TCP Socket programming
Introduction to computer networking

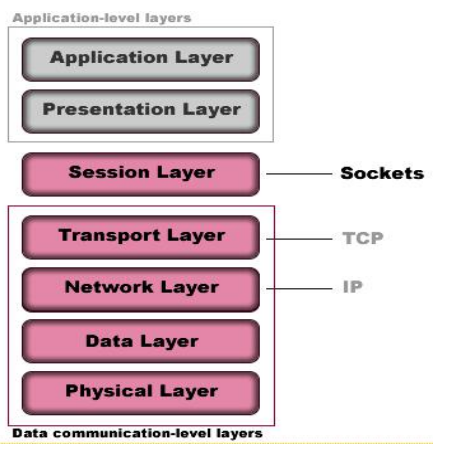







Introduction to Socket and ServerSocket
Introduction to relevant knowledge
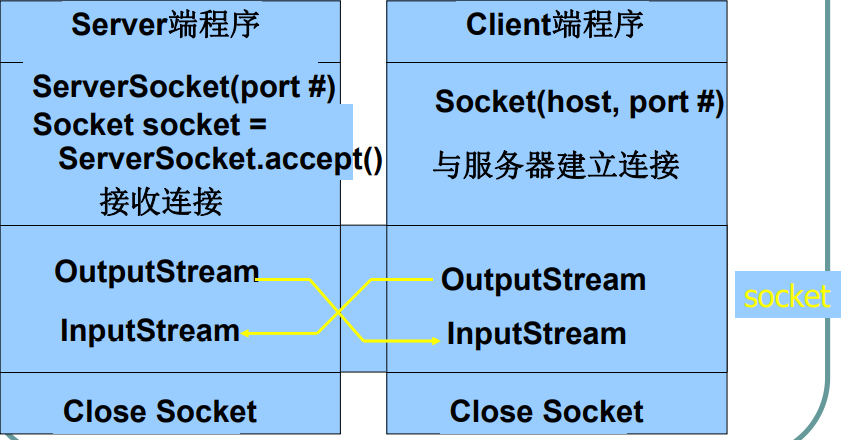
The process of using Socket for network communication
- The server program binds a socket to a specific port, and waits for and listens to the client's connection request through this socket
- The client program sends a connection request according to the host name and port name where the server program is located
- If everything is OK, the server accepts the client connection request. And get a new socket bound to different port addresses
- The client and server communicate through write and read sockets
No matter how complete and complex a Socket communication program is, its basic structure is the same, including the following four basic steps:
- Create Socket/ServerSocket instances on the client and server sides
- Open the input / output stream linked to the Socket
- Use the input / output stream to read / write to the Socket according to a certain protocol
- Close the I / O stream and socket
The programmer's main job is to program the functions to be completed in the third step
Introduction to main Socket methods
Construction method
- public Socket(String host,int port) / / remote server IP and response port
- public Socket(InetAddress address,int port)
- public Socket(String host,int port,InetAddress localAddr,int localPort)
- Public socket (InetAddress, address, int port, InetAddress, localaddr, int localport) / / run on the specified port on the specified machine
These methods will throw an exception IOException, and the program summary needs to be captured and processed
Socket input / output stream management
- public InputStream getInputStream()
- public void shutdownInput()
- public OutputStream getOutputStream()
- public void shutdownOutput()
These methods will throw an exception IOException, which needs to be caught in the program
Close Socket
public void close() throws IOException
Set / get Socket data
- public InetAddress getInetAddress()
- public int getPort()
- public void setSoTimeout(int timeout)
These methods throw an exception SocketException, which needs to be caught in the program
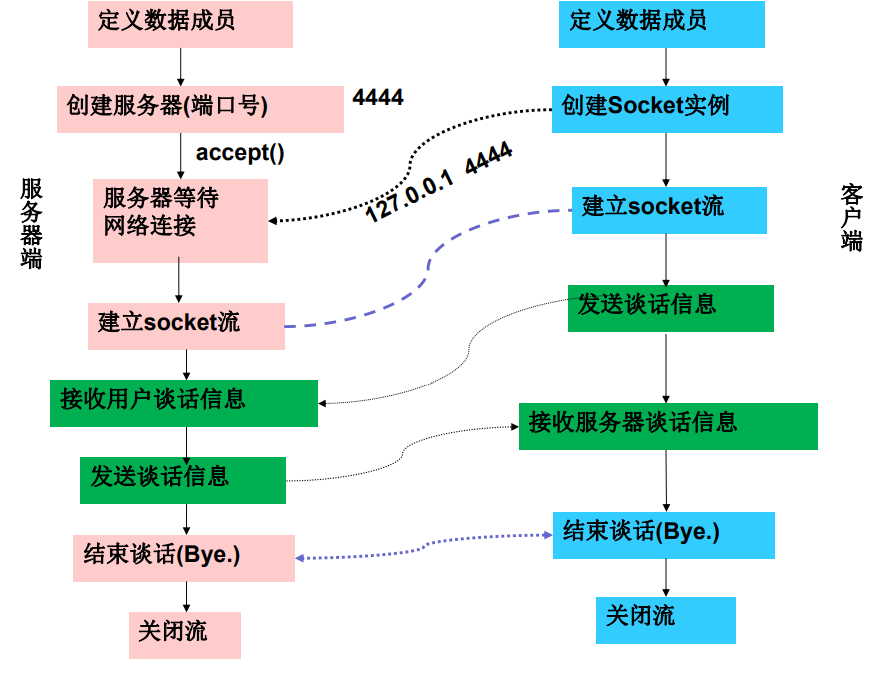
Socket demo
Establish Socket – on the client side
try{
Socket client = new Socket(host,4444);
}catch(IOException e){}
Establish Socket - on the server side
try{
ServerSocket server = new ServerSocket(4444);
}catch(IOException e){}
Socket socket = null;
try{
socket = server.accept();//Waiting for client connection
}catch(IOException e){}
Open input / output streams on both the client and server sides
- Class Socket provides methods getInputStream() and getOutputStream() to get the input / output stream corresponding to the Socket for data reading and writing operations. They return InputStream object and OutputStream object respectively
- In order to facilitate reading and writing data, filter streams should be established on the returned input / output stream objects, such as BufferedReader and PrintStream
- BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(socket.getInputStream()));
- PrintStream out = new PrintStream(socket.getOutputStream()));
Close the I / O stream and Socket
Close the I / O stream and Socket on the client and server respectively: close all relevant I / O streams first, and then close the Socket
Code example
Port scan
import java.net.*;
import java.io.*;
public class ScanPort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for(int i = 1;i <= 1024;i++){
try{
Socket s = new Socket(args[0],i);
System.out.println(" "+i);
s.close();
}catch (IOException e){}
}
}
}
client
import java.net.*;
import java.io.*;
public class MyClientA {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try{
Socket s = new Socket("127.0.0.1",5432);
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(s.getInputStream()));
String x = in.readLine();
System.out.println(x);
in.close();
}catch(IOException e){}
}
}
Server side
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintStream;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.*;
public class MyServerA {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try{
ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(5432);
while(true){
Socket s = ss.accept();
PrintStream out = new PrintStream(s.getOutputStream());
out.println("Hi");
out.close();
s.close();
}
}catch(IOException e){}
}
}