1 - Programming Language
1.1 programming
- Programming:
- Is to let the computer use a programming language to write program code to solve a problem, and finally get the result.
- Computer program:
- It is a series of instructions executed by the computer, and all the programs are written in the language we master, so people must send commands to the computer through the computer language if they want to control the computer.
1.2 computer language
-
Computer language refers to the language used for communication between people and computers. It is the medium for transmitting information between people and computers.
-
There are many kinds of computer languages. Generally speaking, they can be divided into three categories: machine language, assembly language and high-level language.
-
In fact, the final execution of the computer is machine language. It is a binary number composed of "0" and "1". Binary is the basis of computer language.
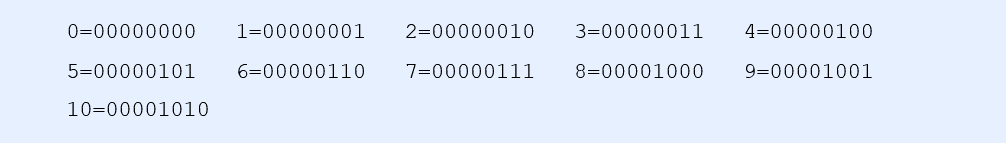
1.3 programming language
programing language: We can control the computer through a "language" similar to human language and let the computer do things for us. Such a language is called programming language( Programming Language). Programming language is a series of instructions used to control the computer. It has a fixed format and vocabulary (the format and vocabulary of different programming languages are different), which must be observed. Nowadays, there are two common programming languages: assembly language and high-level language.
| Language type | explain |
|---|---|
| assembly language | Assembly language and machine language are essentially the same. They operate directly on hardware, but the instructions use English abbreviation identifiers, which are easy to identify and remember. |
| high-level language | Compared with low-level languages, high-level languages do not specifically refer to a specific language, but include many programming languages, such as C language, C + +, Java, c#, Python, PHP, JavaScript, Go language, Objective-C, Swift, etc. |

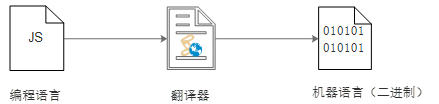
1.4 translator
