IO Classification
IO Classification: Blocking IO, Non-Blocking IO, IO Multiplexing, Asynchronous IO, etc.
Blocking IO
1. Definition: Block if the execution condition is not satisfied when performing an IO operation.Blocking IO is the default form of IO.
2. Efficiency: Blocking IO is a very inefficient type of IO.But because of its simplicity, it is the default IO behavior.
3. Blockage:
-
Function blocking caused by an unsatisfactory execution condition
e.g. accept input recv -
Blocking state due to long IO processing time
e.g. Network Transport, Large Files Read and Write
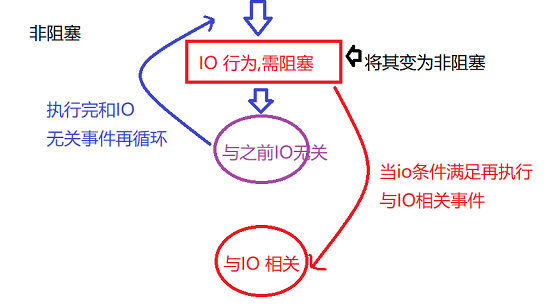
non-blocking IO
1. Definition: By modifying the IO property behavior, the originally blocked IO will become non-blocked.
Set socket to non-blocking IO
sockfd.setblocking(bool)
- Function: Set socket to non-blocking IO
- Parameters: The default is True, meaning socket IO is blocked; False makes socket IO non-blocked
Timeout detection: Set a maximum blocking time beyond which no blocking wait will occur.
sockfd.settimeout(sec)
- Function: Set timeout for sockets
- Parameter: Set time
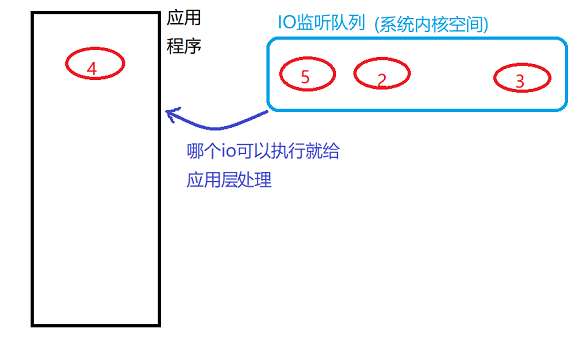
IO Multiplex
1. Definition: Monitor multiple IO events simultaneously, when which IO event is ready to execute which IO event.This creates a behavior that can handle multiple IOs simultaneously, avoids one IO blocking causing other IOs to fail to execute, and improves the efficiency of IO execution.
2. Specific plan:
- select method: windows linux unix
- poll method: linux unix
- epoll method: linux
select method
rs, ws, xs=select(rlist, wlist, xlist[, timeout])
- Function: Monitor IO events, block waiting for IO to occur
-
Parameters:
- The rlist list holds focused IO events waiting to occur
- The wlist list holds the IO events of interest to be proactively processed
- The xlist list list holds IO to handle for focused exceptions
- Timeout timeout
-
Return value:
- Ready IO in rs list rlist
- Ready IO in ws list wlist
- Ready IO in xs list xlist
select implements tcp service
1. Put IO of interest in the list of corresponding monitoring categories
2. Monitoring through the select function
3. Traverse through the list of returned select s to determine ready IO events
4. Handle IO events that occur
Be careful:
If there is an IO event in wlist, select immediately returns to ws
Do not have Dead Loop Occupying Server during IO Processing
IO multiplexing consumes less resources and is more efficient
select tcp service model 1 """ 2 Key Codes 3 4 Idea analysis: 5 1.Will Focus on IO Put in the list of corresponding monitoring categories 6 2.adopt select Functions for monitoring 7 3.ergodic select Return a list of values to make sure you're ready IO Event 8 4.Handle Occurring IO Event 9 """ 10 11 from socket import * 12 from select import select 13 14 # Create a listening socket as a concernIO 15 s = socket() 16 s.setsockopt(SOL_SOCKET,SO_REUSEADDR,1) 17 s.bind(('0.0.0.0',8888)) 18 s.listen(3) 19 20 # Set up a list of concerns 21 rlist = [s] 22 wlist = [] 23 xlist = [s] 24 25 # Cycle MonitoringIO 26 while True: 27 rs,ws,xs = select(rlist,wlist,xlist) 28 # Traverse through three return lists,HandleIO 29 for r in rs: 30 # Based on traversal toIODifferent usesifCase-by-case processing 31 if r is s: 32 c,addr = r.accept() 33 print("Connect from",addr) 34 rlist.append(c) # Add NewIOEvent 35 # else Client Socket Ready 36 else: 37 data = r.recv(1024) 38 # Client Exit 39 if not data: 40 rlist.remove(r) # Remove from the list of concerns 41 r.close() 42 continue # Continue with other readinessIO 43 print("Receive:",data.decode()) 44 # r.send(b'OK') 45 # We want to take the initiative in dealing with thisIOobject 46 wlist.append(r) 47 48 for w in ws: 49 w.send(b'OK') 50 wlist.remove(w) # Remove after Using 51 52 for x in xs: 53 pass
1 """ 2 Key Codes 3 4 Idea analysis: 5 1.Will Focus on IO Put in the list of corresponding monitoring categories 6 2.adopt select Functions for monitoring 7 3.ergodic select Return a list of values to make sure you're ready IO Event 8 4.Handle Occurring IO Event 9 """ 10 11 from socket import * 12 from select import select 13 14 # Create a listening socket as a concernIO 15 s = socket() 16 s.setsockopt(SOL_SOCKET,SO_REUSEADDR,1) 17 s.bind(('0.0.0.0',8888)) 18 s.listen(3) 19 20 # Set up a list of concerns 21 rlist = [s] 22 wlist = [] 23 xlist = [s] 24 25 # Cycle MonitoringIO 26 while True: 27 rs,ws,xs = select(rlist,wlist,xlist) 28 # Traverse through three return lists,HandleIO 29 for r in rs: 30 # Based on traversal toIODifferent usesifCase-by-case processing 31 if r is s: 32 c,addr = r.accept() 33 print("Connect from",addr) 34 rlist.append(c) # Add NewIOEvent 35 # else Client Socket Ready 36 else: 37 data = r.recv(1024) 38 # Client Exit 39 if not data: 40 rlist.remove(r) # Remove from the list of concerns 41 r.close() 42 continue # Continue with other readinessIO 43 print("Receive:",data.decode()) 44 # r.send(b'OK') 45 # We want to take the initiative in dealing with thisIOobject 46 wlist.append(r) 47 48 for w in ws: 49 w.send(b'OK') 50 wlist.remove(w) # Remove after Using 51 52 for x in xs: 53 pass