1.Servlet
Server applet: a small program running on the server side
public class ServletDemo implements Servlet {
@Override
public void init(ServletConfig servletConfig) throws ServletException {
}
@Override
public ServletConfig getServletConfig() {
return null;
}
@Override
public void service(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse) throws ServletException, IOException {
}
@Override
public String getServletInfo() {
return null;
}
@Override
public void destroy() {
}
}1.1 Servlet life cycle
-
init
-
Initialization method: executed when the Servlet is created, only once
-
-
service
-
Execute multiple times each time the Servlet is accessed
-
-
destory
-
Execute once when the server shuts down normally
-
-
getServletConfig
-
Gets the configuration object of the Servlet
-
-
getServletInfo
-
Get some information about the Servlet, version, author, etc
-
1.2 Servlet architecture
@WebServlet("/httpServletTest")
public class HttpServletDemo extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
super.doGet(req, resp);
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
super.doPost(req, resp);
}
}2 Hypertext Transfer Protocol Http
2.1 introduction
-
Transmission protocol: defines the format of sending data when the client and server communicate
-
characteristic
-
Advanced protocol based on TCP/IP
-
The default port number is 80
-
Based on request / correspondence model: one request corresponds to one correspondence
-
Stateless: each request is independent of each other and cannot interact with data
-
-
Historical version
-
1.0: each request response will establish a new connection
-
1.1: multiplex connection
-
2.2 request message data format
2.2.1 request line
| Request mode | Request url | Request protocol / version |
|---|---|---|
| Get | Baidu once, you know | HTTP/1.1 |
-
Request method:
-
There are seven request modes in HTTP protocol, two of which are commonly used
-
GET :
-
The request parameters are in the request line, after the url (? Name = aoligei & age = 22)
-
The length of the requested url is limited
-
Not very safe
-
-
POST :
-
The request parameter is in the request body
-
There is no limit on the length of the requested url
-
Relative safety
-
-
-
-
Results after advanced browser parsing:

2.2.2 request header
Request header: (some information that the client browser tells the server itself)
-
Results after advanced browser parsing
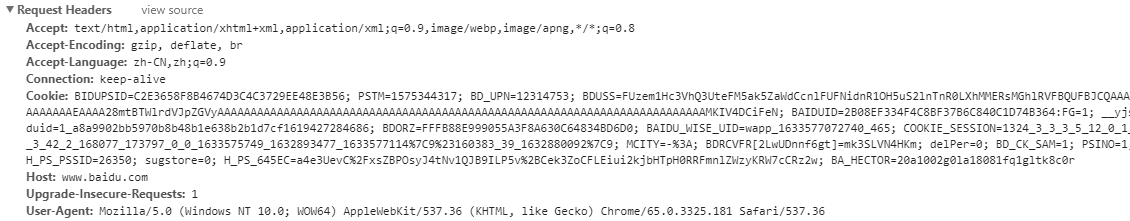
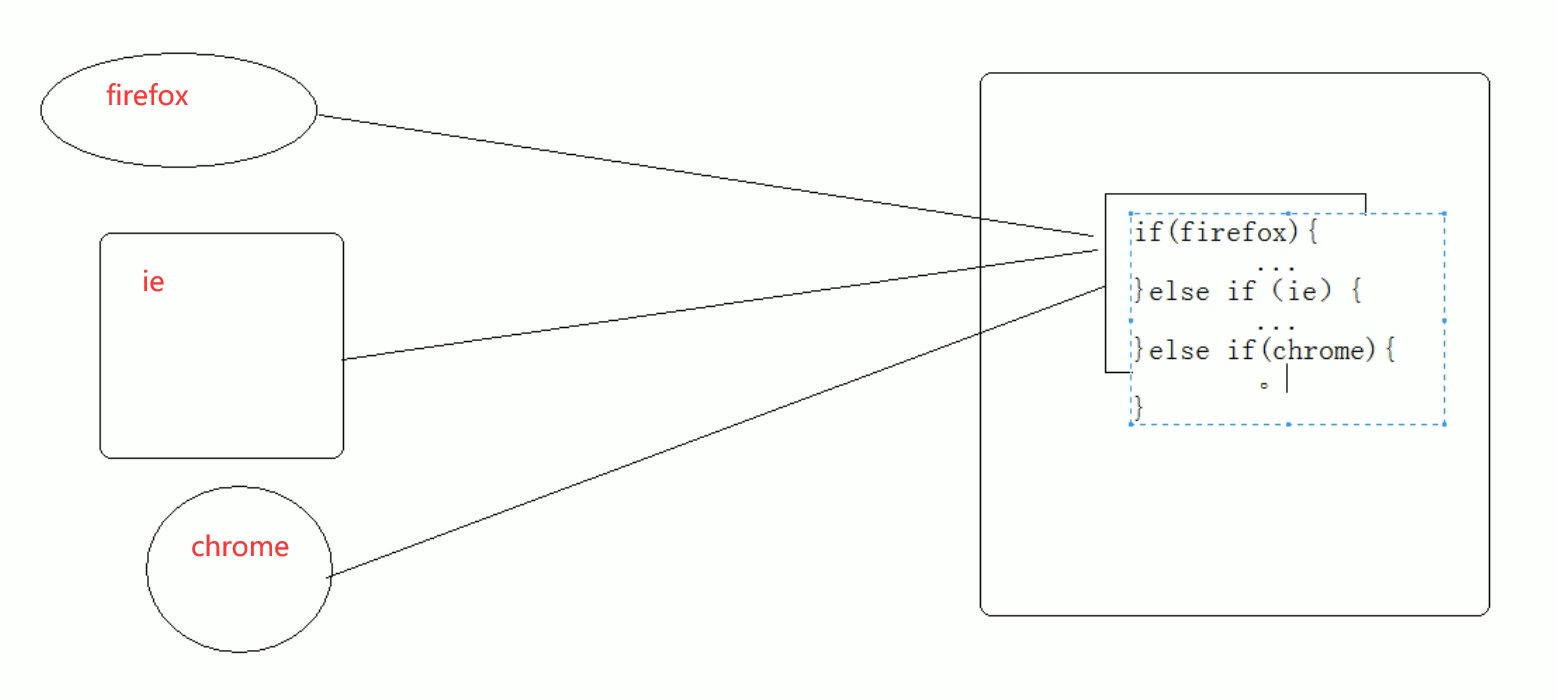
User agent: the browser tells the server that I can access the version information of the browser you use
-
The header information can be obtained on the server side to solve the compatibility problem of the browser
-
Accept: tell the server, as a browser, what kind of corresponding information format can I accept from you
-
Accept language: tell the server the locale I support as a browser
-
Accept encoding: tell the server that as a browser, I support compression
-
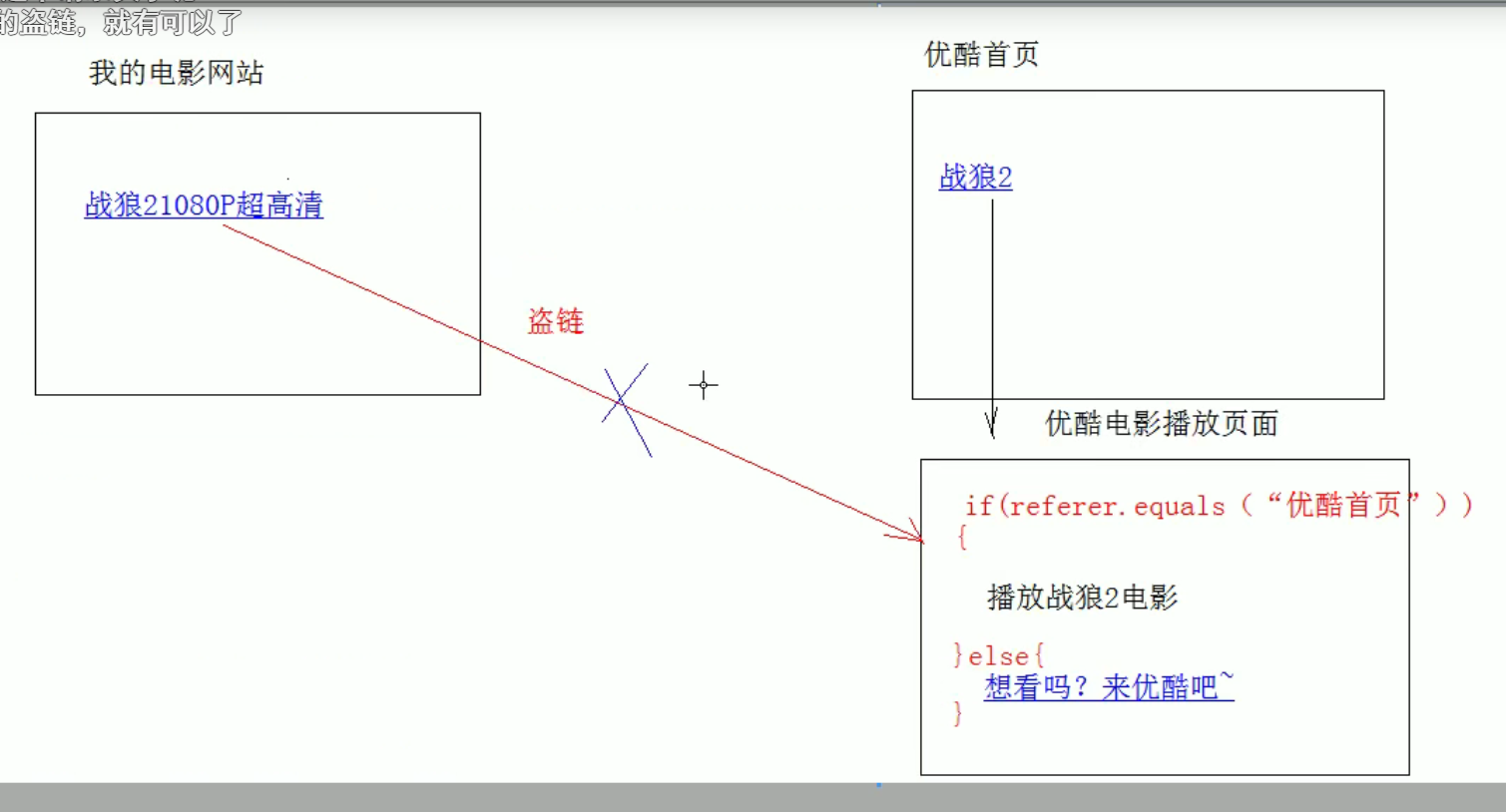
Referer: tells the server where the current request comes from (where i comes)
-
effect
-
Anti theft chain
-
-
statistical work
-
Connection: this link can be reused
2.2.3 request blank line
Blank line: separates the request header from the request body
2.2.4 request body (text)
-
The of the request body that encapsulates the POST request
-
The get method has no request body
-
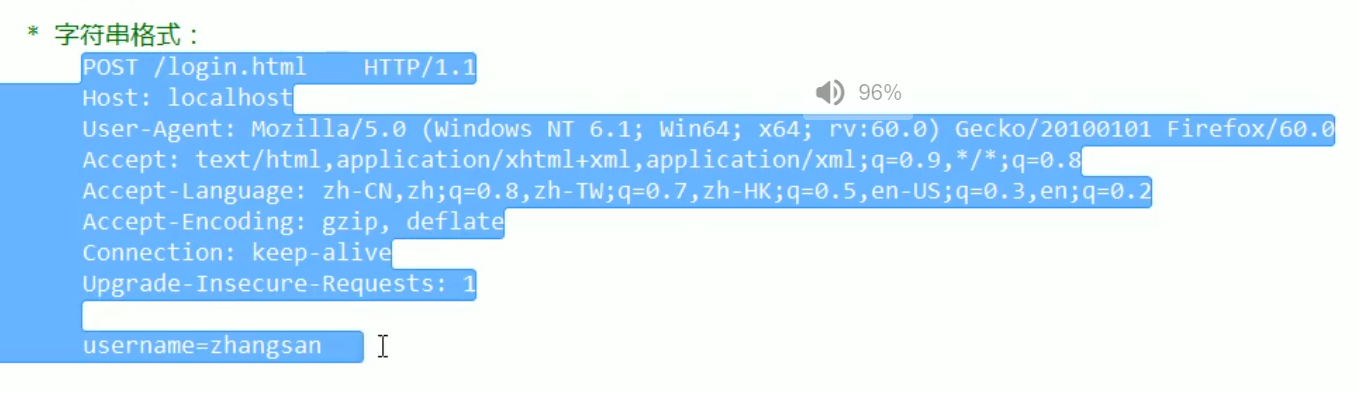
The original format of the request message
2.3 Request
-
Principle of request object and response object
-
The request and respnse objects are created by the server, and we will use them
