3. JSR303 data verification and multi environment switching
3.1 JSR303 data verification
1. Verify with JSR303
In Springboot, @ validated can be used to verify the data. If the data is abnormal, exceptions will be thrown uniformly to facilitate the unified processing of the exception center.
Let's write a comment here so that our name can only support Email format
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person")
@Validated
public class Person {
@Email(message = "User name is not a legal email address")
private String name;
private Integer age;
private Boolean happy;
private Date birht;
private Map<String,Object> maps;
private List<Object> lists;
private Dog dog;
// Parameterless construction, get, set method, toString() method
}
Running result: default message [user name is not a legal email address]

Using data verification can ensure the correctness of data;
2. JSR303 common parameters
@NotNull(message="Name cannot be empty")
private String userName;
@Max(value=120,message="The oldest can't check 120")
private int age;
@Email(message="Mailbox format error")
private String email;
Empty check
@Null Verify that the object is null
@NotNull Verify that the object is not null, Cannot check string with length 0
@NotBlank Check whether the constraint string is Null And by Trim Is the length greater than 0,String only,And the front and back spaces will be removed.
@NotEmpty Check whether the constraint element is NULL Or EMPTY.
Booelan inspect
@AssertTrue verification Boolean Whether the object is true
@AssertFalse verification Boolean Whether the object is false
Length check
@Size(min=, max=) Validation object( Array,Collection,Map,String)Is the length within the given range
@Length(min=, max=) string is between min and max included.
Date check
@Past verification Date and Calendar Is the object before the current time
@Future verification Date and Calendar Is the object after the current time
@Pattern verification String Whether the object conforms to the rules of regular expressions
.......wait
In addition, we can also customize some data verification rules
3.2 multi environment switching
profile is Spring's support for different configuration functions for different environments. You can quickly switch environments by activating different environment versions;
1. Multi environment configuration
When we write the main configuration file, the file name can be application-{profile}.properties/yml, which is used to specify multiple environment versions;
For example:
application-test.properties represents the test environment configuration
application-dev.properties represents the development environment configuration
However, Springboot does not directly start these configuration files. It uses the application.properties main configuration file by default;
We need to select the environment to be activated through a configuration in the main configuration file (application.properties):
#For example, if the dev environment is specified in the configuration file, we can test by setting different port numbers; #When we start SpringBoot, we can see that the configuration has been switched to dev; spring.profiles.active=dev
2. yaml multi document Fast
It is the same as in the properties configuration file, but it is more convenient to use yml to implement it without creating multiple configuration files!
server:
port: 8081 #8081 is used by default
#Select the environment block to activate
spring:
profiles:
active: prod
---
server:
port: 8082
spring:
profiles: dev #Name of the configuration environment
---
server:
port: 8083
spring:
profiles: prod #Name of the configuration environment
Note: if both yml and properties are configured with ports and no other environment is activated, the properties configuration file will be used by default!
3. Configuration file loading location
There are many ways to load configuration files externally. We can select the most commonly used one and configure it in the developed resource file!
Official external configuration file description reference document
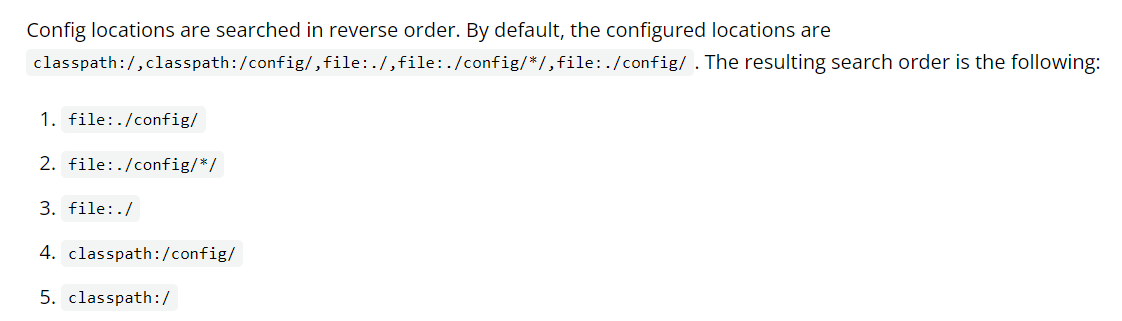
springboot startup will scan the application.properties or application.yml file in the following location as the default configuration file of Spring boot:
Priority 1: under the project path config Folder profile Priority 2: configuration file under project path Priority 3: Resources( resources)Under path config Folder profile Priority 4: Resources( resources)Configuration file under path
The priority is from high to bottom, and the configuration of high priority will overwrite the configuration of low priority;
SpringBoot will load the main configuration file from these four locations; complementary configuration;
We set up a project access path configuration in the lowest level configuration file to test the complementarity problem;
#Configure the access path of the project server.servlet.context-path=/dzj
4. Development, operation and Maintenance Tips
Load the configuration file at the specified location
We can also change the default configuration file location through spring.config.location
After the project is packaged, we can use the form of command line parameters to specify the new location of the configuration file when starting the project. In this case, there are usually many operations in the later stage. For the same configuration, the externally specified configuration file has the highest priority
java -jar spring-boot-config.jar --spring.config.location=F:/application.properties