catalogue
Filter filter
1,Filter
Filter it is
JavaWeb
One of the three components of. The three components are:
Servlet
Procedures
Listener
Listener
Filter
filter
2,Filter
Filter it is
JavaEE
Specifications. That is, the interface
3,Filter
Filter is used to:
Intercept request
, filter the response.
Common application scenarios for intercepting requests include:
1. Permission check
2. Journal operation
3. Transaction management
... wait
Filter instance
Requirement: in your
web
Under the project, there is one
admin
catalogue this
admin
All resources in the directory(
html
Page
jpg
Pictures
jsp
Files, etc.) must be
Access is not allowed until the user logs in
.
Thinking: according to what we have learned before, we know that after a user logs in, the user's login information will be saved to the Session
Domain. Therefore, to check whether the user logs in, you can judge whether the Session contains the user login information!!!
<%
Object user = session.getAttribute("user");
// If it is equal to null, it indicates that you have not logged in
if (user == null) {
request.getRequestDispatcher("/login.jsp").forward(request,response);
return;
}
%>
The above method is only suitable for JSP, so it has limitations
Filter
Workflow diagram of:
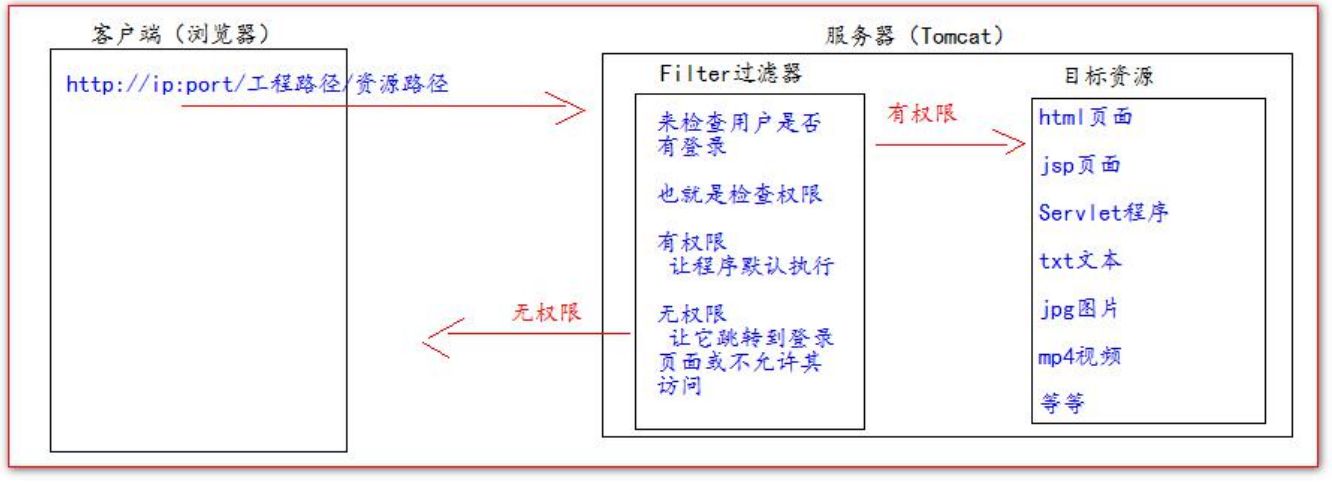
The Filter filter will intercept the address to be accessed and judge whether it has access permission.
