I. understanding reflection (three ways to realize reflection)
1. Instantiate the object first, and then reflect it
Date date = new Date(); //The generics here can only be "?" Class<?> dts = date.getClass(); System.out.println(dts.getName());
2. First import the package of the class, and then reflect
import java.util.Date; ------ Class<?> dts2 = Date.class; System.out.println(dts2.getName());
3. Reflect according to the full path name of the class
Class<?> dts3 = Class.forName("java.util.Date");
System.out.println(dts3.getName());2. Instantiation reflection (only when the instantiation reflection has the real operation right of this class)
Class<?> cls = Class.forName("java.util.Date");
Object obj = cls.newInstance();//Instantiation object, equivalent to: new java.util.Date
//Downward transformation of Object type
Date date = (Date) obj;
System.out.println(date.getTime());3. Get the package name, parent class (Interface) name and package path name of the reflected object
There are two main methods
cls.getPackage() //Package name with package cls.getPackage().getName() //Without package
Specific examples:
package refelect.twoday;
interface IPeopleOne{}
interface IPeopleTwo{}
class Persion implements IPeopleOne,IPeopleTwo{}
/**
* Get package name and class name
* @author 76519
*
*/
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Reflection gets the instantiated object of the class
Class<?> cls = Persion.class;
//Get the package name of the class
System.out.println(cls.getPackage());//Package select. Next day
System.out.println(cls.getPackage().getName());//The next day
//Get the Class object of the parent Class
System.out.println(cls.getSuperclass());//class java.lang.Object
System.out.println(cls.getSuperclass().getName());//java.lang.Object
//Get parent interface information
Class<?>[] itf = cls.getInterfaces();
for (Class<?> class1 : itf) {
System.out.println(class1.getName());
}
}
}IV. construction method of obtaining class
Specific methods used
cls.getConstructors(); //Get array of constructor directly --------------------------------------------- constructor.getModifiers();//Returns the level of a specific construction object in the construction method array (int number corresponding to public, etc.) Modifier.toString(constructor.getModifiers());//Convert the corresponding int number to the string corresponding to the public level constructor.getName();//Get the name of the construction method Class<?> params[] = constructor.getParameterTypes();//Get the parameters passed in the construction method (with parameter construction) Class<?>[] exception = constructor.getExceptionTypes();//Get the exception thrown by the constructor
Specific examples:
package refelect.twoday;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Modifier;
class People{
public People() {}
public People(String name) throws RuntimeException{}
public People(String name,int age)throws RuntimeException,Exception {}
}
/**
* Construction method of calling class
* @author 76519
*
*/
public class TestDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Class<?> cls = People.class;
//Get all the construction methods (encapsulate the construction into a class --- Constructor)
Constructor<?>[] cons = cls.getConstructors();
for (Constructor<?> constructor : cons) {
//************
System.out.println(constructor);
}
System.out.println("****************");
//Get the construction method of the class to understand the principle of the above Constructor class toString()
for (Constructor<?> constructor : cons) {
//Get the previous package name constructor. Getmodifiers() -- > int
System.out.println("constructor.getModifiers()-->"+constructor.getModifiers());
//Convert the obtained int to the corresponding permission name through Modifier.toString
System.out.println("Modifier.toString(constructor.getModifiers())---->"+Modifier.toString(constructor.getModifiers()));
System.out.print(Modifier.toString(constructor.getModifiers())+" ");
//Get the name of the construct, select. Next day. People
System.out.print(constructor.getName() + "(");
//Get the parameters in the construction
Class<?> params[] = constructor.getParameterTypes();
for (int i = 0; i < params.length; i++) {
//Get each incoming parameter
System.out.print(params[i].getName());
//Comma separated
if(i < params.length - 1) {
System.out.print(",");
}
}
System.out.print(")");
//If there is an exception
Class<?>[] exception = constructor.getExceptionTypes();
if(exception.length > 0) {//Indicates an exception
System.out.print(" throws ");
for (int j = 0 ; j < exception.length ; j ++) {
System.out.print(exception[j].getName());
//Multiple exceptions of the same method need to be separated by commas
if(j < exception.length - 1) {
System.out.print(",");
}
}
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
results of enforcement
public refelect.twoday.People() public refelect.twoday.People(java.lang.String) throws java.lang.RuntimeException public refelect.twoday.People(java.lang.String,int) throws java.lang.RuntimeException,java.lang.Exception **************** constructor.getModifiers()-->1 Modifier.toString(constructor.getModifiers())---->public public refelect.twoday.People() constructor.getModifiers()-->1 Modifier.toString(constructor.getModifiers())---->public public refelect.twoday.People(java.lang.String) throws java.lang.RuntimeException constructor.getModifiers()-->1 Modifier.toString(constructor.getModifiers())---->public public refelect.twoday.People(java.lang.String,int) throws java.lang.RuntimeException,java.lang.Exception