The program written in high-level language can not be directly recognized by the computer, and can only be executed after conversion. Therefore, we need a translator. The translator can convert the source code we write into machine language, which is also called binarization.
1.5 differences between programming language and markup language
| language | explain |
|---|---|
| programing language | Programming language has strong logic and behavior ability. In the programming language, you will see many if, else, for, while and other logical and behavioral instructions, which are active. |
| Markup Language | Markup language (html) is not used to issue instructions to the computer. It is often used for formatting and linking. The existence of markup language is used to be read. It is passive. |
summary
- Computers can help humans solve some problems
- Programmers use programming language to write programs and send instructions to control the computer to realize these tasks
- Programming languages include machine language, assembly language and high-level language
- A high-level language requires a translator to convert it into a machine language recognized by the computer
- Programming language is active and has strong logic
2 - Fundamentals of computer
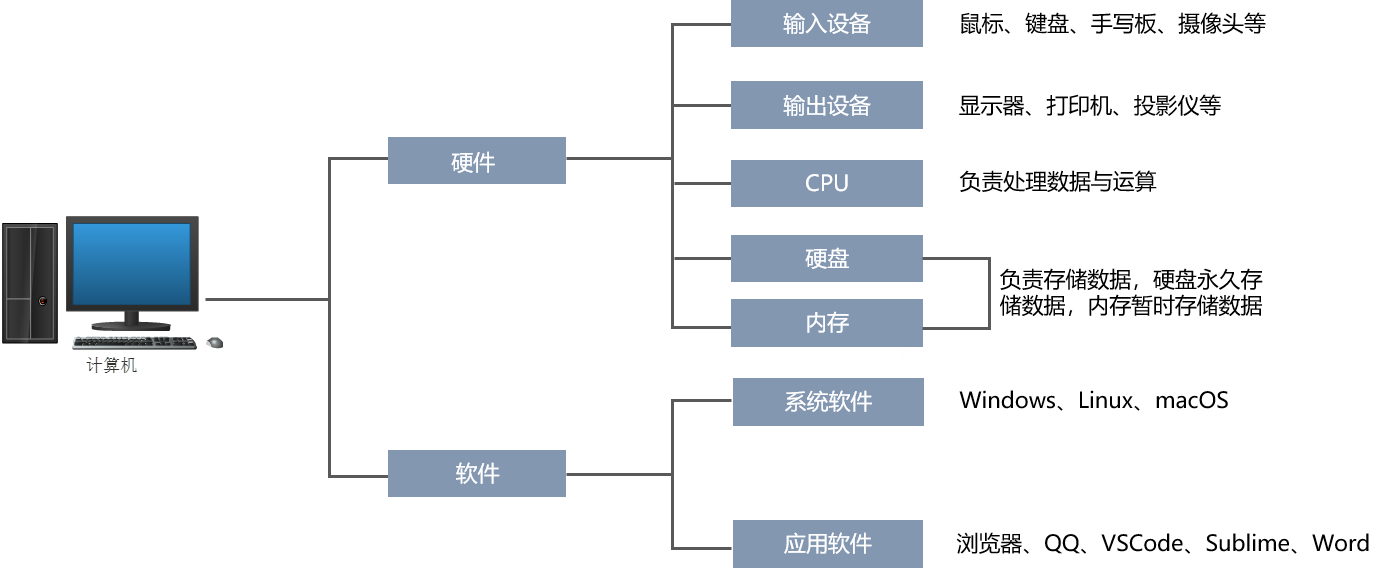
2.1 computer composition

2.2 data storage
- The computer internally uses binary 0 and 1 to represent data.
- All data, including files and pictures, are finally stored in the hard disk in the form of binary data (0 and 1).
- All programs, including the operating system, are essentially all kinds of data, which are also stored in the hard disk in the form of binary data. Usually what we call installing software is actually copying the program files to the hard disk.
- Hard disk and memory are stored binary data.
2.3 data storage unit
Size relationship: bit < byte < kb < GB < TB<.....
- Bit: 1 bit can store a 0 or 1 (the smallest storage unit)
- Byte: 1B = 8b
- Kilobytes (KB): 1KB = 1024B
- Megabytes (MB): 1MB = 1024KB
- Gigabyte (GB): 1GB = 1024MB
- Terabyte (TB): 1TB = 1024gb
2.4 program operation
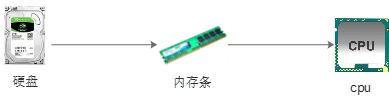
