
try {
if (event.candidate) {
// If the candidate data is exchanged directly, it does not need to be transmitted through the signaling server
await that.remoteConnection.addIceCandidate(event.candidate)
console.log("remoteConnection IceCandidate----------")
console.log(event)
that.onAddIceCandidateSuccess(that.remoteConnection)
}
} catch (e) {
that.onAddIceCandidateError(that.remoteConnection, e)
}
console.log("onIceCandidateA data:" + event.candidate)
}
,
onIceCandidateB: async function (event) {
let that = this
try {
if (event.candidate) {
await that.localConnection.addIceCandidate(event.candidate)
console.log("localConnection IceCandidate----------")
console.log(event)
that.onAddIceCandidateSuccess(that.localConnection)
}
} catch (e) {
that.onAddIceCandidateError(that.localConnection, e)
}
console.log("onIceCandidateB data:" + event.candidate)
},
//
onAddIceCandidateSuccess: function (pc) {
console.log("add to" + this.getPcName(pc) + " IceCandidate success")
},
onAddIceCandidateError: function (pc, err) {
console.log("add to" + this.getPcName(pc) + " IceCandidate fail" + err.toString())
},
getPcName: function (pc) {
return (pc === this.localConnection) ? "localConnection" : "remoteConnection"
},
}
})
</script>
</html>
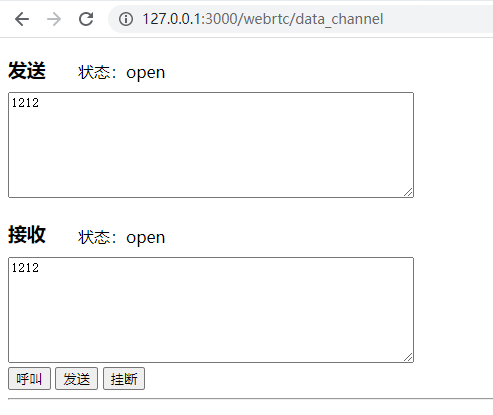
In the above example, simple functions of sending and receiving are realized.
3, Summary
This chapter introduces the basic knowledge and use of WebRtc data channel. This chapter carries out the function of data transmission on the basis of channel connection. The data channel supports secondary data, text messages, text and other data, which is very practical for WebRtc, which focuses on audio and video transmission, so it does not need to be realized with the help of third-party services.
The function of data channel is similar to that realized by Websocket. Both of them have onmessage and send methods. But there are differences between the two
1.Websocket needs background services for data transfer, which is troublesome but highly creative. Based on tcp protocol transmission, the data is more secure and more concerned about data security and reliability
2.RTC realizes point-to-point data transmission faster, and uses ICE server to penetrate nat, which is relative to data reliability. In some scenarios, there may be an additional layer of TURN server forwarding. WebRtc pays more attention to the real-time performance of data, because the loss of data such as video or audio is relatively tolerant and error. Data loss can be compensated by algorithm.
3. Constructing a Websocket requires a url to connect with the server and create a unique SocketSessionId. The connection of DataChannel depends on an RTCPeerConnection object. After the RTCPeerConnection is established, it can contain one or more rtcdatachannels.
4.Websocket allows full duplex communication between browsers and web services. Based on TCP protocol
5. PeerConnection of webrtc allows full duplex communication between two browsers based on SCTP protocol
The point-to-point data transmission is faster. Using ICE server to penetrate nat is relative to data reliability. In some scenarios, there may be an additional layer of TURN server forwarding. WebRtc pays more attention to the real-time performance of data, because the loss of data such as video or audio is relatively tolerant and error. Data loss can be compensated by algorithm.
3. Constructing a Websocket requires a url to connect with the server and create a unique SocketSessionId. The connection of DataChannel depends on an RTCPeerConnection object. After the RTCPeerConnection is established, it can contain one or more rtcdatachannels.
4.Websocket allows full duplex communication between browsers and web services. Based on TCP protocol
5. PeerConnection of webrtc allows full duplex communication between two browsers based on SCTP protocol