Getting started with JVM
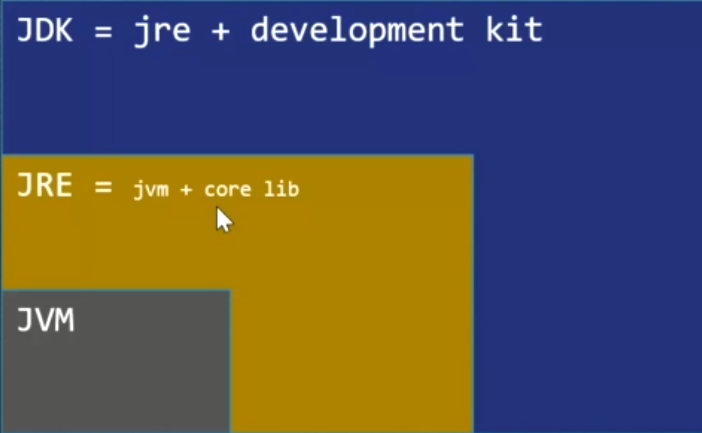
Inclusion relationship of JDK, JRE and JVM
JVM features
- Some people say that classLoader does not belong to the JVM, and the concept does not matter
- Interpretation and compilation mix
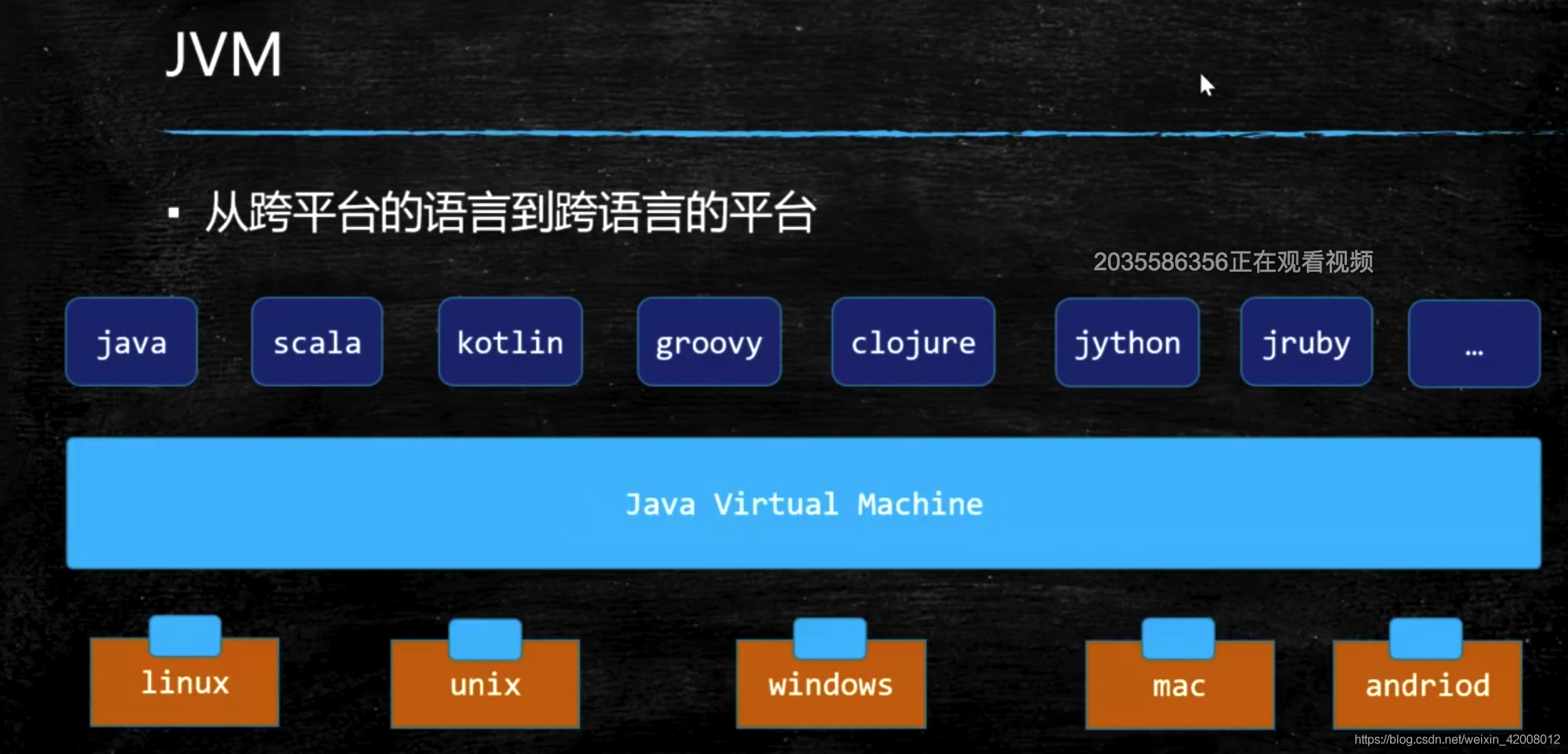
- Cross language platform
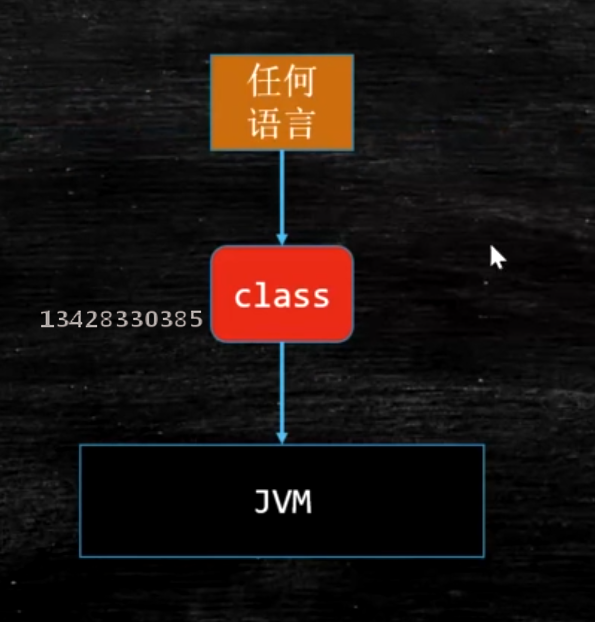
- The JVM is java independent
Any language - compile or dynamically generate - > Class file - run in - > JVM
- A JVM is a specification
java virtual machine specifications - A fictional computer
- Bytecode instruction set (assembly language)
- Memory management: stack heap method area, etc
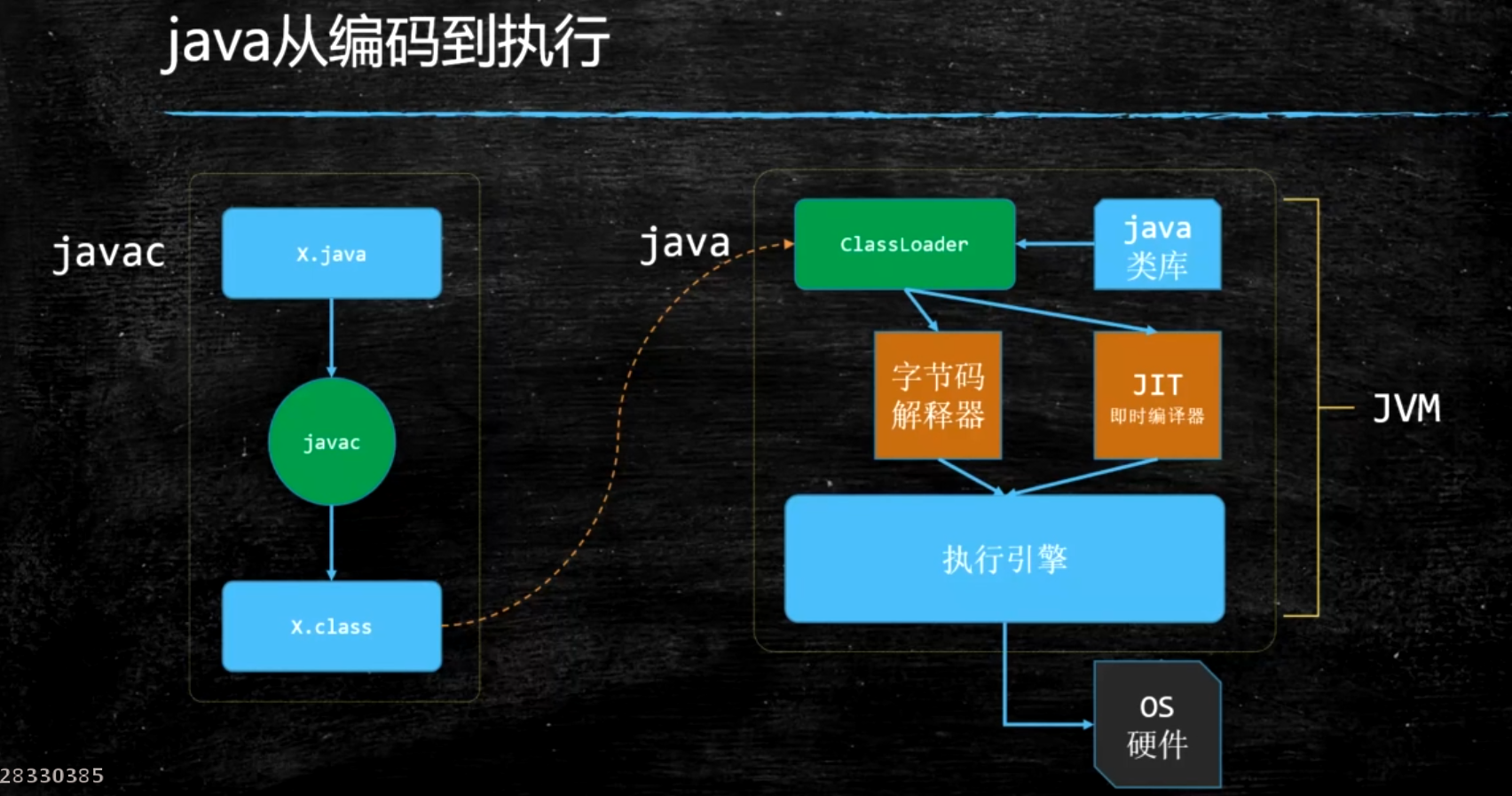
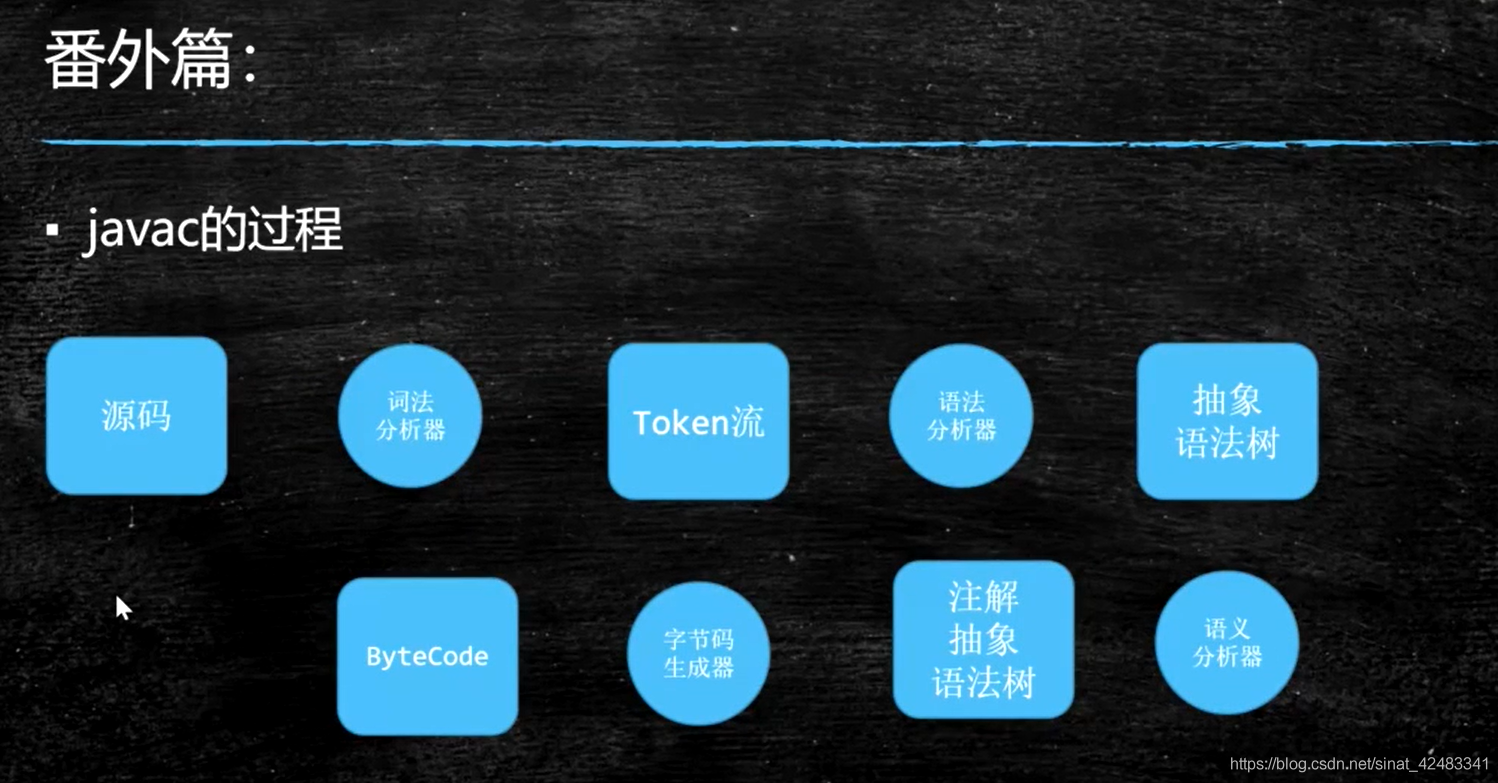
javac process
Common JVM implementations
java -version, you can see the details of the JVM you use