The process of running software on the computer: 1. When opening a program, first load the program code from the hard disk into memory 2. CPU Execute code in memory Note: an important reason for memory is because cpu It runs too fast. If you only read data from the hard disk, it will be wasted cpu Performance, so we use memory with faster access speed to save run-time data. (memory is electric, hard disk is mechanical)
3 - initial JavaScript
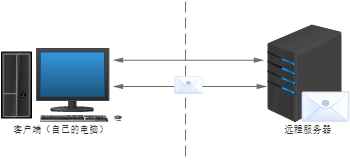
3.1 what is JavaScript

-
JavaScript is one of the most popular languages in the world. It is a scripting language running on the client (Script means Script)
-
Scripting language: no compilation is required. The js interpreter (js engine) interprets and executes it line by line during operation
-
Now it can also be based on node JS technology for server-side programming
3.2 role of JavaScript
- Form dynamic verification (password strength detection) (the original purpose of JS generation)
- Web effects
- Server development (Node.js)
- Desktop program (Electron)
- App(Cordova)
- Control hardware - Internet of things (Ruff)
- Game development (cocos2d JS)
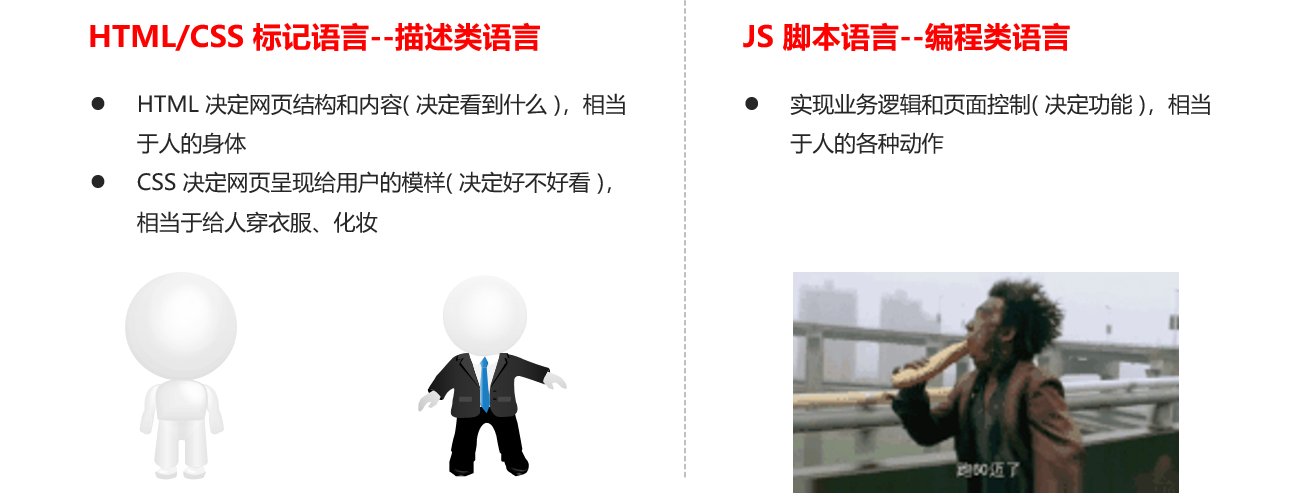
3.3 relationship between HTML / CSS / JS
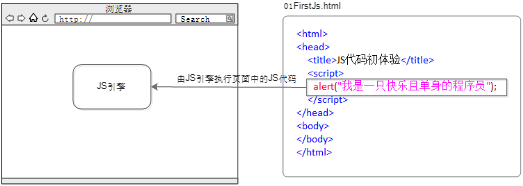
3.4 introduction to JS execution by browser
The browser is divided into two parts: rendering engine and JS engine

The browser itself does not execute JS Code, but through built-in JavaScript engine(interpreter) To execute JS code. JS When the engine executes the code, it explains the source code of each sentence line by line (converted into machine language), and then the computer executes it, so JavaScript Language is classified as script language and will be interpreted and executed line by line.
3.5 composition of JS
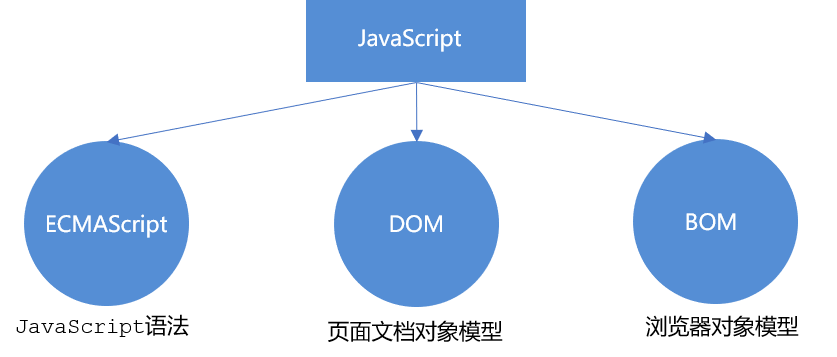
-
ECMAScript
ECMAScript By ECMA A programming language standardized by the International (formerly European Computer Manufacturers Association). This language is widely used on the world wide web. It is often called JavaScript or JScript,But in fact, the latter two are ECMAScript Implementation and extension of language.
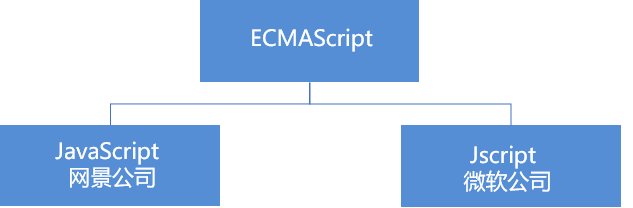
ECMAScript: it specifies the programming syntax and basic core knowledge of JS. It is a set of JS syntax industry standards that all browser manufacturers abide by.
