catalogue
iii. direct insertion sorting algorithm
4. Method and array bicolor ball case
1, Methods and arrays
1. Method
i. Definition of method
The method is a code block with specific function, also known as function, to improve the reusability and readability of the program.
ii. Format of method
Syntax:
Access right modifier [other modifiers such as static] return value type method name (parameter type 1, parameter type 2, parameter 2...) {
/ / formal parameter list
/ / method body
Return return value;
}
The return value type, that is, the data type of the function, after which we can define the entity;
Method name: see the name to know the meaning, the first letter is in lowercase, and the hump is named;
public class Test{
public static void main(String[] args){
getMenu(); //Call the method, and then the method will run.
printStar(1);
}
// public access modifier
// Static static modifier. The described method can be called directly
// Void (no return value)
public static void getMenu(){
System.out.println("This is a way!");
}
// Method with parameters
// Parameters in method definition are called formal parameters, and parameters in call
public static void printStar(int line){
System.out.println("This is a method!");
}
}iii. parameters
Actual parameters: the parameters actually involved in the operation;
Formal parameter: it is defined in the method and used to receive actual parameters;
Parameter type: the data type of the parameter;
Parameter name: variable name;
Method language sentence: it is the code that completes the function
Note: if the formal parameter is not used in the current method, the formal parameter list can be empty;
The types of arguments and formal parameters should be compatible with each other, and the range of arguments should be less than or equal to the range of formal parameters.
iv. return value
return: used to end the method.
Return value: the result of the function or the final result of the method operation, which is brought to the caller by return.
Note: if the current method does not have a return value type, that is, the return value is void, then return can not be written in the current method;
Return means to end a method, or return the return value to the caller calling the current method
Return when returning a value, you can only return one value at a time. You can't return multiple values;
There can be multiple return s in a method, but only one can be executed, so you need to judge;
v. Method overload method
Multiple methods can be created in a class. They have the same name, but different parameters and different definitions;
The return value cannot be used as an overloaded condition.
public class Test{
public static void main(String[] args){
int result = add(10,20);
System.out.println(result)
}
public static int add(int a,int b){
return a+b
}
public static int add(float a,float b){
return a+b
}
}2. Array
i. Definition of array
A set of variables that can store the same data type.
Array is a linear data storage structure, which has the characteristics of high access efficiency and continuous memory space. Array must have a fixed, long-term and commonly used data structure.
ii. Define array
Initialize each element in the array with the default initial value
Array element type [] array name = new array element type [number of elements in the array (length of the array)];
int [] scores = new int[3];
First declare, and then give the array the default initial value
Array element type [] array name;
Array name = new array element type [number of elements in the array (length of the array)];
int [] scores;
scores = new int[3];
Declare before initializing with the specified value.
Array element type [] array name = new array element type [] {element 1, element 2,...};
int[] scores = new int[]{56,78,98};
Simplified writing:
int [] scores = {56,78,98};
public class Test{
public static void main(String[] args){
int[] nums = new int[5];
nums[0]=1;
nums[1]=2;
nums[2]=3;
nums[3]=4;
nums[4]=5;
int[] num;
num = new int[5];
for(int i=0;i<num.length;i++){
num[i]=i+1;
}
int[] num1={1,2,3,4,5};
}
}iii. traversal of array
Find the length of the array with x.length
Access the elements in the array by subscript.
Subscript: from 0 to array length - 1
Traversal: take out each element in the array in turn.
Traversal mode: ordinary for loop
For (int i = 0; I < array length; I + +){
/ / i: circular variable, which is also the subscript of the array
Type variable of element in array = array name [i];
}
jdk1.5. New: forearch traversal
for(int x:scores){
Systen.out.println(x)
}
Note: the variable parameter can be used as an array. The variable parameter must be the last parameter in the parameter list, followed by three points in the data type; When the method is called, the value is passed directly, and there is no need to define the array.