-
The request object is used to get the request message, and the respise object is used to set the corresponding message
-
2.3.1 request object inheritance architecture
ServletRequest -- Interface
| extends
HttpServletRequest -- Interface
| implements
org.apache.catalina.connector.RequestFacade class (tomcat Implementation)
2.3.2 functions
2.3.2.1 get request line data
-
Get request line data : GET /day14/demo1?name=zhangsan HTTP/1.1
-
GET request method: GET
-
request.getMethod();
-
-
Get virtual directory: / day14
-
request.getContextPath();
-
-
Get Servlet path: / demo1
-
request.getServletPath();
-
-
Get get mode request parameters: name=zhangsan
-
request.getQueryString();
-
-
Get request URI /day14/demo1
-
request.getRequestURI();
-
request.getRequestURL();
-
-
Get protocol and version: HTTP/1.1
-
request.getProtocol();
-
-
Get the IP address of the client:
-
request.getRemoteAddr();
-
-
2.3.2.2 get request header data
-
Get request header data
-
Get the value of the request header by the name of the request header
-
request.getHeader(String name)
-
request.getHeader("referer");// If you input directly through the browser address bar, you can't get the referer header information (the same as other methods, such as hyperlinks)
-
-
Gets the names of all request headers
-
Enumeration<String> request.getHeaderNames
-
-
2.3.2.3 obtaining request body data
-
Get request body data
-
Only the POST request mode has a request body, which encapsulates the request parameters of the POST request
-
step
-
Get stream object
-
BufferedReader getReader(): gets the character input stream. Only character data can be manipulated
-
ServletInputStream getInputStream(): get byte input stream, which can operate on all types of data
-
-
Then get the data from the stream object
-
-
@PostMapping("/test")
public String test(HttpServletRequest request) throws IOException {
//1. Get character stream
BufferedReader br = request.getReader();
//2. Read data
String line = null;
while((line = br.readLine()) != null){
System.out.println(line);
}
return "Project start test";
}2.3.2.4 general method for obtaining request parameters
-
General method for obtaining request parameters
-
Get parameter value according to parameter name
-
request.getParameter(String name)
-
-
Get the array of parameter values according to the parameter name (such as? Hobby = swimming & Hobby = basketball)
-
String[ ] request.getParameterValues(String name)
-
-
Gets the parameter names for all requests
-
Enumeration<String> getParameterNames():
-
-
Gets the map collection of all parameters
-
Map<String,String[ ]> getParamterMap()
-
-
@PostMapping("/test")
public String test(HttpServletRequest request) throws IOException {
//Get parameter age
String age = request.getParameter("age");
System.out.println("age===>"+age);
//Get the hobby parameter array
String[] bobbies = request.getParameterValues("bobby");
for (String bobby : bobbies) {
System.out.println("hobby===>"+bobby);
}
//Get all parameter names
Enumeration<String> parameterNames = request.getParameterNames();
while (parameterNames.hasMoreElements()) {
System.out.println("The parameter name is"+parameterNames.nextElement());
}
//Get parameter key value pair
Map<String, String[]> parameterMap = request.getParameterMap();
String[] ages = parameterMap.get("age");
for (String s : ages) {
System.out.println(s);
}
String[] bobbies1 = parameterMap.get("bobby");
for (String s : bobbies1) {
System.out.println(s);
}
return "Project start test";
}POST request mode garbled
-
Sets the character set of the stream