- HotSpot:
Official implementation of Oracle (originally sun, later acquired by Oracle) - Jrockit:
BEA, once known as the world's fastest JVM, was acquired and merged in HotSpot by Oracle - J9:
IBM implementation - Microsoft VM
- TaobaoVM:
HotSpot deep customization - LiquidVM:
Direct to hardware - azul zing:
The latest industry benchmark for garbage collection is said to be particularly expensive and garbage collection is particularly fast
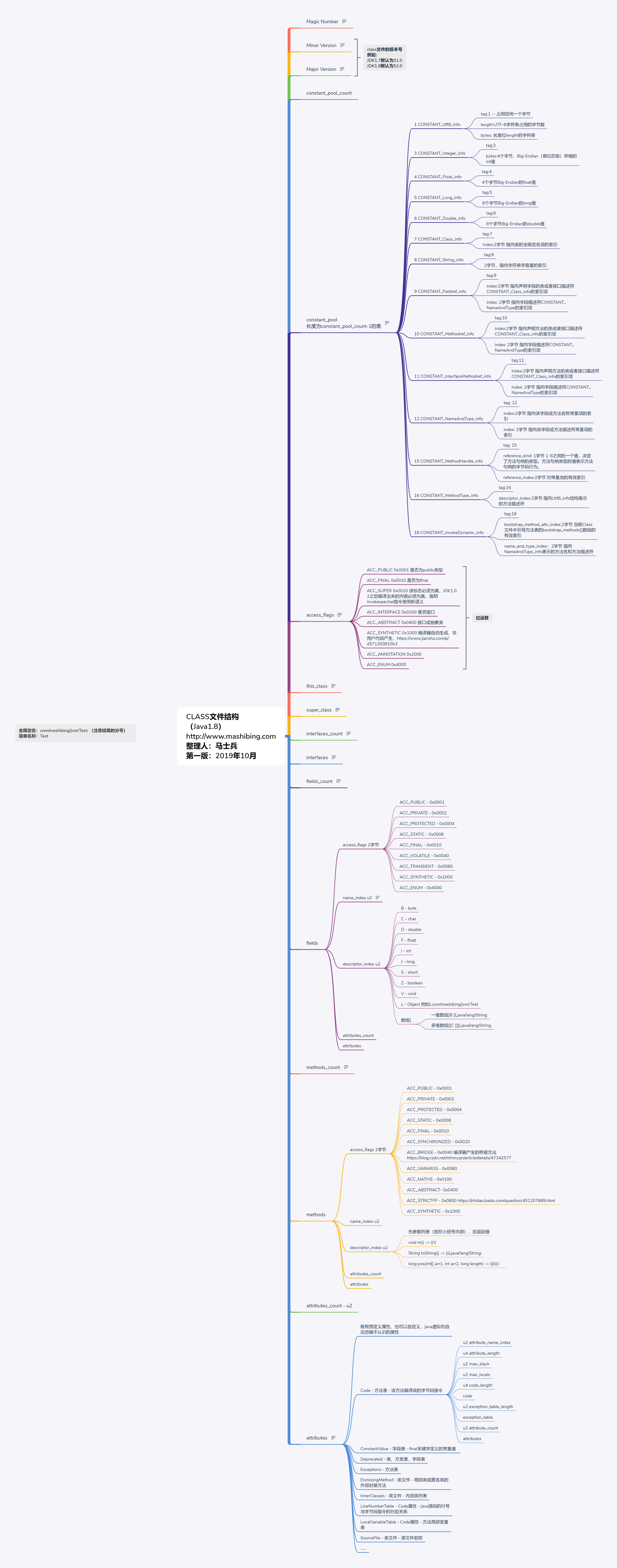
Class File Format
Interview basically won't ask, as an interest to learn
- class file is a binary byte stream;
- Data types: u1 u2 u4 u8 and_ info (table type)
_ The source of info is the writing method in the Hotspot source code
