Java drawing class
1.Graphics class
It provides common drawing methods, which can be used to draw text and pictures such as lines, rectangles and polygons. Its operations mainly include color, font, brush, text, image and so on
2.Graphics2D class
Using the Graphics2D class can achieve stronger image rendering functions
3. Cast Graphics to Graphics2D class:
public static void paint(Graphics g){
Graphics2D g2 = (Graphics2D)g;
}
Drawing graphics
Common Graphics drawing methods of Graphics class
| method | explain |
|---|---|
| draw(int x,int y,int height,int startAngle,int arcAngle) | Arc |
| drawLine(int x1,int y1,int x2,int y2) | straight line |
| drawOval(int x,int y,int width,int height) | ellipse |
| drawPolygon(int[] xPoints,int[] yPoints,int nPoints) | polygon |
| drawPolyline(int[] xPoints,int[] yPoints,int nPoints) | trace polygone |
| drawRect(int x,int y,int width,int height) | rectangle |
| drawRoundRect(int x,int y,int width,int height,int arcWidth,int arcAngle) | Rounded rectangle |
| fillArc(int x,int y,int width,int height,int startAngle,int arcAngle) | Solid arc |
| fillOval(int x,int y,int width,int height) | Solid ellipse |
| fillPolygon(int[] xPoints,int[] yPoints,int nPoints) | Solid polygon |
| fillRect(int x,int y,int width,int height) | Solid rectangle |
| fillRoundRect(int x,int y,int width,int height,int arcWidth,int arcHeight) | Solid rounded rectangle |
When we want to draw graphics, we must create and initialize graphics class objects. These graphics must be the implementation class of the Shape interface, and then drawn using the draw method of the Graphics2D class, or filled with the fill method.
Syntax:
draw(Shape form) fill(Shape form)
Common graphics classes:
Main function:
public static void main(String[] args) {
new G_1().setVisible(true);
}
- Arc2D class: Arc
Graphics2D g2d =(Graphics2D)g;
Shape[] shapes = new Shape[3];
shapes[0] = new Arc2D.Double(50,50,185,160,10,90,Arc2D.OPEN);//Coordinate position (50, 50), width 85, height 60, starting angle 5 degrees and ending angle 90 degrees
