iptables
firewall
Function: prevent others from entering your own computer and attacking your own computer. You can't kill viruses
Attack mode:
dos
ddos
cc
syn flooding et al
SNMP protocol --- simple network manager protocol
Simple network management protocol port 161 tcp/udp
Software firewall
The firewall function of linux system is realized by the kernel
Firewall: data filtering mechanism
The packet filtering mechanism is netfilter and the management tool is iptables
netfilter is the "kernel state" of linux firewall
iptables is the "user mode" of linux firewall
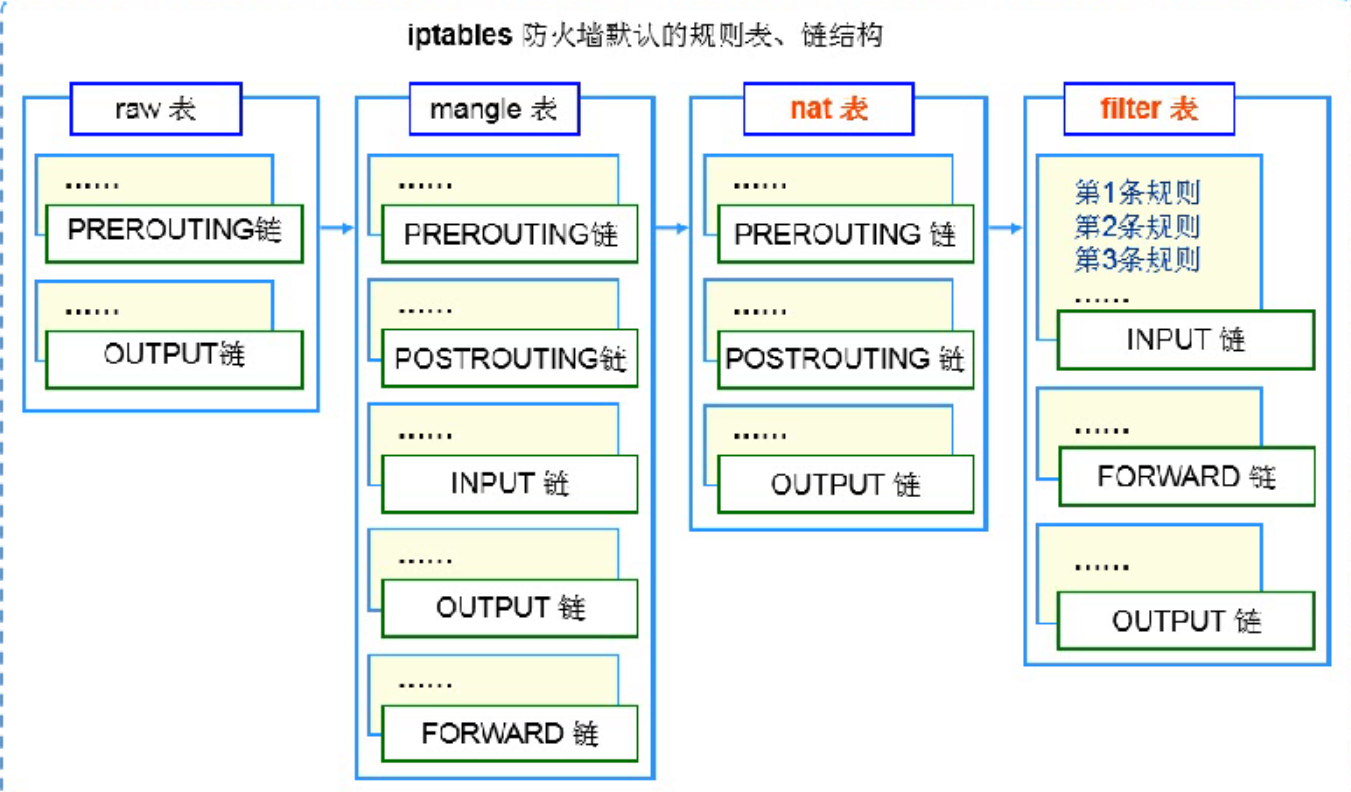
Rule chain
There are five default rule chains:
INPUT: process inbound packets
OUTPUT: process outbound packets
FORWARD: process forwarded packets
POSTROUTING chain: process packets after routing
Routing chain: process packets before routing
Rule table: there are many rule chains in the table
There are four default rule tables:
raw table: determines whether to track the status of the packet
mangle table: setting tags for packets
nat table: modify the source, destination IP address or port in the packet
Filter table: determine whether to release the packet (filter) -- protect application data and routing data
[root@peipei ~]# iptables -L -t filter Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination
Default rule table and chain structure
raw
[root@peipei ~]# iptables -L -t raw Chain PREROUTING (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination
mangle
[root@peipei ~]# iptables -L -t mangle Chain PREROUTING (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination Chain POSTROUTING (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination
nat
[root@peipei ~]# iptables -L -t nat Chain PREROUTING (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination Chain POSTROUTING (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination
filter
[root@peipei ~]# iptables -L -t filter Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination
iptables -L does not connect the table name by default, and the filter is viewed
[root@peipei ~]# iptables -L Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination
Priority between rule tables
raw,mangle,nat,filter
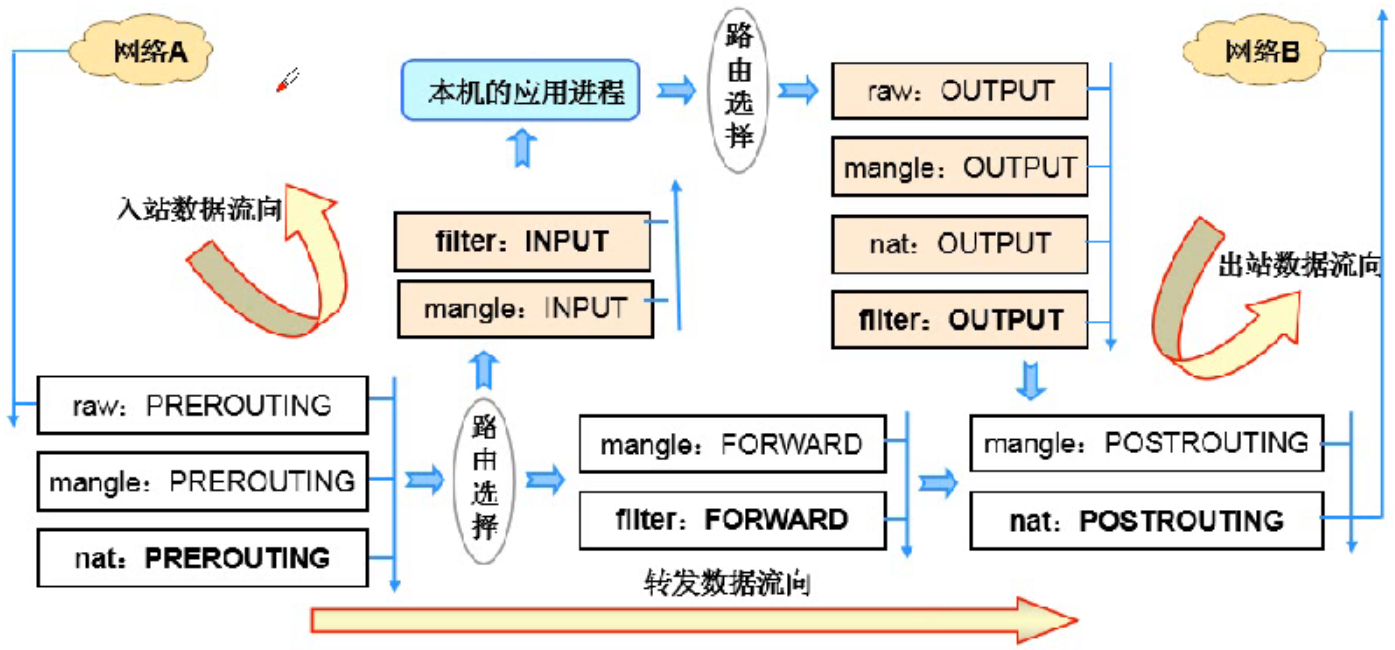
Matching order between rule chains
Inbound data: preouting, INPUT
Battle data: output, POSTROUTING