See MDN: MDN manual
-
DOM -- Document Object Model
**Document object model**(DocumentObject Model,abbreviation DOM),yes W3C The standard programming interface recommended by the organization to handle extensible markup languages. adopt DOM The interface provided can operate various elements on the page (size, position, color, etc.)
-
BOM - browser object model
**Browser object model**(Browser Object Model,abbreviation BOM) It refers to the browser object model, which provides a content independent object structure that can interact with the browser window. adopt BOM You can operate the browser window, such as pop-up box, control browser jump, obtain resolution, etc.
3.6 JS initial experience
JS There are three writing positions: inline, inline and external.
- Inline
<input type="button" value="Let me try" onclick="alert('Hello World')" />
- You can write a single line or a small amount of JS code in the event attribute of HTML tag (attribute starting with on), such as onclick
- Note the use of single and double quotation marks: we recommend using double quotation marks in HTML and single quotation marks in JS
- Poor readability, inconvenient to read when writing a large amount of JS code in html;
- Quotation marks are easy to make mistakes. When quotation marks are nested and matched in multiple layers, they are very easy to be confused;
- Use under special circumstances
-
embedded
<script> alert('Hello World~!'); </script>- You can write multiple lines of JS code to the script tag
- Embedded JS is a common way of learning
-
External JS file
<script src="my.js"></script>
- It is conducive to the structure of HTML page code, and a large section of JS code is independent of HTML page, which is not only beautiful, but also convenient for file level reuse
- No code can be written in the middle of the script tag that references the external JS file
- It is suitable for a large amount of JS code
4 - JavaScript comments
4.1 single line notes
In order to improve the readability of the code, JS And CSS Similarly, annotation is also provided. JS There are two main types of comments in: single line comments and multi line comments.
Single line notes are annotated as follows:
// I'm a line of text. I don't want to be executed by the JS engine, so I annotate it
// Used to annotate single line text (Shortcut ctrl + /)
4.2 multiline notes
The annotation method of multiline annotation is as follows:
/* Get user age and name And displayed through the prompt box */
/* */ Used to annotate multiline text (default shortcut) alt + shift + a )
The shortcut key is changed to: ctrl + shift +/
vscode → preference button → keyboard shortcut → find the original shortcut → modify to a new shortcut → enter to confirm
5 - JavaScript input and output statements
In order to facilitate the input and output of information, JS provides some input and output statements. The common statements are as follows:
| method | explain | ascription |
|---|---|---|
| alert(msg) | Browser pop-up alert box | browser |
| console.log(msg) | Browser console printout information | browser |
| prompt(info) | The browser pops up an input box, which can be entered by the user | browser |
- Note: alert() is mainly used to display messages to users, console Log () is used to show the runtime messages to the programmer.
6 - concept of variables
6.1 what are variables
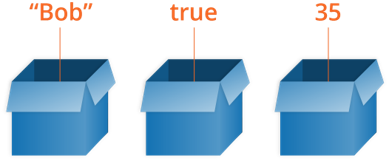
Vernacular: a variable is a box of things.
Popular: variables are containers for storing data. We get the data through the variable name, and even the data can be modified.
6.2 storage of variables in memory
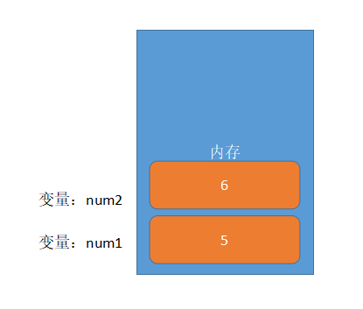
Essence: a variable is a piece of space applied by a program in memory for storing data. Similar to our hotel room, a room can be regarded as a variable.
7 - use of variables
- Declaration of variables
- Assignment of variables
7.1 declared variables
// Declare variable var age; // Declare a variable named age
-
var is a JS keyword used to declare variables (the meaning of variable). After using this keyword to declare a variable, the computer will automatically allocate memory space for the variable, which does not need to be managed by the programmer
-
age is the variable name defined by the programmer. We need to access the allocated space in memory through the variable name
7.2 assignment
age = 10; // Assign a value of 10 to this variable
- =It is used to assign the value on the right to the variable space on the left, which means assignment
- The variable value is the value that the programmer saves in the variable space
7.3 initialization of variables
var age = 18; // The declared variable is also assigned a value of 18 // Declaring and assigning a variable is called variable initialization.
