The original connection of this paper is:
https://blog.csdn.net/freewebsys/article/details/83618119
The blogger's address is: http://blog.csdn.net/freewebsys
1. About kube video
The first section is shared by foreigners. I'm too lazy to listen to English.
Look straight from the second section. Chinese is still comfortable to listen to.
https://www.kubernetes.org.cn/3546.html/2
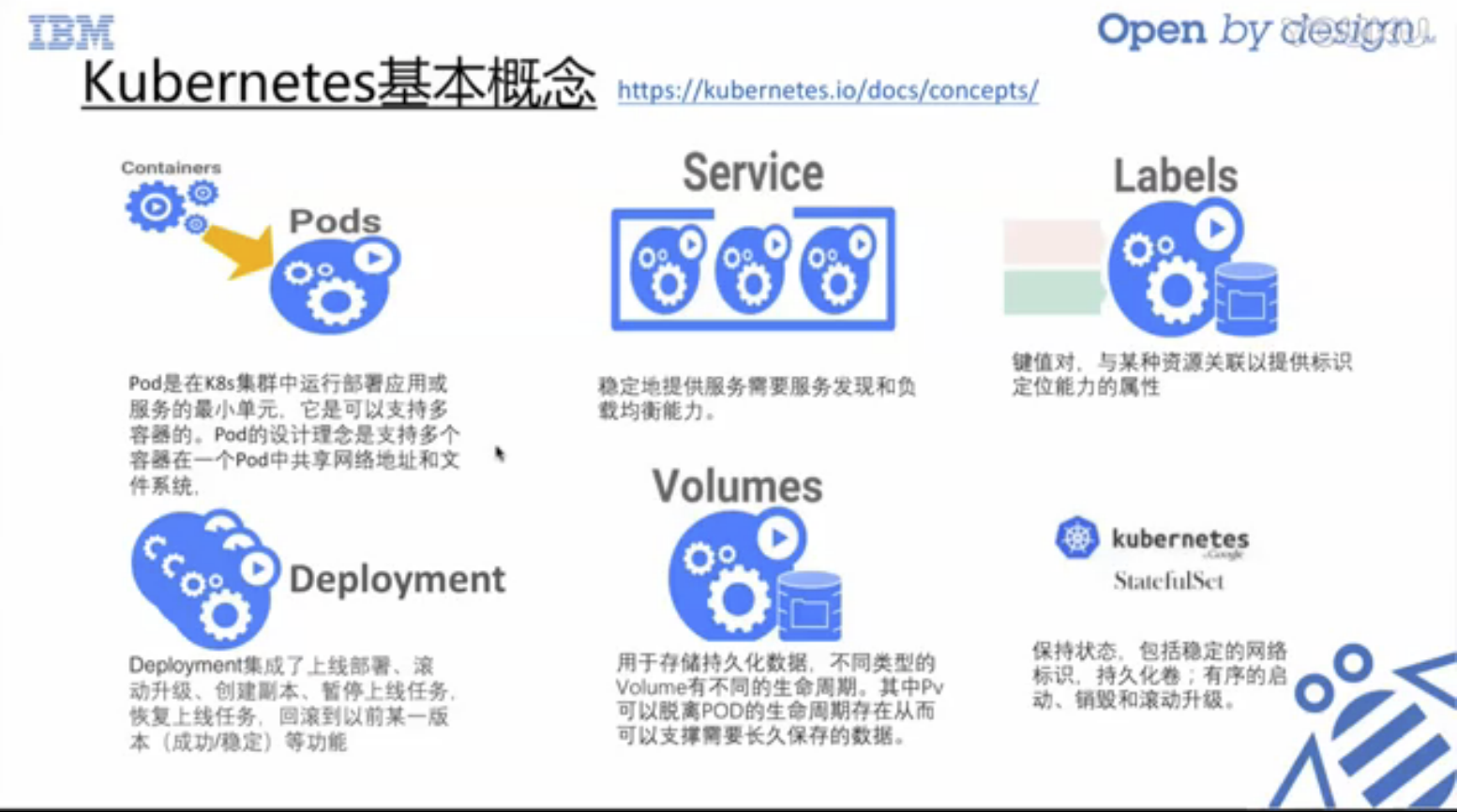
Of course, IBM launched this learning course to promote its products.
