1. Foundation type
1.1 INTRODUCTION
1.2 exercise 1: test maximum and minimum
Create a Basic project
Create cn.qile.basic package
Create test1 scope.java
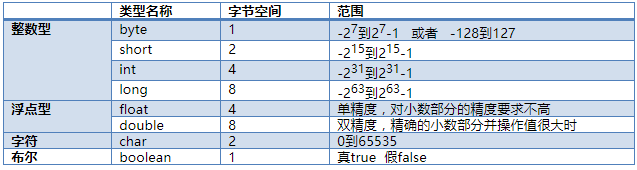
package cn.qile.basic; //This class is used to test the value range public class Test1_Scope { public static void main(String[] args) { //Test integer data range byte short int long //Create variable save byte value -- variable type variable name = variable value byte min = Byte.MIN_VALUE; byte max = Byte.MAX_VALUE; System.out.println(min);//-128, print value of variable System.out.println(max);//127 short smin = Short.MIN_VALUE; short smax = Short.MAX_VALUE; System.out.println(smin);//-32768 System.out.println(smax);//32767 //long -- Long long lmin = Long.MIN_VALUE; long lmax = Long.MAX_VALUE; System.out.println(lmin);//-9223372036854775808 System.out.println(lmax);//9223372036854775807 //TODO int -- Integer int imin = Integer.MIN_VALUE; int imax = Integer.MAX_VALUE; System.out.println(imin);//-2147483648 System.out.println(imax);//2147483647 //TODO float -- float double -- double float fmin = Float.MIN_VALUE; float fmax = Float.MAX_VALUE; System.out.println(fmin);//1.4E-45 System.out.println(fmax);//3.4028235E38 double dmin = Double.MIN_VALUE; double dmax = Double.MAX_VALUE; System.out.println(dmin);//4.9E-324 System.out.println(dmax);//1.7976931348623157E308 //Boolean type boolean b = true;//True, usually 1 for true boolean b2 = false;//False, usually 0 for false //Character type char c = 'a'; char c2 = 'in';//char type can store a Chinese character char c3 = 97; System.out.println(c); System.out.println(c2); //char type data can save numbers, but when it is used, it is not the numbers themselves, but, //Take the numbers to check the ascii code table, take out the characters corresponding to the numbers and use them System.out.println(c3);//a. Because the number 97 of ascii code table corresponds to a character } }
1.3 exercise 2: circular area
The area of a circle: π rr
Circumference of circle: 2 π r
import java.util.Scanner;//Automatic guide package //Find the area of circle public class Test2_Area { public static void main(String[] args) { //1. Define variable record radius // double r = 10.1; / / dead //Dynamically receive the value of keyboard input double r = new Scanner(System.in).nextDouble(); //2. Bring in formula calculation result double result = 3.14*r*r; //Dynamic concatenation string:+ System.out.println("The area of a circle is"+result); } }
1.4 exercise 3: variable exchange
Receive values a and b entered by the user.
Suppose that a = 1 and b = 2 exchange the values of a and b.
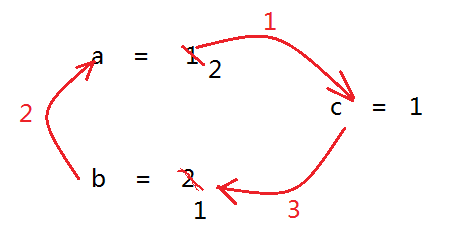
package cn.qile.basic; import java.util.Scanner; //Test variable exchange public class Test3_Exchange { public static void main(String[] args) { //1. Two integers a and b for keyboard input System.out.print("a = "); int a = new Scanner(System.in).nextInt(); System.out.print("b = "); int b = new Scanner(System.in).nextInt(); //2. Exchange int c = a ;//Define c and record the value of a a = b ;//The value of b is given to a b = c ;//Give the value of c to b //3. Print values for a and b System.out.println("a = "+a); System.out.println("b = "+b); } }
2. Literal value of base type
2.1 integer face value is int type
int a = 999999999999999; //int out of range
2.2 three integers smaller than int, byte, short and char, can be assigned directly with the values in the range
byte b = 127;//Yes, because 127 is within the value range of byte byte b2 = 128; //Error, because the literal value of 128 is int type, 4 bytes, byte is 1 byte, cannot be put
2.3 the literal value of a floating-point number is of type double
double b = 1.5;
2.4 suffix LFD of face value
long a = 999999999999L;// 9999999999 literal value is of type int, but if it exceeds the value range of int, an error will be reported. You can only expand the data range, add suffix L, and change from int to long float b = 3.0F;//3.0 literal value is of double type, with suffix L, from double to float double d = 3D;//3. The literal value is of type int, with suffix D, from int to double
2.5 base prefix
0b-2 system, for example: 0b0010 0-8 base, for example: 076 For example: 0x0986 \U - char type, hexadecimal as follows:
3. Type conversion of basic type
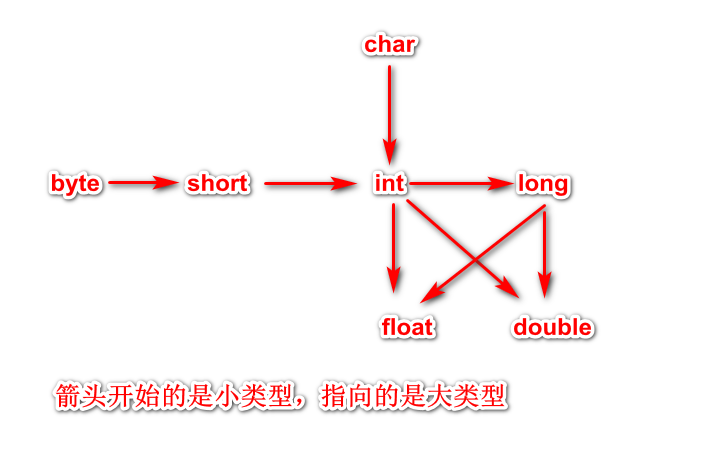
3.1 small to large / implicit conversion
3.2 large to small / display conversion
Cast required
package cn.qile.basic; public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { //Small to large -- implicit transformation short a = 10; //Turn small to large, a on the right is small type, b on the left is large type. For details, take small type to large type, and you can assign values directly long b = a; //Large to small -- explicit conversion -- cast -- (small type) double m = 10.8; //m on the right is a large type, n on the left is a small type. Take the large type and assign values to the small type directly -- no way int n = (int)m; } }
3.3 convert floating-point number to integer and discard decimal number directly
Either 0.1 or 0.9 are abandoned.