Both process oriented and object-oriented are a way of thinking in programming.
-
Process oriented programming is the process of thinking about "what should I do" and realizing it step by step. For example, when cleaning the company (cleaning the glass, sweeping the floor, mopping the floor, taking out the garbage, etc.), according to the process oriented programming method, I will think about "what should I do for cleaning, and then finish it one by one", and finally clean the company.
-
Object oriented programming is to think about "who should I let do it" when you encounter something, and then the "who" is the object. How he wants to do it is his own business. Anyway, it's ok if the last group of objects can work together to do it. For example, The company cleans (cleaning the glass, sweeping the floor, mopping the floor, taking out the garbage, etc.) according to the object-oriented programming method, it will think "who should I let do it, such as Xiaoming cleaning the glass, Xiaoli sweeping the floor, Xiaoguo mopping the floor, Xiaoqiang taking out the garbage, etc." here is "Xiaoming, Xiaoli, Xiaoguo, Xiaoqiang" It's the object. They want to clean up. How to clean up is their own business. Anyway, the last group of objects work together to clean up the company.
give an example:
- Buy a computer (assembly machine)
First use the process oriented description to buy a computer: if we need to buy and assemble a computer, we will first query the parameters and quotation of each hardware on the Internet. Then they will go to the computer city to make multiple inquiries, then go home after the inquiry, analyze which quotation they are satisfied with according to the specific results, and then go to this store for assembly. During assembly, on-site supervision is also required. After assembly, install the corresponding system, and then take the computer home.
The analysis of the above whole process is roughly divided into the following steps: online query parameters and quotation, computer city inquiry, on-site installation and supervision, holding the computer home. In the whole process, we participated in every detail and felt quite tired.
Use object-oriented to explain the matter of buying a computer: if we need to buy an assembly machine, we should find a person who understands computer hardware to help us check parameters and quotations, make inquiries and bargain, and supervise on-site assembly. And we don't need to personally experience what to do, just tell this person the specific needs we want.
Analyzing the whole process, we find that it becomes very easy in an instant. As long as we find the person who understands computer hardware, our problems can be solved. And we don't have to work so hard in this process.
Benefits of object-oriented thinking:
After using object-oriented analysis in real life scenes, we begin to analyze the differences between process-oriented and object-oriented and make a summary:
-
Object-oriented thinking mode is a kind of thinking more in line with people's thinking habits
-
In the process oriented thinking mode, the executor (doing things by himself) is more reflected, and in the object-oriented thinking mode, the commander (directing the object to do things) is more reflected.
-
Object oriented thinking mode simplifies complex problems.
Classes and objects:
In my previous article Blog Classes and objects are described in detail. You can have a look.
encapsulation
–
When it comes to packaging, everyone is no stranger. When learning methods, we mentioned encapsulating specific functions into methods. When learning objects, we also mentioned encapsulating methods in classes. In fact, these are encapsulation.
Encapsulation, which is also one of the characteristics of object-oriented thought. Object oriented has three characteristics: encapsulation, inheritance and polymorphism. Next, let's learn about encapsulation.
Encapsulation performance:
1. Method is a basic package.
2. Class is also a wrapper.
From the above two points, it can be concluded that the benefits of packaging are:
-
It improves the reusability of the code.
-
It hides the implementation details and provides external access. It is convenient for the caller to use. This is one of the core, which can also be understood as the concept of encapsulation.
-
Improved security.
Packaging example:
Chassis:
A computer consists of CPU, motherboard, graphics card, memory, hard disk, power supply and other components. In fact, we can use the computer by assembling these components together. However, we find that these components are scattered outside, which can cause unsafe factors. Therefore, we use the chassis shell to install these components inside, and leave some sockets on the chassis shell, If you don't leave a socket, let's think about what will happen.
Conclusion: the chassis actually hides the details of card handling equipment, and provides external access to internal details such as sockets and switches.
private
After understanding the embodiment of encapsulation in life, we have to go back to Java and elaborate on the embodiment of encapsulation in Java code, starting with the description of Person.
Describe the person. Person
Attribute: age.