IBM ® Cloud Private private cloud system:
https://www.ibm.com/support/knowledgecenter/en/SSBS6K/product_welcome_cloud_private.html
The latest is 3.1.0, which is also a simple way to deploy kubernetes.
The installation of minikube
https://kubernetes.cn/docs/tasks/tools/install-minikube/
Of course, you can also directly use the gui of docker for installation. It's very convenient now.
Reference article:
https://blog.csdn.net/freewebsys/article/details/83536077
2. Use command
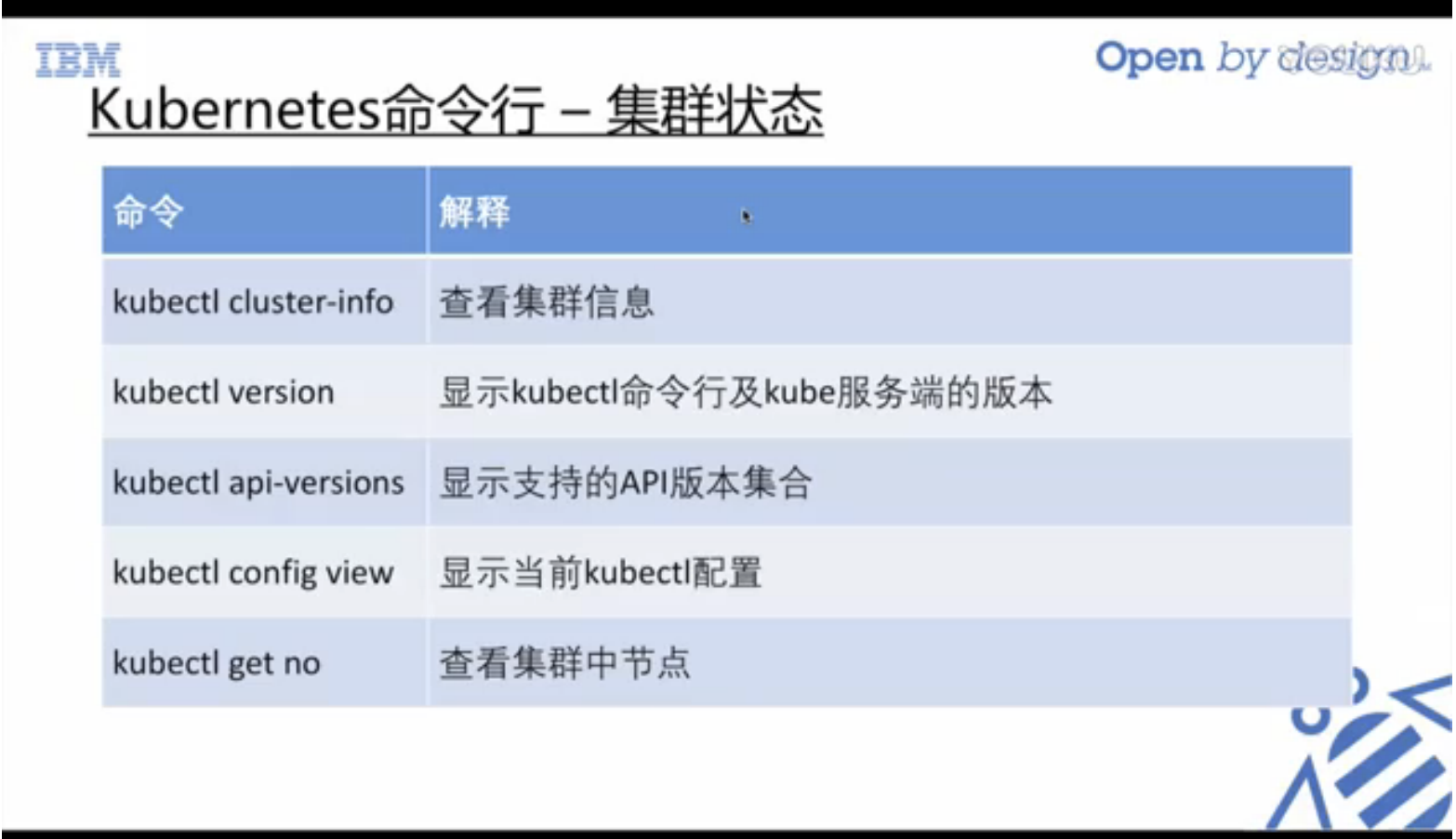
$ kubectl -n kube-system get pods -o wide NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE etcd-docker-for-desktop 1/1 Running 1 13d 192.168.65.3 docker-for-desktop kube-apiserver-docker-for-desktop 1/1 Running 1 13d 192.168.65.3 docker-for-desktop kube-controller-manager-docker-for-desktop 1/1 Running 1 13d 192.168.65.3 docker-for-desktop kube-dns-86f4d74b45-m9tw8 3/3 Running 0 13d 10.1.0.5 docker-for-desktop kube-proxy-jqblr 1/1 Running 0 13d 192.168.65.3 docker-for-desktop kube-scheduler-docker-for-desktop 1/1 Running 1 13d 192.168.65.3 docker-for-desktop kubernetes-dashboard-7b9c7bc8c9-xpvzw 1/1 Running 0 1d 10.1.0.6 docker-for-desktop
View cluster
$ kubectl cluster-info Kubernetes master is running at https://localhost:6443 KubeDNS is running at https://localhost:6443/api/v1/namespaces/kube-system/services/kube-dns:dns/proxy
$ kubectl version
Client Version: version.Info{Major:"1", Minor:"10", GitVersion:"v1.10.3", GitCommit:"2bba0127d85d5a46ab4b778548be28623b32d0b0", GitTreeState:"clean", BuildDate:"2018-05-21T09:17:39Z", GoVersion:"go1.9.3", Compiler:"gc", Platform:"darwin/amd64"}
Server Version: version.Info{Major:"1", Minor:"10", GitVersion:"v1.10.3", GitCommit:"2bba0127d85d5a46ab4b778548be28623b32d0b0", GitTreeState:"clean", BuildDate:"2018-05-21T09:05:37Z", GoVersion:"go1.9.3", Compiler:"gc", Platform:"linux/amd64"}
$ kubectl api-versions
admissionregistration.k8s.io/v1beta1
apiextensions.k8s.io/v1beta1
apiregistration.k8s.io/v1
apiregistration.k8s.io/v1beta1
apps/v1
apps/v1beta1
apps/v1beta2