The format design of the class file is very compact, without any separator, and has been recognized by many big cattle. Therefore, when designing the language, they will choose to translate it into class and run it on the JVM
It needs to cooperate with section 7 of the JVM specification on the official website (assembly language of java)
Understand the class file generated by compilation
Create an empty class
package character01;
/**
* @Author laimouren
* @Date 2022/1/7 9:55
*/
public class Empty {
}
After compiling, check its class file. IDEA decompiles automatically. You can see that there is an additional parameterless construction method
//
// Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA
// (powered by FernFlower decompiler)
//
package character01;
public class Empty {
public Empty() {
}
}
IntelliJ IDEA can install a BinEd plug-in and open it to view the class file
If opened with SublimeText, it is opened in hexadecimal:
cafe babe 0000 0034 0010 0a00 0300 0d07 000e 0700 0f01 0006 3c69 6e69 743e 0100 0328 2956 0100 0443 6f64 6501 000f 4c69 6e65 4e75 6d62 6572 5461 626c 6501 0012 4c6f 6361 6c56 6172 6961 626c 6554 6162 6c65 0100 0474 6869 7301 0021 4c63 6f6d 2f65 7861 6d70 6c65 2f64 656d 6f2f 6a76 6d2f 456d 7074 7943 6c61 7373 3b01 000a 536f 7572 6365 4669 6c65 0100 0f45 6d70 7479 436c 6173 732e 6a61 7661 0c00 0400 0501 001f 636f 6d2f 6578 616d 706c 652f 6465 6d6f 2f6a 766d 2f45 6d70 7479 436c 6173 7301 0010 6a61 7661 2f6c 616e 672f 4f62 6a65 6374 0021 0002 0003 0000 0000 0001 0001 0004 0005 0001 0006 0000 002f 0001 0001 0000 0005 2ab7 0001 b100 0000 0200 0700 0000 0600 0100 0000 0700 0800 0000 0c00 0100 0000 0500 0900 0a00 0000 0100 0b00 0000 0200 0c
