1, Encapsulation
1. There can only be one class modified by public in the file. If there is more than one class, an error will be reported:

2. Four access modifiers:
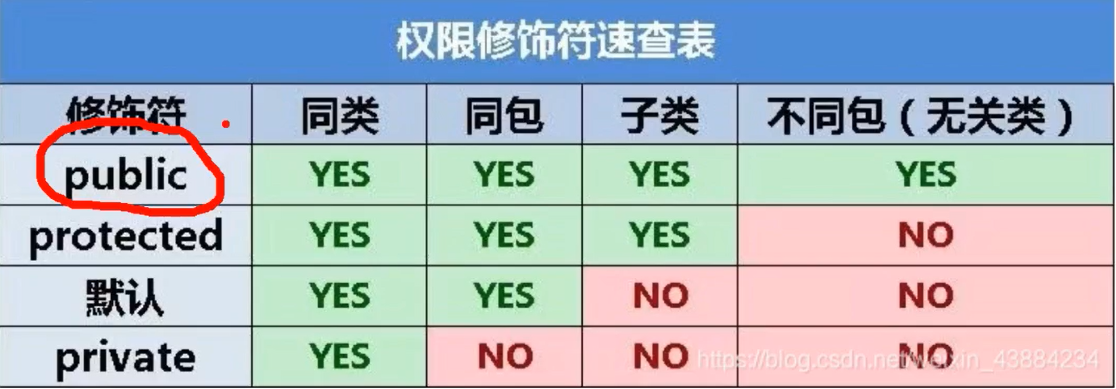
3. private for encapsulation
① it can be seen from 2 that variable methods modified by private can only be used in this class. How to use them
As follows:
class Student{
private String name;
private int sno;
private String subject;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getSno() {
return sno;
}
public void setSno(int sno) {
this.sno = sno;
}
public String getSubject() {
return subject;
}
public void setSubject(String subject) {
this.subject = subject;
}
}
Note: the get and set methods are used to set and call variables modified by private by creating objects. After the this keyword, just know it first.
② how to call? As follows
public class TextStudent {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student student = new Student();
student.setName("Wang ");
student.setSno(2);
student.setSubject("language");
System.out.println(student.getName()+student.getSno()+student.getSubject());
//Wang Zhenya 2 Chinese
}
}4. Construction method
① function: initialize the object, and each instantiation of the object will call the construction method
② format: the method with the same name as the class and no return value type has no return value
③ use and call of construction method
class Car{
public Car(){
System.out.println("Welcome to the car home");
}
public class CarText {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Car car = new Car();
}}5. Method overload
① concept: there are multiple methods in the same class with the same method name but different parameter lists
② this keyword: This represents this class, which can be understood as Cat cat = new Cat();
The following is this sum=20;
class Cat{
int sum = 20;
int s=30;
public void eat(){
int sum=10;
System.out.println(sum);
System.out.println(s);
System.out.println(this.sum);
}
}
③ use and call
For overloading of construction methods:
class Car{
public Car(){
System.out.println("Welcome to the car home");
}public Car(String color){
this.color=color;
}}public class CarText {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Car car = new Car();
Car car2 = new Car("red");}}For overloading of functional methods:
class Car{
public void start(){
System.out.println("My car started");
}
public void start(String color){
System.out.println("My car started");
}public class CarText {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Car car = new Car();
car.start();}}6. Code block
① Construct code blocks and local code blocks:
Execution order: triggered every time the constructor is called, and it takes precedence over the execution of the constructor
public class TeacherTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Teacher teacher1 = new Teacher();// The construction code block is called before the construction method
}
}
class Teacher{
String name;
String age;
public Teacher(){
System.out.println("good morning");
}
{
System.out.println("I'm building blocks");
}
public void cals(){
System.out.println("I'm teaching");
{
System.out.println("I'm a local code block");
int i=10;
System.out.println(i);
}
//System.out.println(i);,, An error will be reported because local code blocks can be used locally
}
}
② sequence of code blocks
Construction code block -- > construction method -- > object created successfully -- > local code block
7. Application of this keyword
//this(): call the parameter free constructor of benzene class
//The statement related to this must be written on the first line
//This (parameter): call the line parameter constructor of this class
class Dog{
String name;
int age;
public Dog(){
this(666);
}
public Dog(int age){
this.age=age;
}
}