authentication.k8s.io/v1
authentication.k8s.io/v1beta1
authorization.k8s.io/v1
authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1
autoscaling/v1
autoscaling/v2beta1
batch/v1
batch/v1beta1
certificates.k8s.io/v1beta1
compose.docker.com/v1beta1
compose.docker.com/v1beta2
events.k8s.io/v1beta1
extensions/v1beta1
networking.k8s.io/v1
policy/v1beta1
rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1
storage.k8s.io/v1
storage.k8s.io/v1beta1
v1
$ kubectl get no
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
docker-for-desktop Ready master 14d v1.10.3
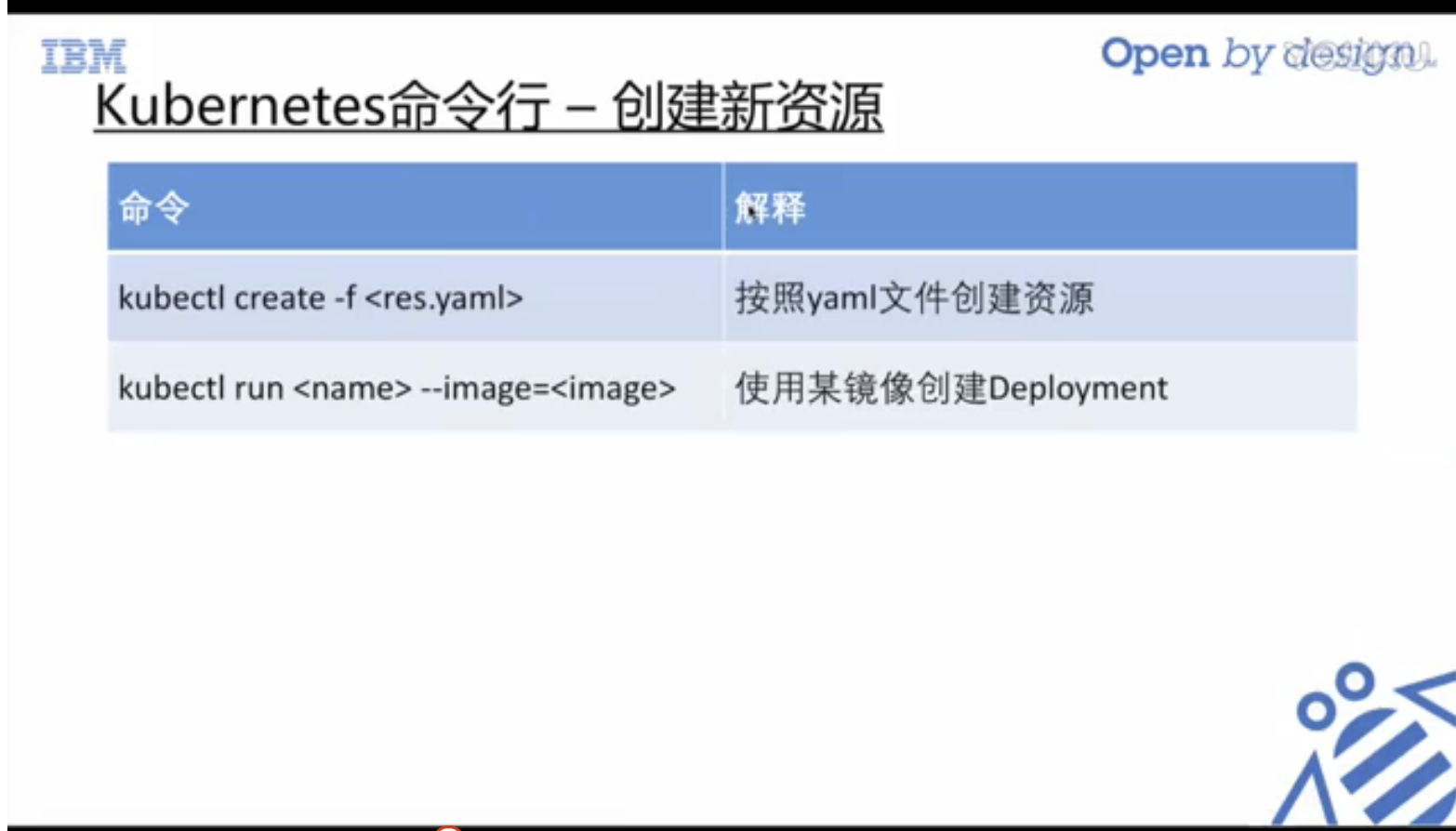

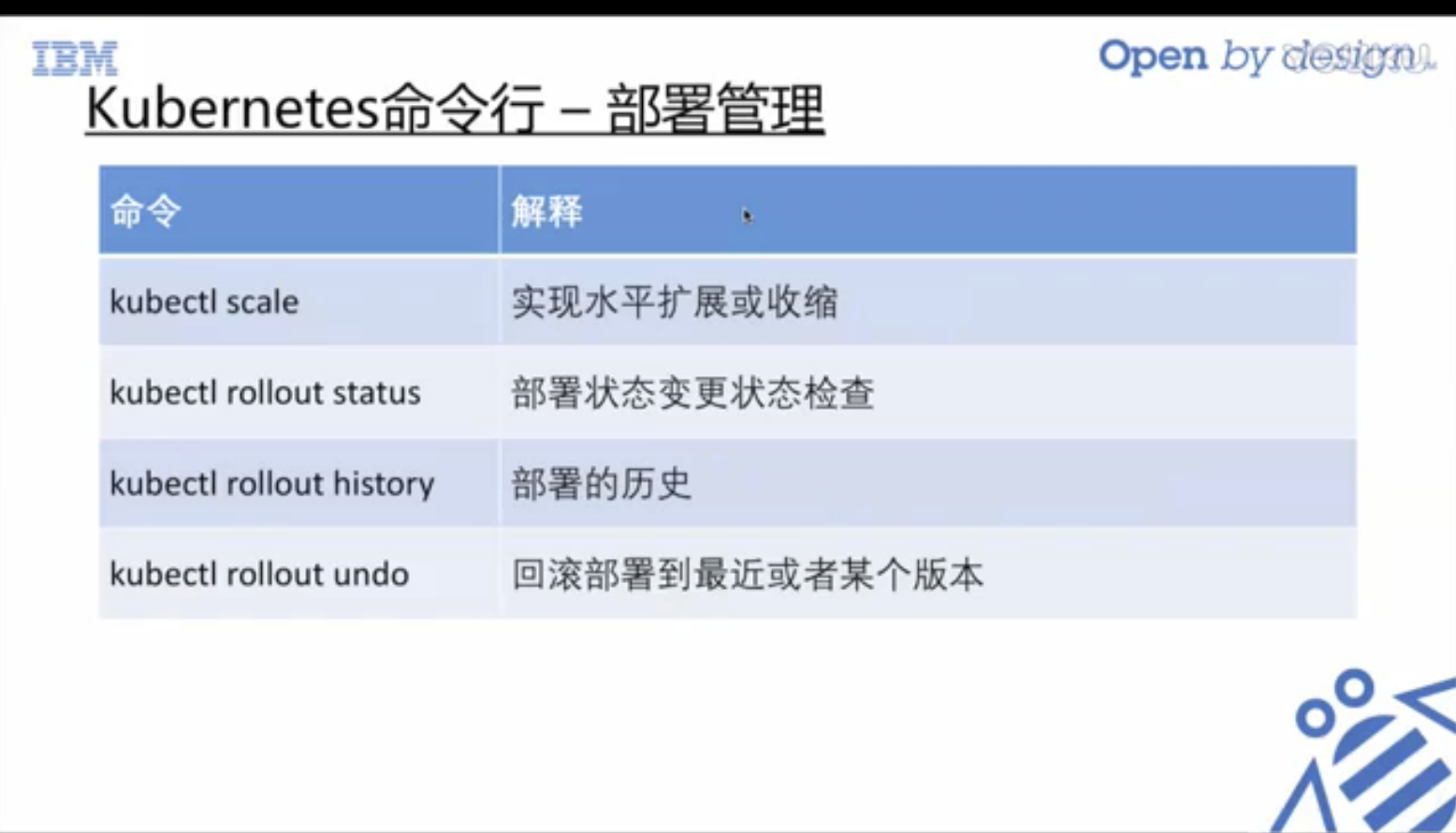
Learning various commands is the foundation.
$ kubectl run nginx --image=nginx:alpine
deployment.apps "nginx" created
$ kubectl get deploy
NAME DESIRED CURRENT UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
nginx 1 1 1 1 21s
$ kubectl describe deploy nginx
Name: nginx
Namespace: default
CreationTimestamp: Thu, 01 Nov 2018 14:42:22 +0800
Labels: run=nginx
Annotations: deployment.kubernetes.io/revision=1
Selector: run=nginx
Replicas: 1 desired | 1 updated | 1 total | 1 available | 0 unavailable
StrategyType: RollingUpdate
MinReadySeconds: 0
RollingUpdateStrategy: 1 max unavailable, 1 max surge
Pod Template:
Labels: run=nginx
Containers:
nginx:
Image: nginx:alpine
Port: <none>
Host Port: <none>
Environment: <none>
Mounts: <none>
Volumes: <none>
Conditions:
Type Status Reason
---- ------ ------
Available True MinimumReplicasAvailable
Progressing True NewReplicaSetAvailable
OldReplicaSets: <none>
NewReplicaSet: nginx-6fc74ccb78 (1/1 replicas created)
Events:
Type Reason Age From Message
---- ------ ---- ---- -------
Normal ScalingReplicaSet 6m deployment-controller Scaled up replica set nginx-6fc74ccb78 to 1
$ kubectl get pod -o wide
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE
nginx-6fc74ccb78-xcgps 1/1 Running 0 19m 10.1.0.7 docker-for-desktop
$ kubectl logs nginx-6fc74ccb78-xcgps
$ kubectl exec -it nginx-6fc74ccb78-xcgps sh
/ # ifconfig
eth0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr E6:F0:2A:8A:33:53
inet addr:10.1.0.7 Bcast:0.0.0.0 Mask:255.255.0.0
UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
RX packets:15 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:1 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:0
RX bytes:1110 (1.0 KiB) TX bytes:42 (42.0 B)
lo Link encap:Local Loopback
inet addr:127.0.0.1 Mask:255.0.0.0
UP LOOPBACK RUNNING MTU:65536 Metric:1
RX packets:0 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:0 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:1
RX bytes:0 (0.0 B) TX bytes:0 (0.0 B)
/ # nginx -v
nginx version: nginx/1.15.5
/ # exit
Create service:
nginx.svc.yaml:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: nginx
spec:
ports:
- name: http
port: 8888
nodePort: 30001
targetPort: 80
selector:
run: nginx
type: NodePort
$ kubectl create -f nginx.svc.yaml service "nginx" created $ kubectl get svc NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE kubernetes ClusterIP 10.96.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 14d nginx NodePort 10.104.36.202 <none> 8888:30001/TCP 21s $ kubectl get ep NAME ENDPOINTS AGE kubernetes 192.168.65.3:6443 14d nginx 10.1.0.7:80 4m $ kubectl scale deploy nginx --replicas=3 deployment.extensions "nginx" scaled $ kubectl get rs NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE nginx-6fc74ccb78 3 3 3 34m $ kubectl get pods NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE nginx-6fc74ccb78-jqpd5 1/1 Running 0 31s nginx-6fc74ccb78-tzwb2 1/1 Running 0 31s nginx-6fc74ccb78-xcgps 1/1 Running 0 34m $ kubectl rollout history deploy deployments "nginx" REVISION CHANGE-CAUSE 1 <none> $ kubectl describe deploy nginx Name: nginx Namespace: default CreationTimestamp: Thu, 01 Nov 2018 14:42:22 +0800 Labels: run=nginx Annotations: deployment.kubernetes.io/revision=1 Selector: run=nginx Replicas: 3 desired | 3 updated | 3 total | 3 available | 0 unavailable StrategyType: RollingUpdate MinReadySeconds: 0 RollingUpdateStrategy: 1 max unavailable, 1 max surge
4, summarize
The most important thing is to learn the kubectl command skillfully.
Similar to the docker command, add parameters to view the cluster.
It is very convenient for container management, view, expansion, operation and maintenance.
At the same time, the operations on the dashboard are similar to those on the direct access api.
It's just visual. I use the default kubernetes of docker instead of minikube, which is the same operation.
Chinese document:
https://k8smeetup.github.io/docs/home/
Now kubernetes has a lot of documents. It's also very convenient to learn.
The original connection of this paper is:
https://blog.csdn.net/freewebsys/article/details/83618119
The blogger's address is: http://blog.csdn.net/freewebsys