Interpretation of class file format
From front to back: Magic Number, Minor version, Major version, etc. see the class file specification below for details
Each hexadecimal digit occupies 4 bits, and a byte is 8 bits, so the next square represents a byte
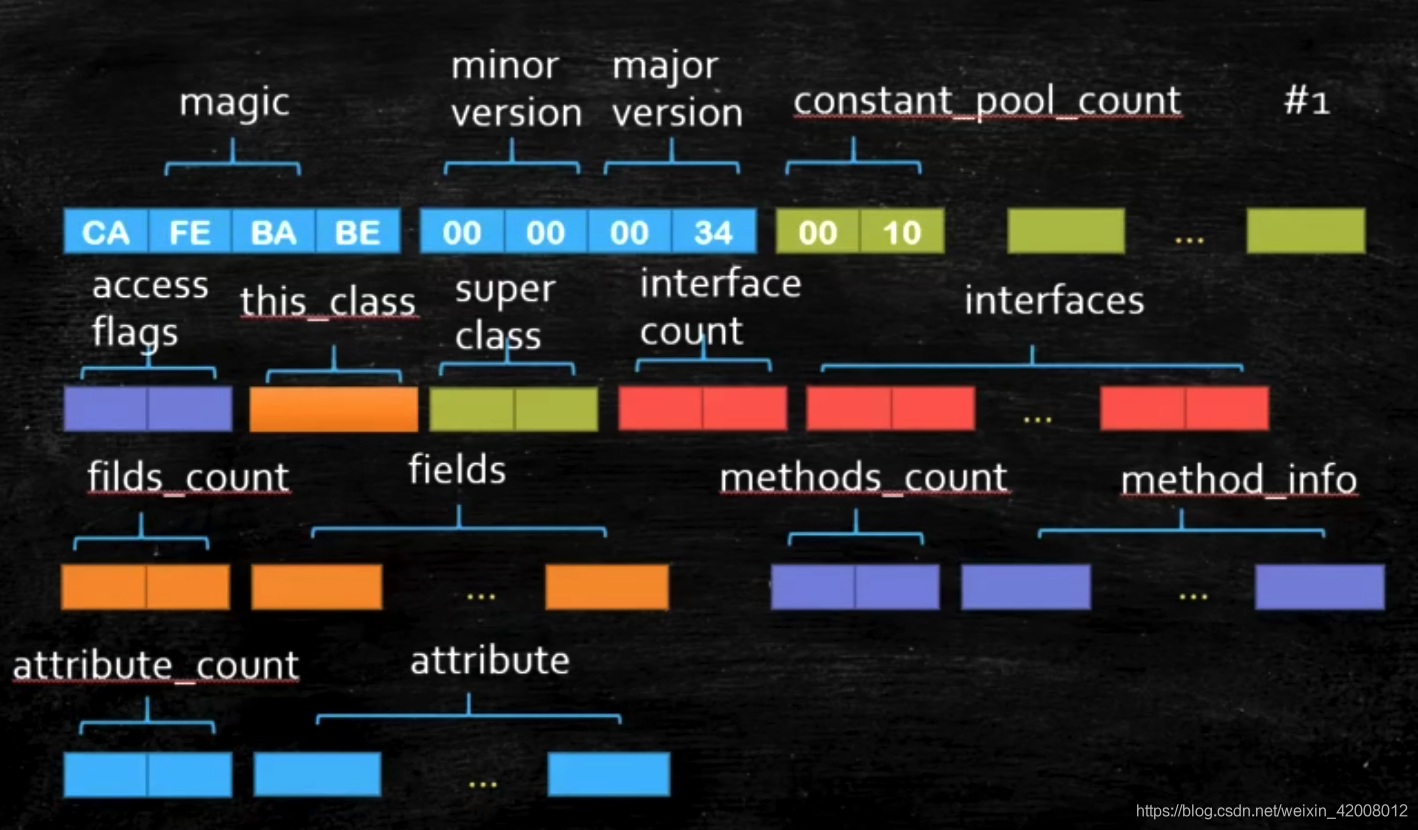
The Magic Number of java class files is usually cafe babe
class file version number: version,JDK7 is 51.0 by default, and jdk8 is 52.0 by default, increasing in sequence; 51 and 52 are major versions, followed by Minor Version
Sometimes when a project compiled with JDK8 runs on the JDK7 environment, we throw an exception: xxxx version 52.0
Then constant_pool_count
Followed by (constant_pool_count-1) constant_ Pool, starting from #1, because #0 makes a reservation, which means that there is no reference to it
