catalogue
2.1 introduction of JavaScript
2.2 introduction to basic grammar
2.3 quick browsing of data types
1, What is JavaScript
- JavaScript is the most popular scripting language on the Internet
- Interpreted or just in time compiled language
- The standard for JavaScript is ECMAScript
- All modern browsers fully support ECMAScript 5
II. JavaScript quick start
2.1 introduction of JavaScript
Create an empty project and create a new HTML file
① Write in page
Write JavaScript code in the script tag in the page, which is generally placed at the bottom of the head tag or body tag
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<!--script Write in label JavaScript code-->
<script>
alert("hello world!"); //Pop up window: Hello, world!
</script>
</head>
<body>
<!--script Write in label JavaScript code-->
<script>
alert("hello world!");
</script>
<!--Can also be stored in body Inside label-->
</body>
</html>Implementation effect: Browser pop-up, content: hello world!

② External introduction
Create a new js folder and store JavaScript files in the folder
out.js
alert("hello JavaScript!"); //Pop up window, content: hello JavaScript!< script SRC = "" > < / script > import external js file out js note: the script tags here must appear in pairs
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<!-- External introduction -->
<!-- be careful: script Labels must appear in pairs -->
<script src="js/out.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>Implementation effect: Browser pop-up, content: hello JavaScript!
2.2 introduction to basic grammar
JavaScript is strictly case sensitive
① Define variables
- Variables must start with a letter
- Variables can also be expressed as $and_ Start with a symbol (but we don't recommend this)
- Variable names are case sensitive (Y and y are different variables)
Variable type: variable name = variable value;
<script>
// 1. Define variable type variable name = variable value;
var num=1; //Define a variable named num and assign a value of 1
alert(num);//Browser pop-up window, content: variable num
</script>Implementation effect: Browser pop-up window, content: num value
② Process control
<script>
//2. Condition control
var score = 71;
if(score>60&&score<70){
alert("60-70")
}else if (score>70 && score<80){
alert("70-80")
}else{
alert("other")
}
//Alert pop-up
// console.log() print variables on the browser console
</script>Score = 71, 70 < score < 80, so the content of the browser pop-up window is 70-80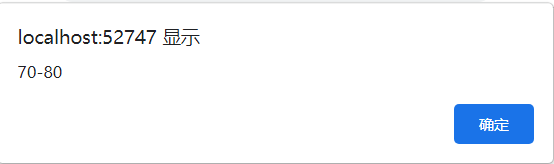
2.3 quick browsing of data types
js provides a typeof operator to detect the type of a variable
① number
js does not distinguish between decimal and integer
123 //integer
123.1 //Floating point number
1.123e3 //Scientific counting method
-99 //negative
NaN //Not a Number
Infinity //infinityKeyboard F12 ﹐ or right mouse button - > check ﹐ enter the browser console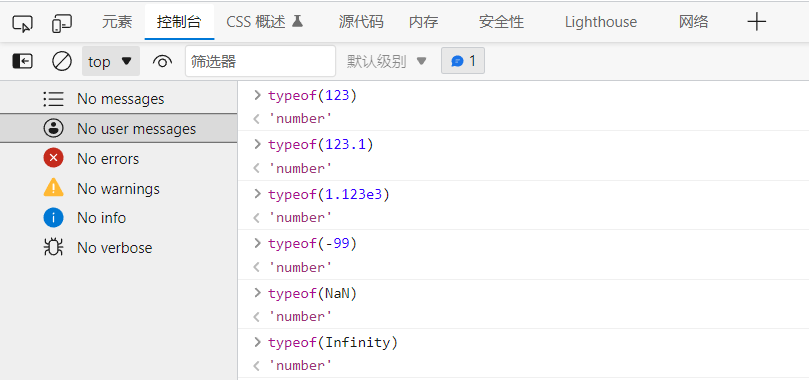
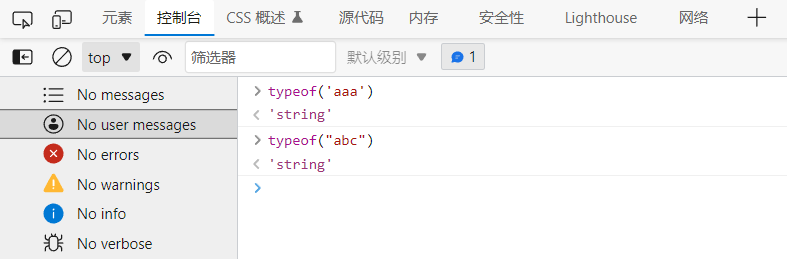
② String
A string can be any character inserted in single or double quotation marks
③ Boolean value
- true
- false
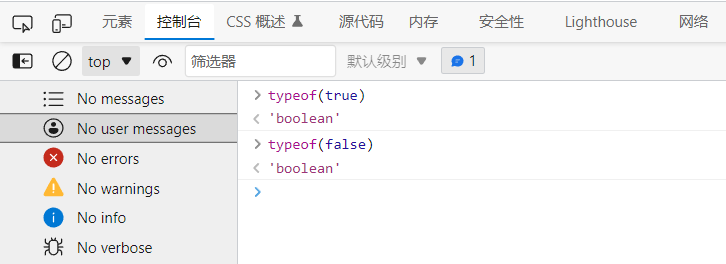
④ Logical operation
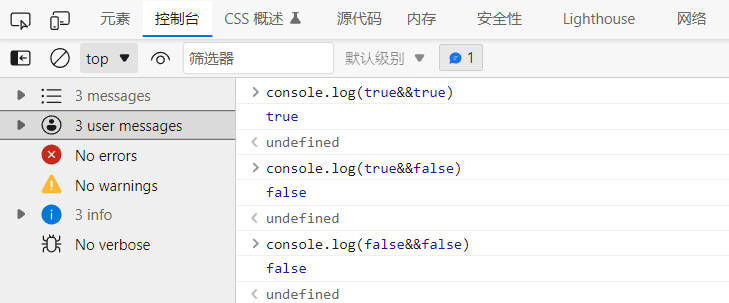
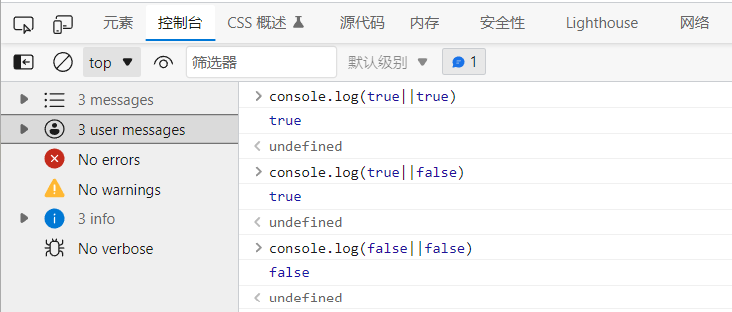
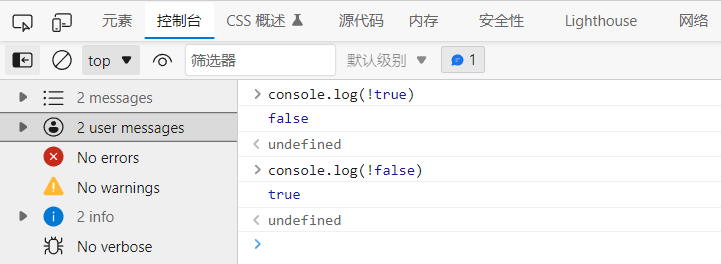
&& //Both are true and the result is true || //One is true and the result is true ! //True is false, false is true
& & both are true and the result is true
𞓜 one is true and the result is true
! True is false, false is true
⑤ Comparison operator
JavaScript defects, insist not to use = = comparison
= //assignment == //If the equal type is different and the value is the same, it will also be judged as true === //Absolutely equal to the same type, the same value, and the result is true
Notice:
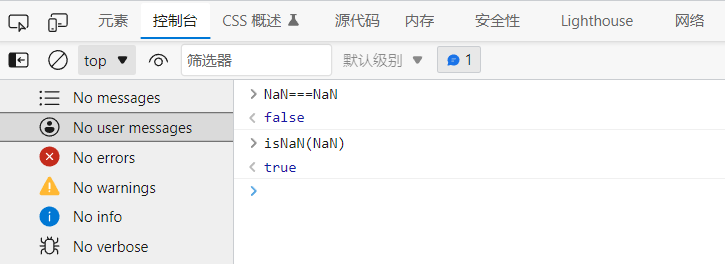
- NaN is not equal to all values, including itself
-
You can only judge whether this number is NaN by isNaN(NaN)
Floating point number problem: (1 / 3) is equal to 1 - (2 / 3)?
Try to avoid using floating-point operation, which has accuracy problems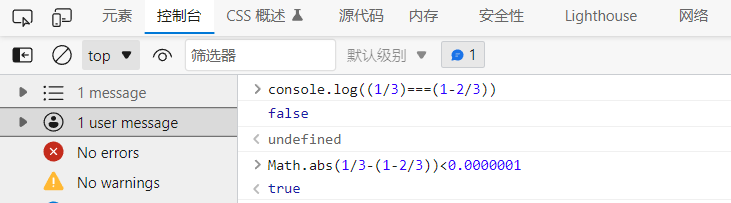
⑥ null and undefined
- Null null
- Undefined undefined
⑦ Array
Java arrays must be some objects with the same type of columns, which is not required in JS
//To ensure code readability, try to use [] var arr=[1,2,3,4,5,'hello',null,true]; new Array(1,12,3,4,'hello',null);
If the array subscript is out of bounds, it will return "undefined"
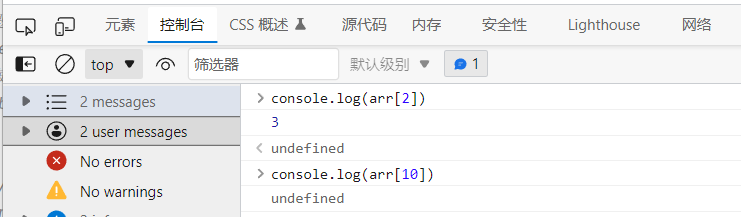
⑧ Object
The object is braces {}, the array is brackets [], and each attribute is separated by commas. The last one is not required.
var person={
name:"hhhhh",
age:3,
tags:['js','java','web']
}Take the value object name of the object attribute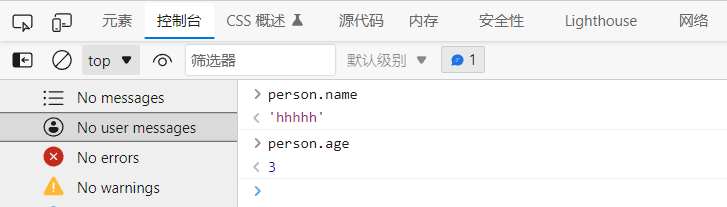
2.4 strict inspection mode
- Settings support ES6 syntax
- Strictly check the mode to prevent some problems caused by the randomness of JS
- It must be written on the first line
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script>
<!--
Setting support ES6 grammar
'use strict';
Strict inspection mode,prevention JS Some problems caused by the randomness of
It must be written on the first line
-->
'use strict';
//global variable
let i=1;
//ES6 local variables are defined with let
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>