request.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");2.3.2.5 request forwarding
-
Request forwarding: a resource jump mode within the server
-
step
-
Get the request forwarder object through the request object: RequestDispatcher getRequestDispatcher(String path)
-
Use the RequestDispatcher object to forward: forward (ServletRequest, servletresponse, response)
-
-
characteristic
-
The browser address bar path does not change
-
It can only be forwarded to internal resources of the current server
-
Forwarding is a request
-
-
@RestController
public class TestController {
@PostMapping("/test")
public void testController(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
System.out.println("test");
//Go to another URL
//RequestDispatcher requestDispatcher = request.getRequestDispatcher("toDestination");
//requestDispatcher.forward(request, response);
request.getRequestDispatcher("toDestination").forward(request, response);
}
@PostMapping("/toDestination")
public void toDestination(){
System.out.println("redirect to ReachDestination");
}
}2.3.2.6 shared data
-
shared data
-
Domain object: an object with scope that can share data within the scope
-
Request field: represents the scope of a request. It is generally used to share data among multiple resources forwarded by a request
-
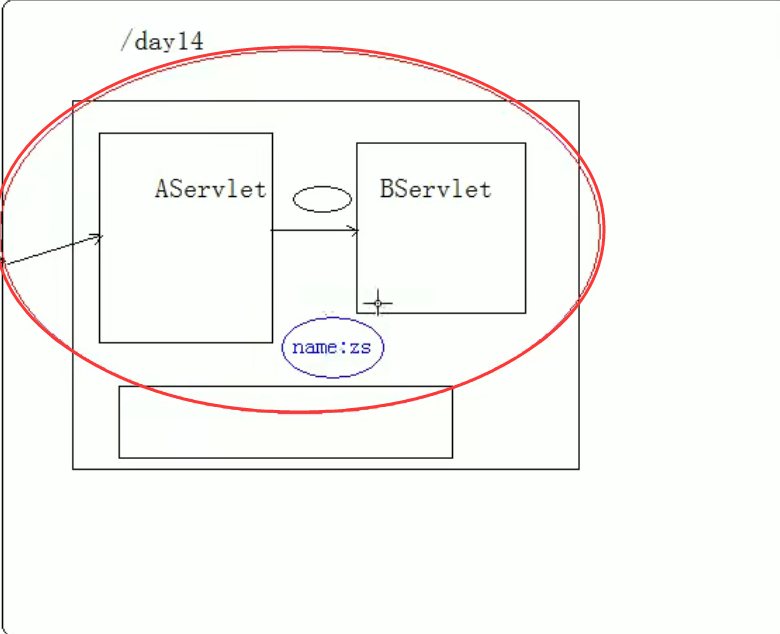
method:
-
void setAttribute(String name,Object obj): stores data
-
Object getAttribute(String name): get the value through the key
-
void removeAttribute(String name): remove key value pairs through keys
@RestController
public class TestController {
@PostMapping("/test")
public void testController(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
System.out.println("test");
//Go to another URL
//RequestDispatcher requestDispatcher = request.getRequestDispatcher("toDestination");
//requestDispatcher.forward(request, response);
request.setAttribute("messageKey", "messageValue");
request.getRequestDispatcher("toDestination").forward(request, response);
}
@PostMapping("/toDestination")
public void toDestination(HttpServletRequest request){
System.out.println("redirect to ReachDestination");
System.out.println(request.getAttribute("messageKey"));
}
}2.3.2.7 get ServletContext
2.3.2.7 get ServletContext
-
Get ServletContext
@RestController
public class TestController {
@PostMapping("/test")
public void testController(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
ServletContext servletContext = request.getServletContext();
System.out.println(servletContext);
}
}
2.4 Response
-
data format
-
Corresponding line
-
Response header
-
Response blank line
-
Responder
-
-
Response string format
Response line
-
Composition: Protocol / version response status code status code description
-
Status code: all three digits
-
Classification:
-
1xx: the server receives the client message, but does not accept it. After waiting for a period of time, it sends 1xx and other status codes
-
2xx: success. Representative: 200
-
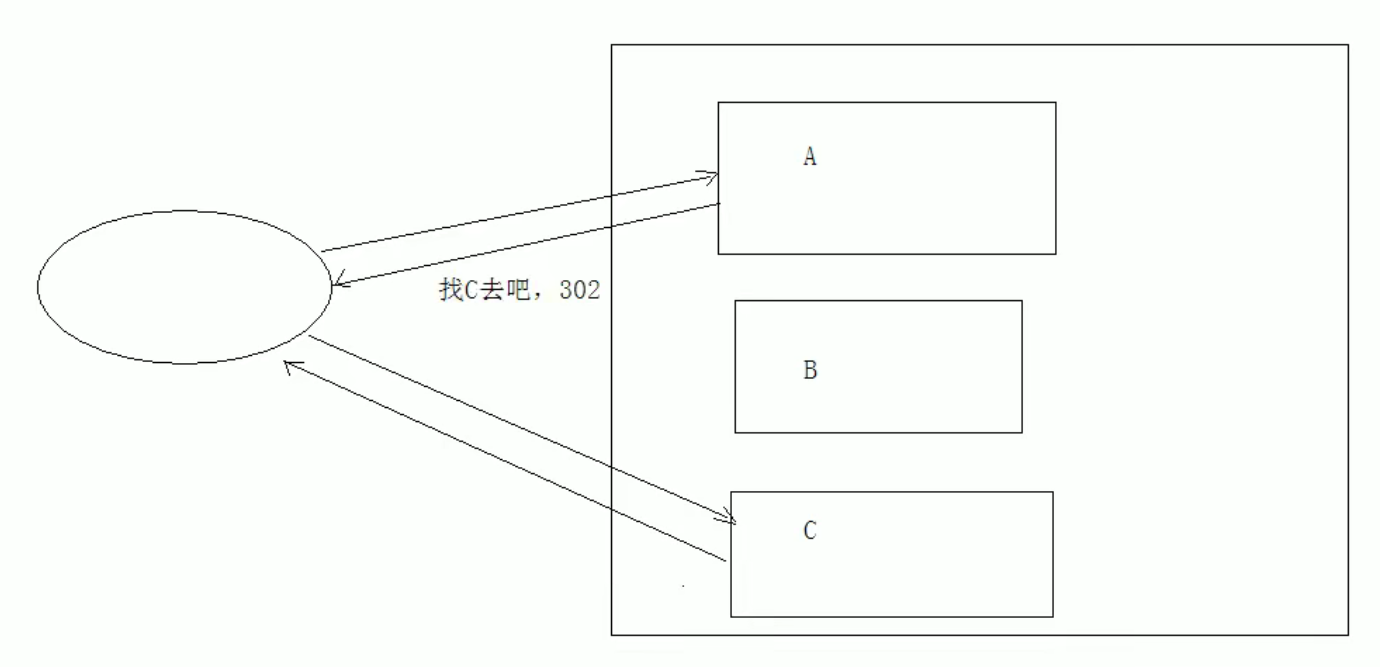
3xx: redirection. Representative: 302 (redirection): the client accesses A. A says I can't do it. Go to C. 304: access the cache. (picture)
-
-
-
4xx: client error. Typical: 404 request path has no corresponding resource: 405 request mode mismatch
-
5xx: server side error typical: 500
Response header
-
Format: header name: value
-
Common response headers:
-
Content type: the server tells the client the data format and encoding format of this response body
-
Content disposition: the server tells the client in what format to open the response body data. The values are as follows
