Network-related concepts
TCP and UDP
TCP Protocol: Transport Control Protocol
- Before using TCP protocol, TCP connection must be established to form transmission data channel
- It is reliable to shake hands three times before transmission
- Two application processes for TCP protocol communication: client and server
- Large amount of data can be transferred in a connection
- When the transfer is complete, the established connection needs to be released, which is inefficient
UDP Protocol
- Encapsulate data, source, and purpose into a package without establishing a connection
- Limit the size of each datagram to 64K
- Unreliable because no connection is required
- Disorderly release of resources when sending data (because it is not connection-oriented) is fast
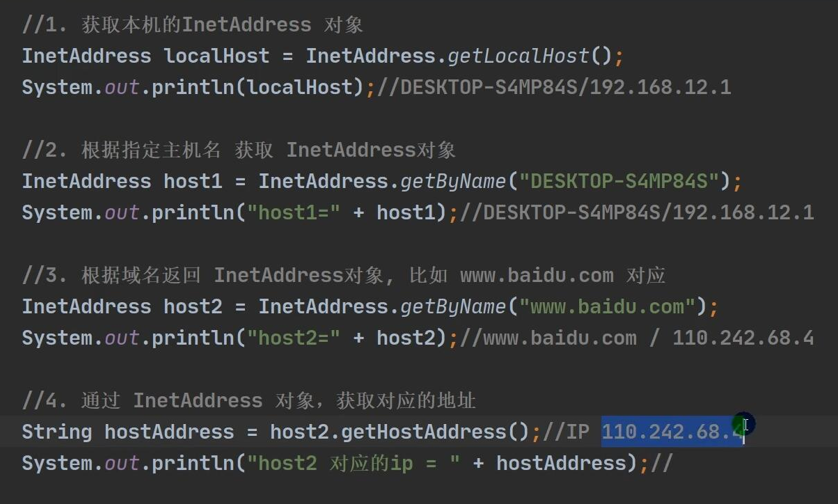
InetAddress class
- getLocalHost Gets Native InetAddress Object
- getByName obtains an ip address object based on the specified host name/domain name
- getHostName gets the host name of the InetAddress object
- getHostAddress gets the address of the InetAddress object
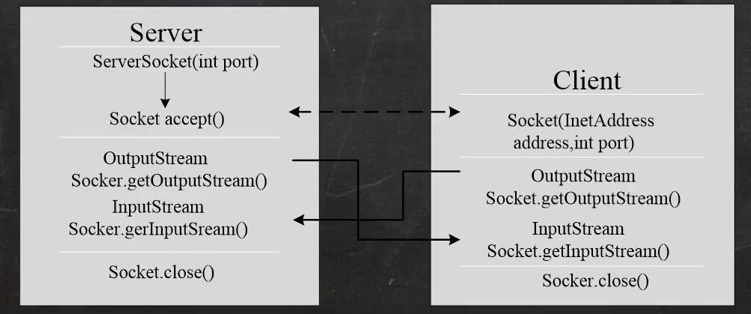
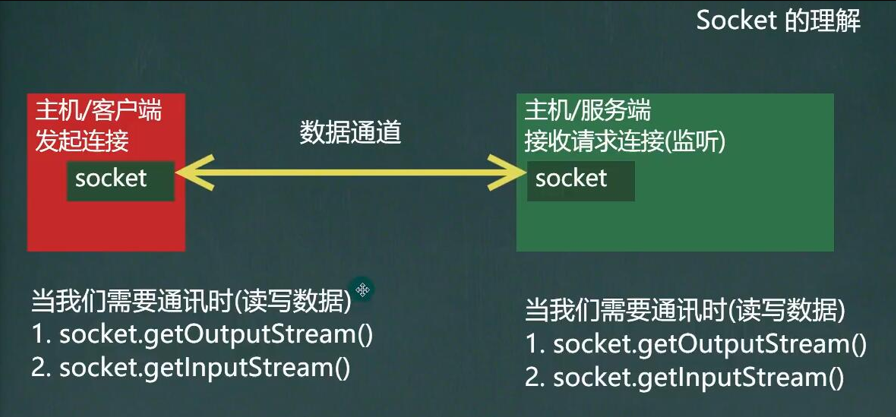
Socket
Basic Introduction
- Sockets are so widely used to develop network applications that they become de facto standards.