Behavior: speak: say your age.
class Person {
int age;
String name;
public void show() {
System.out.println("age=" + age + ",name" + name);
}
}
public class PersonDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create Person object
Person p = new Person();
p.age = -20; // Assign a value to the Person object
p.name = "beauty";
p.show(); // Call the show method of Person
}
}
Through the above code, it is found that although we have clearly described Person in Java code, there is a serious problem that the behavior of attributes in Person can be accessed and used arbitrarily. This obviously does not meet the actual needs.
But how can we not allow access? You need to use a keyword in Java, which is also a modifier private (private, permission modifier). As long as the properties and behaviors of Person are private, they cannot be accessed directly.
class Person {
private int age;
private String name;
public void show() {
System.out.println("age=" + age + ",name" + name);
}
}
Age has been privatized. The wrong value cannot be assigned, but the correct value cannot be assigned. This is still not possible. What should we do? According to the principle of encapsulation learned before, after hiding, you also need to provide access. As long as accessible methods are provided externally, let other programs access these methods. At the same time, the data can be verified in the method.
General access actions to member attributes: assignment (set) and value (get). Therefore, the corresponding setXxx or getXxx methods can be provided for accessing private variables.
class Person {
// Private member variable
private int age;
private String name;
// Provides methods for setting member variables externally
public void setAge(int a) {
// Since the value of the member variable is set, data validation can be added here
if (a < 0 || a > 130) {
System.out.println(a + "Data range not in line with age");
return;
}
age = a;
}
// Provides external access to member variables
public void getAge() {
return age;
}
}
- Summary:
All contents in the class that do not need to be provided externally are privatized, including properties and methods.
We will describe things later. The properties are privatized, and setXxx getXxx method is provided to access them.
- Note: private is just the embodiment of encapsulation.
this keyword:
The problem of duplicate names of member variables and local variables:
You can prefix the member variable name with this To distinguish member variables from local variables
class Person {
private int age;
private String name;
public void speak() {
this.name = "cockroach";
this.age = 18;
System.out.println("name=" + this.name + ",age=" + this.age);
}
}
class PersonDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person p = new Person();
p.speak();
}
}
Explanation of object memory:
Here, you need to draw a diagram to demonstrate step by step, and explain the creation and use process of memory objects in strict accordance with the drawing process.
class Person {
private int age;
public int getAge() {
return this.age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
public class PersonDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person p = new Person();
p.setAge(30);
System.out.println("Hello everyone, this year I" + p.getAge() + "year");
}
}
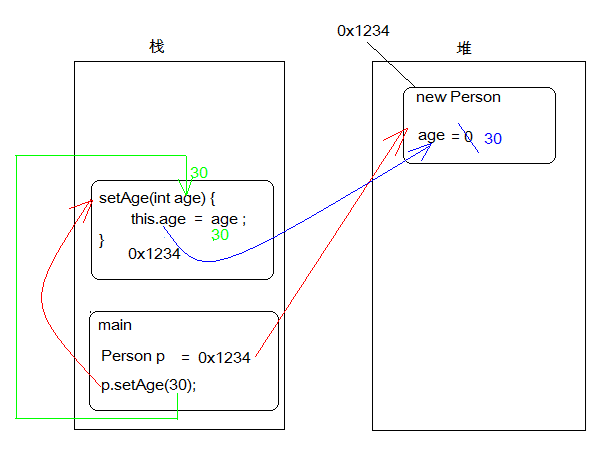
Description of procedure execution process:
1. First execute the main method (stack pressing), and execute the Person p = new Person();
2. Open up space in heap memory and allocate memory address 0x1234 for it, followed by default initialization of member variables (age = 0); Assign the memory address 0x1234 to the Person p variable in the stack
3. Continue to execute the p.setAge(30) statement. At this time, the setAge(int age) method will be called to assign 30 to the "age" variable in the setAge method; Execute this The age = age statement assigns the value of the age variable 30 to the member variable this Age is 30;
4. After the setAge() method is executed (pop the stack), return to the main() method and execute the output statement system out. Println(), the console prints the age value in the p object.
be careful:
What does this mean? This represents an object. Which object does it represent? This represents which object calls the method where this is located.
In the p.setAge(30) statement in the above code, this in the setAge(int age) method represents the P object.
