Notes and notes
notes
Single line//
Multiline / **/
Document comments / * **/
Role of notes
Pass on additional information → programmer
Do not participate in compilation
annotation
Function: pass additional information → compiler
Can participate in compilation
compare
1. Comments and comments are to add additional information to the code
2. Different definitions. Annotation is a data type of Java, which has the same status as class and interface
3. Different functions. Annotations participate in the compiler, but errors will be reported during compilation
4. Different use positions. There are strict restrictions on the use of annotations
5. The function level of annotations is only at the java file level, and subsequent processes are not involved. But annotations can participate.
Custom annotation
How to define annotations
grammar
Permission modifier @interface Annotation name{
// Annotation body
}
// Attention @ cannot be less
How to define annotation body
Permission modifier @interface Annotation name{
// Annotation body
Property type property name();
Property type property name();
// ...
// Similar to abstract method attribute type → method return value type attribute name → method name
}
Attribute type
- Basic data types in java
- String type
- Class type
- Enum type enum
- annotation type
- And arrays of the above types
Use of annotations (key points)
How to use a class, instantiate and assign a value to this object. If there is no default value assigned
If it is to be used in annotations, it must also be instantiated. At this time, new is not needed
@Annotation name(Attribute 1=xxx,Attribute 2=xxx) be careful Each attribute of the annotation must be assigned a value If there is a default value, it can be passed without assignment default To set the default value If there is only 1 attribute in the annotation and the attribute name value , At this time, the assignment can be simplified by filling in only one value, it's fine too value = xx The default value of reference type cannot be taken null
annotation processor
Get the annotation information, and then do some processing according to the requirements of the annotation
practice
Next, we use annotations in combination with our customized annotation processor to realize the following requirements:
Define a Student class that contains two members: name and age
The number of characters contained in name must not exceed the specified value (specific constraint information - > comments)
age must be within the specified range (specific constraint information - > annotation)
The Student object can only be created if both name and age meet the conditions. Otherwise, an exception is thrown. (this effect is implemented by the annotation processor)
package com.cskaoyan.handle;
import com.cskaoyan.anno.AgeBound;
import com.cskaoyan.anno.NameLimit;
import com.cskaoyan.domain.Student;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
/**
* @description:
* @author: songtao@cskaoyan.onaliyun.com
**/
// annotation processor
public class StudentFactory {
// Bytecode file object
Class stucls;
public StudentFactory() throws ClassNotFoundException {
this.stucls = Class.forName("com.cskaoyan.domain.Student");
}
public Student getStudent(int age, String name) throws NoSuchMethodException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException, NoSuchFieldException {
// Judgment age
// First get the member variable
judgeAge(age);
// Judge name
// Get name from bytecode file object
judgeName(name);
// Bytecode file object
// Get the construction method
Constructor declaredConstructor = stucls.getDeclaredConstructor(int.class, String.class);
declaredConstructor.setAccessible(true);
// newInstance
Student student = (Student) declaredConstructor.newInstance(age, name);
// The ultimate goal is to return the student object
return student;
}
private void judgeName(String name) throws NoSuchFieldException {
Field nameField = stucls.getDeclaredField("name");
// Judge whether the annotation isAnnotationPresent(Class anno) is used
//
boolean annotationPresent = nameField.isAnnotationPresent(NameLimit.class);
if (annotationPresent) {
// Get annotation instance
NameLimit annotation = nameField.getAnnotation(NameLimit.class);
// Get property value
int limit = annotation.limit();
// judge
if (name.length() > limit) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("The name is too long");
}
}
}
private void judgeAge(int age) throws NoSuchFieldException {
Field ageField = stucls.getDeclaredField("age");
// First judge whether comments are added
boolean annotationPresent = ageField.isAnnotationPresent(AgeBound.class);
if (annotationPresent) {
// Gets the property value of the annotation instance
// getAnnotation(Class anno) gets the annotation instance
AgeBound annotation = ageField.getAnnotation(AgeBound.class);
int maxAge = annotation.maxAge();
int minAge = annotation.minAge();
// Judge whether the parameters passed in are within the range
if (age < minAge || age > maxAge) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal age!");
}
}
}
}
Meta annotation (Master)
Meta annotation: metadata describing annotation (annotation of annotation) meta data Data describing data
Common meta notes:
1. @Retention Meta annotation to define the retention level of our own annotation.
1. RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME
2. RetentionPolicy.CLASS
3. RetentionPolicy.SOURCE
The default retention level is class level
2. @Target Meta annotation, the goal of annotation
For annotations, the following objectives can be used:
1. Entire class ElementType.TYPE
2. Member variable ElementType.FIELD
3. Construction method ElementType.CONSTRUCTOR
4. Member method ElementType.METHOD
Profile VS annotation
package com.cskaoyan.use;
import com.cskaoyan.anno.DBConfig;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
/**
* @description:
* @author: songtao@cskaoyan.onaliyun.com
**/
public class DButil {
// Get database connection
@DBConfig(host = "localhost", user = "admin", password = "654321", dbName = "test")
public static Connection getConnection() throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException {
// Get bytecode file object
Class c = Class.forName("com.cskaoyan.use.DButil");
// Acquisition method
Method method = c.getDeclaredMethod("getConnection");
// Are annotations used for interpretation
boolean annotationPresent = method.isAnnotationPresent(DBConfig.class);
if (annotationPresent) {
// Get annotation instance
DBConfig annotation = method.getAnnotation(DBConfig.class);
// Get property value
String dbName = annotation.dbName();
String host = annotation.host();
String password = annotation.password();
int port = annotation.port();
String user = annotation.user();
// Get database configuration information