- Socket s are required at both ends of the communication and are the endpoints of communication between two machines
- Network communication is actually communication between Socket s
- Sockets allow programs to view a network connection as a stream, and data is transferred between two Sockets via IO
- Generally, the application that initiates communication actively belongs to the client, and the server waits for the communication request
TCP Network Communication Programming
Basic Introduction
-
Client-server based network communication
-
The underlying layer uses the TCP/IP protocol
-
Scenario: Client sends data, server receives and displays it
-
TCP programming based on Socket
TCP Application Case 1
- Write a server-side and a client-side
- Server listening on port 9999
- Clients connect to the server, send "hello,server", and launch
- Server receives information from client, responds to client and exits
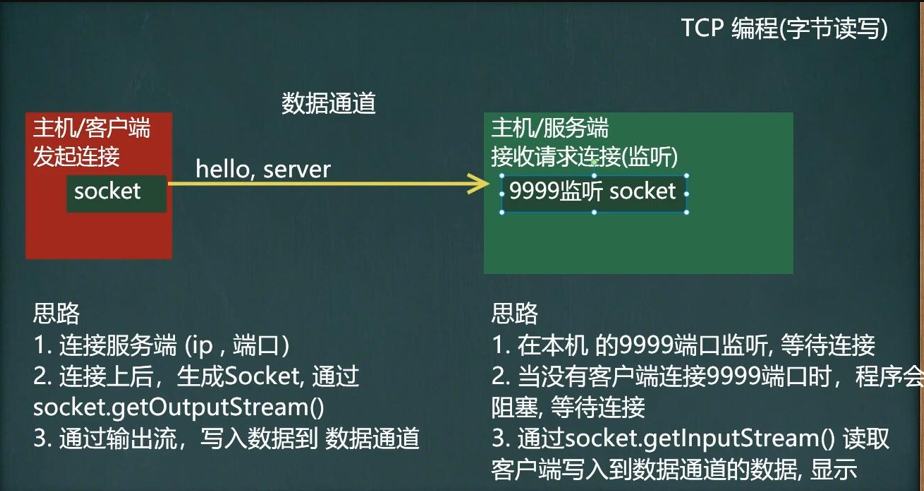
Byte Stream Implementation
Client Code
public class z1_TCP Client {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// Connect server (ip, port)
//Connect to port 9999 of this machine and return the socket object if the connection is successful
Socket socket = new Socket(InetAddress.getLocalHost(), 9999);
//Once connected, the socket is generated, and the output stream object associated with the socket object is obtained from socket.getOutputStream().
OutputStream outputStream = socket.getOutputStream();
//Write data to data channel through output stream
outputStream.write("hello , socker!".getBytes());
//Set Write End Tag
socket.shutdownOutput();
InputStream inputStream = socket.getInputStream();
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024] ;
int readLen ;
while( (readLen = inputStream.read(bytes)) != -1 ){
System.out.print(new String(bytes , 0 , readLen));
}
System.out.println("");
//Close Stream Objects and Sockets
inputStream.close();
outputStream.close();
socket.close();
System.out.println("Client Exit!!!");
}
}
Service-side code
public class z1_Server {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//Listen on port 9999 locally, wait for connection
//Details: 1. Require that no other server is listening on 9999 locally
// 2. This ServerSocket can return multiple Sockets via accept() [concurrency of multiple client connections to servers]
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(9999);
System.out.println("Waiting for Client Connection~~~");
//When no client connects to port 9999, the program will block and wait for the connection
//If there is a client connection, the Socket object is returned and the program continues
Socket accept = serverSocket.accept();
//Read data written by client to data channel through socket.getInputStream()
InputStream inputStream = accept.getInputStream();
//read
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024] ;
int readLen ;
while( (readLen = inputStream.read(bytes)) != -1 ){
System.out.print(new String(bytes , 0 , readLen));
}
OutputStream outputStream = accept.getOutputStream();
outputStream.write("hello , client".getBytes());
//Set Write End Tag
accept.shutdownOutput();
System.out.println("Server Exit!!!");
//close resource
outputStream.close();
inputStream.close();
accept.close();
serverSocket.close();
}
}
Character streams fulfill these requirements
Client Code
public class z2_z1 Character stream implementation for_Client {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Socket socket = new Socket(InetAddress.getLocalHost(), 9999);
OutputStream outputStream = socket.getOutputStream();
BufferedWriter bufferedWriter = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(outputStream));
bufferedWriter.write("hello , server");
bufferedWriter.flush();
socket.shutdownOutput();
InputStream inputStream = socket.getInputStream();
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(inputStream));
String readLine ;
while( (readLine = bufferedReader.readLine() ) != null ){
System.out.println(readLine);
}
//close resource
bufferedReader.close();
bufferedWriter.close();
socket.close();
}
}
Service-side code
public class z2_z1 Character stream implementation for_Server {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(9999);
//Waiting for connection
Socket socket = serverSocket.accept() ;
//Get information from client via character stream
InputStream inputStream = socket.getInputStream();
//Convert Byte Stream to Character Stream
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(inputStream));
String readLine ;
while( (readLine = bufferedReader.readLine()) != null ){
System.out.println(readLine);
}
OutputStream outputStream = socket.getOutputStream();
BufferedWriter bufferedWriter = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(outputStream));
bufferedWriter.write("hello , client!");
bufferedWriter.flush(); //Using character streams requires manual refresh or data will not be written to the data channel
socket.shutdownOutput(); //Write End Tag
//close resource
bufferedReader.close();