5. Instantiate objects by constructing methods with or without parameters
Method used
humenCls.newInstance();
humenCls.getConstructor(String.class,int.class);
cons.newInstance("Mr. banana",25);Specific examples:
package refelect.twoday;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
class Humen{
private String userName;
private int age;
//Non parametric structure
//public Humen() {}
//Parametric structure
public Humen(String userName,int age) {
this.userName = userName;
this.age=age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Humen [userName=" + userName + ", age=" + age + "]";
}
}
/**
* The importance of nonparticipation
* @author 76519
*/
public class TestDemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
Class<?> humenCls = Humen.class;
//When there is no parameterless construction
//Java. Lang. nosuchmethodexception: Select. Next day. Humen. < init > ()
//System.out.println(humenCls.newInstance());
//Solutions
//Instantiate the object by obtaining the constructor in the reflection object -- the method used here is to obtain the specified constructor according to the specified type
Constructor<?> cons = humenCls.getConstructor(String.class,int.class);
//Get the constructed object and instantiate it
System.out.println(cons.newInstance("Mr. banana",25));
}
}
Vi. common methods for obtaining reflected classes
Specific methods:
Object obj = cls.newInstance(); Method setMethod = cls.getMethod(...); Object o1 = setMethod.invoke(...);
Specific examples:
package refelect.twoday;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
class Student {
private String userName;
private int age;
public Student() {
}
public Student(String userName, int age) {
this.userName = userName;
this.age = age;
}
public String getUserName() {
return userName;
}
public void setUserName(String userName) {
this.userName = userName;
}
public void testPrint(String userName,int age) {
System.out.println("[Student] username = "+userName+ " age = "+age);
}
}
/**
* Common methods in reflection acquisition class
* Take getter/setter method as an example
* All normal methods can only be called after the object is instantiated
* @author 76519
*
*/
public class TestDemo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// Specify the method name and the parameters to be passed in the method name
String attribute = "userName";//Property name of the specified set/get
String value = "Banana";//Value to be passed in
// Get the specified class by reflection
Class<?> cls = Class.forName("refelect.twoday.Student");
// In any case, ordinary methods in the calling class must be instantiated
Object obj = cls.newInstance();
// Get the method of the class by reflection
// Get setUserName, the instantiation object of this common method, and set the method name and parameter type
// Note: setUserName() is a method. The method name is based on the given property information. At the same time, the method needs to receive a String type parameter
Method setMethod = cls.getMethod("set"+initCap(attribute), String.class);
Object o1 = setMethod.invoke(obj, value);//Equivalent to Student object. setUserName(...)
System.out.println("o1 "+o1);
//Get method and get value
Method getMethod = cls.getMethod("get"+initCap(attribute));
Object o2 = getMethod.invoke(obj);
System.out.println("o2 "+o2);
//When passing in multiple attribute values by self test -- Test common methods
Method testMethod = cls.getMethod("testPrint", String.class,int.class);
testMethod.invoke(obj, "Mr. banana",25);//The test found that if the specified method is static, the parameter obj here can be written as null
}
/**
* set or get method names pieced together based on property names
* @param str Attribute name
* @return Modified string type
*/
public static String initCap(String str) {
return str.substring(0,1).toUpperCase()+str.substring(1);
}
}
7. Get the attribute information reflected in the class
Methods used
Class<?> cls = Class.forName("refelect.threeeDays.Sun");//Get reflected objects
Field[] fields = cls.getFields();//Get all the properties (inheritance) of the parent object and put them into the property collection
Field[] fields = cls.getDeclaredFields();//Get all property values in this class and store them in the property collection
Specific examples:
package refelect.threeeDays;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
class Father{
private String name;
/*public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}*/
}
class Sun extends Father{
private int age;
/*public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}*/
}
/**
* Get property value in class or parent class
* @author 76519
*
*/
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Class<?> cls = Class.forName("refelect.threeeDays.Sun");
//If it is simply to get the attribute name in the Class and not operate on it, just use getFields or getFile(String name) in the Class class
//Common code block
{
//Get all properties of the parent class
Field[] fields = cls.getFields();
for (int i = 0; i < fields.length; i++) {
System.out.println(fields[i]);//Of the parent class is not printed
}
}
System.out.println("--------------------------");
//getDeclaredFields get all the properties in this class
