There are two data types in ECMAScript: basic data type and reference data type.
Basic data type
Basic data types are also called simple data types, which are Undefined, Null, Boolean, Number, String and Symbol.
The basic data type is characterized by a fixed size of space in memory and stored on the stack.
1. Undefined type
The undefined type has only one value, undefined. If a variable is declared without initialization, the value of the variable is undefined.
var message; console.log(message); // undefined var example; console.log(example); // undefined
2. Null type
The null type has only one value, null. Null represents a null object pointer.
As long as the variable that saves the object does not really save the object, you should let the variable save null values, so that you can further distinguish between null and undefined.
var obj = null; alert(obj); // null
3. Boolean type
Boolean has only two values: true and false. Case sensitive, true and false are not Boolean values.
var boo = true; alert(obj); // true var lost = false; alert(lost); // false
The conversion rules between Boolean type and data type are as follows:
| data type | Value converted to true | Value converted to false |
| Boolean | true | false |
| Undefined | Not applicable | undefined |
| String | Any non empty string | Empty string ('') |
| Number | Any non-zero numeric value | 0 and NaN |
| Object | Any object | null |
4. String type
The String type represents a String, which can be expressed in single quotation marks (') or double quotation marks (").
var a = 'a'; // Effective var b = "a"; // Effective
Once strings are created, their values cannot be changed. If you change the value of the string, destroy the original value, and then fill the variable with the string with the new value.
var lang = "Java"; lang = lang + "Script"; console.log(lang); // JavaScript
You can convert to a string using toString().
var age = 11; age.toString(); // "11"
Note: if you don't know whether the converted value is null or undefined, you can use string (). The String() function follows the following conversion rules:
- If the value has a toString() method, call this method to return the corresponding result;
- If the value is null, return "null";
- If the value is undefined, return "undefined";
5. Number type
The Number type is divided into integer and floating point numbers. Numerical values can be expressed in decimal, octal and hexadecimal.
The range of values that ECMAScript can save can be number MIN_ Value and number MAX_ Value.
5.1 floating point value
var floatNum = 1.1; var floatNum1 = 0.1; var floatNum2 = .1; // Valid, but not recommended var floatNum3 = 1.; // Resolve to 1 var floatNum4 = 3.145e7; // Resolved to 3145000, e Means 3.145 * (10 (7th power of)
5.2. Number, parseInt, parseFloat value conversion
parseInt can convert a value to an integer, and parseFloat can convert a value to a floating point number.
var num1 = parseInt("11.5"); // 11 var num2 = parseFloat("2.5"); // 2.5
5.3 value range
Value range available number MIN_ Value and number MAX_ Value = indicates;
5.4,NaN
NaN is a non numeric value and is a special value. Indicates that an operation book that originally wants a value does not return a value. NaN and any value do not want to wait, including NaN itself.
alert(NaN == NaN); // false
isNaN() will judge whether the number is a value. After receiving a parameter, it will convert the value to a value. If it cannot be converted to a numeric value, it returns true.
alert(isNaN(NaN)); // true alert(isNaN(10)); // false,10 Is a numeric value alert(isNaN("10")); // false,Can be converted to a value of 10 alert(isNaN("blue")); // true,Cannot be converted to a numeric value alert(isNaN(true)); // false,Converted to value 1
6,Symbol
The object attribute names in ES5 are strings, which can easily lead to attribute name conflicts. If there is a mechanism to ensure that the attribute name is unique, Symbol is introduced in ES6.
Symbol is an original basic data type newly added in ES6, representing unique values. The symbol value is generated by the symbol function and cannot be used as a constructor.
const symbol1 = Symbol(); const symbol2 = Symbol(42); const symbol3 = Symbol('foo'); console.log(typeof symbol1);// "symbol" console.log(symbol2 === 42);// false console.log(Symbol('foo') === Symbol('foo'));// false
Reference data type
In ECMAScript, a reference data type is a data structure that organizes data and functions together.
1. Object type
So far, most reference type values are instances of Object type.
// 1,use new Heel Object Constructor var person = new Object(); person.name = "Tom"; // 2,Object literal representation var person = { name: "Tom", age:12 } console.log(person.name); // Tom console.log(person.age); // 12 var person1 = {}; person1.name = "Tom"; console.log(person1.name); // Tom console.log(person1.age); // undefined
2. Array type
Array type is one of the most commonly used reference types.
