String base:
Declaration string:
String a; String a,b;
Assignment:
String a="";//If the value is not assigned null String b,c; b=""; C="";
Construction method instantiation:
String a =new String(); String b =new String(a);
Character array instantiation:
Create a string using a character array
Construction method: public String (char[] value)
char[] charArray={ };
String a =new String(charArray,3,2);/*charArray Represents an array that is converted to a string.
3 Represents the number from which to start, and 2 represents the extraction of several elements*/Split string:
Grammar: public String concat(Stringstr)//str is a string ready to be stitched at the end
String str="abc";
str=str.concat("de");
output str Display results: abcdeGet the string length:
Grammar: public int length()
String password ="1234567890"; int size =password.length(); output size Display results: 10
Gets the character at the specified position:
Grammar: public char charAt(int index)//Index is the index position to get
String name ="Kirito; char ch =name.charAt(0); output ch Display results: K
Gets the substring index position:
Grammar: public int indexOf(String str)//str is the substring to get
String str ="King of the world";
int index =str.indexOf("o");//Return to the first occurrence of o
output index Display results: 5Determine what is at the end of the string:
Grammar: public boolean endsWith(String suffix)//suffix is a string to compare with
String fileName ="HelloWorld.java";
Boolean bool1 =fileName.endsWith(".java");//This method can only determine if all strings at the end must contain all
Boolean bool2 =fileName.endsWith(".jpg");
output boo1 Display results: true
output boo2 Display results: false
To determine the beginning of a string sentence:
Grammar: public boolean startsWith(String prefix)//prefix is the string to compare with
String str ="Would you like to fry fish with Kelly? Although being caught is a whole day's confinement, the fish is delicious, so it's worth it!";
Boolean bool1 =str.startsWith("To be with Collie");
Boolean bool2 =str.startsWith("To be with the piano");
output bool1 Display results: true
output bool2 Display results: falseGet the string array:
Grammar: public char[] toCharArray()
String str ="Collie is here to report"; char[] ch=str.toCharArray();
Query whether a substring exists:
Grammar: public boolean contains(String string)//string is the substring to find
String str ="8888B888";
Boolean bool1 =str.contains("B");
Boolean bool1 =str.contains("A");
output bool1 Display results: true
output bool1 Display results: falseCompare strings to be equal:
Grammar: public boolean equals(String abotherString)
String name =new String("keli");
String adv =new String("keli");
boolean bool =name.equals(adv);Ignore case comparison:
Grammar: public boolean equalslgnoreCase(String anotherString)//AntherString Compared String
String str1 =new String("abc");
String str2 =new String("ABC");
boolean bool =str1.equalslgnoreCase(str2);String operations:
Intercept string:
1. Intercept from the specified location:
Grammar: public String substring(int beginindex)//Location to start interception
String id ="123456789123456789"; String birthdate =id.substring(6);
2. Intercept the specified location:
Grammar: public String substring(int beginindex,int endindex)
String id="123456789123456789"; String birthdate =id.substring(6,14);
Replace string:
1. Replace the old string with the new one
Grammar: public String replace(CharSequence target,CharSequce replacement) //target old character, replacement new character sequence
String str="1212";
String replaceStr =str.replace("one","one");
output replaceStr Display results:2. Replace strings, support regular expressions