Forwarding data: forwarding, FPRWARD, POSTROUTING
Matching order within the rule chain
Check in sequence, and stop when a matching rule is found (there will be exceptions to the LOG Policy)
If no matching rule is found in the chain, it will be handled according to the default policy of the chain
#Clear filter rules iptables -F #Set default policy iptables -P INPUT DROP #Disable web iptables -A INPUT -s 192.168.186.135 -p tcp --dport 80 -j DROP #Disable MYSQL iptables -A INPUT -s 192.168.186.135 -p tcp --dport 3306 -j DROP #Disable someone else PING this machine iptables -A INPUT -p icmp --icmp-type 8 -j DROP #Allow this machine to ping other hosts iptables -A INPUT -p icmp --icmp-type 0 -j ACCEPT #Allow ssh iptables -A INPUT -s 192.168.186.135 -p tcp --dport 22 -j ACCEPT
Set default policy
iptables -P INPUT DROP
This command will cause the service of local ssh connection not to be opened and the server cannot be connected remotely.
It is best to set rules for clearing iptables for scheduled tasks
View chain order
[root@peipei ~]# iptables -L -n --line-num -v Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 511 packets, 69681 bytes) num pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination 1 3 228 DROP icmp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 icmptype 8 2 2 168 ACCEPT icmp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 icmptype 0 Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes) num pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 497 packets, 88995 bytes) num pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
-n display in digital form
-
- Line num displays the number of the rule
-v displays the number of matched packets and bytes
Data filtering flow chart
Syntax format of iptables command
iptables -t table name chain name condition matching -j target action or jump
matters needing attention
- When the table name is not specified, the default is the filter table
- When chain name is not specified, it means all chains in the table by default
- Unless you set the default policy for the rule chain, you need to specify the matching criteria
Set rule content:
-A: Add a new rule at the end of the chain
-1: I nsert a new rule at the specified position (or head of chain)
Default insert to head of chain