a) method for detecting numerical elements: forEach , some , every , map , filter
b) methods of changing array length: pop and push (stack method), unshift and shift (queue method), slice splice concat
var a = [1, 2, 3]; var b = a.pop(); //b=3,a=[1,2],pop()Returns the last item of the array, so b The value of is an array a Last item var c = a.push(4); //c=3, [1,2,4],c yes a.length var d = a.unshift("red"); //d=4, ["red",1,2,4],d by a.length var e = a.shift(); //e="red",a=[1,2,4],e Is the first item of the removed array and returns that item, the array a The length of the should be reduced by 1 var sliceA = a.slice(1, 2); //sliceA=2,4, a=[1,2,4] var spliceA = a.splice(0, 1);//spliceA=1, a=[2,4]
c) Element search: findIndex, lastFindIndex, indexOf and lastIndexOf (location method), filter includes
var a = [1, 2, 3, 2]; alert(a.indexOf(2)); // 1 alert(a.lastIndexOf(2)); // 3
d) Sort: sort reverse
var a = [2, 1, 3, 5, 4]; a.sort(); // 1,2,3,4,5 b.reverse(); // 5,4,3,2,1
e) Type conversion or detection: join toString isArray
var a = [1, 2, 3, 2]; Array.isArray(a); // true a instanceof Array //true,instanceof Non array method a.toString(); //'1,2,3,2',a=[1, 2, 3, 2] a.join(); //'1,2,3,2',a=[1, 2, 3, 2]
f) Merge method: reduce} reduceRight
Both methods iterate over all items and return the final value. The functions of the two methods are the same, but the directions are different.
reduce() traverses from the first item to the last, and reducereight() traverses from the last item to the first item.
var a = [1, 2, 3, 2]; var b = a.reduce((x, y) => { return x + y });//b=8; var c = a.reduceRight((x, y) => { return x + y });//c=8;
3. Date type
List some common methods to obtain time:
| getDate() | Returns the day of the month (from 1 to 31). |
| getDay() | Returns the day of the week (0-6). |
| getFullYear() | Returns the year. |
| getHours() | Return hours (0-23). |
| getMinutes() | Returns minutes (0-59). |
| getMonth() | Returns the month (0-11). |
| getSeconds() | Returns the number of seconds (0-59). |
| getTime() | Returns the number of milliseconds since midnight on January 1, 1970, and the specified date. |
| now() | Returns the number of milliseconds of the date and time when this method was called |
4. RegExp type
| exec | A RegExp method that finds a match in a string, which returns an array (null if it does not match). |
| test | A RegExp method that tests for a match in a string and returns true or false. |
| match | A String method that finds a match in a String. It returns an array and returns null when it does not match. |
| matchAll | A String method that finds all matches in a String and returns an iterator. |
| search | A String method that tests for a match in a String, which returns the location index to match, or - 1 if it fails. |
| replace | A String method that performs a search for a match in a String and replaces the matched substring with a replacement String. |
| split | A String method that uses a regular expression or a fixed String to separate a String and stores the separated substrings in the array. |
View common regular expression .
5. Function type
Please check This article.
6. Map type
7. Set type
8. Basic package type
Boolean type (not recommended):
The usage method is new Boolean();
See the difference below. Because new Boolean() is an instance of boolean type and is an object, it returns true.
var a = new Boolean(false); // Not recommended alert(a); // true var b = false; alert(a); // false
String type
The usage method is new String();
var a = new String("hello"); // "hello"
Number type
The usage method is new Number();
var a = new Number(1); // Not recommended var b = 1; alert(typeof a); // "object",Number Object is Number Type, so return"object" alert(typeof b); // "number",b Is a basic type, so it returns"number" alert( a instanceof Number); // true alert( b instanceof Number); // false
9. Single built-in object
9.1 Global objects
URI encoding method
The encodeURI() and encodeURIComponent() methods can encode the URI (replace all invalid characters with special UTF8 encoding) so that it can be sent to the browser for easy understanding.
| encodeURI() | code | Mainly used for the entire URI. Special characters that are themselves URIs are not encoded. |
| decodeURI() | decode | Decode the URI encoded by encodeURI() |
| encodeURIComponent() | code | It is mainly used for a segment in the URI. Encode any non-standard characters found. |
| decodeURIComponent() | decode | Decode the URI encoded by decodeURIComponent() |
Example:
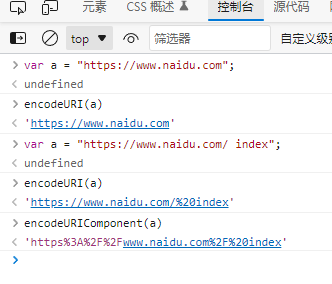
eval() method
The eval() method, like the ES parser, accepts only one parameter.
eval("var ms = 'hello world';")
alert(ms); // "hello world"
window object
9.2 Math object
Math objects provide calculation capabilities. List some common methods:
| floor(x) | Rounds x down. |
| max(x,y,z,...,n) | Returns x, y, Z, The highest value in n. |
| min(x,y,z,...,n) | Returns x, y, Z, The lowest value in n. |
| random() | Returns a random number between 0 and 1. |
| round(x) | rounding. |
Reference article:
https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/JavaScript/Guide/Regular_Expressions