iv. array precautions
Null pointer exception (NullPointerException)
When a variable is null (no assignment), we call the properties and methods of the variable
Array out of bounds exception (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException)
That is, it exceeds the length of the array;
Array memory data structure analysis:
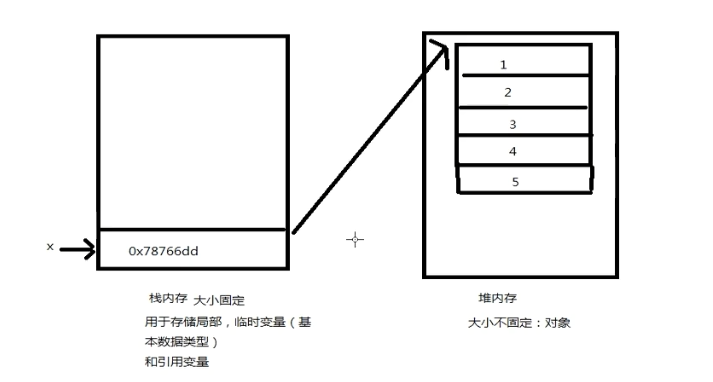
Array is a reference type and will be stored in the heap;
v. Examples
import java.util.Scanner
public class Test{
public static void main(String[] args){
int[] nums={12,13,15,34,23};
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Please enter the number you want to guess:");
int userNum = input.nextInt();
boolean flag = false;
for(int x:nums){
if(userNum==x){
flag = true;
break;
}
}
if(flag){
System.out.println("Congratulations! You guessed right!");
}else{
System.out.println("I didn't guess right");
}
}
}Two dimensional array: there is no real multi-dimensional array in java. The representation of multi-dimensional array is the element in the array or the array.
Question: there are three students from three classes participating in the competition. Record the results of each student and calculate the average score of each class
public class Test{
public static void main(String[] args){
int[][] scores = {{78,98,88},{87,99,89},{67,87,89}};
int classLen = scores.length;
for(int i=0;i<classLen;i++){
int sum = 0;
int count = scores[i].length;
for(int j=0;j<count;j++){
sum+=scores[i][j];
}
int avg = sum/count;
System.out.println("The first"+(i+1)+"The average grade of the class is:"+ avg);
}
}
}3. Algorithm
i. Bubble sorting algorithm
Compare adjacent elements. If the first is larger than the second, exchange them.
Do the same for each team of adjacent elements, from the first pair at the beginning to the last pair at the end. At this point, the last element should be the largest number.
Repeat the above steps for all elements except the last one.
Repeat the above steps until there are fewer and fewer pairs of elements to compare each time.
The sequence of the same elements has not changed, so bubble sorting is a stable sorting algorithm.
public class Test{
public static void main(String[] args){
int[] nums = {1,45,32,24,26,56,78,23};
//Number of external circulation control wheels
for(int i=0;i<nums.length-1;i++){ //The number of comparison rounds is equal to the length of the sequence - 1
for(int j=0;j<nums.length-1-i;j++){
if(nums[j]>nums[j+1]){
nums[j]=nums[j]+nums[j+1];
nums[j+1]= nums[j]-nums[j+1];
nums[j] = nums[j]-nums[j+1];
}
}
}
for(int n: nums){
System.out.println(n)
}
}
}
/**
* 1 45 32 24 26 56 78 23
* 1 32 34 26 45 56 23 78 7 second
* 1 32 26 34 45 23 56 6 second
* 1 26 32 34 23 45 5 second
* 1 26 32 23 34 4 second
* 1 26 23 32 3 second
* 1 23 26 2 second
* 1 23 1 second
*/
//Exchange data a = a+b;b=a-b;a=a-b;ii. Select Sorting Algorithm
Each time, the smallest (or largest) element is selected from the data elements to be sorted, and the order is placed at the end of the arranged sequence. It is known that all the data elements to be sorted are finished. Selecting sorting is an unstable sorting method.