-
In line: the default value, which is opened on the current page
-
attachment;filename=xxx: open the response body as an attachment. File download
-
-
Content - Length: page character length
-
Response body: transmitted data
2.4.1 function of response object
2.4.1.1 set corresponding row
-
Set corresponding row
-
Set status code: void setStatus(int StatusCode)
-
2.4.1.2 set response header
-
Set response header
-
void setHeadr(String ,name,String value)
-
2.4.1.3 setting the responder
-
Use steps
-
Get output stream
-
Character output stream
-
PrintWriter getWriter();
-
-
Byte output stream
-
ServletOutPutStream getOutputStream();
-
-
-
Use output stream
-
Export data to client browser
-
-
2.4.2 redirection cases
-
Redirection: how resources jump
-
When accessing A resource, A tells the browser to redirect, and the status code is 302
-
Tell the browser the path of the B resource, and the response header location: the path of the B resource
-
@RestController
public class TestController {
@GetMapping("/test")
public void testController(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
System.out.println("servlet A");
//Set status code 302
response.setStatus(302);
//2. Set response header
response.setHeader("location", "/redirect");
}
@GetMapping("/redirect")
public void test2(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response){
System.out.println("servlet B");
}
} Simplify response.sendRedirect(String url);
@RestController
public class TestController {
@GetMapping("/test")
public void testController(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
System.out.println("servlet A");
//simplify
response.sendRedirect("/redirect");
}
@GetMapping("/redirect")
public void test2(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response){
System.out.println("servlet B");
}
}-
Characteristics of redirection
-
Address bar send change
-
Redirect resources that can access other sites (servers)
-
Redirection is a two-time request. Data cannot be shared using the requse object t
-
-
route
-
classification
-
Relative path: unique resources cannot be determined through relative path
-
Absolute path: unique resources can be determined by absolute path
-
For example, htttp:// www.baidu.com /day15/responseDemo2
-
Get virtual directory dynamically: request.getContextPath();
-
-
-
2.4.3 case of server outputting byte data to browser
@GetMapping("/test")
public void testController(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
//1. Get character output stream
PrintWriter writer = response.getWriter();
writer.write("<h1>hello print writer</h1>");
}Chinese garbled code problem
-
Cause: the character sets used for encoding and decoding are inconsistent
-
Solution: set the browser encoding format and tell the browser to use this encoding rule
@GetMapping("/test")
public void testController(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
//Before obtaining the stream object, set the default encoding of the stream: ISO-8859-1 GBK
//response.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
//Tell the browser the encoding of the message body data sent by the server. It is recommended that the browser use this encoding for decoding
response.setHeader("content-type", "text/html;charset=utf-8");
//1. Get character output stream
PrintWriter writer = response.getWriter();
writer.write("<h1>Hello print writer</h1>");
}Simplification: use the response method setContentType
@GetMapping("/test")
public void testController(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8");
//1. Get character output stream
