Simple understanding of Socket
Socket is a connection oriented communication protocol. Socket application is a C/S (Client / Server) structured application
Socket is the end point of communication between two machines.
Socket is a two-way communication endpoint connecting two programs running on the network.
Socket communication principle
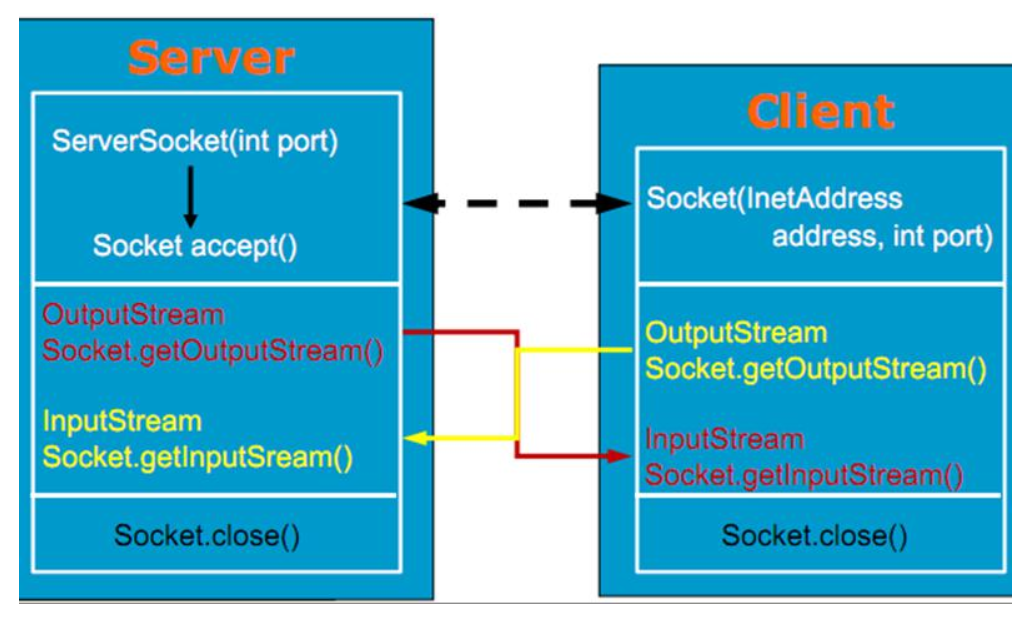
- The input stream of Server server is equivalent to the output stream of Client
- The output stream of Server server is equivalent to the input stream of Client
Be careful
- File transfer uses byte stream
- Using DataOutputStream, DataOutputStream can pass java basic types and streams
Code
Server.java
package csmode2;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
/**
* @author StarsOne
* @date Create in 2019-4-14 0014 10:53:58
* @description
*/
class Server {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(9090)){
System.out.println("Server started...");
while (true) {
System.out.println("Waiting to receive file");
//After the accept method is called, it is always waiting for the file to be accepted
Socket socket = serverSocket.accept();//Receive data from client
//To the background thread
new AcceptThread(socket.getInputStream()).start();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
AcceptThread.java
package csmode2;
import java.io.DataInputStream;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
/**
* @author StarsOne
* @date Create in 2019/4/15 0015 14:17
* @description
*/
class AcceptThread extends Thread {
private InputStream inputStream;
public AcceptThread(InputStream inputStream) {
this.inputStream = inputStream;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
//Wrapping the input stream with DataInputStream
DataInputStream dataInputStream = new DataInputStream(inputStream);
String fileName = dataInputStream.readUTF();
System.out.println(fileName);//Display the filename in the console
//Write files to a location
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("Q:\\MY" + File.separator + fileName);
int c = -1;
while ((c = dataInputStream.read()) != -1) {
fileOutputStream.write(c);
fileOutputStream.flush();
}
System.out.println("File upload succeeded!");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Client.java
package csmode2;
import java.io.*;
import java.net.Socket;
/**
* @author StarsOne
* @date Create in 2019-4-14 0014 10:53:49
* @description
*/
class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// File[] files = new File("E:\\wan\\testfile").listFiles();
//If there are multiple files, just put them into a list or array, and use the for loop to upload all the files of the array to the server
//Uploaded files
File file = new File("R:\\Cartoon pictures\\test.jpg");
try(Socket socket = new Socket("localhost", 9090)) {
OutputStream outputStream = socket.getOutputStream();
//Using DataOutputStream
DataOutputStream dataOutputStream = new DataOutputStream(outputStream);
//File name to server
dataOutputStream.writeUTF(file.getName());
dataOutputStream.flush();//Refresh stream, transfer to server
//File transfer to server through byte stream
//Byte stream read hard disk file first
BufferedInputStream bufferedInputStream = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(file));
int c = -1;
while ((c=bufferedInputStream.read())!=-1) {
//Write the read file to DataOutputStream in bytes, and then transfer it to the server
//Here you can also use byte [] data for reading and writing
dataOutputStream.write(c);
dataOutputStream.flush();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}