Use steps of Filter:
1. Write a class to implement Filter
Interface
2. Implement the filtering method doFilter()
3. To web.xml
De configuration in
Filter
Interception path
Filter
Code of:
public class AdminFilter implements Filter {
/**
* doFilter Method, which is specially used to intercept requests. Permission checks can be performed
*/
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse, FilterChain filterChain) throws IOException, ServletException {
HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest = (HttpServletRequest) servletRequest;
HttpSession session = httpServletRequest.getSession();
Object user = session.getAttribute("user");
// If it is equal to null, it indicates that you have not logged in
if (user == null) { servletRequest.getRequestDispatcher("/login.jsp").forward(servletRequest,servletResponse);
return;
} else {
// Let the program continue to access the user's target resources
filterChain.doFilter(servletRequest,servletResponse);
}
}
}filterChain.doFilter(servletRequest,servletResponse);
web.xml
Configuration in:
<!--filter Label is used to configure a Filter filter-->
<filter>
<!--to filter Create an alias-->
<filter-name>AdminFilter</filter-name>
<!--to configure filter Full class name of-->
<filter-class>com.atguigu.filter.AdminFilter</filter-class>
</filter>
<!--filter-mapping to configure Filter Intercepting path of filter-->
<filter-mapping>
<!--filter-name Indicates to which of the current interception paths filter use-->
<filter-name>AdminFilter</filter-name>
<!--url-pattern Configure interception path
/ Indicates that the request address is: http://ip:port / Project path / web Directory mapped to IDEA
/admin/* Indicates that the request address is: http://ip:port / Project path / admin/*
-->
<url-pattern>/admin/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
Complete user login
login.jsp page==
login form
This is the login page. login.jsp page <br>
<form action="http://localhost:8080/15_filter/loginServlet" method="get">
user name:<input type="text" name="username"/> <br>
password:<input type="password" name="password"/> <br>
<input type="submit" />
</form>
LoginServlet
program
public class LoginServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException,IOException {
resp.setContentType("text/html; charset=UTF-8");
String username = req.getParameter("username");
String password = req.getParameter("password");
if ("wzg168".equals(username) && "123456".equals(password)) {
req.getSession().setAttribute("user",username);
resp.getWriter().write("Login succeeded!!!");
} else {
req.getRequestDispatcher("/login.jsp").forward(req,resp);
}
}
}Filter lifecycle
Filter
The lifecycle of contains several methods
1. Constructor method
2,init
Initialization method
Chapter 1, 2
Step, in
web
Execute when the project starts(
Filter
(already created)
3,doFilter
Filtering method
Step 3: every time a request is intercepted, it will be executed