PrintWriter writer = response.getWriter();
writer.write("<h1>Hello print writer</h1>");
}2.4.4 case of server outputting byte data to browser
-
step
-
Get byte output stream
-
output data
-
@GetMapping("/test")
public void testController(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8");
ServletOutputStream outputStream = response.getOutputStream();
outputStream.write("You also".getBytes());
}2.4.5 verification code
-
Create an object, a picture in memory (verification code picture object)
-
Beautify pictures
-
Output picture to page
@GetMapping("/test")
public void testController(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
int width = 200;
int height = 100;
//Create an object, a picture in memory (verification code picture object)
BufferedImage image = new BufferedImage(width, height, BufferedImage.TYPE_INT_RGB);
//Output pictures to page display
ImageIO.write(image, "jpg", response.getOutputStream());
}2.5 ServletContext
-
Concept: it represents the whole web application and can communicate with the container (server) of the program
-
obtain
-
Get through the request object: request.getServletContext();
-
Get through HttpServlet: this.getServletContext();
-
-
function
-
Get MIME type:
-
Domain objects: sharing data
-
Gets the real (server) path of the file
-
2.5.1 get MIME type
-
Get MIME type
-
MIME type: a file data type defined in the process of Internet communication
-
Format large type / small type text/html image/jpeg
-
-
Get: getMimeType(String file)
-
@GetMapping("/test")
public void testController(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
//obtain
ServletContext servletContext = request.getServletContext();
//Definition file name
String filename = "a.jpg";
//Get MIME type
String mimeType = servletContext.getMimeType(filename);
System.out.println(mimeType); //image/jpeg
}2.5.2 domain object: shared data (use with caution)
Domain object: shared data (use with caution)
-
ServletContext object scope: data requested by all users
servletContext.setAttribute("messageKey", "messageValue");Object messageKey = servletContext.getAttribute("messageKey");servletContext.removeAttribute("messageKey");@RestController
public class TestController {
@GetMapping("/test")
public void testController(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
//obtain
ServletContext servletContext = request.getServletContext();
servletContext.setAttribute("messageKey", "messageValue");
}
@GetMapping("/redirect")
public void test2(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response){
ServletContext servletContext = request.getServletContext();
Object messageKey = servletContext.getAttribute("messageKey");
System.out.println(messageKey);
}
}2.5.3 get the real (server) path of the file
-
Gets the real (server) path of the file
-
servletContext.getRealPath(String path);
-
@GetMapping("/test")
public void testController(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
//obtain
ServletContext servletContext = request.getServletContext();
//Get real path (tomcat)
String realPath = servletContext.getRealPath("src\\main\\resources\\application.properties");
System.out.println(realPath);
}2.6 file download cases
-
File download requirements
-
Page display hyperlink
-
Click the hyperlink to pop up the download prompt box
-
Complete picture file download
-
-
analysis
-
If the resource pointed to by the hyperlink can be parsed by the browser, it will be displayed in the browser. If it cannot be parsed, a download prompt box will pop up. It does not meet the requirements
-
The download prompt box must pop up for any resource