Application:
Requirement: define the function in the Person class to judge whether two people are peers
class Person {
private int age;
private String name;
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void speak() {
System.out.println("name=" + this.name + ",age=" + this.age);
}
// Judge whether they are peers
public boolean equalsAge(Person p) {
// Compares the age that currently calls the equalsAge method object with the age that is passed in p.
// Since it is impossible to determine which object calls the equalsAge method, this can be used instead
/*
* if(this.age == p.age) { return true; } return false;
*/
return this.age == p.age;
}
}
Now summarize this keyword:
-
This is used in a method. If that object calls the method, this represents the object reference that calls the method
-
When does this exist? This exists when the object is created
-
This is used to distinguish member variables with the same name from local variables (this. Member variables)
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
inherit
–
Concept:
In real life, inheritance generally means that children inherit the property of their parents. In the program, inheritance describes the ownership relationship between things. Through inheritance, a relationship system can be formed between a variety of things. For example, the employees of the R & D department and the maintenance department in the company belong to employees. In the program, it can be described that the employees of the R & D department and the maintenance department inherit from the employees. Similarly, Java EE engineers and Android engineers inherit from the employees of the R & D department, while dimension network maintenance engineers and hardware maintenance engineers inherit from the employees of the maintenance department. An inheritance system will be formed among these employees, as shown in the figure below.
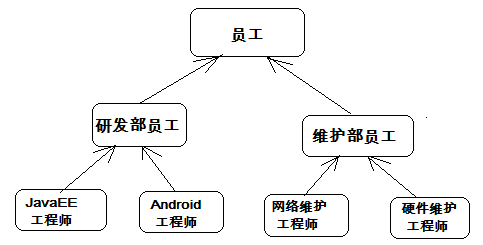
In Java, class inheritance refers to the construction of a new class on the basis of an existing class. The constructed new class is called a subclass, and the existing class is called a parent class. The child class will automatically own all inheritable properties and methods of the parent class.
Inherited format and usage
Format:
class Subclass extends Parent class {}
Next, learn how the subclass inherits from the parent class through a code
/*
* Define Employee class
*/
class Employee {
String name; // Define the name attribute
// Define employee's working methods
public void work() {
System.out.println("Work hard");
}
}
/*
* Define the R & D department employee class. Developer inherits the Employee class employee
*/
class Developer extends Employee {
// Define a method to print name
public void printName() {
System.out.println("name=" + name);
}
}
/*
* Define test class
*/
public class Example01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Developer d = new Developer(); // Create an R & D Employee class object
d.name = "Xiao Ming"; // Assign a value to the name attribute of the Employee class
d.printName(); // Call the printName() method of the employee
d.work(); // Call the work() method inherited from the Developer class
}
}
In the above code, the Developer class inherits the Employee class through the extends keyword, so the Developer class is a subclass of the Employee class. It is not difficult to see from the running results that although the subclass does not define the name attribute and work() method, it can access these two members. This means that when a subclass inherits from the parent class, it will automatically have the members of the parent class.
Benefits and considerations of inheritance
Benefits of inheritance:
1. The emergence of inheritance improves the reusability of code and improves the efficiency of software development.
2. The emergence of inheritance makes the relationship between classes and provides the premise of polymorphism.
last
Here comes gold, silver and four. Give me a small welfare!
Data collection method: click the blue portal here



Department employee object
d.name = "Xiao Ming"; // Assign a value to the name attribute of the Employee class
d.printName(); // Call the printName() method of the employee
d.work(); // Call the work() method inherited from the Developer class
}
}
In the above code, Developer Class pass extends Keywords inherited Employee Class, so Developer Class is Employee Class. It is not difficult to see from the running results that although subclasses are not defined name Properties and work()Method, but can access both members. This means that when a subclass inherits from the parent class, it will automatically have the members of the parent class. **Benefits and considerations of inheritance** Benefits of inheritance: 1,The emergence of inheritance improves the reusability of code and improves the efficiency of software development. 2,The emergence of inheritance makes the relationship between classes and provides the premise of polymorphism. ### last Here comes gold, silver and four. Give me a small welfare! **[Data collection method: click the blue portal here](https://gitee.com/vip204888/java-p7)** [External chain picture transfer...(img-ZZV1k0XI-1628579912227)] [External chain picture transfer...(img-0jcUBZKk-1628579912230)] [External chain picture transfer...(img-x2wim59Z-1628579912231)]