7.4 variable syntax extension
-
Update variable
After a variable is re assigned, its original value will be overwritten, and the variable value will be subject to the last assigned value.
var age = 18; age = 81; // The end result is 81 because 18 is covered
-
Declare multiple variables at the same time
When declaring multiple variables at the same time, you only need to write a var, and the names of multiple variables are separated by English commas.
var age = 10, name = 'zs', sex = 2;
-
Declare variable special cases
situation explain result var age ; console.log (age); Only declaration without assignment undefined console.log(age) No declaration, no assignment, direct use report errors age = 10; console.log (age); No declaration, only assignment 10
7.5 variable naming specification
Rules:
- Consists of letters (A-Za-z), numbers (0-9), underscores () Dollar sign ($), such as usrage, num01_ name
- Strictly case sensitive. var App; And var App; Are two variables
- Cannot start with a number. 18age is wrong
- Cannot be keyword or reserved word. For example: var, for, while
- Variable names must be meaningful. MMD BBD nl → age
- Follow the hump nomenclature. The first letter is lowercase, and the first letter of the following word needs to be capitalized. myFirstName

Youdao ICIBA
8 - data type
8.1 introduction to data types
-
Why do I need a data type
In the computer, the storage space occupied by different data is different. In order to divide the data into data with different memory sizes and make full use of the storage space, different data types are defined. Simply put, the data type is the category and model of the data. For example, the name "Zhang San" and age 18 are different types of data.
-
Data type of variable
Variables are where values are stored. They have names and data types. The data type of a variable determines how bits representing these values are stored in the computer's memory. JavaScript Is a weakly typed or dynamic language. This means that there is no need to declare the type of variable in advance. During the running process of the program, the type will be determined automatically:
var age = 10; // This is a numeric type var areYouOk = 'yes'; // This is a string
When the code runs, the data type of the variable is determined by the JS engine according to the data type of the variable value on the right. After running, the variable determines the data type. JavaScript has dynamic types, which also means that the same variables can be used as different types:
var x = 6; // x is a number var x = "Bill"; // x is a string
-
Classification of data types
JS divides data types into two categories:
-
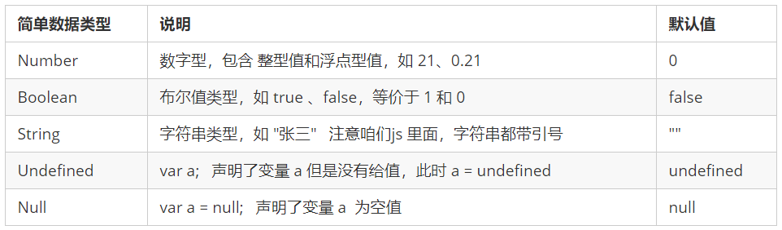
Simple data type (Number,String,Boolean,Undefined,Null)
-
Complex data type (object)
-
8.2 simple data types
Simple data type (basic data type)
Simple data types in JavaScript and their descriptions are as follows:
-
Digital Number
JavaScript numeric types can hold both integers and decimals (floating point numbers).
var age = 21; // integer var Age = 21.3747; // decimal
-
Digital hexadecimal
The most common base systems are binary, octal, decimal and hexadecimal.
// 1. Octal digit sequence range: 0 ~ 7 var num1 = 07; // Corresponding to decimal 7 var num2 = 019; // Corresponding to decimal 19 var num3 = 08; // 8 corresponding to decimal // 2. Hexadecimal digit sequence range: 0 ~ 9 and A~F var num = 0xA;
At this stage, we only need to remember to add 0 before octal and 0x before hexadecimal in JS
-
Digital range
Maximum and minimum values of values in JavaScript
-
Maximum value: number MAX_ Value: 1.7976931348623157e+308
-
Minimum value: number MIN_ Value: 5e-32
-
-
-
Digital three special values
-
Infinity, representing infinity, greater than any value
-
-Infinity, representing infinitesimal, less than any value
-
NaN, Not a number, represents a non numeric value
-
-
isNaN
It is used to judge whether a variable is of non numeric type and returns true or false

var usrAge = 21; var isOk = isNaN(userAge); console.log(isNum); // false, 21 is not a non number var usrName = "andy"; console.log(isNaN(userName));// true, "andy" is a non number
-
String type string
String type can be any text in quotation marks, and its syntax is double quotation mark '' and single quotation mark ''
var strMsg = "I Love Beijing Tiananmen ~"; // Use double quotation marks to represent strings var strMsg2 = 'I love pig feet~'; // Use single quotation marks to represent strings // Common errors var strMsg3 = I love big elbows; // If an error is reported and quotation marks are not used, it will be considered as js code, but js does not have these syntax
Because the attributes in HTML tags use double quotation marks, we prefer to use single quotation marks in JS.
