1, Environment preparation: MiniKube+Docker:
Recently, I began to try to learn and understand k8s, and the purpose of writing this article is to make a record,
Learn through exploration. Welcome to visit and exchange.
1. Install Docker:
Continue the simple packaged deployment series with IDEA+Docker
2. Install the MiniKube:
2, Preparation:
Create yaml file:
vi deployment.yaml
Configuration content:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment # Configuration type
metadata:
name: getway-server # Project name to deploy
labels:
app: getway-app # Item label
spec: # Specification parameters
# replicas: 2 # Indicates a Pod with two docker demos
selector:
matchLabels:
app: getway-app
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: getway-app
spec:
containers:
- name: getway # Container name
# image: getway:v1.0 # Image name:tag # Local warehouse
image: registry.cn-chengdu.aliyuncs.com/xx/xx:getway-v1.0 # Remote warehouse
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent #Never only uses local images. Always downloads images every time, IfNotPresent Give priority to using local instead of downloading
ports:
- containerPort: 3010 # Container port
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service # Configuration type
metadata:
name: getway-service # Name of the service
# namespace: demo # Namespace kubectl create namespace demo
spec: # Specification parameters
ports:
- port: 3010 # Cluster internal access Service port number
protocol: TCP
# nodePort: 30001 # Cluster external access Service port number
targetPort: 3010 # Pod port number
type: LoadBalancer # Four types: LoadBalance, ExternalName, NodePort and ClusterIP
selector:
app: getway-app # The name of the Pod managed by the Server
The image used in k8s deployment can be a local image or a remote image pulled from the image warehouse.
- Use local image: after packaging the image, you need to push the image to the Docker registry of Minikube; (Minikube is a stand-alone version k8s. If the cluster does not recommend using local image, it is inconvenient to ensure that each node must have this image.)