shapes[1] = new Arc2D.Double(150,150,185,160,10,90,Arc2D.CHORD);
shapes[2] = new Arc2D.Double(200,300,185,160,10,90,Arc2D.PIE);
for (Shape shape:shapes){//Traversal graph array
g2d.draw(shape);//Drawing graphics
}
//Arc2D.OPEN,Arc2D.CHORD,Arc2D.PIE indicates that the arc is open arc, bow arc and pie arc respectively.
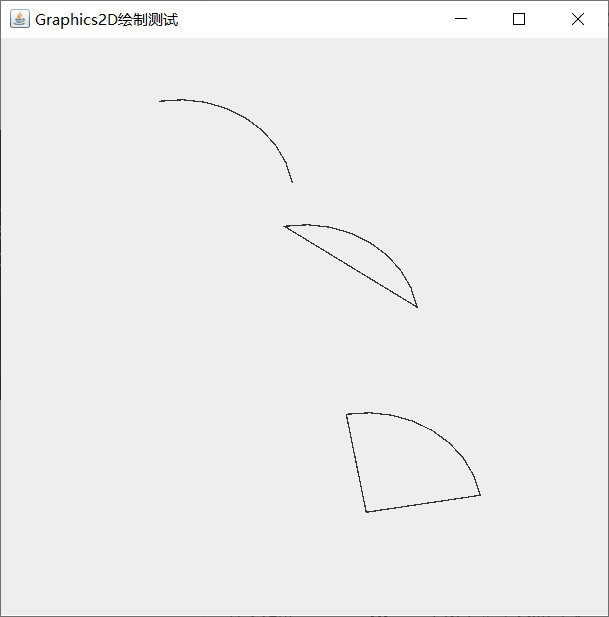
- Class CubicCurve2D: cubic curve
class drawplace extends JPanel{
public void paint(Graphics g){
Graphics2D g2d =(Graphics2D)g;
Shape[] shapes = new Shape[1];
shapes[0] =new CubicCurve2D.Double(100,100,50,75,15,15,260,300);
//The parameters respectively represent the coordinates of the coordinate starting point, control point 1, control point 2 and end point
for (Shape shape:shapes){//Traversal graph array
g2d.draw(shape);//Drawing graphics
}
}
}
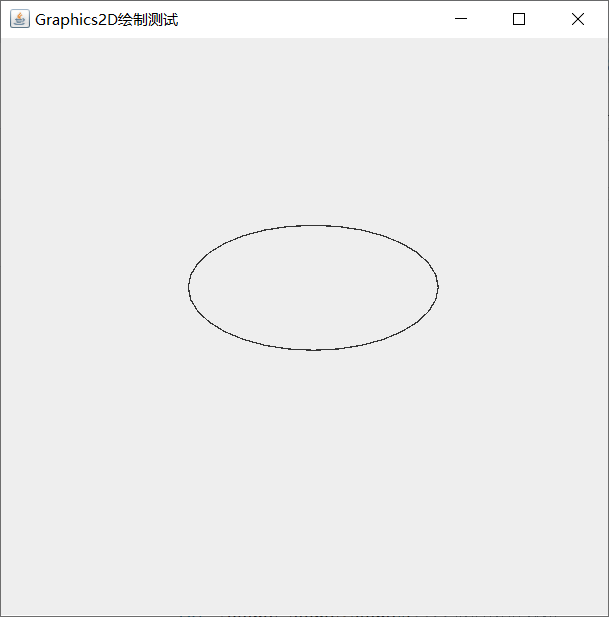
- Ellipse2D class: ellipse
class drawplace extends JPanel{
public void paint(Graphics g){
Graphics2D g2d =(Graphics2D)g;
Shape[] shapes = new Shape[1];
shapes[0] = new Ellipse2D.Double(150,150,200,100);
//Parameters represent the starting point, width and height
for (Shape shape:shapes){//Traversal graph array
g2d.draw(shape);//Drawing graphics
}
}
}
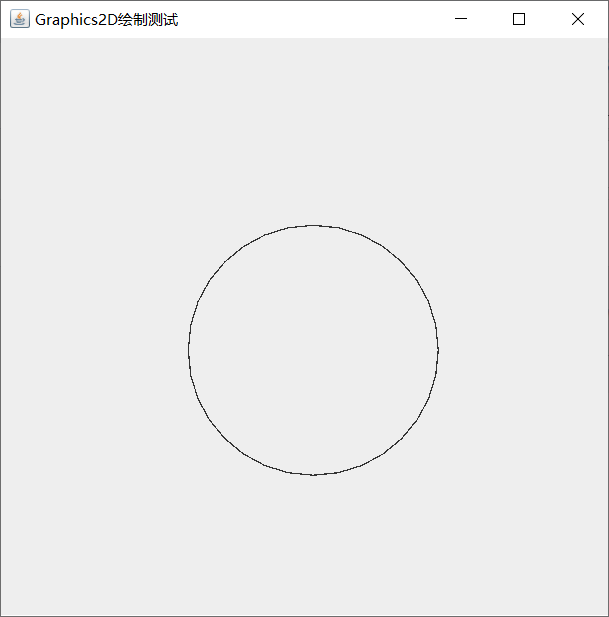
class drawplace extends JPanel{
public void paint(Graphics g){
Graphics2D g2d =(Graphics2D)g;
Shape[] shapes = new Shape[1];
shapes[0] = new Ellipse2D.Double(150,150,200,100);
//Parameters represent the starting point, width and height
for (Shape shape:shapes){//Traversal graph array
g2d.draw(shape);//Drawing graphics
}
}
}
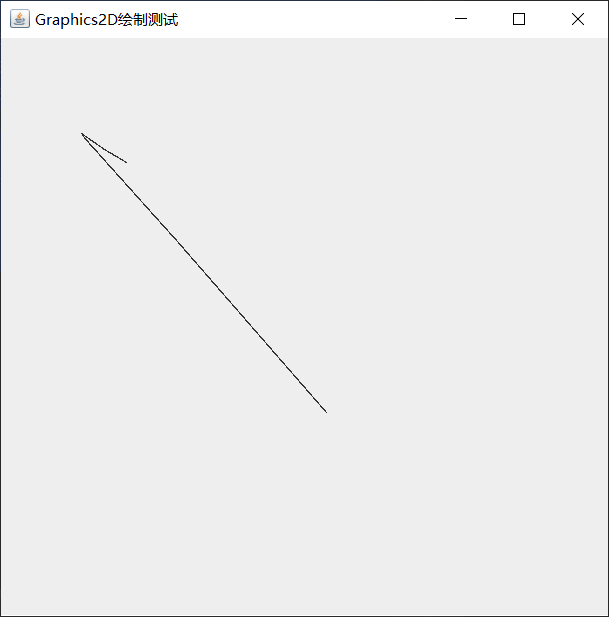
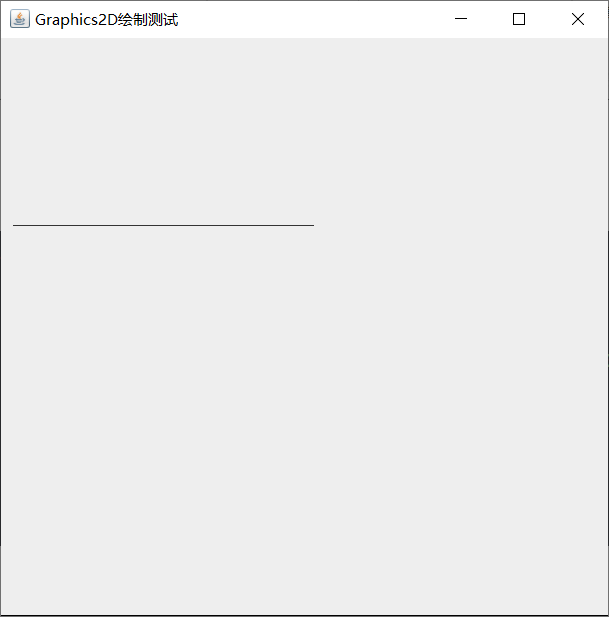
- Line2D class: Lines
class drawplace extends JPanel{
public void paint(Graphics g){
Graphics2D g2d =(Graphics2D)g;
Shape[] shapes = new Shape[1];
shapes[0] = new Line2D.Double(10,150,250,150);
//Parameters represent start and end points
for (Shape shape:shapes){//Traversal graph array
g2d.draw(shape);//Drawing graphics
}
}
}
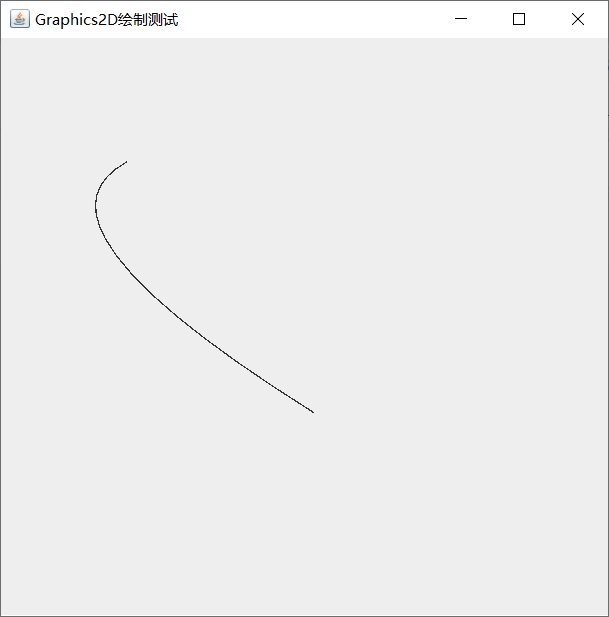
-
Point2D class: points
-
QuadCurve2D class: conic
class drawplace extends JPanel{