public class Test{
public static void main(String[] args){
int[] nums = {1,45,32,24,26,56,78,23};
int minIndex = 0;// The minimum subscript used to record each comparison
//Number of external circulation control wheels
for(int i=0;i<nums.length-1;i++){ //The number of comparison rounds is equal to the length of the sequence - 1
minIndex = i;// Each round assumes a minimum subscript
for(int j=i+1;j<nums.length;j++){
if(nums[minIndex]>nums[j]){
minIndex=j;
}
}
//Judge whether the subscript of the number to be exchanged is itself
if(minIndex != i){
nums[minIndex] = nums[minIndex] + nums[i];
nums[i] = nums[minIndex]-nums[i];
nums[minIndex]=nums[minIndex]-nums[i];
}
}
for(int n: nums){
System.out.println(n)
}
}
}
/**
* 1 45 32 24 26 56 78 23
* 1 45 32 24 26 56 78 23 7 second
* 1 23 32 24 26 56 78 45 6 second
* 1 23 24 32 26 56 78 45 5 second
* 1 23 24 26 32 56 78 45 4 second
* 1 23 24 26 32 56 78 45 3 second
* 1 23 24 26 32 45 78 56 2 second
* 1 23 24 26 32 56 56 78 1 second
*/
iii. direct insertion sorting algorithm
Find the appropriate position from the back to the front and insert it. In each step, insert a record to be sorted into the appropriate position of the previously sorted word sequence according to its sequence code size until all the records are inserted and sorted;
public class Test{
public static void main(String[] args){
int[] nums = {1,45,32,24,26,56,78,23};
int minIndex = 0;// The minimum subscript used to record each comparison
//Number of external circulation control wheels
for(int i=1;i<nums.length;i++){ //The number of comparison rounds is equal to the length of the sequence
int temp = nums[i];// Record operand
int j = 0;
for(int j=i-1;j>=0;j--){
if(nums[j]>nums[temp]){
nums[j+1]=nums[j]
}else{
break;
}
}
//Judge whether the subscript of the number to be exchanged is itself
if(nums[j+1] != temp){
nums[j+1]=temp
}
}
for(int n: nums){
System.out.println(n)
}
}
}
/**
* 1 45 32 24 26 56 78 23
* First round I = 1 45 32 24 26 56 78 23
* 1 45 32 24 26 56 78 23
*
* Second round I = 2 1 45 45 24 26 56 78 23
* 1 32 45 24 26 56 78 23
*
* Third round I = 3 1 32 45 45 26 56 78 23
* 1 32 24 45 26 56 78 23
1 24 32 45 26 56 78 23
*
* Fourth round I = 4 1 24 32 45 56 78 23
* 1 24 32 26 45 56 78 23
* 1 24 26 32 45 56 78 23
*
* Fifth round I = 5 1 24 26 32 45 56 78 23
*
* Sixth round I = 6 1 24 26 32 45 56 78 23
*
* Seventh round I = 7 1 24 26 32 45 56 78 78
* 1 24 26 32 45 56 23 78
* 1 24 26 32 45 23 56 78
* 1 24 26 32 23 45 56 78
* 1 24 26 23 32 45 56 78
* 1 24 23 26 32 45 56 78
* 1 23 24 26 32 45 56 78
*/
iv. binary search algorithm
Binary search (half search): the premise is that in the ordered array, the elements to be searched are compared with the elements corresponding to the intermediate index value. If it is greater than the elements corresponding to the intermediate index value, go to the right half for search. Otherwise, go to the left half for search until the position is not found, and a negative number is returned.
public class Test{
public static void main(String[] args){
//It must be ensured that the sequence is orderly
int[] num ={10,20,50,65,88,90}
int index = binarySearch(num,88)
}
public static int binarySearch(int[] num,int key){
int start =0;
int end = num.length-1;
while(start<=end){
int middle =(start+end)/2;
if(num[middle]>key){
end=middle-1;
}else if(num[middle]<key){
start = middle+1;
}else{
return middle;
}
}
return -1;
}
}
v. Arrays class
Arrays tool class: various methods used to manipulate arrays
Common methods:
Use binary search
Arrays.binarySearch(int[] array,int value);
The contents of the array are output in the form of string
Arrays.toString(int[] array);
Array sorting
Arrays.sort(int[] array);
Copies the specified array
Arrays.copyOf(int[] array,int length);
Arrays.copyOf(int[] array,int from,int to);
System,arraycopy(Object src,int srcPos,Object dest,int desPos,int length)
Determine whether two arrays are equal
Arrays.equels();
Fills the array with the specified elements
Arrays.fill();
public class Test{
public static void main(String[] args){
int[] nums = {1,45,32,24,26,56,78,23};
//Binary search
int index = Array.binarySearch(nums,88);
System.out.println(index);
}
}
4. Method and array bicolor ball case
Steps:
The user selects whether the number is selected by machine or by hand;
Receive user selected number (6 red, 1 blue);
Generate system number (6 red, 1 blue);