[root@peipei ~]# iptables -I INPUT -s 192.168.186.135 -p tcp --dport 80 -j DROP [root@peipei ~]# iptables -L Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination DROP tcp -- 192.168.186.135 anywhere tcp dpt:http DROP icmp -- anywhere anywhere icmp echo-request ACCEPT icmp -- anywhere anywhere icmp echo-reply DROP tcp -- 192.168.186.135 anywhere tcp dpt:mysql Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination
Insert at specified location
[root@peipei ~]# iptables -L Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination DROP tcp -- 192.168.186.135 anywhere tcp dpt:http ACCEPT tcp -- 192.168.186.135 anywhere tcp dpt:ssh DROP icmp -- anywhere anywhere icmp echo-request ACCEPT icmp -- anywhere anywhere icmp echo-reply DROP tcp -- 192.168.186.135 anywhere tcp dpt:mysql Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination
-R: Rules for modifying and replacing specified locations or contents
-P: Sets the default policy for the specified chain
List view rules
-50: View rule information in the list
- -Line numbers: displays the line number of the rule when viewing rule information
-n: Display IP address, port and other information in digital form
-v: Displays details such as the number of packets and bytes
Clear rule
-D: Delete rules for the specified location or content
[root@peipei ~]# iptables -D INPUT 5 [root@peipei ~]# iptables -L Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination DROP tcp -- 192.168.186.135 anywhere tcp dpt:http ACCEPT tcp -- 192.168.186.135 anywhere tcp dpt:ssh DROP icmp -- anywhere anywhere icmp echo-request ACCEPT icmp -- anywhere anywhere icmp echo-reply Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination
-F: Clear all rules in the rule chain
Custom rule chain
-N: Create a new rule chain
User defined chain name: passed to the rules in the user-defined chain for processing
1. Create a custom chain
[root@peipei ~]# iptables -N WEB [root@peipei ~]# iptables -L Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination Chain WEB (0 references) target prot opt source destination
2. Add rules to the custom chain
[root@peipei ~]# iptables -I WEB -p tcp --dport 80 -s 192.168.186.140 -j REJECT [root@peipei ~]# iptables -L Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination Chain WEB (0 references) target prot opt source destination REJECT tcp -- 192.168.186.140 anywhere tcp dpt:http reject-with icmp-port-unreachable
