1 Overview
Computer network:
- It refers to a computer system that connects multiple computers and their external devices with independent functions in different geographical locations through communication lines and realizes resource sharing and information transmission under the management and coordination of network operating system, network management software and network communication protocol
Network programming
- Under the network communication protocol, data can be exchanged between programs running on different computers to realize network interconnection
Three elements of network programming
-
IP address
In order for computers in the network to communicate with each other, each computer must be assigned an identification number, which specifies the computer to receive data and identifies the computer to send data, and the lP address is this identification number. That is, the identification of the equipment -
port
If the IP address can uniquely identify the device in the network, the port number can uniquely identify the application in the device. That is, the identity of the application -
agreement
The rules of connection and communication are called network communication protocol. It makes unified provisions on data transmission format, transmission rate and transmission steps. Both sides of communication must abide by them at the same time to complete data exchange. The common protocols are UDP and TCP
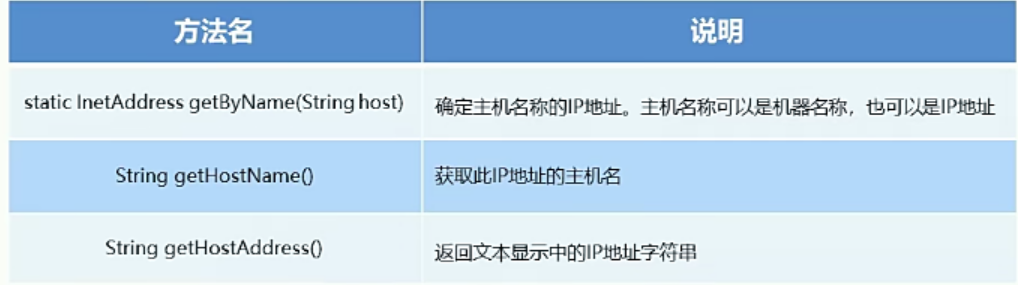
2 InetAddress (ip)
This class represents an ip address
port
Port: the unique identification of the application on the device
Port number: an integer represented by two bytes. Its value range is 0 ~ 65535. Among them, the port number between 0 and 1023 is used for some well-known network services and applications. Ordinary applications need to use a port number of more than 1024. If the port number is occupied by another service or application, the current program will fail to start
3 agreement
Protocol: in computer networks, the rules of connection and communication are called network communication protocol
UDP
No connection, unreliable transmission
TCP
Connection oriented, reliable and error free
Three handshakes
4 UDP communication
UDP protocol is an unreliable network protocol. It establishes a Socket object at both ends of the communication, but the two sockets are only objects for sending and receiving data
Both sides of communication have no client and server
Java provides DatagramSocket class as a Socket based on UDP protocol
To send data using UDP
1. Create the Socket object (DatagranSocket) of the sender
Datagram socket() constructs a datagram socket and binds it to any available port on the local host
2 create data and package the data
Create data and package it
DatagramPacket (byte[ ] buf, int length,InetAddress oddress, int port)
3. Call the method of DatagramSocket object to send data
Call the method of DatagramSocket object to send data
Void send (datagram packet P) sends datagram packets from this socket
4 close the sender
Close sender
void close close this datagram socket
package com.yy;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.net.DatagramPacket;
import java.net.DatagramSocket;
import java.net.InetAddress;
public class UDPTest {
@Test
public void SendTest() throws Exception {
//Datagram socket() constructs a datagram socket and binds it to any available port on the local host
DatagramSocket ds = new DatagramSocket();
//Create data and package it
//DatagramPacket (byte[ ] buf, int length,InetAddress oddress, int port)
//Construct a packet and send the packet with length to the specified port number on the specified host.
