1. Kafka concept
Kafka is a distributed message system with high throughput. It is similar to HDFS, which is used to store data. However, HDFS is persistent and file data will be retained all the time. Kafka only stores data for a period of time and will be automatically deleted if it is not consumed for a long time. At the same time, the storage adopts zero copy technology, which can eliminate the need to consume resources in memory
2. kafka architecture
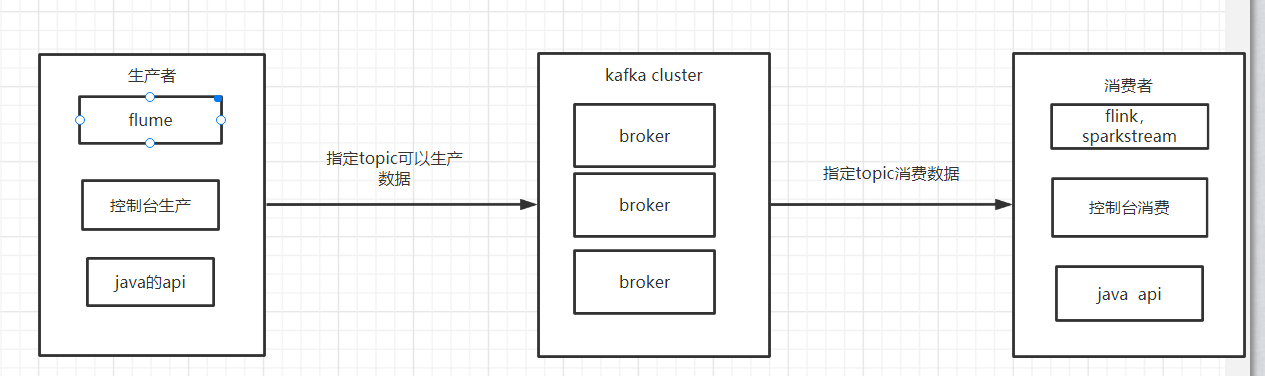
1. broker: the server of Kafka cluster, which can be responsible for processing read-write messages and storing them. Multiple brokers make use of the cooperative service of zookeeper, and can backup data distributed
2. topic:topic is equivalent to message queue, which is also in K-V format in essence. But in fact, each topic can be divided into multiple partitions, and each partition is equivalent to a small file. A partition corresponds to a broker, and a broker can manage multiple partitions
3. Partition: the messages inside each partition are provided with sequence number offset and are sorted, so that there is no need to start over when reading and writing errors. The producer can also customize which partition to write to when carrying out production data. To achieve load balancing, it is similar to the hashcode based partition operation in the shuffle stage
4. The intermediate message adopts zero copy technology. The data does not need to be copied in memory, which consumes resources, greatly speeds up the speed, and the writing to the disk is sequential. Common zero copy technologies: sendfile() in Linux and filechannel. In java NIO transferTo()
5. The stored data is deleted according to the specified or default policy for a period of time, not after consumption
3. Kafka consumption model
1. Consumers need to consume the data in kafka cluster, so every consumer needs to maintain the offset to which they consume
2. Each consumer has its own corresponding group. Within the group is the consumption model in the message queue. Each group consumes independently and does not affect each other. At the same time, each consumer consumes different partition s. Therefore, a message is consumed only once in the group
4. Realize the production end of Kafka
package com.dtc.bigdata.kafka;
import java.util.Properties;
import org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.ProducerRecord;
public class KafkaProducer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Properties properties = new Properties();
//Specify the address of kafka's broker
properties.setProperty("bootstrap.servers","master2:9092");
//If the serialization of key and value is set, the "key.serializer" error will be reported
properties.setProperty("key.serializer", "org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer");
properties.setProperty("value.serializer", "org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer");
//Create producer
org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.KafkaProducer<String, String> producer = new org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.KafkaProducer<>(properties);
//Pass in the value of topic
//If the topic value does not exist, a topic with partition 1 and copy 1 will be automatically created
ProducerRecord<String, String> producerRecord = new ProducerRecord<>("zhenyun", "zyliyuiyuizylzyl");
producer.send(producerRecord);
producer.flush();
producer.close();
}
}
5. Realize Kafka's consumer end
package com.dtc.bigdata.kafka;
import org.apache.kafka.clients.consumer.ConsumerRecord;
import org.apache.kafka.clients.consumer.ConsumerRecords;
import org.apache.kafka.clients.consumer.KafkaConsumer;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Properties;
public class KafakaComsumer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.setProperty("bootstrap.servers", "master2:9092");
//Deserialization
properties.setProperty("key.deserializer", "org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringDeserializer");
properties.setProperty("value.deserializer", "org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringDeserializer");
//Add group
properties.setProperty("group.id", "aaaa");
//Show initial data
properties.put("auto.offset.reset", "earliest");
//Create consumer
KafkaConsumer<String, String> consumer = new KafkaConsumer<>(properties);
System.out.println("Consumer created successfully");
//Subscribe to topic
ArrayList<String> topics = new ArrayList<>();
topics.add("zhenyun");
consumer.subscribe(topics);
while (true) {
ConsumerRecords<String, String> poll = consumer.poll(1000);
Iterator<ConsumerRecord<String, String>> it = poll.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
ConsumerRecord<String, String> consumerRecord = it.next();
//Take topic, partition, offset and value respectively
String topic = consumerRecord.topic();
int partition = consumerRecord.partition();
long offset = consumerRecord.offset();
String value = consumerRecord.value();
System.out.println(topic + "," + partition + "," + offset + "," + value);
}
}
}
}
6. Flume integrates Kafka
1. Adjust the configuration file of flume and monitor the log file of namenode
agent.sources=s1 agent.channels=c1 agent.sinks=k1 agent.sources.s1.type=exec #Listening file address agent.sources.s1.command=tail -F /usr/local/soft/hadoop-2.7.6/logs/hadoop-root-namenode-master.log agent.channels.c1.type=memory agent.channels.c1.capacity=10000 agent.channels.c1.transactionCapacity=100 #Set up Kafka receiver agent.sinks.k1.type=org.apache.flume.sink.kafka.KafkaSink #Set the broker address and port number of Kafka agent.sinks.k1.brokerList=master:9092,node1:9092,node2:9092 #Set the topic of Kafka. If the topic does not exist, a topic will be created automatically. The default partition is 1 and the copy is 1 agent.sinks.k1.topic=hadoop-namenode-log #Set serialization mode agent.sinks.k1.serializer.class=kafka.serializer.StringEncoder #Connect the three main parts in series agent.sources.s1.channels=c1 agent.sinks.k1.channel=c1 #flume-ng agent -n agent -f ./FlumeToKafka.properties -Dflume.root.logger=DEBUG,console #kafka-console-consumer.sh --zookeeper node1:2181 --from-beginning --topic flume
2. Start flume
flume-ng agent -n agent -f ./FlumeToKafka.properties -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
3. Launch kafka console to view data for consumers
kafka-console-consumer.sh --bootstrap-server master2:9092, --from-beginning --topic flume