-10: Delete custom rule chain
other
-h: View help for using iptables command
Common packet processing methods
ACCEPT: release data package
DROP: DROP packets
REJECT: REJECT packet
LOG: record LOG information and pass it to the next rule for processing
Set conditions for matching packets

Protocol matching
-p protocol name
Address matching
-s source address
-d destination address
Interface matching
-i network interface name (receive)
-o network interface name (send)
REJECT
Will reply
[root@peipei ~]# iptables -A INPUT -p icmp -j REJECT

Port matching
-
-sport source port
-
-dport destination port
20: 80 indicates a range of ports
TCP tag matching
-
- tcp-flags SYN,RST,ACK SYN
Indicates to check syn, RST and ACK. Only when SYN is 1, the condition is met - three handshakes
ICMP type matching
- -ICMP type
echo-request 8 echo-reply 0
MAC address matching
-M MAC -- MAC source MAC address
Multi port matching
-M multiport -- Sport source port list / -- dports destination port list
Multiple ports are separated, and continuous ports are represented by:
Packet state matching
-M state -- state type
Common packet states include:
NEW (first connection), ESTABLISHED (ESTABLISHED connection), RELATED (associated -- establish another connection according to one connection)
Multiple states, split
[root@peipei ~]# iptables -A INPUT -p tcp -m state --state ESTABLISHED,RELATED -j ACCEPT [root@peipei ~]# iptables -L Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination DROP tcp -- 192.168.186.135 anywhere tcp dpt:http ACCEPT tcp -- 192.168.186.135 anywhere tcp dpt:ssh DROP icmp -- anywhere anywhere icmp echo-request ACCEPT icmp -- anywhere anywhere icmp echo-reply REJECT icmp -- anywhere anywhere reject-with icmp-port-unreachable ACCEPT tcp -- anywhere anywhere state RELATED,ESTABLISHED Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination
FTP --- file transfer protocol
Active mode: in TCP/IP protocol, the TCP Port number of FTP standard command is 21, and the data Port of Port mode is 20.
Turn on passive mode --- passive
iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 21 -j ACCEPT iptables -A INPUT -m state --state ESTABLIED,RELATED -j ACCEPT
Load modules that support ftp status tracking
modprobe ip_conntrack_ftp
lsmod
lsmod is a command line utility that displays information about loaded Linux kernel modules.