//getDeclaredField(String name) gets the property specified in this class according to the name
{
//Get all properties of subclass
Field[] fields = cls.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field : fields) {
System.out.println(field);//private int refelect.threeeDays.Sun.age
}
}
//Why didn't the parent get it *******************
//In the actual development, the attributes are basically encapsulated, so it is not necessary to pay attention to the attributes in the parent class, that is to say, the attributes obtained in the later operations are mainly the attributes of this class
//Additional supplement: the private property of the parent class can only be inherited by the child class after get/set
/*Sun s = new Sun();
s.setName("6666");
System.out.println(s.getName());*/
}
}
8. Obtain the properties of this class and perform the operation of value assignment. (it is generally implemented through set/get)
package refelect.threeeDays;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
class Perion{
private String userName;//At this time, the class only explicitly provides a property
}
/**
* Get the properties of this class and set and get the values (understand) - in actual development, you must use get/set method to give users the opportunity to operate
* @author 76519
*
*/
public class TestDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//Obtain the operands of the reflected class through reflection
Class<?> cls = Class.forName("refelect.threeeDays.Perion");
//This is no longer just to get the name. You need to assign and value the variables you get ----- >
//It is necessary to obtain the instantiated object of the reflected class - only after the class object is instantiated can all the properties in the class be allocated in space
Object obj = cls.newInstance();//Instantiate objects of this class
//Get the specified property in this class according to the specific property name
Field field = cls.getDeclaredField("userName");
//******************
//Dynamic setting encapsulation: AccessibleObject.setAccessible(boolean flag) throws SecurityException
//Unpacking (because the attribute is private, it means it is encapsulated. If you want to use the attribute in it, you must unpack it)
//----If you do not add the following statements, you will get an error
field.setAccessible(true);
//Set the value of the acquired property
field.set(obj, "Don't take bananas");
//Take out the set value
Object getUserName = field.get(obj);
System.out.println(getUserName);
}
}
IX. get the type value of member variable
package refelect.fourDay;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
class Persion{
private String userName;
}
/**
* java.lang.reflect.Field.getType() Get the type of the member variable in the method
* @author 76519
*
*/
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Class<?> cls = Class.forName("refelect.fourDay.Persion");
//Object obj = cls.newInstance();
Field field = cls.getDeclaredField("userName");
System.out.println(field.getName());//userName
System.out.println(field.getType().getName());//java.lang.String
System.out.println(field.getType().getSimpleName());//String
}
}
X. use reflection to call the set/get method in the class
package refelect.five Simplicity of reflection java class.utils;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
/**
* Call the corresponding getter and setter methods in the class according to the property name
* @author 76519
*
*/
public class ObjectUtils {
//Constructor privatization
private ObjectUtils() {}
/**
* Set the properties in the class according to the specified class object, and call the setter method
* @param wrapObject Instantiated object of the class in which the property is located
* @param attribute Attribute name
* @param value Value to be set to property
* @throws Exception
*/
public static void setObjectValue(Object wrapObject,String attribute,String value) throws Exception {
//Get the properties of the subclass according to the instantiation
Field field = wrapObject.getClass().getDeclaredField(attribute);
//No corresponding attribute exists in the subclass ---- inherited parent attribute
if(field == null) {
//Query from parent class
field = wrapObject.getClass().getField(attribute);
}
//If it is still not found in the parent class
if(field == null) {
//The attribute must not exist
return;
}
//Pieced set property name
String methodName = "set"+StringUtils.initcap(attribute);
//Get the corresponding method
Method method = wrapObject.getClass().getMethod(methodName, field.getType());
method.invoke(wrapObject, value);
}
/**
* Responsible for calling the getter method in the specified class
* @param wrapObject Class object representing the method to be called
* @param attribute Attribute name
* @return End of call object
* @throws Exception
*/
public static Object getObject(Object wrapObject,String attribute) throws Exception {
String methodName = "get"+StringUtils.initcap(attribute);
Field field = wrapObject.getClass().getDeclaredField(methodName);
if(field == null) {
field = wrapObject.getClass().getField(methodName);
}
if(field == null) {
return null;
}
Method method = wrapObject.getClass().getMethod(methodName);
return method.invoke(wrapObject);
}
}
Xi. Loader
Reflection is implemented according to the way in the Class, but it deals with the loading operation of the Class under classPath.