bufferedWriter.close();
socket.close();
serverSocket.close();
}
}
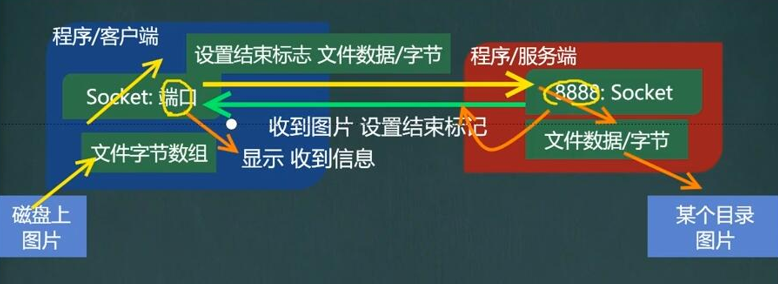
TCP Application Case 2 - File Upload
- Write a server and a client
- Server listening on port 8888
- The client connects to the server and sends a picture "D:\zaizai.jpg"
- The server receives the picture sent by the client, saves it under src, sends "Received Picture" and exits
- Client receives "Picture Received" from server and exits
- Byte stream for binary files
Client Code
public class z1_Client {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Socket socket = new Socket(InetAddress.getLocalHost(), 8888);
String srcFilePath = "D:\\zaizai.jpg" ;
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(srcFilePath));
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(socket.getOutputStream());
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024] ;
int readLen ;
while( (readLen = bis.read(bytes)) != -1 ){
bos.write(bytes , 0 , readLen);
}
socket.shutdownOutput();
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(socket.getInputStream()));
String readLine ;
while( (readLine = br.readLine()) != null ){
System.out.println(readLine);
}
//close resource
br.close();
bis.close();
// bos.close();
socket.close();
}
}
Service-side code
public class z2_Server {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(8888);
String destFilePath = "src\\1.jpg" ;
System.out.println("Waiting for Client Connection~~~~");
//Get Client Connection
Socket socket = serverSocket.accept();
System.out.println("Client Connection Successful~~~~");
//Get socket related input stream
InputStream inputStream = socket.getInputStream();
//Wrap input stream as processing byte stream
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(inputStream);
//Instance Byte Output Stream
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(destFilePath);
//Wrap Output Stream as Processing Byte Stream
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos);
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024] ;
int readLine ;
while( (readLine = bis.read(bytes)) != -1 ){
bos.write(bytes , 0 , readLine);
}
System.out.println("File upload complete!");
OutputStream outputStream = socket.getOutputStream();
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(outputStream));
bw.write("Server side notification: file upload complete");
bw.flush();
socket.shutdownOutput();
//close resource
bw.close();
bos.close();
bis.close();
socket.close();
serverSocket.close();
}
}
TCP Application Case 3 - File Download
Client Code
public class TCPClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Socket socket = new Socket(InetAddress.getLocalHost(), 9999);
OutputStream outputStream = socket.getOutputStream();
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(outputStream));
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
String s = scanner.nextLine();
bw.write(s);
bw.flush();
socket.shutdownOutput();
InputStream is = socket.getInputStream();
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(is);
String filePath = "D:\\2.jpg" ;
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(filePath);
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos);
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024] ;
int leng ;
while( (leng = bis.read(bytes)) != -1 ){
bos.write(bytes , 0 , leng);
}
System.out.println("File downloaded successfully");
bw.close();
bis.close();
bos.close();
socket.close();
}
}
Service-side code
public class TCPServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//Server listens on port 9999
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(9999);
System.out.println("Waiting for Client Connection~~~~");
//Stage Client Connection
Socket socket = serverSocket.accept();
//Get socket-related byte output stream
InputStream is = socket.getInputStream();
//Wrap as character processing stream
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(is));
String readLine ;
String fileName = null ;
while( (readLine = br.readLine()) != null ){
fileName = readLine ;
}
String filePath = "src\\" + fileName ;
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(filePath);
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis);
OutputStream outputStream = socket.getOutputStream();
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(outputStream);
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024] ;
int leng ;
while( (leng = bis.read(bytes)) != -1 ){
bos.write(bytes , 0 , leng) ;
}
//Executing the shutdownOutput() method will close the output stream bos
socket.shutdownOutput();
br.close();
bis.close();
// bos.close();
socket.close();
serverSocket.close();
}
}
TCP Network Programming Details
netstat directive
- Netstat-an can view the current host network, including port listening and network connectivity
- Netstat-an|more can be paginated
- Require execution under dos console
Client Details
- When a client connects to a service, it actually communicates through a port that is assigned by TCP/IP and is indeterminate and random.