public void paint(Graphics g){
Graphics2D g2d =(Graphics2D)g;
Shape[] shapes = new Shape[1];
shapes[0] = new QuadCurve2D.Double(100,100,10,150,250,300);
//Parameters represent start point, control point and end point
for (Shape shape:shapes){//Traversal graph array
g2d.draw(shape);//Drawing graphics
}
}
}
- Rectangle2D class: rectangle
- RoundRectangle2D class: rounded rectangle
example:
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.geom.Ellipse2D;
import java.awt.geom.Rectangle2D;
public class G_1 extends JFrame {
public G_1(){
setTitle("Drawing example");
setSize(500,500);//Set form size
setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);//Sets the closing mode of the form
add(new CanvasPanel());//Set the form palette as a drawing palette object
}
class CanvasPanel extends JPanel{ //Drawing board
public void paint(Graphics g){
Graphics2D g2d = (Graphics2D)g;
Shape[] shapes = new Shape[4];//Declare a graph array
shapes[0] = new Ellipse2D.Double(5,5,100,100);//Create a circular object
shapes[1] = new Rectangle2D.Double(110,5,160,40);//rectangle
shapes[2] = new Ellipse2D.Double(120,15,80,80);
shapes[3] = new Rectangle2D.Double(35,15,80,80);
for (Shape shape:shapes){//Traversal graph array
Rectangle2D bounds = shape.getBounds2D();
if (bounds.getWidth()==80){
g2d.fill(shape);//fill
}
else {
g2d.draw(shape);//Drawing graphics
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new G_1().setVisible(true);
}
}
Program presentation:
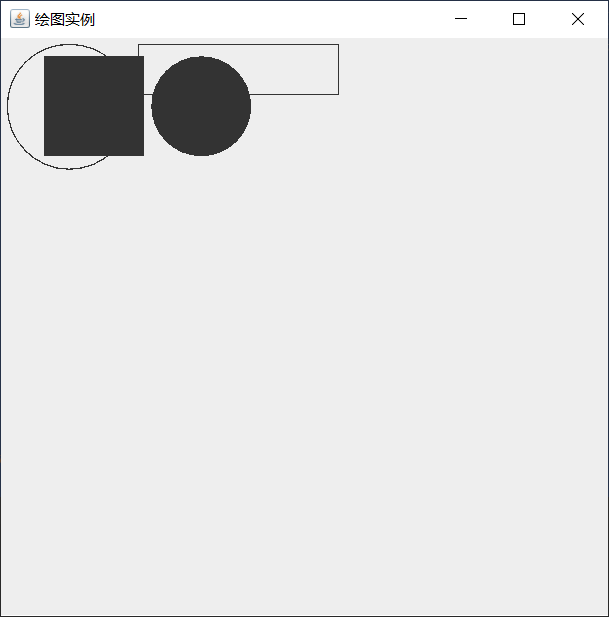
Drawing color and brush properties
1. Set color
Syntax:
Color col = new Color(int r,ing g,int b);//The parameter represents three primary colors Color col = new Color(int rgb);//The parameter represents the color value, which is the sum of the three primary colors
Use the setColor method to quickly set the color in the drawing class
g.setColor(Color.color)//Note that there is of
example:
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.geom.*;
public class G_2 extends JFrame {
public G_2(){
setTitle("Graphics2D Draw test");
setSize(500,500);
setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
add(new drawplace());
}
class drawplace extends JPanel{
public void paint(Graphics g){
Graphics2D g2d =(Graphics2D)g;
g2d.setColor(Color.green);
Shape[] shapes = new Shape[1];
shapes[0] = new Ellipse2D.Double(150,150,200,200);
for (Shape shape:shapes){//Traversal graph array
g2d.fill(shape);
g2d.draw(shape);//Drawing graphics
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new G_2().setVisible(true);
}
}
Program presentation:
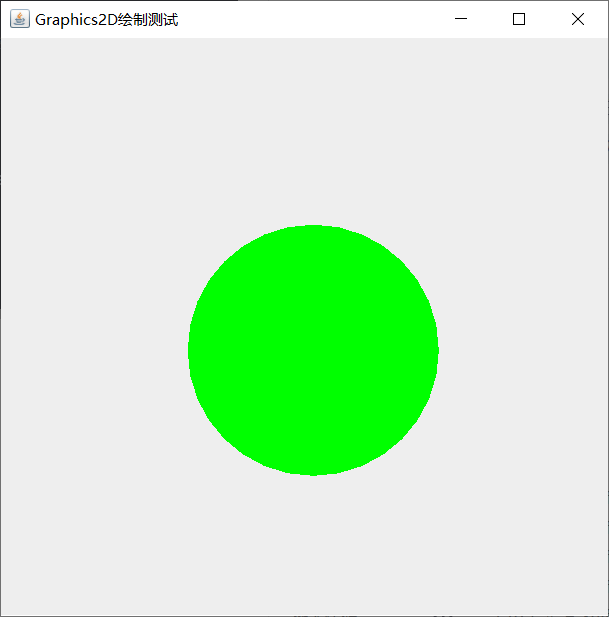
Set brush
Syntax:
Stroke st = new BasicStroke(4); g2d.setStroke(st);
example:
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.geom.*;
public class G_2 extends JFrame {
public G_2(){
setTitle("Graphics2D Draw test");
setSize(500,500);
setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
add(new drawplace());
}
class drawplace extends JPanel{
public void paint(Graphics g){
Graphics2D g2d =(Graphics2D)g;
g2d.setColor(Color.green);
Stroke st = new BasicStroke(15);
g2d.setStroke(st);
Shape[] shapes = new Shape[1];
shapes[0] = new Ellipse2D.Double(150,150,200,200);
for (Shape shape:shapes){//Traversal graph array
//g2d.fill(shape);
g2d.draw(shape);//Drawing graphics
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new G_2().setVisible(true);
}
}
Program presentation:
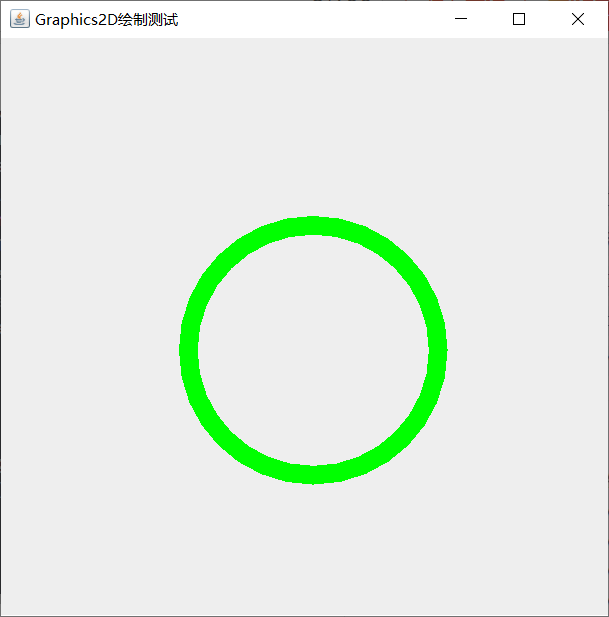
Common construction methods:
- BasicStroke()
- BasicStroke(float width)
- BasicStroke(float width,int cap,int join)
- BasicStroke(float width,int cap,int join,float miterlimit)
- BasicStroke(float width,int cap,int join,float miterlimit,float[] dash,float dash_phase)
Parameter description of basic stroke class construction method
| parameter | explain |
|---|---|
| width | The brush width defaults to 1px |
| cap | Line end decoration |
| join | Decoration applied at the intersection of path segments |
| miterlimit | Clipping limit at miter, the parameter must be greater than or equal to 1.0f |
| dash | Represents an array of dashed patterns |
| dash_phase | Offset to start dashed mode |
Three constants of the cap parameter:
- CAP_BUTT: smooth end
- CAP_ROUND: flat end
- CAP_SQUARE: set a square with the width of the line segment as the side length at the end
Three constants of the join parameter:
- JOIN_BEVEL: flat angle
- JOIN_MITER: sharp corner
- JOIN_ROUND: fillet
Draw text
1. Set font
You can set the name, style and font size
Syntax:
Font f = new Font("Fangzheng shutI",Font.BOLD,25);
g2d.setFont(f);
Constant of Font class:
- PLAIN: normal
- BOLD: BOLD
- ITALIC: ITALIC
- ITALIC|BOLD: italic bold
example:
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
public class G_3 extends JFrame {
public G_3(){
setTitle("font_test");
setSize(400,400);
setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
add(new drawplace());
}
class drawplace extends JPanel{
public void paint(Graphics g){
Graphics2D g2d = (Graphics2D)g;
Font f = new Font("Fangzheng shutI",Font.BOLD,25);
g2d.setFont(f);
g2d.drawString("Text: founder shutI",100,100);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new G_3().setVisible(true);
}
}
Program presentation:
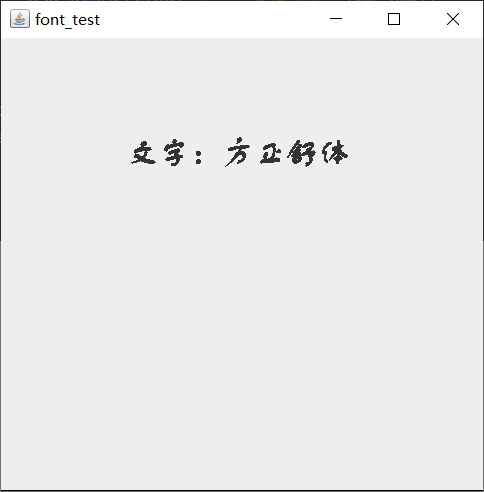
example:
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.util.Date;
public class G_3 extends JFrame {
public G_3(){
setTitle("font_test");
setSize(400,400);
setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
add(new drawplace());
}
class drawplace extends JPanel{
public void paint(Graphics g){
Graphics2D g2d = (Graphics2D)g;
Date time = new Date();
Font f = new Font("Fangzheng shutI",Font.BOLD,25);
g2d.setColor(Color.RED);
g2d.setFont(f);
g2d.drawString("Now:",50,100);
g2d.drawString(String.format("%tr",time),100,200);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new G_3().setVisible(true);
}
}
Program presentation:
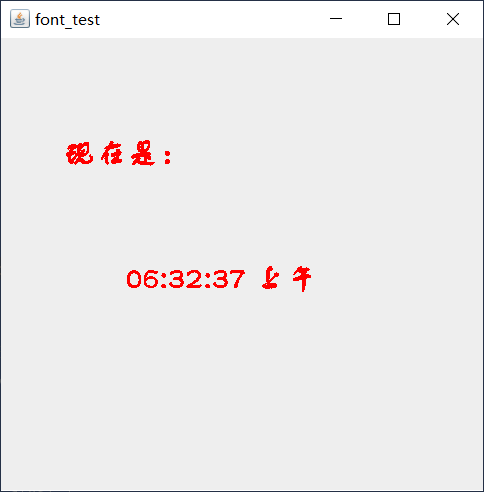
display picture
Use the drawImage method to display a picture in a drawing
Syntax:
drawImage(Image img,int x,int y,ImageObserver observer)
Parameters represent the picture object to be displayed, coordinates, and the image observer to be notified
example:
import javax.imageio.ImageIO;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