-
String quote nesting
JS can nest double quotation marks with single quotation marks, or nest single quotation marks with double quotation marks (outer double inner single, outer single inner double)
var strMsg = 'I am"Gao Shuaifu"Cheng xuape'; // You can include '' with '' var strMsg2 = "I am'Gao Shuaifu'Cheng xuape"; // You can also include '' with '' // Common errors var badQuotes = 'What on earth?"; // An error is reported. Single and double quotation marks are not allowed
-
String escape character
Similar to the special characters in HTML, there are also special characters in the string, which we call escape characters.
Escape characters start with \. Common escape characters and their descriptions are as follows:
Escape character interpretative statement \n Newline, n means newline \ \ Slash\ ' 'single quote " ”Double quotation mark \t tab indent \b b means blank -
String length
A string is composed of several characters. The number of these characters is the length of the string. By string length Property to get the length of the entire string.
var strMsg = "I'm a handsome and golden program ape!"; alert(strMsg.length); // Display 11
-
String splicing
-
Multiple strings can be spliced with + in the form of string + any type = new string after splicing
-
Before splicing, any type added to the string will be converted into a string, and then spliced into a new string
//1.1 string "addition" alert('hello' + ' ' + 'world'); // hello world //1.2 numeric string "addition" alert('100' + '100'); // 100100 //1.3 numeric string + numeric alert('11' + 12); // 1112- +No. summary formula: add values and connect characters
-
-
String splicing enhancement
console.log('pink teacher' + 18); // As long as there are characters, they will be connected var age = 18; console.log('pink teacher age Years old'); // That won't work console.log('pink teacher' + age); // Mr. pink 18 console.log('pink teacher' + age + 'Years old'); // Mr. pink is 18 years old- Strings and variables are often spliced. Variables can easily modify their values
- Variables cannot be quoted because quoted variables will become strings
- If there is string splicing on both sides of the variable, the formula "quote, add", delete the number, and write the variable in the middle
-
-
Boolean
Boolean types have two values: true and false, where true represents true (true) and false represents false (false).
When Boolean and numeric types are added, the value of true is 1 and the value of false is 0.
console.log(true + 1); // 2 console.log(false + 1); // 1
-
Undefined and Null
A variable that has not been assigned a value after declaration will have a default value of undefined (pay attention to the result when connecting or adding)
var variable; console.log(variable); // undefined console.log('Hello' + variable); // Hello, undefined console.log(11 + variable); // NaN console.log(true + variable); // NaN A declared variable is given a null value, and the stored value is null (we continue to study null when learning objects)
var vari = null; console.log('Hello' + vari); // Hello, null console.log(11 + vari); // 11 console.log(true + vari); // 1
8.3 obtaining variable data types
-
Gets the data type of the detection variable
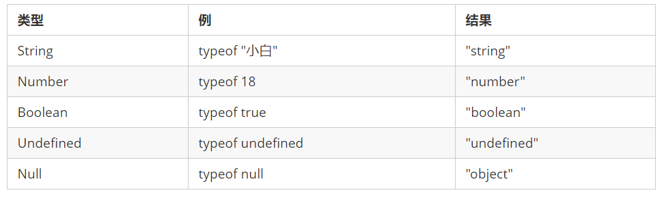
typeof can be used to get the data type of the detection variable
var num = 18; console.log(typeof num) // Result number
Different types of return values
-
Literal
Literal quantity is the representation of a fixed value in the source code. Generally speaking, it means how to express this value.
- Number literal: 8, 9, 10
- String literal: 'dark horse programmer', 'big front end'
- Boolean literal: true, false
8.4 data type conversion
What is data type conversion?