If the loading path that needs to be used is network, file, database, etc., ClassLoader is needed
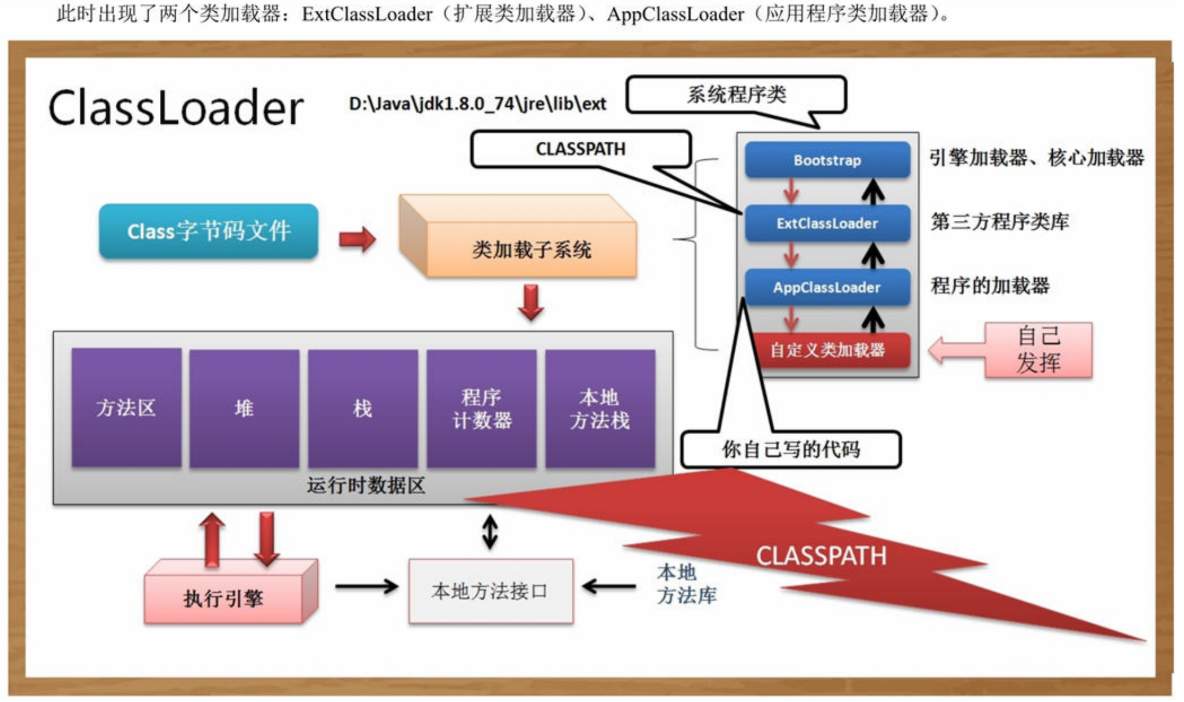
The use of class loader provided by java itself
package refelect.sex Class loader;
//Custom class must be in classPath
class Member {
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Member6666";
}
}
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Class<?> cls = Member.class;
System.out.println(cls.getClassLoader());
System.out.println(cls.getClassLoader().getParent());
System.out.println(cls.getClassLoader().getParent().getParent());
//Understand classloader (system) --- more verbose
System.out.println(Class.forName("refelect.sex Class loader.Member")
.getClassLoader().loadClass("refelect.sex Class loader.Member").newInstance());
}
}
Custom class loader
package refelect.sex Class loader.Custom class loader;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.InputStream;
/**
* Custom class loader must inherit java.lang.ClassLoader
*
* @author 76519
*
*/
class MyClassLoader extends ClassLoader {
/**
* Implement the operation of a custom class loader. After passing in the name of the class, load it through the specified file path
*
* @param className
* Class name
* @return Returns the Class object of a Class
* @throws Exception
*/
public Class<?> loadData(String className) throws Exception {
// Call your own private method to get the binary data read
byte[] classData = this.loadClassData();
// Calling defindClass in the parent class to implement the definition loading of ClassLoader class
return super.defineClass(className, classData, 0, classData.length);
}
/**
* Loading the class file through the specified file path is binary reading
*
* @return Class file data
* @throws Exception
*/
private byte[] loadClassData() throws Exception {
// To manipulate a file, you need to stream to read the file data
// InputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream(
//new File("D:"+File.separator+"Member.class"));
// The code here is equivalent to the code above -------- without new File(...), it has overload operation, so it is unnecessary to write new File()
InputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream("D:" + File.separator + "Member.class");
// Read file information but don't know the specific size of the file -- you can use a memory stream to read
ByteArrayOutputStream byteArrayOutputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream();// There is a way to get all the byte contents
// Define read buffer
byte[] data = new byte[20];
int temp = 0;
while ((temp = inputStream.read(data)) != -1) {
byteArrayOutputStream.write(data, 0, temp);
}
// Write the returned data
byte[] ret = byteArrayOutputStream.toByteArray();// This is how the memory output stream works
byteArrayOutputStream.close();
inputStream.close();
return ret;
}
}
/**
* Read the specified class file in other disks ----- dynamically implement the loading and processing operation of classes ----- generally speaking, it is not only for understanding
*
* @author 76519
*
*/
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//Class full path reduction refselect.sex class loader.TestDemo code flow
Class<?> cls = new MyClassLoader().loadData("cn.mldn.vo.Member");
//System.out.println(cls.newInstance());
System.out.println(cls.getClassLoader());
System.out.println(cls.getClassLoader().getParent());
System.out.println(cls.getClassLoader().getParent().getParent());
}
}