public class show_photos extends JFrame {
Image img;
public show_photos(){
try{
img = ImageIO.read(new File("D:\\work\\tired.png"));
}catch(IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
setTitle("show_photos");
setSize(916,525);
setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
add(new drawplace());
}
class drawplace extends JPanel{
public void paint(Graphics g){
Graphics2D g2d = (Graphics2D)g;
g2d.drawImage(img,0,0,this);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new show_photos().setVisible(true);
}
}
Program presentation:
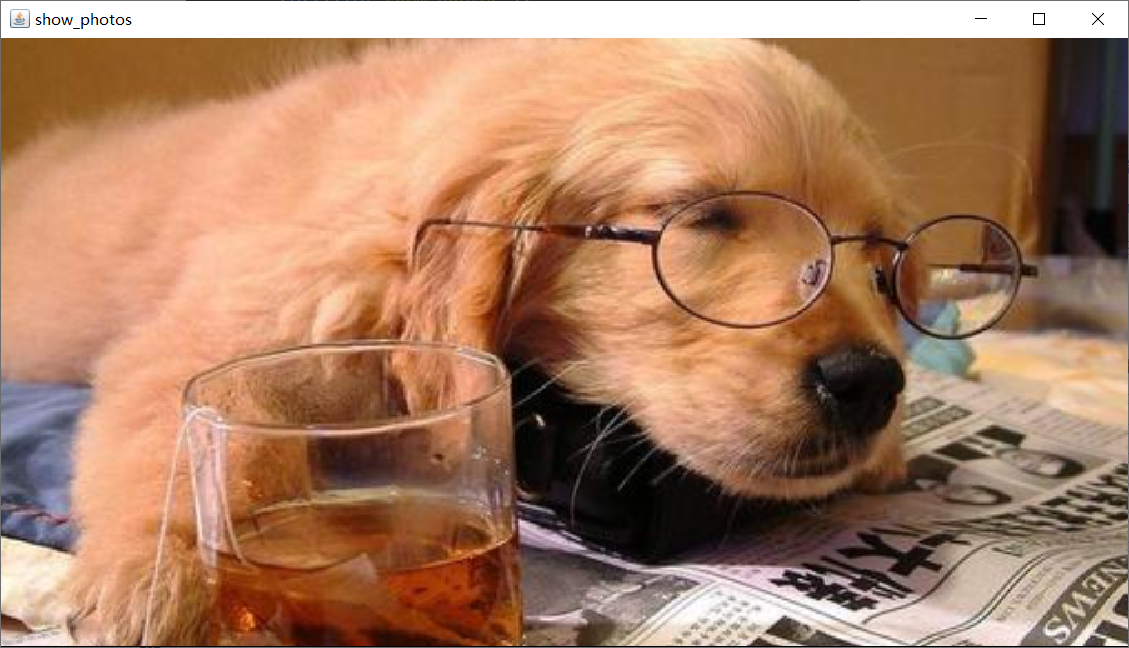

image processing
1. Zoom in and out
Still use the drawImage method syntax:
drawImage(Image img,int x,int y,int width,int height,ImageObserver observer)
example:
import javax.imageio.ImageIO;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
public class show_photos extends JFrame {
Image img;
public show_photos(){
try{
img = ImageIO.read(new File("D:\\work\\tired.png"));
}catch(IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
setTitle("show_photos");
setSize(916,525);
setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
add(new drawplace());
}
class drawplace extends JPanel{
public void paint(Graphics g){
Graphics2D g2d = (Graphics2D)g;
g2d.drawImage(img,0,0,300,200,this);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new show_photos().setVisible(true);
}
}
Program presentation:

Example (change size with scribe):
import javax.imageio.ImageIO;
import javax.swing.*;
import javax.swing.event.ChangeEvent;
import javax.swing.event.ChangeListener;
import java.awt.*;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
public class show_p_change extends JFrame {
Image img;
int imgwidth,imgheight;
private JSlider js;
public show_p_change(){
try{
img = ImageIO.read(new File("D:\\work\\tired.png"));
}catch(IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
showplace sp = new showplace();
js = new JSlider();
js.setMaximum(1500);
js.setValue(50);
js.setMinimum(10);
js.addChangeListener(new ChangeListener() {