UDP Network Programming [Know it]
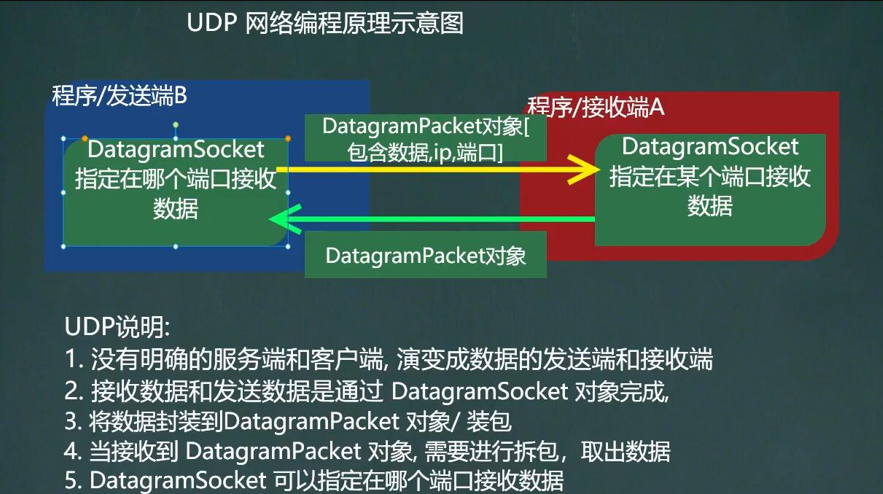
Basic Introduction
- Classes DatagramSocket and DatagramPacket [Packet/Datagram] implement UDP protocol-based network programs
- UDP datagrams are sent and received through the datagram socket DatagramSocket. The system does not guarantee that UDP datagrams will reach their destination safely or when they will arrive.
- The DatagramSocket object encapsulates a UDP datagram that contains the sender and IP addresses and port numbers as well as the receiver's IP addresses and port numbers.
- Each datagram in the UDP protocol gives complete address information, so there is no need to establish a connection between sender and receiver
Operation steps
- Two core classes/objects, DatagramSocket and DatagramPacket
- Create Sender, Receiver
- Create data packages
- Invoke send and receive methods of DatagramSocket
- Close DatagramSocket
UDP Application Cases
receiving end
public class z1_UDP receiving end A {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//Create a DatagramSocket object to receive data at 9999
DatagramSocket ds = new DatagramSocket(9999);
//Build a DatagramPacket object ready to receive data
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024] ;
DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(bytes , bytes.length);
System.out.println("Preparing to receive data~~~~~~");
//Call the receive method and transfer it over the network to the DatagramPacket object
//If received, data will be received, otherwise waiting will be blocked
ds.receive(dp);
//Receive datagrams, unpack and retrieve data
byte[] data = dp.getData();
int length = dp.getLength();
String s = new String(data, 0, length);
System.out.println("A End receives data " + s) ;
byte[] bytes1 = "get your message from port B".getBytes() ;
DatagramPacket dp1 = new DatagramPacket(bytes1, bytes1.length, InetAddress.getLocalHost(), 9998);
ds.send(dp1);
ds.close();
}
}
Sender
public class z1_UDP Sender B {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//Create a DatagramSocket object to receive data on port 9998
DatagramSocket ds = new DatagramSocket(9998);
System.out.println("send data~~~~");
//Data to be sent, encapsulated in a DatagramPacket object
byte[] message = "hello udp to port A".getBytes() ;
DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(message, message.length, InetAddress.getLocalHost(), 9999);
ds.send(dp);
System.out.println("Preparing to receive data~~~~");
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024] ;
DatagramPacket packet = new DatagramPacket(bytes, bytes.length);
ds.receive(packet) ;
byte[] data = packet.getData();
int length = packet.getLength() ;
String s = new String(data, 0 , length);
System.out.println("Received data A End data:" + s );
ds.close();
}
}