4,destroy
Destroy
Step 4, stop the web
When the project is completed, it will be executed (stopped)
web
The project will also be destroyed
Filter
Filter)
FilterConfig class
FilterConfig
Class sees the name and knows the meaning. It is
Filter
The profile class for the filter.
Every time Tomcat creates a Filter
At the same time, one will be created
FilterConfig
Class, which contains
Filter
Configuration information for the configuration file.
The role of the FilterConfig class is to obtain the filter
Configuration content of filter
1. Gets the name of the Filter
filter-name
Content of
2. Gets the value configured in the Filter
init-param
Initialization parameters
3. Get ServletContext object
java
code:
@Override
public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException {
System.out.println("2.Filter of init(FilterConfig filterConfig)initialization");
//1. Get the name of Filter and the content of Filter name
System.out.println("filter-name The values are:" + filterConfig.getFilterName());
//2. Get the init param initialization parameters configured in web.xml
System.out.println("username The values are:" + filterConfig.getInitParameter("username"))
System.out.println("url The values are:" + filterConfig.getInitParameter("url"));
//3. Get ServletContext object
System.out.println(filterConfig.getServletContext());
}
web.xml
to configure:
<!--filter Label is used to configure a Filter filter-->
<filter>
<!--to filter Create an alias-->
<filter-name>AdminFilter</filter-name>
<!--to configure filter Full class name of-->
<filter-class>com.atguigu.filter.AdminFilter</filter-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>username</param-name>
<param-value>root</param-value>
</init-param>
<init-param>
<param-name>url</param-name>
<param-value>jdbc:mysql://localhost3306/test</param-value>
</init-param>
</filter>FilterChain filter chain
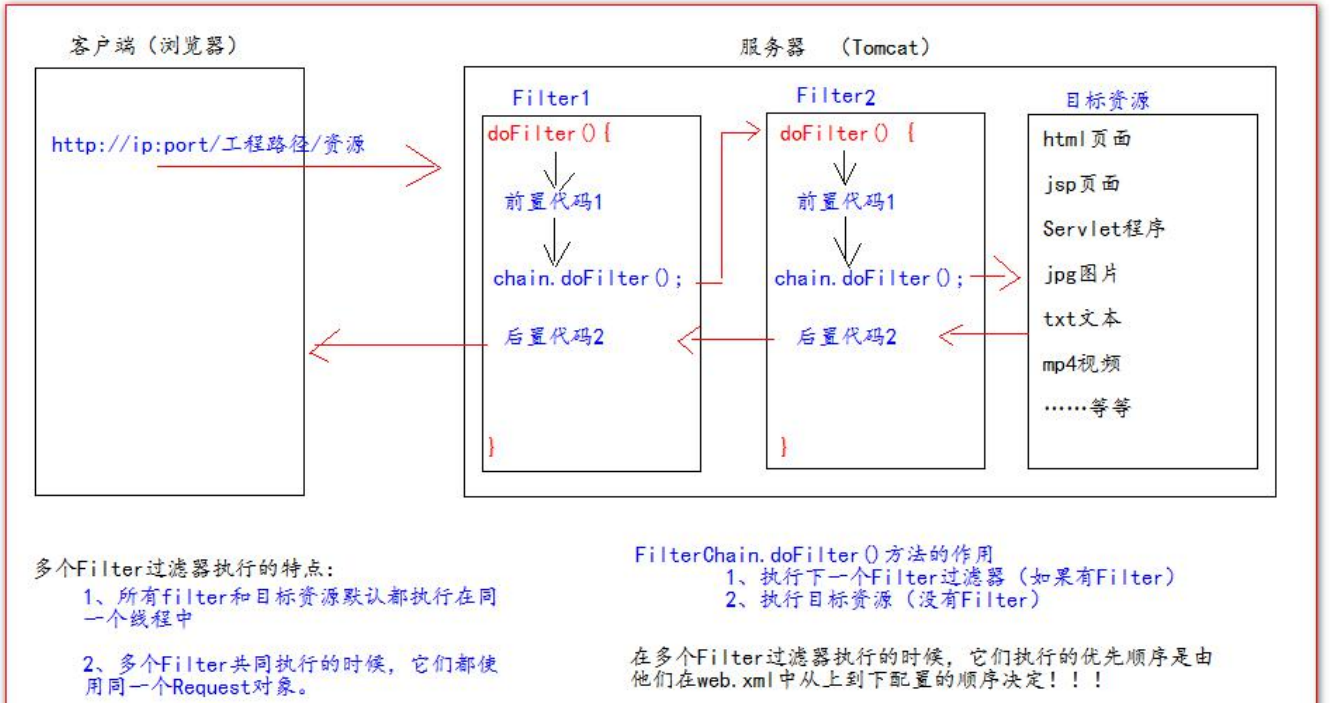
Intercepting path of Filter
--
Exact match
<
url-pattern
>/target.jsp</url-pattern>
The path configured above indicates that the request address must be:
http://ip:port/
Engineering path
/target.jsp
--
Directory matching
<
url-pattern
>/admin/*</url-pattern>
The path configured above indicates that the request address must be: http://ip:port/ Engineering path
/admin/*
--
Suffix matches (don't / before the address at this time)
<
url-pattern
>*.html</url-pattern>
The path configured above indicates that the request address must end in. html to be intercepted
<
url-pattern
>*.do</url-pattern>
The path configured above indicates that the request address must end with. do before it can be intercepted
<
url-pattern
>*.action</url-pattern>
The path configured above indicates that the request address must end with. action before it can be intercepted
Filter filter only cares about whether the requested address matches, not whether the requested resource exists!!!