abnormal
Concepts and Systems of Exceptions


Classification of Exceptions

public static void main(String[] args) throws ParseException {
SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd");
Date date = simpleDateFormat.parse("202106-01"); //ParseException
System.out.println(date);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd");
Date date = null;
try {
date = simpleDateFormat.parse("202106-01");//ParseException
} catch (ParseException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("Follow-up code");
System.out.println(date);
}
int[] a = new int[3];
System.out.println(a[3]); //ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
int[] a = new int[1024*1024*1024];
System.out.println(a[3]);//OutOfMemoryError
The process of generating anomalies

[Note] JVM has a huge role in it
Handling exceptions
Five keywords for exception handling: try,catch,finally,throw,throws.
throw keyword

public static int getElement(int[] arr,int index) {
if (arr == null) {
// NullPointerException Runtime Exception
throw new NullPointerException("The passed array is empty");
}
if (index < 0 || index >= arr.length) {
//ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException is a runtime exception
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException("Array out of bounds!");
}
return arr[index];
}
Methods of objects

Writing below is equivalent
Objects.requireNonNull(arr, "The passed array is empty");
/*if (arr == null) {
// NullPointerException Runtime Exceptions
throw new NullPointerException("The passed array is empty ";
}*/
throws keyword: the first way to handle exceptions

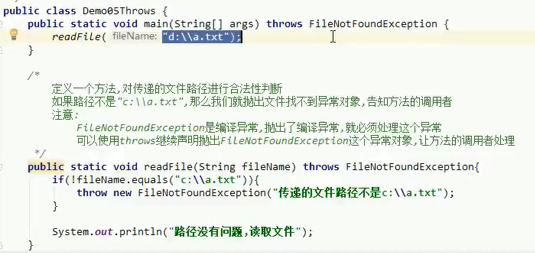
try...catch: The second way to use exceptions

public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
readFile("d:\\a.tx");
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("Wrong file path");
}
System.out.println(666666666);
}
public static void readFile(String fileName) throws IOException{
if (!fileName.endsWith(".txt")) {
throw new IOException("The suffix name of the file is incorrect!");
}
}
Three exception handling for throwable class

finally block of code

Capture and Handling of Multiple Exceptions




return statement in final

[Note] Try to avoid return ing statements in finally.
Character class exception
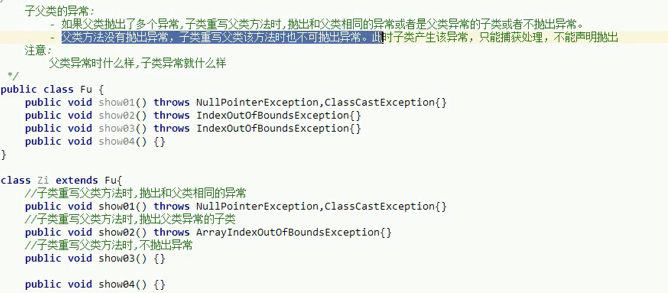

Custom exception class


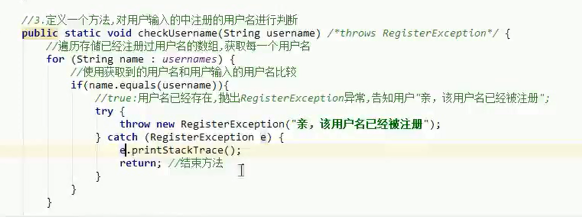
Multithreaded
Concurrency and Parallelism
process
Procedures and Processes
thread

Thread Scheduling
Timesharing
Preemptive (priority, otherwise random), Java uses preemptive.
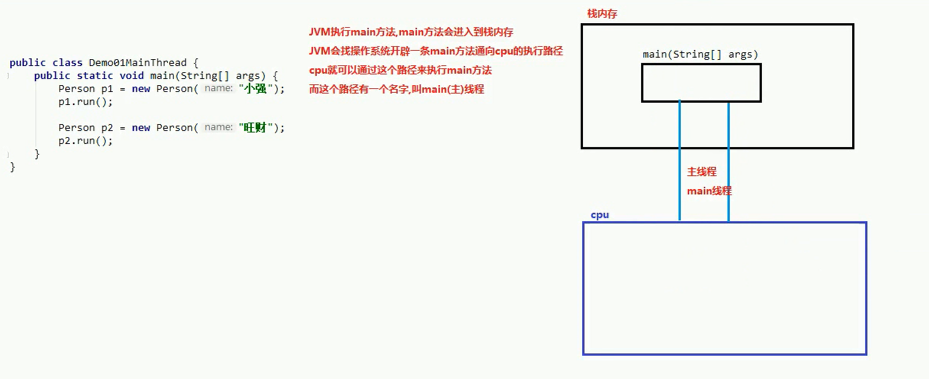
Main Thread (main thread)
Main Thread: The thread that executes the main method
Single-threaded program: There is only one thread in the Java program
Execution starts from main and runs from top to bottom
The first way to create multithreads (inheriting the Thread class)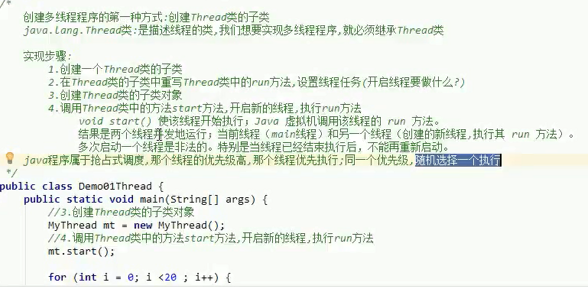
Multithreading principle