Tools for displaying class information
- javap
javap -v EmptyClass.class output:
Classfile /Users/liweizhi/IdeaProjects/msb-class/demo/target/classes/com/example/demo/jvm/EmptyClass.class
Last modified 2020-3-23; size 297 bytes
MD5 checksum a2e3e21cc6e7c6b5d8035663b369a23c
Compiled from "EmptyClass.java"
public class com.example.demo.jvm.EmptyClass
minor version: 0
major version: 52
flags: ACC_PUBLIC, ACC_SUPER
Constant pool:
#1 = Methodref #3.#13 // java/lang/Object."<init>":()V
#2 = Class #14 // com/example/demo/jvm/EmptyClass
#3 = Class #15 // java/lang/Object
#4 = Utf8 <init>
#5 = Utf8 ()V
#6 = Utf8 Code
#7 = Utf8 LineNumberTable
#8 = Utf8 LocalVariableTable
#9 = Utf8 this
#10 = Utf8 Lcom/example/demo/jvm/EmptyClass;
#11 = Utf8 SourceFile
#12 = Utf8 EmptyClass.java
#13 = NameAndType #4:#5 // "<init>":()V
#14 = Utf8 com/example/demo/jvm/EmptyClass
#15 = Utf8 java/lang/Object
{
public com.example.demo.jvm.EmptyClass();
descriptor: ()V
flags: ACC_PUBLIC
Code:
stack=1, locals=1, args_size=1
0: aload_0
1: invokespecial #1 // Method java/lang/Object."<init>":()V
4: return
LineNumberTable:
line 7: 0
LocalVariableTable:
Start Length Slot Name Signature
0 5 0 this Lcom/example/demo/jvm/EmptyClass;
}
SourceFile: "EmptyClass.java"
- JBE, you can view and modify
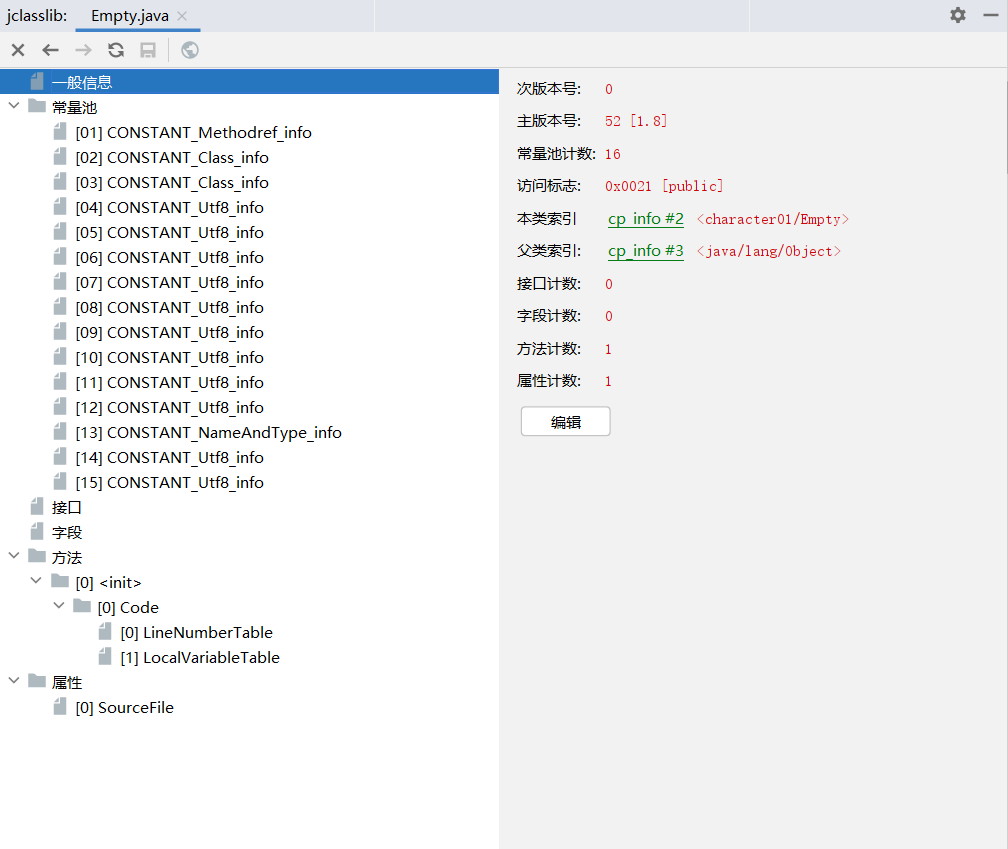
- Jclasslib bytecode viewer, a plug-in of idea, is convenient and easy to use
Install plug-ins
Place the cursor in the class body
Click View - > show bytecode with jclasslib
In the Java language specification, it is specified that the read and write operations of long and double should be atomic.