Compare the system number with the user number and record the number;
Verify whether the prize is won;
System number sorting;
Publish the results;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Define related variables
int[] userRedBall = new int[6];//Red ball number selected by the user
int[] sysRedBall = new int[6];//System generated red ball number
int userBlueBall = 0;//User selected basketball
int sysBlueBall = 0;//System generated basketball
int redCount = 0;//Record the correct number of red balls selected by the user
int blueCount = 0;//Record the correct number of basketball balls selected by the user
int[] redBall = new int[33];//Red ball number for storing 1-33
//It is necessary to randomly generate 6 numbers that are not repeated between 1-33 (algorithm)
for(int i = 0;i<redBall.length;i++){
redBall[i] = i+1;
}
//When the game starts, the system prompts
System.out.println("The two-color ball game begins, good luck!");
System.out.println("Would you like to select the number by machine or by hand (1: machine, 2: hand):");
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
Random r = new Random();
boolean flag = true;
while (flag){
int isAuto = input.nextInt();
switch (isAuto){
case 1:
//Machine selection
computerSelection(redBall,userRedBall);//Machine selected red ball
userBlueBall=r.nextInt(16)+1;//Machine selected basketball
flag=false;
break;
case 2:
//Hand selection
System.out.println("Please select six red ball numbers (1)-33): ");
for (int i=0;i<userRedBall.length;i++){
userRedBall[i] = input.nextInt();
}
System.out.println("Please select a basketball number (1)-16): ");
userBlueBall = input.nextInt();
flag=false;
break;
default:
System.out.println("Please tell me whether you want to select the number by machine or by hand (1: machine, 2: hand):");
break;
}
}
//System randomly generated number
//Red ball
computerSelection(redBall,sysRedBall);
//blue ball
sysBlueBall=r.nextInt(16)+1;
//Statistical results:
//Statistical red ball
for (int i=0;i<userRedBall.length;i++){
for(int j=0;j<sysRedBall.length;j++){
if(userRedBall[i]==sysRedBall[j]){
int temp = sysRedBall[j];
sysRedBall[j] = sysRedBall[sysRedBall.length-1-redCount];
sysRedBall[sysRedBall.length-1-redCount]=temp;
redCount++;
}
}
}
//Statistical basketball
if(userBlueBall==sysBlueBall){
blueCount=1;
}
//Verify whether the winner
if (blueCount==0 && redCount<=3){
System.out.println("The revolution has not yet succeeded, and comrades still need to work hard!");
}else if(blueCount==1 && redCount<3){
System.out.println("Won the sixth prize, 5 yuan!");
}else if((blueCount==1 && redCount==3)||(blueCount==0 && redCount==4)){
System.out.println("Won the fifth prize, 10 yuan!");
}else if((blueCount==1 && redCount==4)||(blueCount==0 && redCount==5)){
System.out.println("Won the fourth prize, 200 yuan!");
}else if(blueCount==1 && redCount==5){
System.out.println("Won the third prize, 3000 yuan!");
}else if(blueCount==0 && redCount==6){
System.out.println("Won the second prize, 150 W!");
}else if(blueCount==1 && redCount==6){
System.out.println("Won the first prize, 500 W!");
}else{
System.out.println("System error, winning is invalid!");
}
//Publish system number
System.out.println("The red ball number of this issue is:");
sort(sysRedBall);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(sysRedBall));
System.out.println("The blue ball number of this award is:"+sysBlueBall);
//Publish user number
System.out.println("The red ball number you selected is:");
sort(userRedBall);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(userRedBall));
System.out.println("The basketball number you selected is:"+userBlueBall);
System.out.println("Buy a two-color ball to benefit you, me and him, thank you!");
}
//Bubble sorting
public static void sort(int[] ball){
for(int i=0;i<ball.length-1;i++){
for(int j=0;j<ball.length-1-i;j++){
if(ball[j]>ball[j+1]){
ball[j]=ball[j]+ball[j+1];
ball[j+1]=ball[j]-ball[j+1];
ball[j]=ball[j]-ball[j+1];
}
}
}
}
//An algorithm for randomly generating multiple non repeating numbers in a specified sequence
public static void computerSelection(int[] redBall,int[] userRedBall){
Random r = new Random();
int index=-1;
for(int i =0;i<userRedBall.length;i++){
index=r.nextInt(redBall.length-i);
userRedBall[i] = redBall[index];
int temp = redBall[index];
redBall[index]=redBall[redBall.length-1-i];
redBall[redBall.length-1-i]=temp;
}
}
}