Multithreading principle_ Multithreaded Memory Diagram
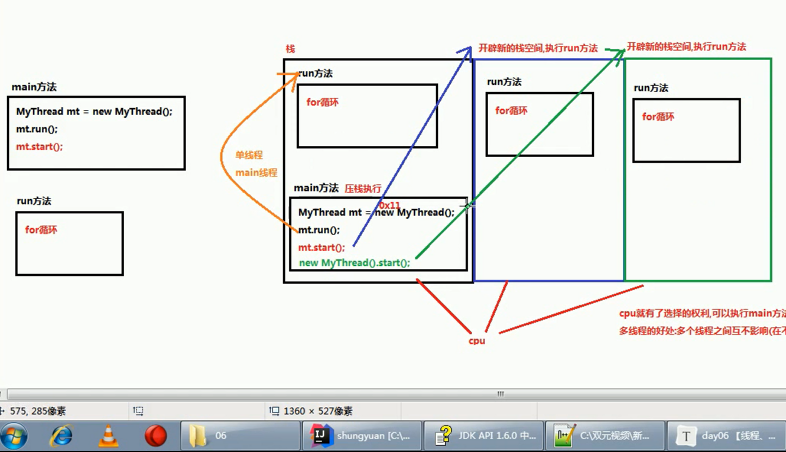
[Note] Stack Space
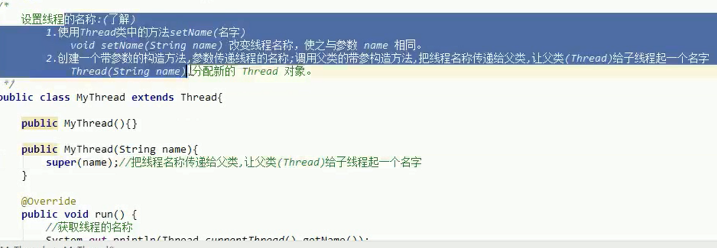
The name of the thread


Set the name of the thread
Common method - Sleep
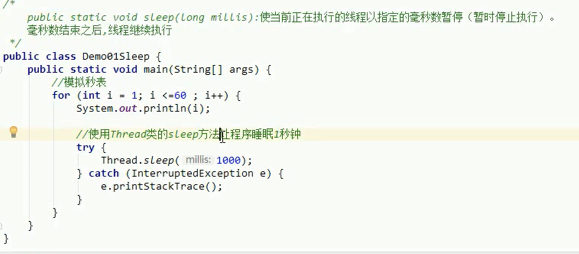
[Note] For the current thread, you can use the static method of Thread.
Second way to create multithreaded programs

public class Demo01Runnable implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("run");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Demo01Runnable demo01Runnable = new Demo01Runnable();
new Thread(demo01Runnable).start();
}
Benefits of using interfaces (difference between thread s and runnable s)

Anonymous internal class implementation thread

public class Demo01InnerClassThread {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(){
@Override
public void run(){
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
System.out.println("liu"+"--->"+i);
}
}
}.start();
Runnable r = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
System.out.println("chun"+"--->"+i);
}
}
};
new Thread(r).start();
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
System.out.println("lei"+"--->"+i);
}
}
}).start();
}
}
Thread synchronization mechanism
Thread Security Overview

Thread security issues arise when multiple threads access shared data.
public class Demo05Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Create an implementation class object for three threads to invoke
RunnableImpl r = new RunnableImpl();
Thread t1 = new Thread(r);
Thread t2 = new Thread(r);
Thread t3 = new Thread(r);
//Open Thread
t1.start();
t2.start();
t3.start();
}
}
How thread security issues arise

Solutions to Thread Security
1. Synchronize Code Blocks
2. Synchronization method
3. Lock mechanism
1. Synchronize Code Blocks