byte[] bytes = "upd,I'm coming.".getBytes();
DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(bytes,bytes.length, InetAddress.getByName("192.168.20.220"),10086);
//Call the method of DatagramSocket object to send data
//Void send (datagram packet P) sends datagram packets from this socket
ds.send(dp);
//Close sender
//void close close this datagram socket
ds.close();
}
}
UDP receive data
To receive data
- Create a Socket object (datagram Socket) at the receiving end
Datagram socket (int port) constructs a datagram socket and binds it to the specified port on the local host - Create a packet to receive data
Datagram packet (byte [J buf, int length) constructs a datagram packet for receiving data packets with length - Call the method of DatagramSocket object to receive data
Call the method of DatagramSocket object to receive data - Parse the data package and display the data on the console
byte[] getData() return data buffer
int getLength() returns the length of data to be sent or received - Close the receiver
@Test
public void sdTest() throws Exception {
//1. Create the Socket object (DatagramSocket) of the receiving end
//Datagram socket (int port) constructs a datagram socket and binds it to the specified port on the local host
DatagramSocket ds = new DatagramSocket(10086);
//2. Create a packet for receiving data
//Datagram packet (byte [J buf, int length) constructs a datagram packet for receiving data packets with length
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(bytes,bytes.length);
//3. Call the method of DatagramSocket object to receive data
ds.receive(dp);
//4. Parse the data package and display the data on the console
// byte[] getData() return data buffer
byte[] datas =dp.getData();
//int getLength() returns the length of data to be sent or received
int length = dp.getLength();
String dataString = new String(datas,0,length);
System.out.println("date is : "+dataString);
//5. Close the receiver
ds.close();
}
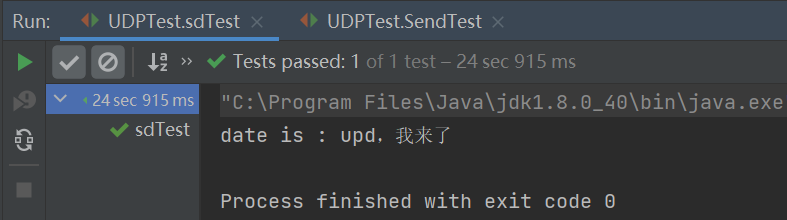
When running this method, execute the above sending method and how to obtain the above results, as shown in the following figure
5 TCP communication
TCP communication protocol is a reliable network protocol. It establishes a Socket object at both ends of the communication, so as to form a network virtual chain at both ends of the communication. Once a virtual network link is established, the programs at both ends can communicate through the virtual link
Java provides a good package for the network based on TCP protocol, uses the Socket object to represent the communication ports at both ends, and generates IO flow through the Socket for network communication
Java provides a Socket class for the client and a ServerSocket class for the server
TCP send data
To send data via TCP
- Create the client's Socket object (Socket)
Socket (string host, int port) creates a stream socket and connects it to the specified port number on the specified host - Get output stream and write data
outputStream getoutputStream() returns the output stream of this socket - Release resources
@Test
public void SendTest() throws Exception {
//1. Create the client's Socket object (Socket)
//Socket (InetAddress, int port) creates a stream socket and connects it to the specified port number of the specified IP address
// InetAddress byName1 = InetAddress.getByName("www.baidu.com");
// InetAddress byName2 = InetAddress.getByName("192.168.20.220");
// InetAddress byName3 = InetAddress.getByName("localhost");
// System.out.println(byName1+"-----"+byName2+"-----------"+byName3);//www.baidu.com/110.242.68.3-----/192.168.20.220-----------localhost/127.0.0.1
//Socket (String host,int port) creates a stream socket and connects it to the specified port number on the specified host
Socket s = new Socket("192.168.20.220",10000);
//2. Obtain the output stream and write data
//outputStream getoutputStream() returns the output stream of this socket
OutputStream os = s.getOutputStream();
os.write("tcp,I am coming".getBytes());
//3. Release resources
os.close();
}
TCP receive data
Steps for TCP to receive data
-
Create a server-side Socket object (ServerSocket)
ServerSocket (int port) creates a server socket bound to a specified port -
Listen to the client connection and return a Socket object
Socket accept() listens for the socket to connect to and accept it -
Get the input stream, read the data, and display the data on the console
InputStream getInputStream() -
Release resources
void close()
@Test
public void sdTest() throws Exception {
//1. Create a server-side Socket object (ServerSocket)
//ServerSocket (int port) creates a server socket bound to a specified port
ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(10086);
//Socket accept() listens for the socket to connect to and accept it
Socket accept = ss.accept();
//2. Obtain the input stream, read the data, and display the data on the console
InputStream is = accept.getInputStream();
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
int len = is.read();
String data = new String(bytes,0,len);
System.out.println("data is : "+ data);
//3. Release resources
ss.close();
accept.close();
}