[root@peipei ~]# lsmod Module Size Used by iptable_raw 12678 0 iptable_mangle 12695 0 iptable_nat 12875 0 nf_nat_ipv4 14115 1 iptable_nat nf_nat 26583 1 nf_nat_ipv4 nf_conntrack_ipv4 15053 2 nf_defrag_ipv4 12729 1 nf_conntrack_ipv4 xt_conntrack 12760 1 nf_conntrack 137239 4 nf_nat,nf_nat_ipv4,xt_conntrack,nf_conntrack_ipv4 libcrc32c 12644 2 nf_nat,nf_conntrack AliSecGuard 22180 2 ipt_REJECT 12541 1 nf_reject_ipv4 13373 1 ipt_REJECT iptable_filter 12810 1
modprobe
You can load a specified individual module or a group of dependent modules
[root@peipei ~]# modprobe ip_conntrack_ftp [root@peipei ~]# lsmod|grep ftp nf_conntrack_ftp 18638 0 nf_conntrack 137239 5 nf_nat,nf_nat_ipv4,xt_conntrack,nf_conntrack_ftp,nf_conntrack_ipv4
Module storage directory
[root@peipei netfilter]# pwd /lib/modules/3.10.0-957.el7.x86_64/kernel/net/netfilter
General structure of firewall script
1. Set variables such as network segment, network card and IP address
2. Load kernel modules related to package filtering
ETP related, ip_nat_ftp, ip_conntrack_ftp
Mail related: ip_nat_irc,ip_ conntrack_irc
3. Confirm that the routing forwarding function is enabled
Method 1: / SBIN / sysctl - W net ipv4. ip_ forward=1
[root@peipei yum.repos.d]# /sbin/sysctl -w net.ipv4.ip_forward=1 net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1
Method 2: echo 1 > / proc / sys / netipv4 / IP_ forward
[root@peipei yum.repos.d]# cat /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward 0
Method 3: modify / etc / sysctl Conf, set net ipv4. ip_ forward = 1
[root@peipei yum.repos.d]# cat /etc/sysctl.conf vm.swappiness = 0 net.ipv4.neigh.default.gc_stale_time = 120 # see details in https://help.aliyun.com/knowledge_detail/39428.html net.ipv4.conf.all.rp_filter = 0 net.ipv4.conf.default.rp_filter = 0 net.ipv4.conf.default.arp_announce = 2 net.ipv4.conf.lo.arp_announce = 2 net.ipv4.conf.all.arp_announce = 2 # see details in https://help.aliyun.com/knowledge_detail/41334.html net.ipv4.tcp_max_tw_buckets = 5000 net.ipv4.tcp_syncookies = 1 net.ipv4.tcp_max_syn_backlog = 1024 net.ipv4.tcp_synack_retries = 2 net.ipv6.conf.all.disable_ipv6 = 1 net.ipv6.conf.default.disable_ipv6 = 1 net.ipv6.conf.lo.disable_ipv6 = 1 kernel.sysrq = 1
4. Specific firewall rule content for adding
Clear the original rules and create new rules
Import and export firewall rules
Export rules
iptables -save
[root@peipei yum.repos.d]# iptables-save # Generated by iptables-save v1.4.21 on Fri May 14 16:44:28 2021 *raw :PREROUTING ACCEPT [1299:345978] :OUTPUT ACCEPT [976:173880] COMMIT # Completed on Fri May 14 16:44:28 2021 # Generated by iptables-save v1.4.21 on Fri May 14 16:44:28 2021 *mangle :PREROUTING ACCEPT [1330:347704] :INPUT ACCEPT [1330:347704] :FORWARD ACCEPT [0:0] :OUTPUT ACCEPT [997:179210] :POSTROUTING ACCEPT [997:179210] COMMIT # Completed on Fri May 14 16:44:28 2021 # Generated by iptables-save v1.4.21 on Fri May 14 16:44:28 2021 *nat :PREROUTING ACCEPT [60:5596] :INPUT ACCEPT [13:672] :OUTPUT ACCEPT [120:8310] :POSTROUTING ACCEPT [120:8310] COMMIT # Completed on Fri May 14 16:44:28 2021 # Generated by iptables-save v1.4.21 on Fri May 14 16:44:28 2021 *filter :INPUT ACCEPT [124:12580] :FORWARD ACCEPT [0:0] :OUTPUT ACCEPT [1367:252554] -A INPUT -s 192.168.186.135/32 -p tcp -m tcp --dport 80 -j DROP -A INPUT -s 192.168.186.135/32 -p tcp -m tcp --dport 22 -j ACCEPT -A INPUT -p icmp -m icmp --icmp-type 8 -j DROP -A INPUT -p icmp -m icmp --icmp-type 0 -j ACCEPT -A INPUT -p icmp -j REJECT --reject-with icmp-port-unreachable -A INPUT -p tcp -m state --state RELATED,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT COMMIT # Completed on Fri May 14 16:44:28 2021
Save rule information in combination with redirection
[root@peipei /]# iptables-save >/lianxi/all_iptables.txt [root@peipei /]# cd /lianxi [root@peipei lianxi]# ls all_iptables.txt [root@peipei lianxi]# cat all_iptables.txt # Generated by iptables-save v1.4.21 on Fri May 14 16:46:26 2021 *raw :PREROUTING ACCEPT [1591:370606] :OUTPUT ACCEPT [1170:204910] COMMIT # Completed on Fri May 14 16:46:26 2021 # Generated by iptables-save v1.4.21 on Fri May 14 16:46:26 2021 *mangle :PREROUTING ACCEPT [1622:372332] :INPUT ACCEPT [1622:372332] :FORWARD ACCEPT [0:0] :OUTPUT ACCEPT [1191:210240] :POSTROUTING ACCEPT [1191:210240] COMMIT # Completed on Fri May 14 16:46:26 2021 # Generated by iptables-save v1.4.21 on Fri May 14 16:46:26 2021 *nat :PREROUTING ACCEPT [61:5656] :INPUT ACCEPT [14:732] :OUTPUT ACCEPT [129:8942] :POSTROUTING ACCEPT [129:8942] COMMIT # Completed on Fri May 14 16:46:26 2021 # Generated by iptables-save v1.4.21 on Fri May 14 16:46:26 2021 *filter :INPUT ACCEPT [132:13330] :FORWARD ACCEPT [0:0] :OUTPUT ACCEPT [1561:283584] -A INPUT -s 192.168.186.135/32 -p tcp -m tcp --dport 80 -j DROP -A INPUT -s 192.168.186.135/32 -p tcp -m tcp --dport 22 -j ACCEPT -A INPUT -p icmp -m icmp --icmp-type 8 -j DROP -A INPUT -p icmp -m icmp --icmp-type 0 -j ACCEPT -A INPUT -p icmp -j REJECT --reject-with icmp-port-unreachable -A INPUT -p tcp -m state --state RELATED,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT COMMIT # Completed on Fri May 14 16:46:26 2021
Import rules
iptables-restore
[root@peipei lianxi]# iptables-restore </lianxi/all_iptables.txt
Boot auto load script
/etc/rc.local
vim /etc/rc.local #!/bin/bash # THIS FILE IS ADDED FOR COMPATIBILITY PURPOSES # # It is highly advisable to create own systemd services or udev rules # to run scripts during boot instead of using this file. # # In contrast to previous versions due to parallel execution during boot # this script will NOT be run after all other services. # # Please note that you must run 'chmod +x /etc/rc.d/rc.local' to ensure # that this script will be executed during boot. touch /var/lock/subsys/local
Need to add permissions
[root@peipei lianxi]# ll /etc/rc.d/rc.local -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 473 Jul 3 2019 /etc/rc.d/rc.local [root@peipei lianxi]# chmod +x /etc/rc.d/rc.local [root@peipei lianxi]# ll /etc/rc.d/rc.local -rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 473 Jul 3 2019 /etc/rc.d/rc.local
/root/.bashrc
[root@peipei lianxi]# vim /root/.bashrc
# .bashrc
# User specific aliases and functions
alias rm='rm -i'
alias cp='cp -i'
alias mv='mv -i'
# Source global definitions
if [ -f /etc/bashrc ]; then
. /etc/bashrc
fi
~