- Use remote warehouse: for example, alicloud image warehouse. Remote image warehouse is divided into public image and private image. If you use private images, you also need to configure ca certificates in the k8s cluster. You do not need to use a public image.
The following are two ways of using local image and remote public image
1. Use local image:
Save the target image locally first
docker save [REPOSITORY]:[TAG] > xx.tar
Docker registry of Minikube (can be understood as k8s internal docker)
eval $(minikube docker-env)
Load docker mirrored to k8s internal
docker load < xx.tar
Configuration of local image in yaml file
containers:
- name: getway # Container name
image: getway:v1.0 # Image name:tag # Local warehouse
#image: registry.cn-chengdu.aliyuncs.com/xx/xx:getway-v1.0 # Remote warehouse
imagePullPolicy: Never #Never only uses the local image. Always downloads the image every time. IfNotPresent gives priority to using the local image instead of downloading it
ports:
- containerPort: 3010 # Container port
2. Use image warehouse:
Configuration of remote warehouse image in yaml
containers:
- name: getway # Container name
# image: getway:v1.0 # Image name:tag # Local warehouse
image: registry.cn-chengdu.aliyuncs.com/xx/xx:getway-v1.0 # Remote warehouse
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent #Never only uses the local image. Always downloads the image every time. IfNotPresent gives priority to the local image and does not download it again
ports:
- containerPort: 3010 # Container port
3, Start:
Execution profile
kubectl apply -f vi deployment.yaml
Check the operation of Pod
kubectl get pod -o wide
Or use the dashboard that comes with Minikube to execute the command
minikube dashboard
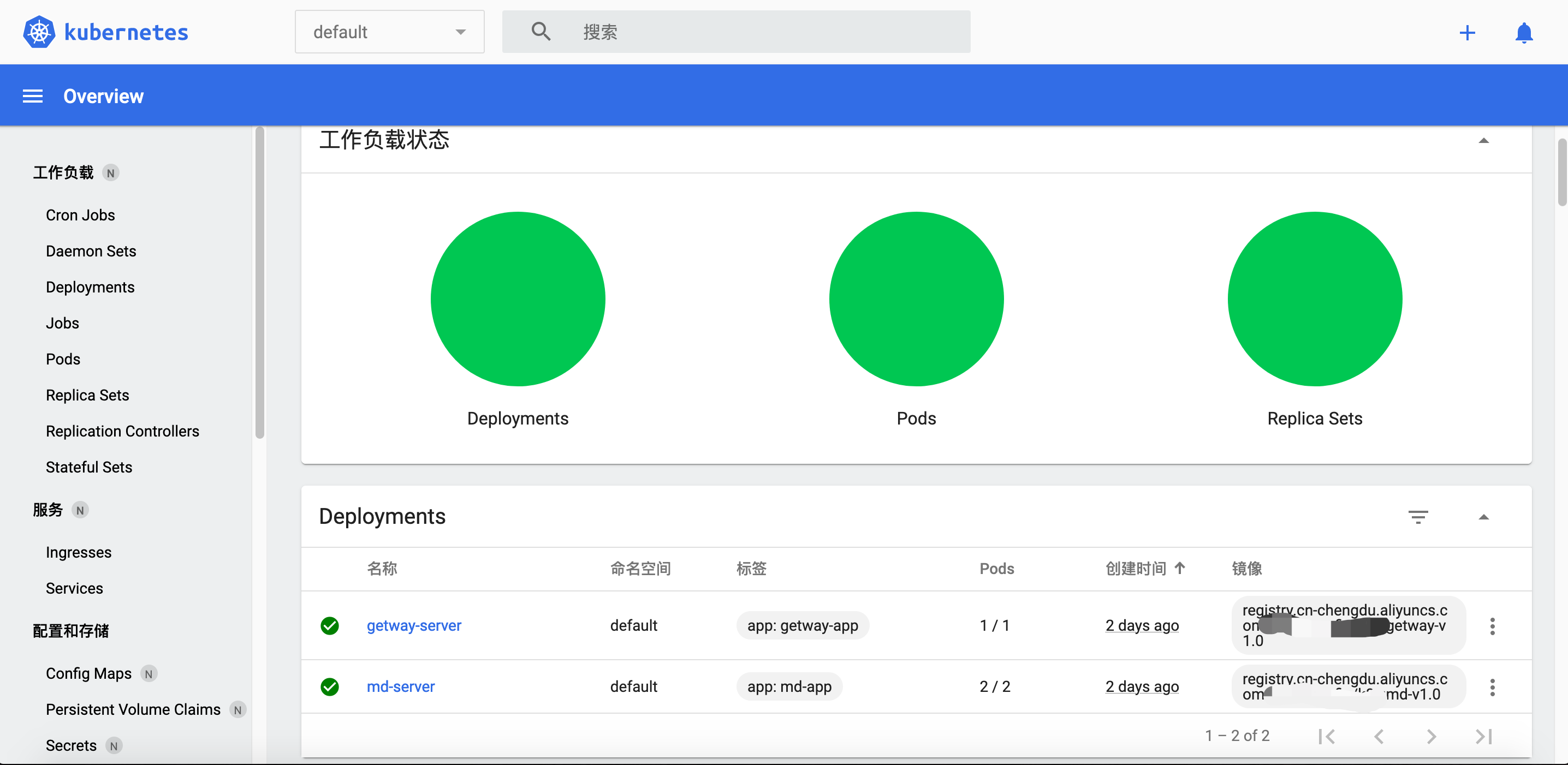
4, Test:
- View all services
kubectl get svc
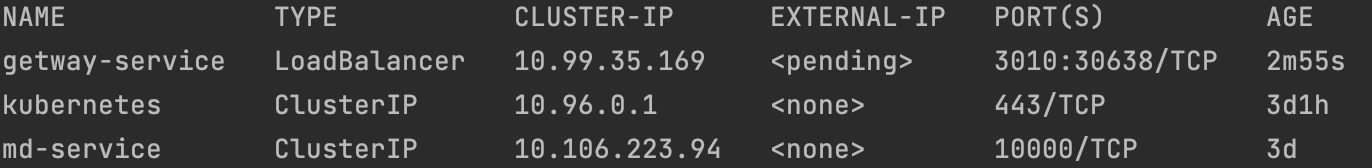
2. Temporary opening to the outside world
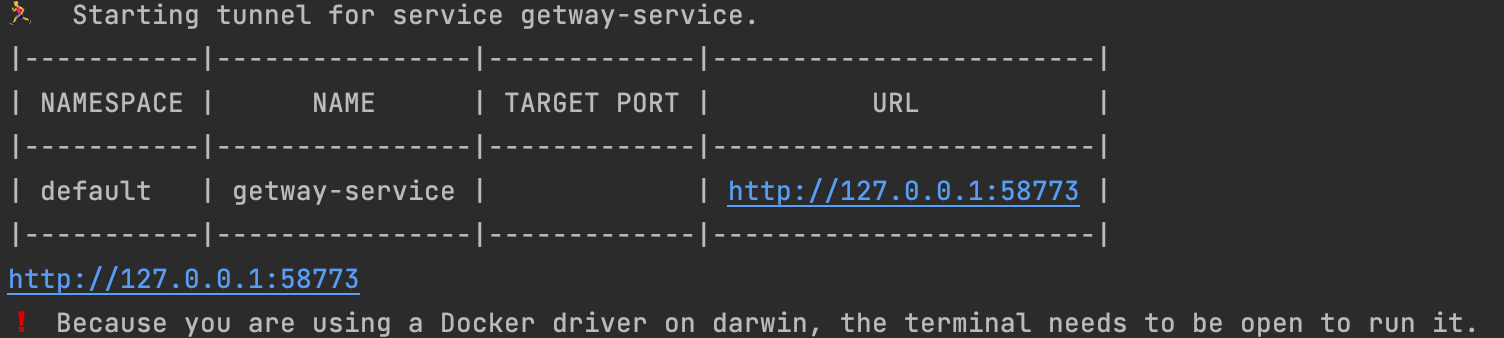
minikube service getway-service --url
After the command is executed, k8s a random port number will be temporarily opened for external access. A wave of tests can be performed using the following URL.
