IO stream

What is iO?
IO is read and write to memory
Both input and output are referenced relative to memory
1 Classification by flow direction
Going to memory is called input, or read
Coming out of memory is called output, or write
2. Different data reading methods
Byte stream
Reading 1 byte is equivalent to 8 binary bits. It can read any type, music and picture
Character stream
Read plain text file
The four top streams are all directly inherited objects
InputStream (byte stream)
OutputStream (byte stream)
Reader (character stream)
Writer (character stream)
Form a good habit. When the flow runs out, it must be closed, otherwise it will consume a lot of resources
close() and flush()
The close () method has four top streams
All output streams are refreshable. There is a flush () method to forcibly output the non output data
File Exclusive
FileInputStream (byte stream)
● int read() reads one byte at a time. Memory and hard disk interact frequently
Return byte value
● int read (byte [] b) reads b.length bytes at a time to improve execution efficiency
Number of bytes returned
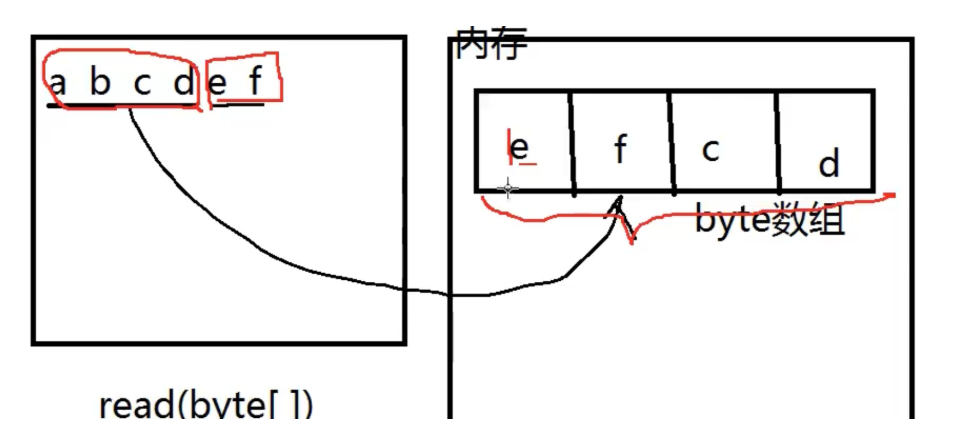
byte []bytes = new byte[4];
int len =0;
while ((len=fis.read(bytes))!=-1){ System.out.print(new String(bytes,0,len));
}//Read byte array length values at a time
Fileoutputstream (byte stream)
int res =0;
byte []bytes =new byte[3];
while ((res=fis.read(bytes))!=-1){ fos.write(bytes,0, res);}
//Write out byte array values at a time
File copy
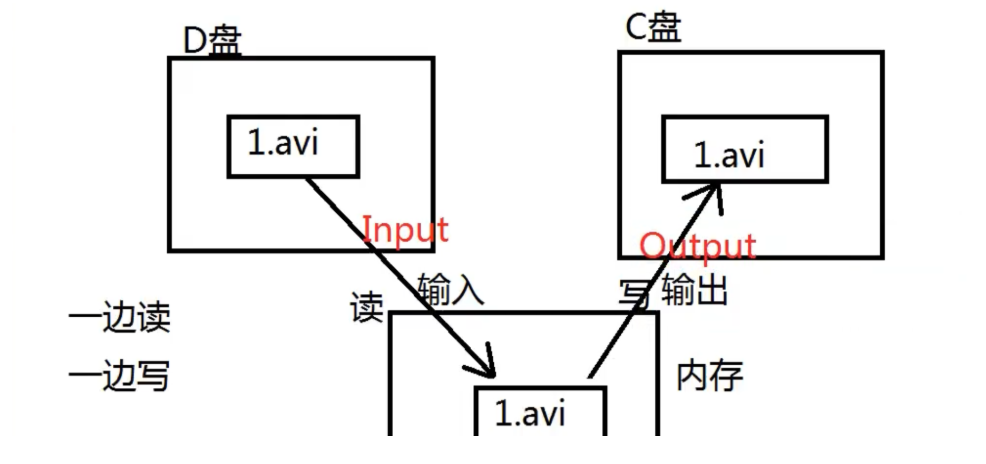
When copying, you can copy any file type
fis = new FileInputStream("src/com/IO/myfile");
fos = new FileOutputStream("src/com/IO/myfile_out");
int res =0;
byte []bytes =new byte[3];
while ((res=fis.read(bytes))!=-1){ fos.write(bytes,0, res);}
FileReader (character stream)
● good at reading ordinary text files
fr = new FileReader("src/com/IO/myfile");
char []chars = new char[1024];
int res = 0;
while ((res=fr.read(chars))!=-1){ System.out.println(new String(chars,0,res));}
Filewriter (character stream)
● good at outputting ordinary text documents
Note: if append is true, the contents of the file will be cleared before writing
fw = new FileWriter("src/com/IO/myfile",true);
//Continue exporting after the contents of the source file
char []chars {'I','yes','in','country','people'};
fw.write(chars);
Convert stream (bytes – > characters)
io.InputStreamReader
When the reader type needs to be passed in, but there is actually an Inputstream that can be converted through the conversion stream
BufferedReader bf = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("src/com/IO/myfile")));
io.OutputStreamWriter
When the Writer type needs to be passed in, but there is actually an Outputstream, it can be converted through the conversion stream
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new InputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("src/com/IO/myfile")));
Buffer stream exclusive
io.BuffereReader
You do not need to define byte/char arrays yourself
new needs to pass in the reader, but the reader is an abstract class. You can pass in the subclass FileReader
● readLine() method
Read a line of data without line breaks
FileReader read =newFileReader("src/com/IO/myfile");
//Node flow
BufferedReader bf = new BufferedReader(read);//Packaging flow
String line = null;
while ((line = bf.readLine())!=null){ System.out.println(line); }
io.BuffereWriter
ditto
io.BuffereInputStream
ditto
io.BuffereOutputStream
ditto
Data flow exclusive
io.DataInputStream
understand
io.DataOutputStream
understand
Standard output stream
io.PrintWriter
io.PrintStream
Object specific flow
io.ObjectInputStream
Reads the instantiated object information of the class stored in the specified file into memory
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("students"));
Object obj = ois.readObject(); System.out.println(obj);
ois.close();
io.ObjectOutputStream
When we need to realize the persistent storage of information, we can write the instantiated object information of a class out of the specified file
Note: the customized class sequence requires this class to implement the Serializable interface, which is only an identification and does not contain any methods
When serialized, each class generates a unique serial versionuid
Student student1 = new Student("zs", 18);
ObjectOutputStream out = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("students")); out.writeObject(student1);
out.flush();
out.close();
}}class Student implements Serializable