// Establish database connection and return
//String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test";
//DriverManager.getConnection(, )
}
return null;
}
}
Annotation VS profile
configuration file
Advantages: configurable without changing the source code. Convenient management
Disadvantages: not intuitive, low development efficiency
annotation
Advantages: intuitive, high development efficiency
Disadvantages: it is hard coded and needs to be recompiled after modification. It is difficult to manage independently from the code
@Test
@Servlet
memory management
Explicit memory management
The memory management is left to the programmer
Distribution recycling C++
malloc() free()
Disadvantages:
- Memory leak
- Field pointer
Implicit memory management
Leave the memory management to the system
Advantages: it increases the reliability of the program and reduces the memory leak
Disadvantages: unable to control GC time and consume system performance
GC
Who is rubbish?
Reference counting algorithm
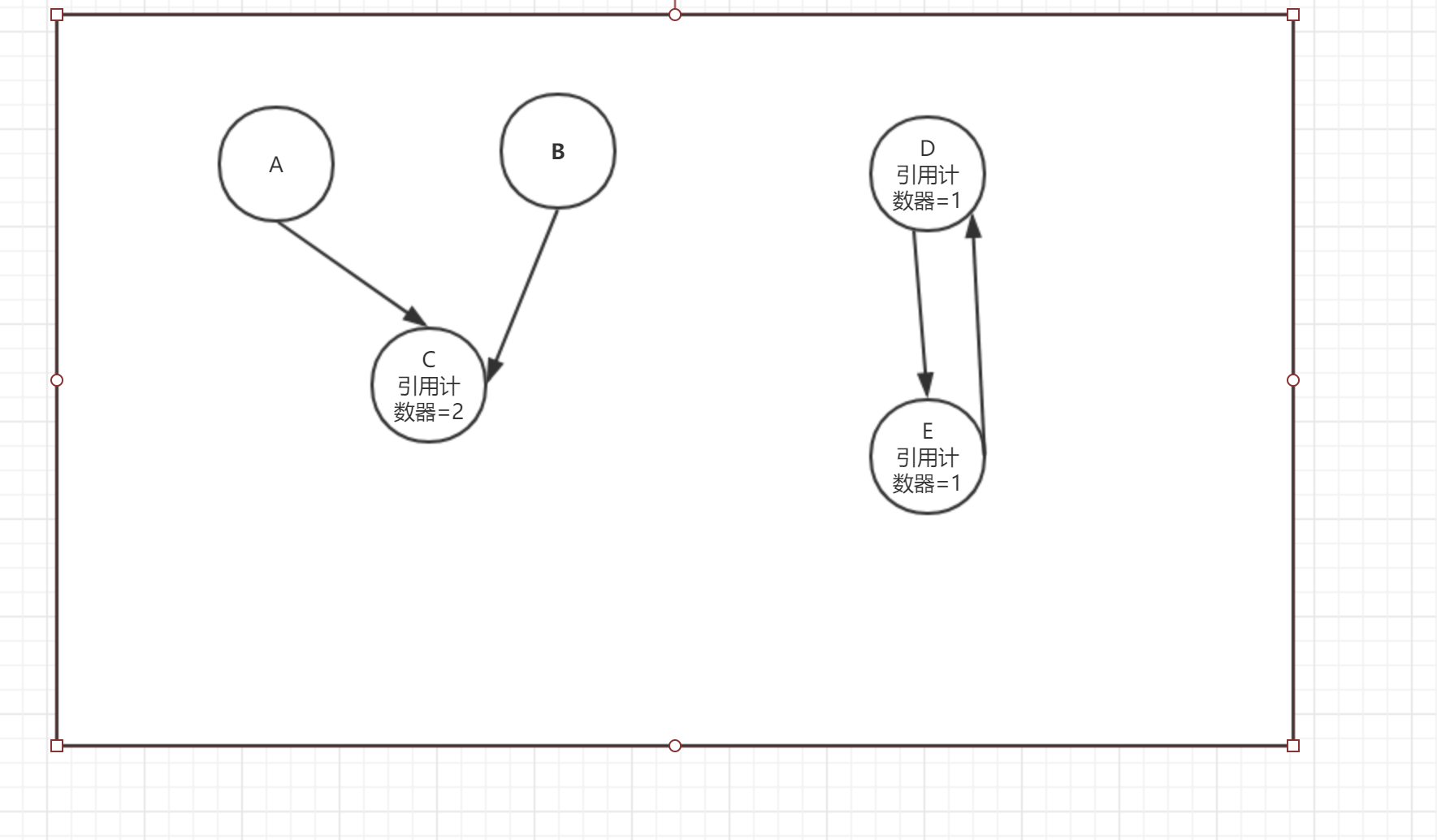
The problem of circular references cannot be resolved
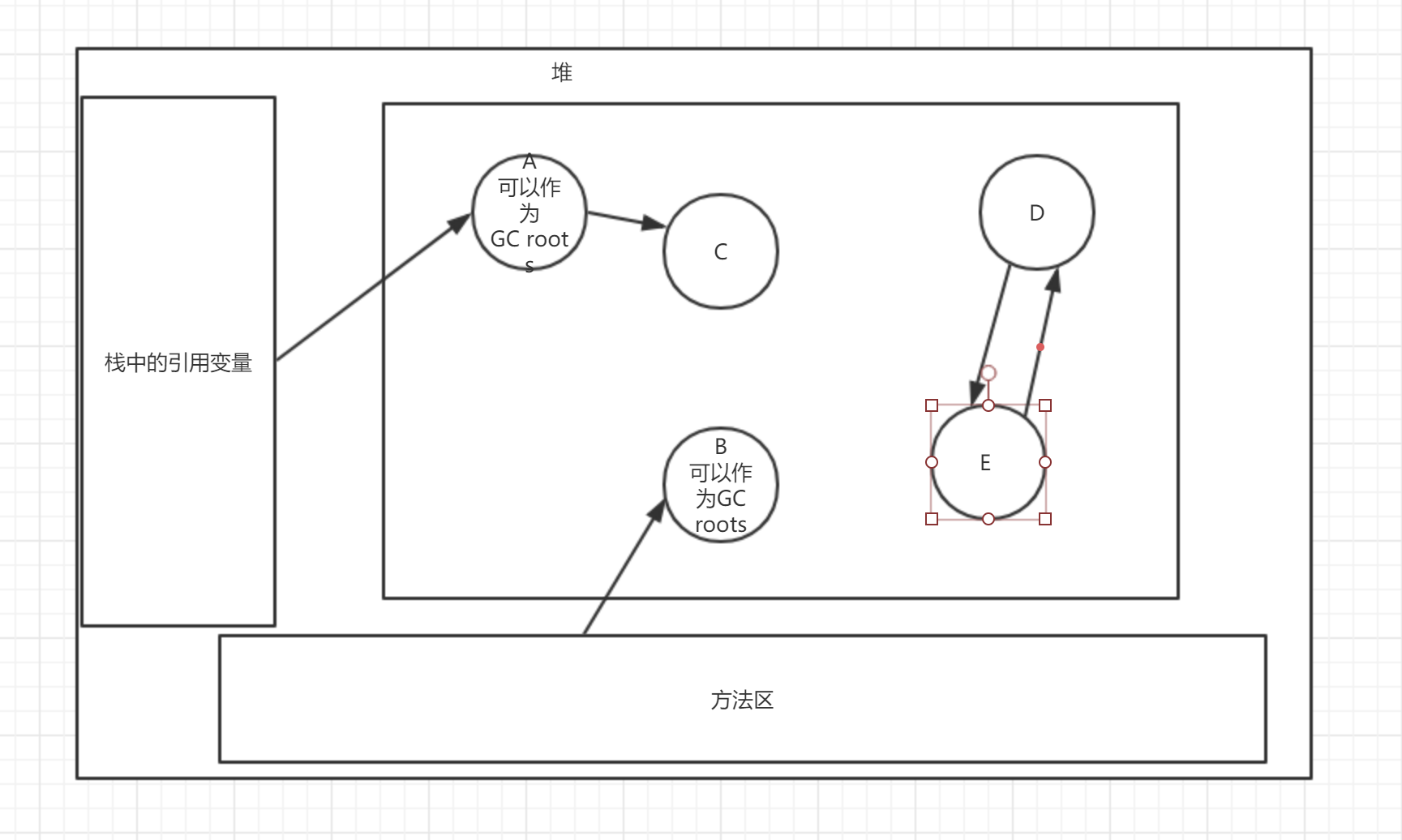
Root search algorithm
The basic idea of this algorithm is to take a series of objects called "GC Roots" as the starting point
Start the drill down from these nodes
The path taken by the search is called the reference chain
When there is no reference chain between an object and all GC root s, the object is considered to be garbage
What about GC Roots containing objects?