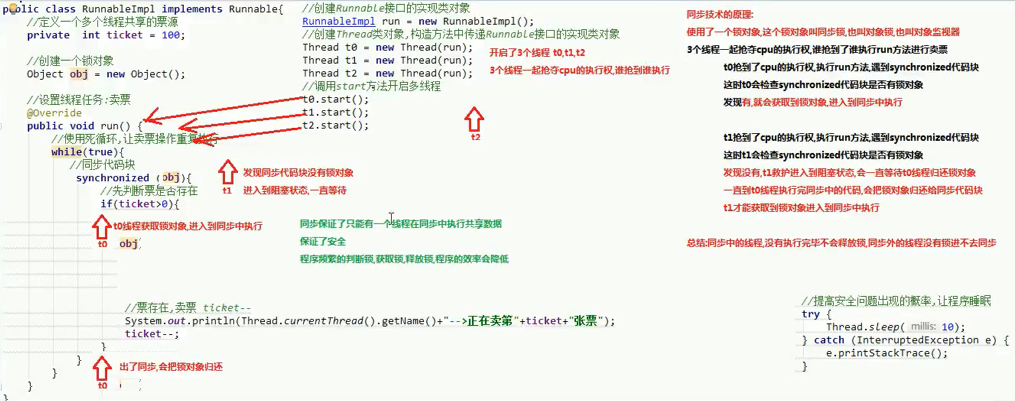
private int ticket=100;
Object obj = new Object();
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
synchronized(obj) {
if (ticket > 0) {
try {
Thread.sleep(10);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "--->Selling" + ticket + "Tickets");
ticket--;
}
}
}
}
Principle of synchronization technology
2. Synchronization method

public synchronized void ticketSent(){
if (ticket > 0) {
try {
Thread.sleep(10);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "--->Selling" + ticket + "Tickets");
ticket--;
}
}
Static synchronization method

[Note] RunnableImpl.class can also be locked
3.Lock Lock

public class RunnableImpl implements Runnable {
private int ticket=100;
Lock l = new ReentrantLock();
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
l.lock();
if (ticket > 0) {
try {
Thread.sleep(10);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "--->Selling" + ticket + "Tickets");
ticket--;
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
l.unlock();//Locks are released regardless of whether the program is exceptional or not
}
}
}
}
}
Thread Wait Wake-up Mechanism
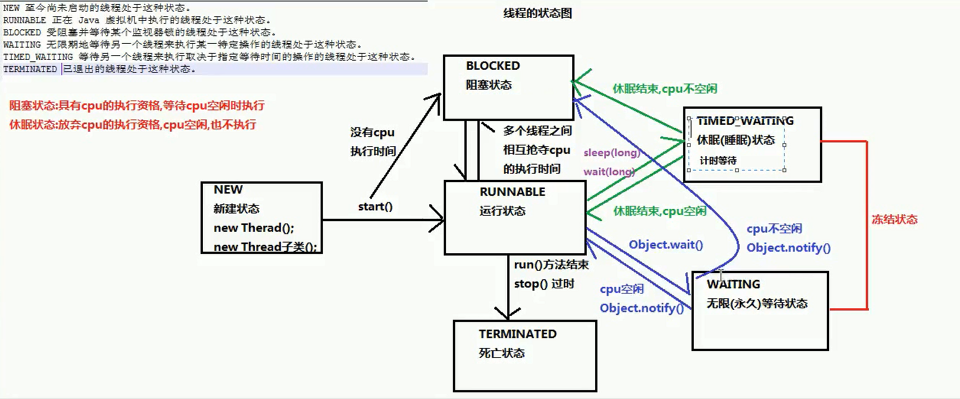
Thread Status Diagram
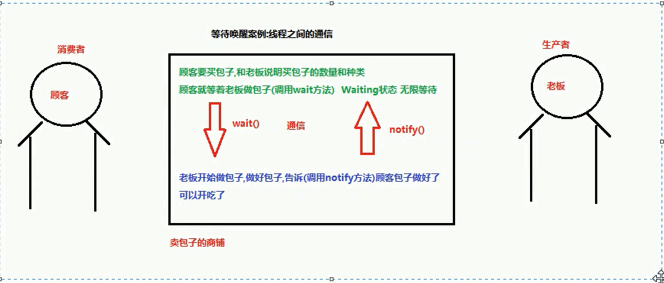
Waiting for wake-up cases

public static void main(String[] args) {
Object obj = new Object();
new Thread(){
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (obj) {
System.out.println("Tell your boss information");
try {
obj.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("Got the buns");
}
}
}.start();
new Thread(){
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Thread.sleep(5000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
synchronized (obj){
System.out.println("The boss took 5 seconds to make the buns");
obj.notify();
}
}
}.start();
}

[Note] Notfy is a random wake-up to a waiting thread
Communication between threads (resource use needs to be discussed)
Waiting for wake-up mechanism


Thread pool: Creating and destroying threads frequently is too resource intensive and thread pools can reuse threads


Thread Pool