Grammar: public String replaceAll(String regex,String replacement) //regex old string or regular expression, replacement new string
String str ="123456abc";
String replaceStr =str.replaceAll("\\d","?");//\d denotes any of the numbers 0~9
output replaceStr Display results:??????abcd3. Replace the first string
Grammar: public String replaceFirst(String regex,String replacement) //regex old string or regular expression, replacement new string
String str ="Java";
String replaceStr =str.replaceFirst("a","A");
output replaceStr Display results: JAvAString Split:
1. Split the string into arrays according to the specified symbol
Grammar: public String[] split(Stirng regex)//For splitting symbols
String str ="abc,def,ghi";
String[] strArray =str.split(",");2. Limit the number of divisions
Limit the number of splits by a parameter
Grammar: public String[] split(String regex,int limit) //regex is used to split characters, limit is used to split characters
String str ="192.168.0.1";
String[] firstArray=str.split("\\.");
String[] secondArray=str.split("\\.",2);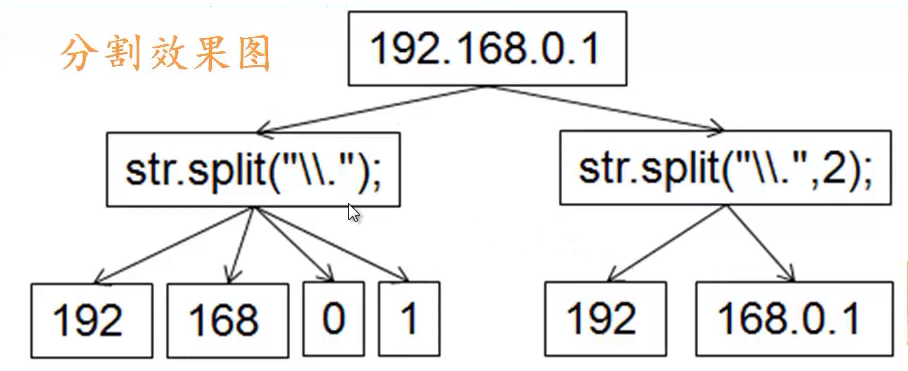
String case conversion:
Make the string uppercase:
Grammar: public String toUpperCase()
Make the string lowercase:
Sentence: public String toLowerCase()
String str ="abc DEF"; String strLOW =str.toLowerCase(); String strUP =str.toUpperCase(); output strLOW Display results: abc def output strUP Display results: AVC DEF
Remove blanks:
Remove whitespace from beginning to end
Grammar: public String trim()
String str =" abc "; String shortStr =str.trim(); output shortStr Display results: abc
Remove all whitespace from the string
String str =" a b cd e f g ";
String shortstr=str.replaceAll("\\s","");//Regular expression, empty content string
output shortstr Display results: abcdefgFormat string:
Time format:
Grammar: String.format(String format,Object....args)
Date date =new Date();
String str =String.format("%tF",date);StringBuffer (variable string):
The StringBuffer class is a thread-safe variable string sequence. It is a class that is a string buffer for a String, and its physical capacity increases automatically as the number of stored strings increases.
grammar:StringBuffer sbt =new StringBuffer();
StringBuffer sbt =new StringBuffer("abc":;
StringBuffer sbt =new StringBuffer(32);//The initial character sequence capacity is 32 charactersAppend character sequence:
Grammar: public StringBuffer append(Object obj)
StringBuffer sbt=new StringBuffer();
sbt.append("City Fire");
sbt.append("Closure room Report");
sbt.append("Bomb injuries");
sbt.append("The piano finds its door");
output sbt Display results: The city's gun closure reported that the bomb wounded the harp found its doorModify the character at the specified index:
Grammar: public void setCharAt(int index,char ch)
StringBuffer sbt =new StringBuffer("0123456");
sbt.setCharAt(3,'A');
output sbt Display results: 123 A56String reverse order:
Grammar: public StringBuffer reverse()
StringBuffer sbt =new StringBuffer("1234567");
sbt.reverse();
output sbt Display results: 7654321Delete substring:
Grammar: public StringBuffer delete(int start,int end)
StringBuffer sbt=new StringBuffer("Bag flower bell hug");
sbt.delete(2,4);//Delete from index 2 to 4, including index 2 but not index 4
output sbt Display results: Bag hugSimilar to String:
sbt.length() Gets the length of the string sequence
sbt.charAt(5) Gets the character with index 5
sbt.indexOf("DEF") Gets the index position of the DEF string
sbt.substring(0,2) intercepts strings from index 0 to index 2
sbt.replace(2,5,"1234") replaces the character sequence from index 2 to index 5 with "1234"