The data obtained by using the form and prompt is of string type by default. At this time, you can't simply add directly, but need to convert the data type of the variable. Generally speaking, it is to convert a variable of one data type into another. There are usually three ways to convert:
Convert to string type Convert to digital Convert to Boolean
-
Convert to string
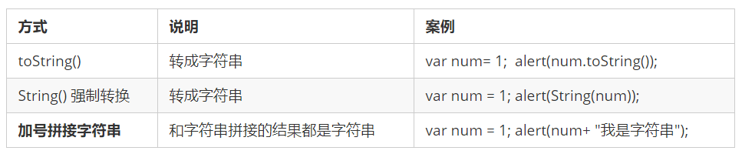
- toString() and String() are used differently.
- There are three conversion methods, and the third plus sign splicing string conversion method is also called implicit conversion.
-
Convert to digital (key)
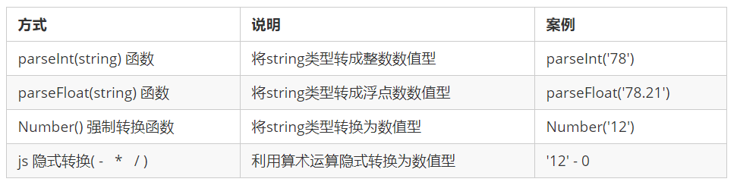
- Pay attention to the case of parseInt and parseFloat words, which are the key points
- Implicit conversion is that JS automatically converts data types when we perform arithmetic operations
-
Convert to Boolean

-
Values representing null and negative will be converted to false, such as' ', 0, NaN, null and undefined
-
The remaining values are converted to true
console.log(Boolean('')); // false console.log(Boolean(0)); // false console.log(Boolean(NaN)); // false console.log(Boolean(null)); // false console.log(Boolean(undefined)); // false console.log(Boolean('Xiaobai')); // true console.log(Boolean(12)); // true
9 - interpreted and compiled languages
9.1 general
The computer cannot directly understand any language other than machine language, so the program language written by the programmer must be translated into machine language to execute the program. The tool for translating program language into machine language is called translator.

- There are two ways for translators to translate: one is compilation, the other is interpretation. The difference between the two methods lies in the different time points of translation
- The compiler compiles before code execution to generate intermediate code files
- The interpreter is interpreted in time and executed immediately at run time (when the compiler runs in interpretation mode, it is also called the interpreter)
9.2 execution process
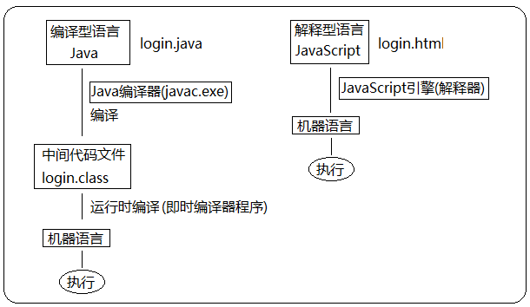
It is similar to a dinner party: Compile language: first make all the dishes well before you can eat at the table Explanation language: it's like eating hot pot, rinsing while eating, and doing it at the same time
10 - keywords and reserved words
10.1 identifier
identification(zhi)Character: refers to the name given by the developer for variables, attributes, functions and parameters. Identifiers cannot be keywords or reserved words.
10.2 keywords
Keyword: refers to JS Words that have been used by themselves can no longer be used as variable names and method names. include: break,case,catch,continue,default,delete,do,else,finally,for,function,if,in,instanceof,new,return,switch,this,throw,try,typeof,var,void,while,with Wait.
10.3 reserved words
Reserved words: actually, they are reserved "Keywords", which means that although they are not keywords now, they may become keywords in the future. Similarly, they cannot be used as variable names or method names. include: boolean,byte,char,class,const,debugger,double,enum,export,extends,fimal,float,goto,implements,import,int,interface,long,mative,package,private,protected,public,short,static,super,synchronized,throws,transient,volatile Wait. Note: if a reserved word is used as a variable name or function name, it is likely that no error message will be received unless the reserved word is implemented in a future browser. When the browser implements it, the word will be regarded as a keyword, so a keyword error will appear.