1. Date class
java. The util package provides a Date class to encapsulate the current Date and time. The Date class provides two constructors to instantiate a Date object.
constructor
date(): get the number of milliseconds from January 1, 1970
Methods in Date
Long getTime(): get timestamp (i.e. milliseconds)
int compareTo(Date date)
Compare the Date object when this method is called with the specified Date. Returns 0 when the two are equal. The calling object returns a negative number before the specified Date. The calling object returns a positive number after the specified Date.
2. Format
There are two ways: use printf to format the date and use the SimpleDateFormat class
printf format date
Format: start with% t and add conversion character. The specific meanings of conversion symbols are shown in the table below:
| Conversion character | explain | Example |
|---|---|---|
| c | Include all date and time information | Saturday October 27 14:21:20 CST 2007 |
| F | "Year Month Day" format | 2007-10-27 |
| D | "Month / day / year" format | 10/27/07 |
| r | "HH:MM:SS PM" format (12 hour system) | 02:25:51 PM |
| T | "HH:MM:SS" format (24 hour system) | 14:28:16 |
| R | "HH:MM" format (24 hour system) | 14:28 |
code:
//Date objects use printf to format dates
System.out.printf("Current date format:%tF%n",date);
System.out.printf("Current date format:%tD%n",date);
System.out.printf("Current date format:%tr%n",date);
System.out.printf("Current date format:%tT%n",date);
System.out.printf("Current date format:%tR%n",date);Effect:

SimpleDateFormat class
Description: SimpleDateFormat class is thread unsafe. The SimpleDateFormat class uses a string as the encoding format.
In this mode, all ASCII letters are reserved as mode letters, which are defined as follows:
| letter | describe | Example |
|---|---|---|
| G | Epoch mark | AD |
| y | Four digit year | 2001 |
| M | month | July or 07 |
| d | Date of one month | 10 |
| h | A.M./P.M. (1~12) format hours | 12 |
| H | Hours of the day (0-23) | 22 |
| m | Minutes | 30 |
| s | Seconds | 55 |
| S | Msec | 234 |
| E | What day is today? | Tuesday |
| D | Days of the year | 360 |
| F | The day of the week of the month | 2 (second Wed. in July) |
| w | What week of the year | 40 |
| W | Week of the month | 1 |
| a | A.M./P.M. mark | PM |
| k | Hours of the day (1-24) | 24 |
| K | A.M./P.M. (0~11) format hours | 10 |
| z | time zone | Eastern Standard Time |
| ' | Text delimiter | Delimiter |
| " | Single quotation mark | ` |
code:
//Format conversion of date object SimpleDateFormat format
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss");
String date1 = sdf.format(date);
System.out.println(date1);
//SimpleDateFormat exercise
//Date conversion format contact
SimpleDateFormat sdf1 = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd");
SimpleDateFormat sdf2 = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM");
String date2 = sdf1.format(date);
String date3 = sdf2.format(date);
System.out.println(date2);
System.out.println(date3);
effect:

The SimpleDateFormat class is converted to a Date object
code:
//Convert SimpleDateFormat to date format. Note: if the format is yyyy MM DD, the conversion is wrong. I changed yyyy to yyyy
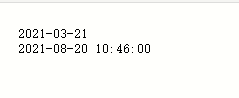
String dateS = "2021-03-21 ";
SimpleDateFormat sdf3 = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd");
try {
Date date4 = sdf3.parse(dateS);
System.out.println(sdf3.format(date4));
} catch (ParseException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
String dates1 = "2021-08-20 10:45:60";
SimpleDateFormat sdf4 = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss");
try {
Date date5 = sdf4.parse(dates1);
System.out.println(sdf4.format(date5));
} catch (ParseException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}effect:
3.calendar Class
The calendar class can obtain specific parts of time, such as hours, minutes and seconds, and can add and subtract dates.
Note: the calendar class is an abstract class.
Understand through code
//Basic usage of Calendar class for date time calculation
//Create calendar class
Calendar calendar = Calendar.getInstance();//This is to get the current time
Date date5 = calendar.getTime(); //This is to convert calendar to date
System.out.println(date5);
//Create a calendar to specify the time
Calendar calendar1 = Calendar.getInstance();
calendar1.set(2021,6-1,12);
Date cDate = calendar1.getTime();
SimpleDateFormat CSdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd");
System.out.println(CSdf.format(cDate));
//Set time using set
Calendar calendar2 = Calendar.getInstance();
calendar2.set(2021,8-1,20);
Date cDate1 = calendar2.getTime();
SimpleDateFormat cSdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd");
System.out.println(cSdf.format(cDate1));
//Use add settings
Calendar calendar3 = Calendar.getInstance();
calendar3.add(Calendar.DATE,10); //The parameter of 10 indicates the date ten days after the current date
Date cDate2 = calendar3.getTime();
SimpleDateFormat cSdf2 = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd");
System.out.println(cSdf2.format(cDate2));
//Use add to set the time
Calendar calendar4 = Calendar.getInstance();
calendar4.add(Calendar.YEAR,2);
Date cDate3 = calendar4.getTime();
System.out.println(cDate3);
//Acquisition of calendar class object information
Calendar calendar5 = Calendar.getInstance();
int year = calendar5.get(Calendar.YEAR);
int month = calendar5.get(Calendar.MONTH);
int day = calendar5.get(Calendar.DATE);
int hour = calendar5.get(Calendar.HOUR);
int minute = calendar5.get(Calendar.MINUTE);
int second = calendar5.get(Calendar.SECOND);
System.out.println(year+" "+month+" "+day+" "+hour+" "+minute+" "+second);