5, Several ways to expose services:
Several ways of k8s external exposure services:
1. ClusterIp:
The private ip inside the cluster is very convenient to access services inside the cluster. It is the default mode of kuberentes cluster, but it is inaccessible outside the cluster.
2. NodePort:
To enable the external to directly access the service, you need to modify the service type to nodePort, specify nodePort, and map the service listening port to the node node.
(nodePort port range: 30000-32767)
spec: # Specification parameters
ports:
- port: 3010 # Cluster internal access Service port number
protocol: TCP
nodePort: 30001 # Cluster external access Service port number
targetPort: 3010 # Pod port number
type: NodePort # Four types: LoadBalance, ExternalName, NodePort and ClusterIP
selector:
app: getway-app # The name of the Pod managed by the Server
3. LoadBalance:
ports:
- port: 3010 #Cluster internal access Service port number
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 3010 # Pod port number
type: LoadBalancer # Four types: LoadBalance, ExternalName, NodePort and ClusterIP
During the above test, check all Services, and you can see that the EXTERNAL-IP of the Getway service is in the state. Then execute the following command.
minikube tunnel
At this time, the dashborad view Service has exposed the IP:Port required for external access
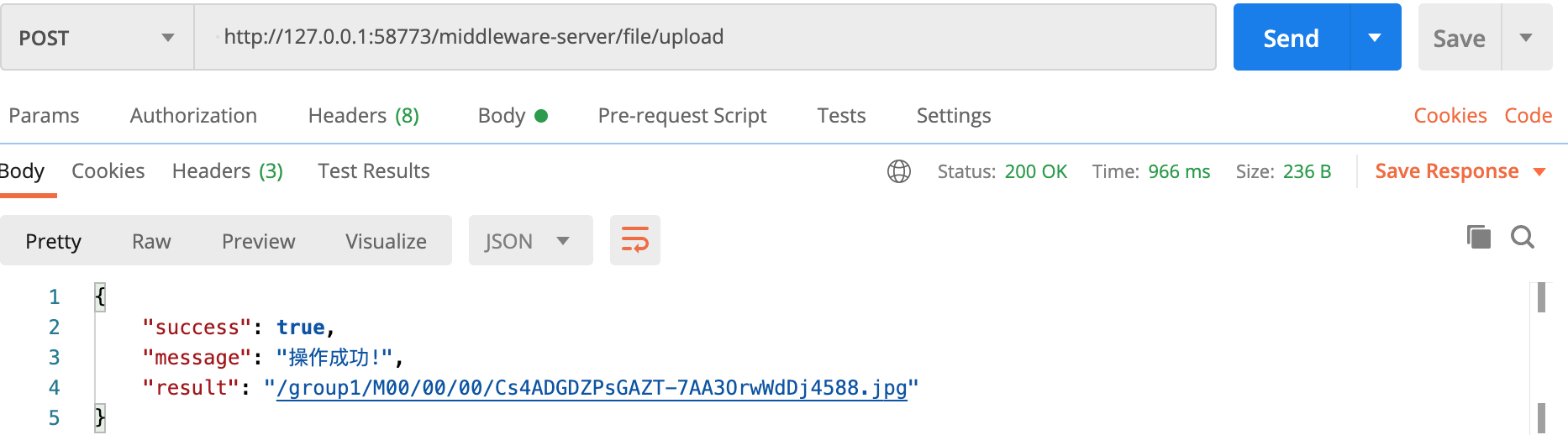
 Test with PostMan:
Test with PostMan:
4. Ingress:
Friendship connection between Ingress and Ingress Controller