@Override
public void stateChanged(ChangeEvent e) {
sp.repaint();
}
});
JPanel center = new JPanel();
center.setLayout(new BorderLayout());
center.add(js,BorderLayout.SOUTH);
center.add(sp,BorderLayout.CENTER);
setContentPane(center);
setTitle("change_p_show");
setBounds(100,100,800,600);//Set form size and position
setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
}
class showplace extends JPanel{
public void paint(Graphics g){
Graphics2D g2d = (Graphics2D)g;
int n_w = 0,n_h = 0;
imgwidth = img.getWidth(this);
imgheight = img.getHeight(this);
float value = js.getValue();
n_w = (int)(imgwidth*value/100);
n_h = (int)(imgheight*value/100);
g2d.drawImage(img,0,0,n_w,n_h,this);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new show_p_change().setVisible(true);
}
}
Program presentation:
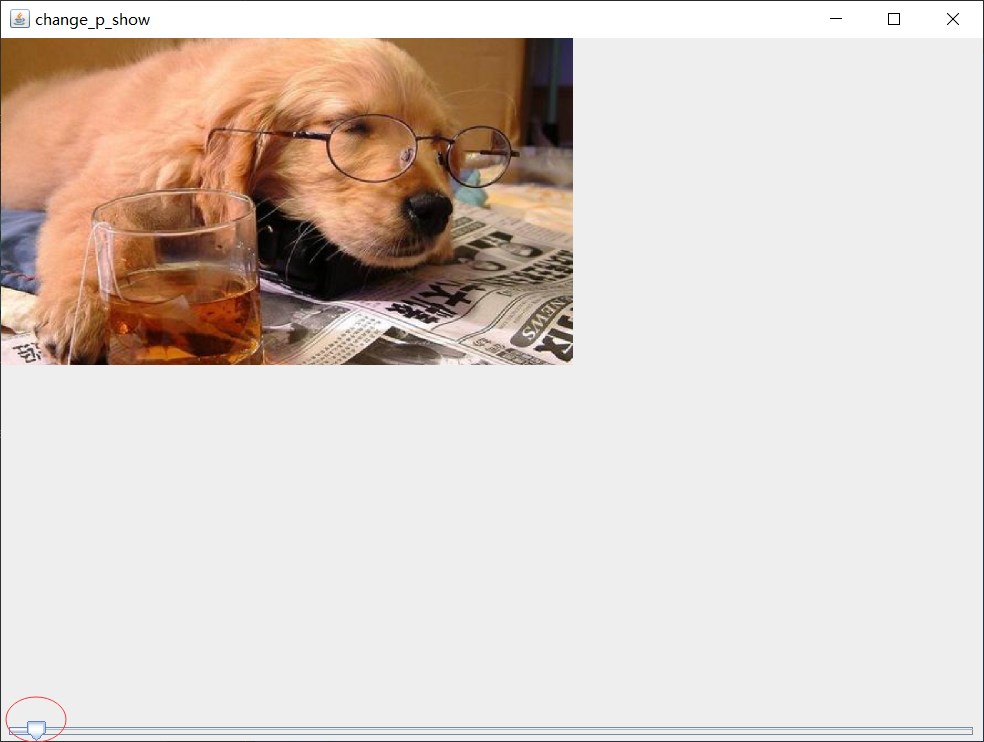
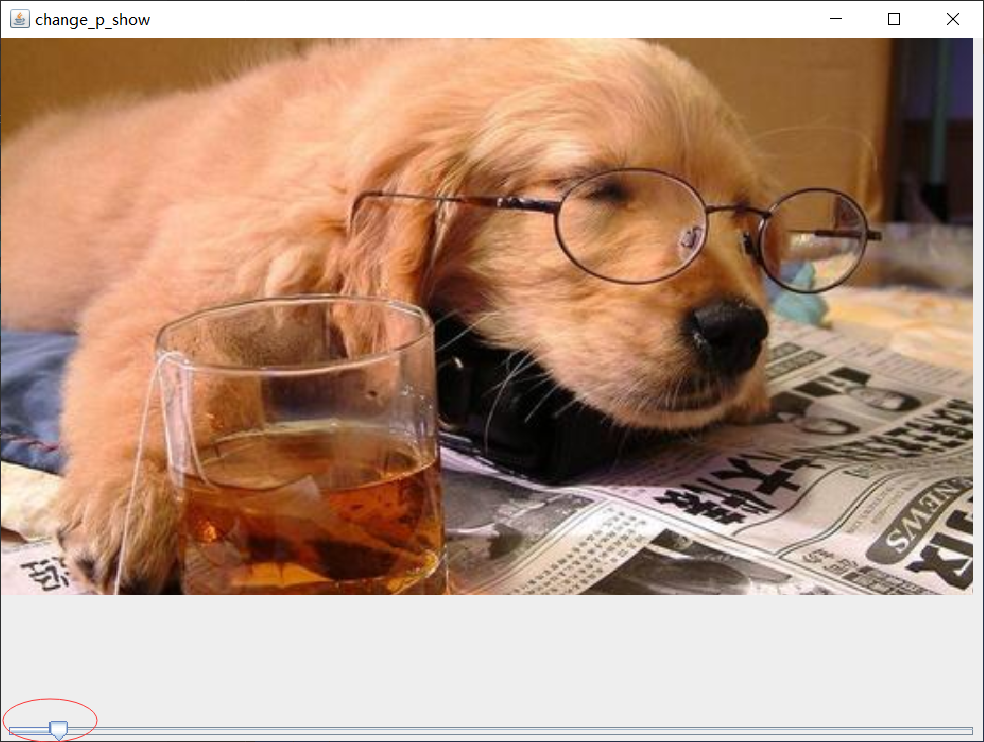
Image flip
Syntax:
drawImage(image img,int x1,int y1,int x2,int y2,int x3,int y3,int x4,int y4,ImageObserver observer)
Parameter Description:
| parameter | explain |
|---|---|
| img | Objects to draw |
| x1 | x position of the first coordinate of the target matrix |
| y1 | y position of the first coordinate of the target matrix |
| x2 | x position of the second coordinate of the target matrix |
| y2 | y position of the second coordinate of the target matrix |
| x3 | x position of the first coordinate of the source matrix |
| y3 | y position of the first coordinate of the source matrix |
| x4 | x position of the second coordinate of the source matrix |
| y4 | y position of the second coordinate of the source matrix |
| observer | Image viewer to notify |
example:
import javax.imageio.ImageIO;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
public class G_flip extends JFrame {
Image img;
int dx1,dy1,dx2,dy2;
int sx1,sx2,sy1,sy2;
int imgw= 800,imgh=500;//Width and height of the photo
JButton vbtn = null;//Flip vertically
JButton hbtn = null;//Flip horizontally
Cpanel canvas = null;
public G_flip(){
try{
img = ImageIO.read(new File("D:\\work\\tired.png"));