-
Use the response header to set how resources are opened:
-
content-disposition : attachment;filename = xxx
-
-
-
step
-
Define the page, edit the href attribute of the hyperlink, point to the Servlet, and pass the resource name filename
-
Define Servlet
-
Get file name
-
Load file into memory using byte input stream
-
Specify the response header of reply: content disposition: attach; filename=xxx
-
Write data out to the response output stream
-
-
@GetMapping("/downServlet")
public void test2(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {
//Get parameters
String fileName = request.getParameter("fileName");
//Get the real path of the server and load the file into memory using the byte input stream
ServletContext servletContext = request.getServletContext();
String realPath = servletContext.getRealPath("src\\main\\resources\\img\\"+fileName);
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(realPath);
//Set the response header, download the file as an attachment and MIME type
response.setHeader("content-type",servletContext.getMimeType(fileName));
response.setHeader("content-disposition", "attachment;filename="+fileName);
//Write input stream to output stream
ServletOutputStream servletOutputStream = response.getOutputStream();
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int len = 0;
while((len=fileInputStream.read(buffer)) != -1){
servletOutputStream.write(buffer,0,len);
}
}
Chinese file name problem
-
Tool class
public class DownUtils {
public static String getFileName(String agent,String filename) throws UnsupportedEncodingException {
if(agent.contains("MSIE")){
//IE
filename = URLEncoder.encode(filename, "utf-8");
filename = filename.replace("+", " ");
}else if(agent.contains("Firefox")){
//Firefox
BASE64Encoder base64Encoder = new BASE64Encoder();
filename = "?utf-8?B?" +base64Encoder.encode(filename.getBytes("utf-8"))+"?=";
}else {
//Other browsers
filename = URLEncoder.encode(filename, "utf-8");
}
return filename;
}
}step
-
Get user agent request header
-
Use tool classes to encode file names according to different browsers
@GetMapping("/downServlet")
public void test2(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {
//Get parameters
String fileName = request.getParameter("fileName");
//Get the real path of the server and load the file into memory using the byte input stream
ServletContext servletContext = request.getServletContext();
String realPath = servletContext.getRealPath("src\\main\\resources\\img\\"+fileName);
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(realPath);
//Set the response header, download the file as an attachment and MIME type
response.setHeader("content-type",servletContext.getMimeType(fileName));
//Solve the problem of Chinese file name
//Get user agent request header
String agent = request.getHeader("user-agent");
//Encode file names according to different browsers
fileName = DownUtils.getFileName(agent, fileName);
response.setHeader("content-disposition", "attachment;filename="+fileName);
//Write input stream to output stream
ServletOutputStream servletOutputStream = response.getOutputStream();
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int len = 0;
while((len=fileInputStream.read(buffer)) != -1){
servletOutputStream.write(buffer,0,len);
}
}3. Session Technology: Cookie
-
Session: a session contains multiple requests and responses
-
One session: the browser sends a request to the server resource for the first time, and the session is established until one party is disconnected (the browser is closed, or the server is closed, etc.)
-
Function: share data among multiple requests within the scope of a session
-
Method:
-
Client session Technology: cookies
-
Server side Session Technology: Session
-
-
3.1 concept
-
Concept: client session technology, which saves data to the client
-
Use steps
-
Create Cookie object and bind data
-
new Cookie(String name,String value);
-
-
Send Cookie object
-
response.addCookie(Cookie cookie);
-
-
Get cookies and get data
-
Cookie[] request.getCookie();
-
-
-
@RestController
public class TestController {
@GetMapping("/cookieTest")
public void testController(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
//Create Cookie object
Cookie cookie = new Cookie("cookieKey", "cookieValue");
//Send cookies to client browsers
response.addCookie(cookie);
}
@GetMapping("/getCookie")
public void test2(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {
//Get Cookie
Cookie[] cookies = request.getCookies();
//Get data and traverse cookies
if(cookies != null){
for (Cookie cookie : cookies) {
String cookieKey = cookie.getValue();
System.out.println(cookieKey);
}
}
}
}
3.2 sending multiple cookies at a time+
-
Send multiple cookies at a time
@GetMapping("/cookieTest")
public void testController(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
//Create Cookie object
Cookie cookie = new Cookie("cookieKey", "cookieValue");
Cookie cookie1 = new Cookie("cookieKey2", "cookieValue2");
//Send cookies to client browsers
response.addCookie(cookie);
response.addCookie(cookie1);
}3.3 Cookie lifetime
-
By default, when the browser is closed, the Cookie data is destroyed
-
Persistent storage:
-
setMaxAge(int seconds)
-
Positive number: write cookie data to the file on the hard disk. Persistent storage. Cookie lifetime. (start timing after the browser is closed)
-
Negative: default
-
Zero: delete cookie information
-
-
3.4 Cookie storage Chinese
-
The key name of the cookie cannot be Chinese
-
Before Tomcat 8, Chinese data could not be stored directly in cookie s
-
Chinese (special character) data needs to be transcoded --- generally URL encoding ()
-
3.5 cookie acquisition scope
-
cookie sharing problem
-
Suppose multiple web applications are deployed in a tomcat server, can cookie s be shared in these web projects?
-
Cookies cannot be shared by default
-
cookie.setPaht(String path): sets the cookie acquisition range. By default, the current virtual directory is set
-
If you want all projects on the current server to be shared, you can set the path to "/"
-
-
-
@GetMapping("/cookieTest")
public void testController(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
//Create Cookie object
Cookie cookie = new Cookie("cookieKey", "cookie value");
//Set shared scope server scope
cookie.setPath("/");
//Send cookies to client browsers
response.addCookie(cookie);
}-
See the cookie sharing problem for different tomcat servers?
-
cookie.setDomain(String path): if the primary domain name is set to be the same, cookies can share data before multiple servers
-
cookie.setDomain(".baidu.com"), then cookies in tieba.baidu.com and news.baidu.com can be shared
-
Mostly used for distributed
-
3.6 characteristics and functions of cookies
-
characteristic:
-
Cookies store data in the client browser (relatively low security)
-
The browser also limits the size of a single cookie (4kb) and the total number of cookies under the same domain name (20)
-
-
effect:
-
Cookies are generally used to store a small amount of less sensitive data
-
Complete the identification of the client by the server without logging in
-
3.7 cases
-
demand
-
Access a Servlet. If it is the first time, you will be prompted: Hello, welcome to visit for the first time
-
If it is not your first visit, you will be prompted: Welcome back. Your last visit time is: display the time string
-
-
analysis:
-
This can be done using cookies
-
The Servlet in the server determines whether there is a Cookie named lastTime
-
Yes: not the first visit
-
Response data: Welcome back. Your last visit was at 11:50:20, June 10, 2018
-
Write back Cookie: lasttime = 11:50:20, June 12, 2018
-
-
No,
-
Response data: Hello, welcome to visit for the first time
-
Write back Cookie: lasttime = 11:50:20, June 12, 2018
-
-
-
@RestController
public class TestController {
public static SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
public static Date now = new Date();
@GetMapping("/cookieLastTime")
public String testController(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
Boolean flag = false;
//1. Get all cookies
Cookie[] cookies = request.getCookies();
//Traversal cookie array
if (cookies != null || cookies.length != 0){
for (Cookie cookie : cookies) {
String cookieName = cookie.getName();
if("lastTime".equals(cookieName)){ //There is a lastTime Cookie
flag = true;
//set
String format = sdf.format(now);
System.out.println("Before coding:"+format);
//URL encoding
format = URLEncoder.encode(format, "utf-8");
cookie.setValue(format);
cookie.setMaxAge(60*60*24*30); // one month
response.addCookie(cookie);
//get
String lastTimeValue = cookie.getValue();
//decode
System.out.println("Before decoding:"+lastTimeValue);
//URL decoding
lastTimeValue = URLDecoder.decode(lastTimeValue, "utf-8");
System.out.println("After decoding:"+lastTimeValue);
return "Your last visit was"+lastTimeValue;
}
}
}
if(cookies == null || cookies.length == 0 || flag ==false){
//No, first visit
String format = URLEncoder.encode(sdf.format(now), "utf-8");
Cookie cookie = new Cookie("lastTime", format);
cookie.setMaxAge(60*60*24*30);
response.addCookie(cookie);
return "Hello!,Welcome to your first visit";
}
return null;
}
}4. Session Technology: session
-
Concept: server-side session technology, which shares data between multiple requests of a session and saves the data in the server-side object. HttpSession
-
Quick start:
-
Get HttpSession object
-
Using the HttpSession object
-
HttpSession object:
-
Object getAttribute(String name)
-
void setAttribute(String name,Object value)
-
void removeAttribute(String name)
-
-
@RestController
public class TestController {
@GetMapping("/sessionSet")
public void testController(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
//Get Session object
HttpSession session = request.getSession();
//set
session.setAttribute("sessionKey","sessionValue");
}
@GetMapping("/sessionGet")
public void test2(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {
HttpSession session = request.getSession();
//get
Object sessionValue = session.getAttribute("sessionKey");
System.out.println(sessionValue);
}
}4.1 Session principle
-
How does the server ensure that the Session object you get multiple times is the same in a Session scope?
-
Session depends on cookies!
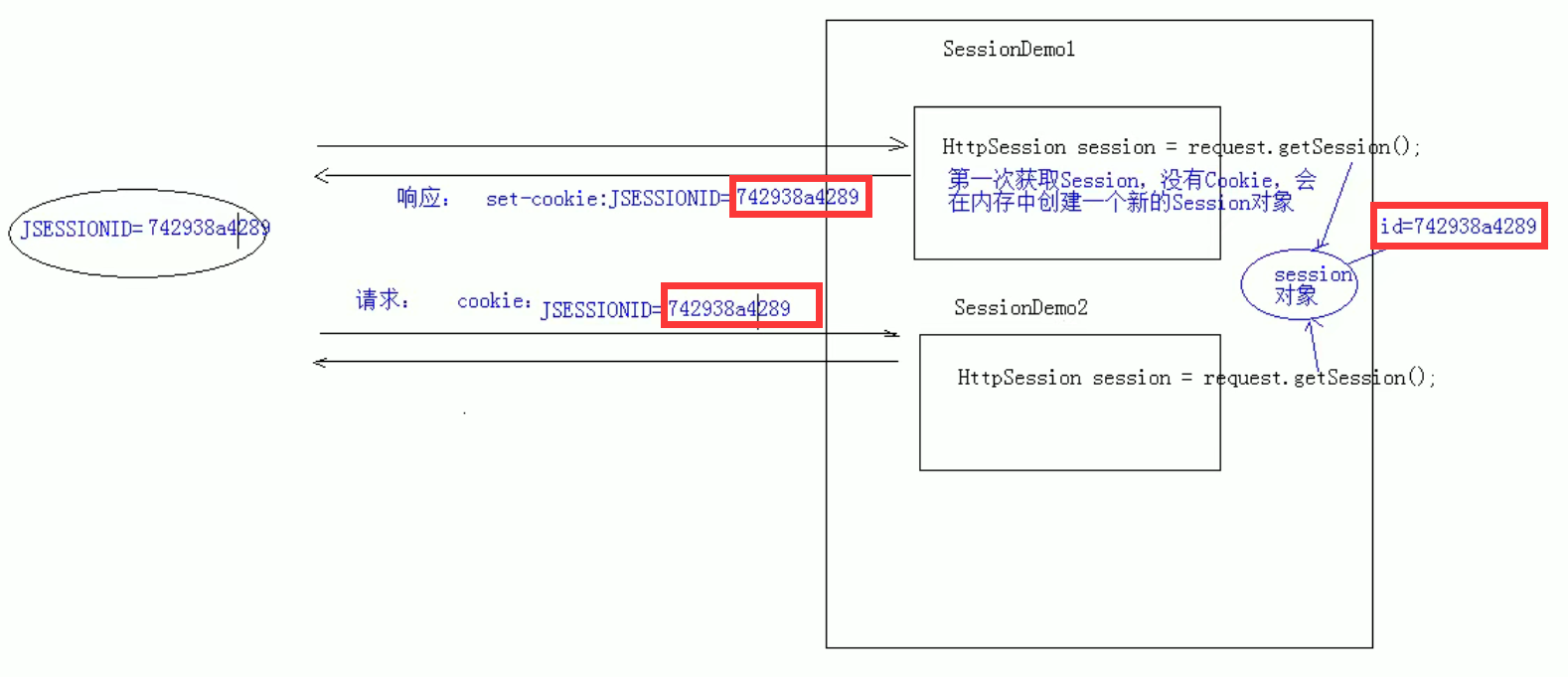
4.2 Session uniformity X
-
When the client is shut down, the server is not shut down. Is the Session obtained twice one?
-
By default, it is not. Because the last session has ended
-
If you need the same, you can create a cookie, key JSESSIONID, set the maximum survival time, and make the cookie persistent
-
Cookie c = new Cookie("JSESSIONID",session.getId());
c.setMaxAge(60*60);
response.addCookie(c);4.3 Session uniformity Ω
-
When the server is shut down, the Session is not unique
-
Although the Session object is not the same, make sure that the data is not lost
-
Passivation of Session:
-
Serialize the session object to the hard disk before the server shuts down normally
-
-
Activation of Session:
-
After the server starts, convert the session file into a session object in memory
-
-
-
4.4 Session aging
-
When was the Session destroyed
-
Server shutdown
-
The session object calls invalidate();
-
The default session expiration time is 30min (there is no operation when the page is opened)
-
4.5 characteristics of session
-
Session is used to store the data of multiple requests of a session, which is stored on the server side
-
session can store any type of data and any size of data