Objects referenced in the virtual machine stack
The object referenced by the static property in the method area
Resolve circular references
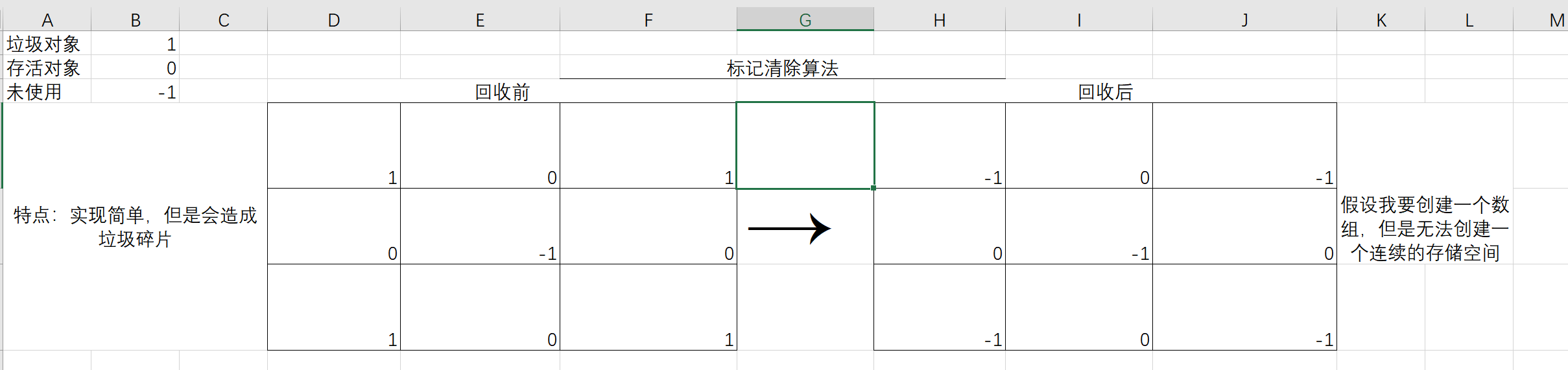
How to recycle garbage?
Mark removal algorithm
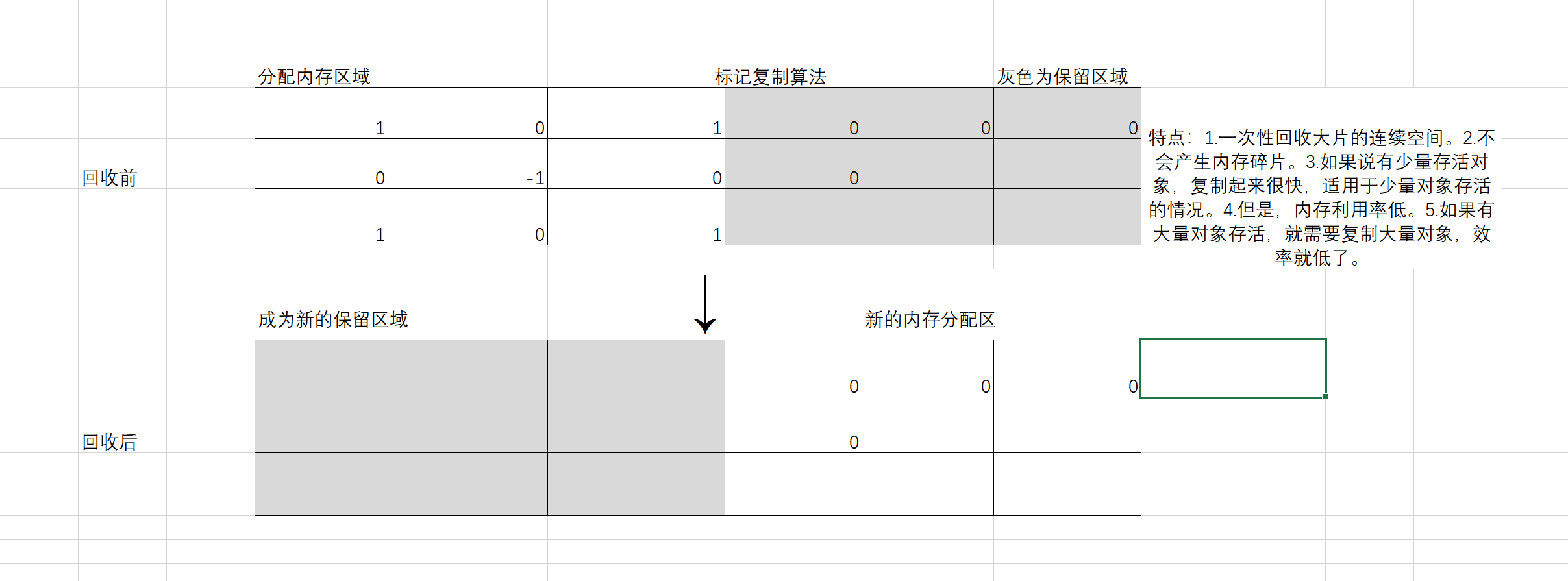
Label replication algorithm
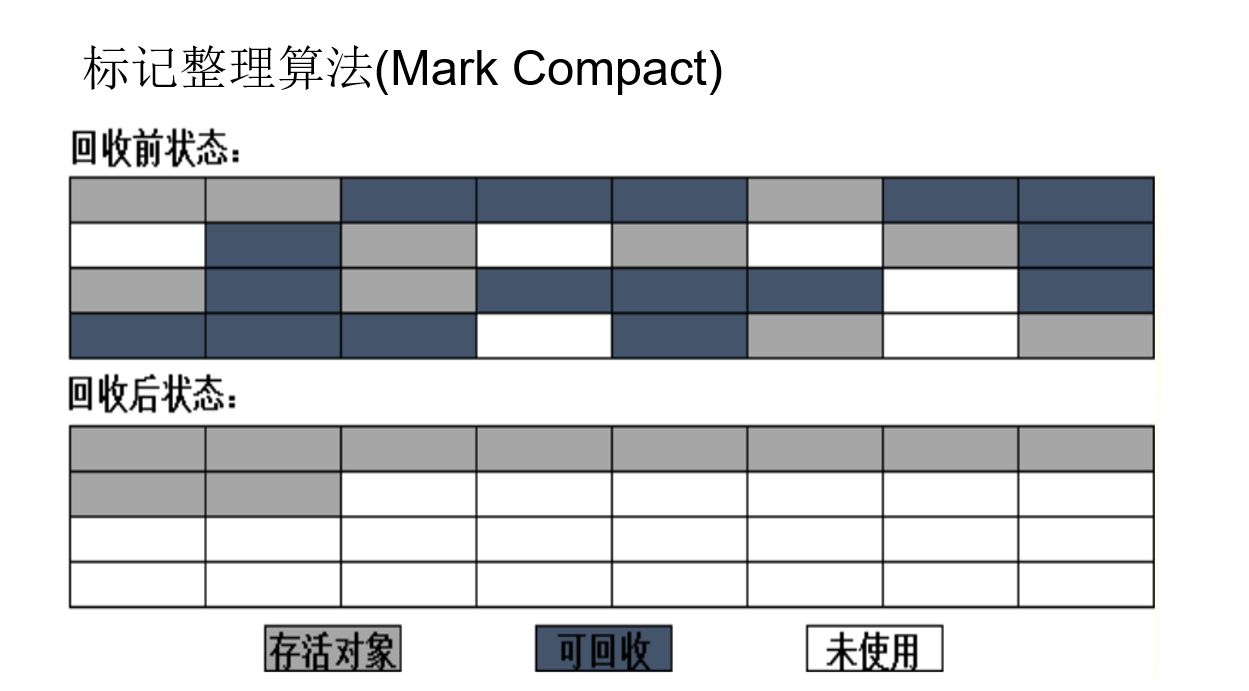
Label collation (compression) algorithm
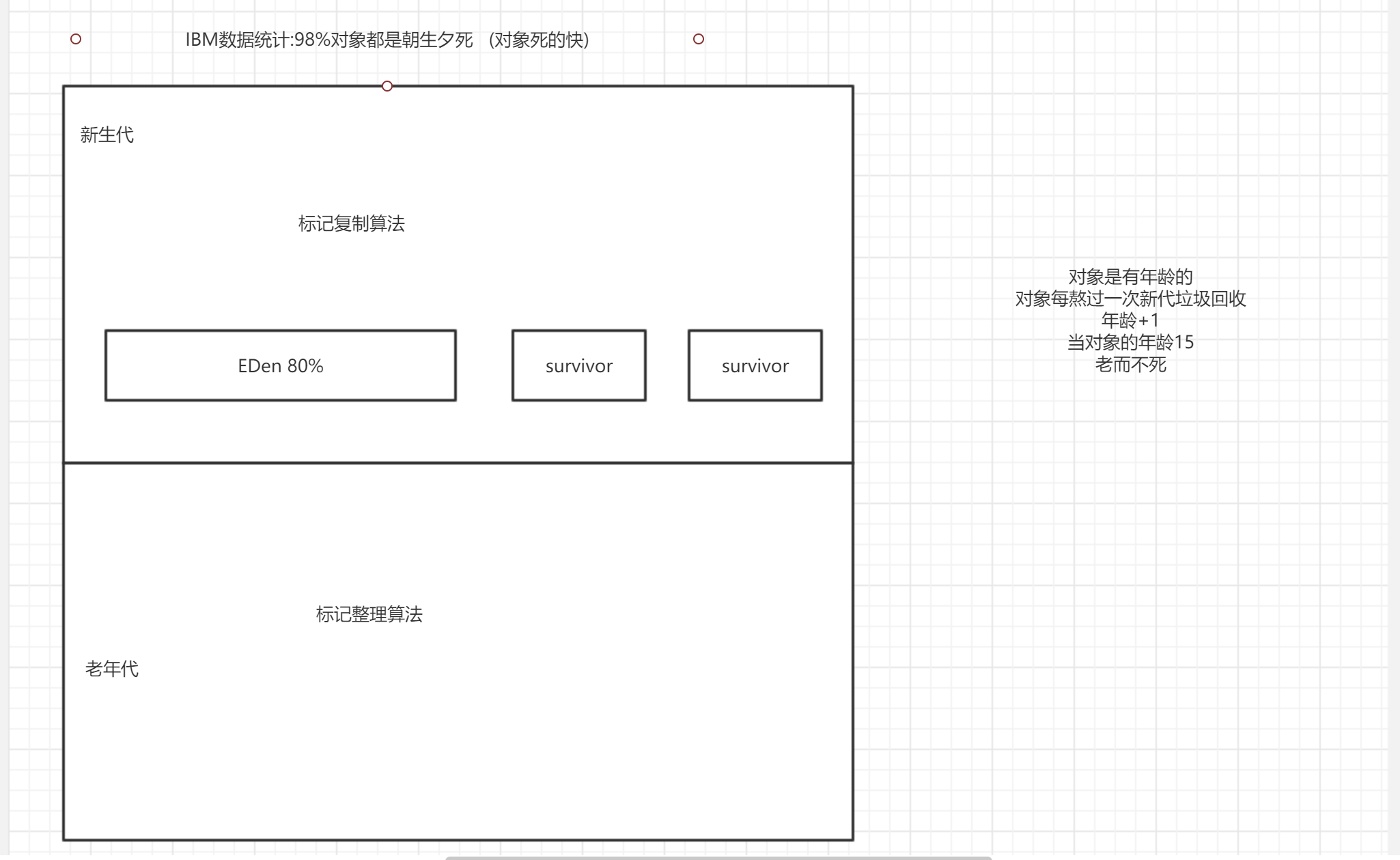
Generational collection algorithm
When to recycle?
- Failed to request heap memory
- The program goes to sleep
- System.gc() manual recycle
GC related concepts
Shallow size
Is the memory size occupied by the object itself, that is, the object header plus member variables
The total amount of memory used
Retained size
Is the object's own share size plus only accessible from the object (straight)
The sum of the share sizes of the objects accessed (directly or indirectly).
Retained size
Is the total amount of memory that can be reclaimed after the object is GC.