}catch(IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
dx2 = sx2 =imgw;
dy2 = sy2 = imgh;
vbtn = new JButton("Flip vertically");
hbtn = new JButton("Flip horizontally");
JPanel bottom = new JPanel();
bottom.add(vbtn);
bottom.add(hbtn);
Container c = getContentPane();
c.add(bottom,BorderLayout.SOUTH);
canvas = new Cpanel();
c.add(canvas,BorderLayout.CENTER);
addL();
setBounds(100,100,800,700);
setTitle("Image flip");
setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
}
void addL(){
vbtn.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
sy1 = Math.abs(sy1-imgh); //Ordinate exchange
sy2 = Math.abs(sy2-imgh);
canvas.repaint();
}
});
hbtn.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
sx1 = Math.abs(sx1-imgw); //Abscissa exchange
sx2 = Math.abs(sx2-imgw);
canvas.repaint();
}
});
}
class Cpanel extends JPanel{
public void paint(Graphics g){
Graphics2D g2d = (Graphics2D)g;
g2d.drawImage(img,dx1,dy1,dx2,dy2,sx1,sy1,sx2,sy2,this);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new G_flip().setVisible(true);
}
}
Program presentation:

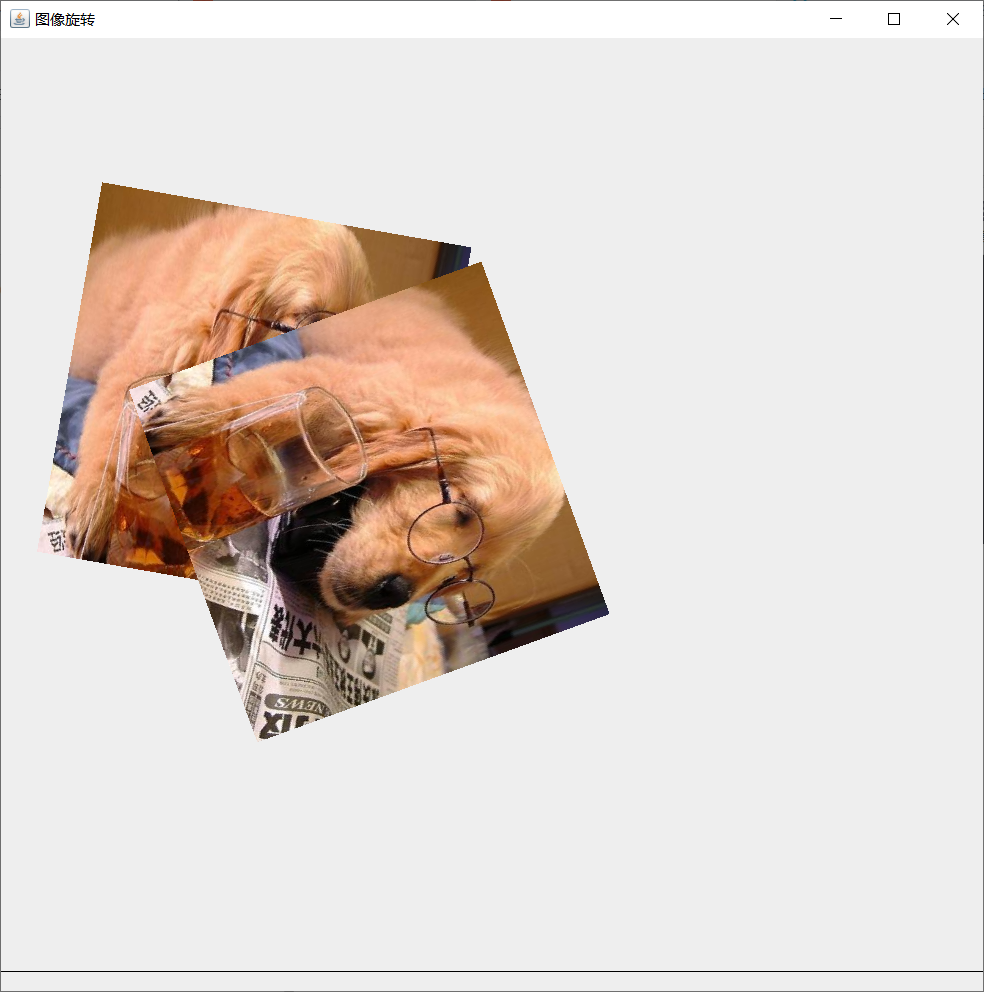
Image rotation
Use the rotate method in Graphics2D to rotate the image according to radians. Syntax:
rotate(double Rotation radian)
We can use the toRadians method in the Math class to convert the rotation angle into radians
example:
import javax.imageio.ImageIO;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
public class G_route extends JFrame {
Image img;
public G_route(){
try{
img = ImageIO.read(new File("D:\\work\\tired.png"));
}catch(IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
setBounds(100,100,800,800);
setTitle("Image rotation");
setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
add(new Cp());
}
class Cp extends JPanel{
public void paint(Graphics g){
Graphics2D g2d = (Graphics2D)g;
g2d.rotate(Math.toRadians(10));
g2d.drawImage(img,100,100,300,300,this);
g2d.rotate(Math.toRadians(60));
g2d.drawImage(img,300,-300,300,300,this);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new G_route().setVisible(true);
}
}
Program presentation: