Previous review
To deploy a k8s multi node, you must first deploy a k8s cluster with a single master node For details, please refer to:
blog.csdn.net/caozhengtao1213/article/details/103987039
Content of this article
1. Deploy Master2
2.Nginx load balancing deployment keepalived service
3.node node modify configuration file unified VIP
4. create Pod
5. Create UI display interface
Environmental preparation
| role | address | Installation components |
|---|---|---|
| master | 192.168.142.129 | kube-apiserver kube-controller-manager kube-scheduler etcd |
| master2 | 192.168.142.120 | kube-apiserver kube-controller-manager kube-scheduler |
| node1 | 192.168.142.130 | kubelet kube-proxy docker flannel etcd |
| node2 | 192.168.142.131 | kubelet kube-proxy docker flannel etcd |
| nginx1(lbm) | 192.168.142.140 | nginx keepalived |
| nginx2(lbb) | 192.168.142.150 | nginx keepalived |
| VIP | 192.168.142.20 | - |
1, Deploy Master2
1. Remote replication master related directory
- Turn off firewall and security functions
systemctl stop firewalld.service setenforce 0
- Copy kubernetes directory to master2
scp -r /opt/kubernetes/ root@192.168.142.120:/opt
- Copy etcd directory to master2 (with certificate)
scp -r /opt/etcd/ root@192.168.142.120:/opt
- Copy service startup script to master2
scp /usr/lib/systemd/system/{kube-apiserver,kube-controller-manager,kube-scheduler}.service root@192.168.142.120:/usr/lib/systemd/system/
2. Modify the Kube API server configuration file
vim /opt/kubernetes/cfg/kube-apiserver #Change the IP address of lines 5 and 7 to the address of the master 2 host --bind-address=192.168.142.120 \ --advertise-address=192.168.142.120 \
3. Start the service and set the start-up mode
systemctl start kube-apiserver.service systemctl enable kube-apiserver.service systemctl start kube-controller-manager.service systemctl enable kube-controller-manager.service systemctl start kube-scheduler.service systemctl enable kube-scheduler.service
4. Add environment variables and take effect
vim /etc/profile #Append at the end export PATH=$PATH:/opt/kubernetes/bin/ source /etc/profile
5. View node
kubectl get node
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION 192.168.142.130 Ready <none> 10d12h v1.12.3 192.168.142.131 Ready <none> 10d11h v1.12.3
2, Nginx load balancing deployment keepalived service
1. Operation at LBM & LBB end, installation of nginx service
- Copy the nginx.sh and preserved.conf scripts to the home directory (to be used later)
#nginx.sh
cat > /etc/yum.repos.d/nginx.repo << EOF
[nginx]
name=nginx repo
baseurl=http://nginx.org/packages/centos/7/$basearch/
gpgcheck=0
EOF
stream {
log_format main '$remote_addr $upstream_addr - [$time_local] $status $upstream_bytes_sent';
access_log /var/log/nginx/k8s-access.log main;
upstream k8s-apiserver {
server 10.0.0.3:6443;
server 10.0.0.8:6443;
}
server {
listen 6443;
proxy_pass k8s-apiserver;
}
}
#keepalived.conf
! Configuration File for keepalived
global_defs {
# Receiving email address
notification_email {
acassen@firewall.loc
failover@firewall.loc
sysadmin@firewall.loc
}
# Mailing address
notification_email_from Alexandre.Cassen@firewall.loc
smtp_server 127.0.0.1
smtp_connect_timeout 30
router_id NGINX_MASTER
}
vrrp_script check_nginx {
script "/usr/local/nginx/sbin/check_nginx.sh"
}
vrrp_instance VI_1 {
state MASTER
interface eth0
virtual_router_id 51 # VRRP route ID instance, each instance is unique
priority 100 # Priority, standby server setting 90
advert_int 1 # Specifies the notification interval of VRRP heartbeat package, 1 second by default
authentication {
auth_type PASS
auth_pass 1111
}
virtual_ipaddress {
10.0.0.188/24
}
track_script {
check_nginx
}
}
mkdir /usr/local/nginx/sbin/ -p
vim /usr/local/nginx/sbin/check_nginx.sh
count=$(ps -ef |grep nginx |egrep -cv "grep|$$")
if [ "$count" -eq 0 ];then
/etc/init.d/keepalived stop
fi
chmod +x /usr/local/nginx/sbin/check_nginx.sh
- Edit nginx.repo file
vim /etc/yum.repos.d/nginx.repo [nginx] name=nginx repo baseurl=http://nginx.org/packages/centos/7/$basearch/ gpgcheck=0
- Install nginx service
yum install nginx -y
- Add layer 4 forwarding
vim /etc/nginx/nginx.conf #Add the following under line 12 stream { log_format main '$remote_addr $upstream_addr - [$time_local] $status $upstream_bytes_sent'; access_log /var/log/nginx/k8s-access.log main; upstream k8s-apiserver { server 192.168.142.129:6443; #Here is the ip address of the master server 192.168.142.120:6443; #Here is the ip address of master2 } server { listen 6443; proxy_pass k8s-apiserver; } }
2. Deploy keepalived service
#Install keepalived yum install keepalived -y //Copy the previous keepalived.conf configuration file, and overwrite the original configuration file after installation cp keepalived.conf /etc/keepalived/keepalived.conf vim /etc/keepalived/keepalived.conf script "/etc/nginx/check_nginx.sh" #Line 18, change the directory to / etc/nginx /, write after the script interface ens33 #Line 23, eth0 is changed to ens33, where the network card name can be queried with ifconfig command virtual_router_id 51 #24 lines, vrrp route ID instance, each instance is unique priority 100 #25 lines, priority, standby server setting 90 virtual_ipaddress { #The 31 element, 192.168.142.20/24 #32 lines, change the vip address to 192.168.142.20 set before #38 delete all lines below vim /etc/nginx/check_nginx.sh #Statistical quantity count=$(ps -ef |grep nginx |egrep -cv "grep|$$") #Statistical quantity #Match to 0, shut down the keepalived service if [ "$count" -eq 0 ];then systemctl stop keepalived fi chmod +x /etc/nginx/check_nginx.sh #Startup service systemctl start keepalived
- View address information
ip a
# lbm address information
2: ens33: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state UP qlen 1000
link/ether 00:0c:29:eb:11:2a brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 192.168.142.140/24 brd 192.168.142.255 scope global ens33
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet 192.168.142.20/24 scope global secondary ens33 //Drift address in lb01
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 fe80::53ba:daab:3e22:e711/64 scope link
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
#lbb address information
2: ens33: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state UP qlen 1000
link/ether 00:0c:29:c9:9d:88 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 192.168.142.150/24 brd 192.168.142.255 scope global ens33
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 fe80::55c0:6788:9feb:550d/64 scope link
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
- Verify address drift
#Stop nginx service on lbm side pkill nginx #View service status systemctl status nginx systemctl status keepalived.service #At this time, if the judgment condition is 0, the maintained service is stopped ps -ef |grep nginx |egrep -cv "grep|$$"
- View address information
ip a
# lbm address information
2: ens33: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state UP qlen 1000
link/ether 00:0c:29:eb:11:2a brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 192.168.142.140/24 brd 192.168.142.255 scope global ens33
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 fe80::53ba:daab:3e22:e711/64 scope link
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
#lbb address information
2: ens33: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state UP qlen 1000
link/ether 00:0c:29:c9:9d:88 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 192.168.142.150/24 brd 192.168.142.255 scope global ens33
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet 192.168.142.20/24 scope global secondary ens33 //Drift address in lb01
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 fe80::55c0:6788:9feb:550d/64 scope link
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
- Recovery operation
#Start nginx and maintained services on the lbm side
systemctl start nginx
systemctl start keepalived
- lbm end of drift address regression
ip a
# lbm address information
2: ens33: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state UP qlen 1000
link/ether 00:0c:29:eb:11:2a brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 192.168.142.140/24 brd 192.168.142.255 scope global ens33
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet 192.168.142.20/24 scope global secondary ens33 //Drift address in lb01
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 fe80::53ba:daab:3e22:e711/64 scope link
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
3, Node node modify configuration file unified VIP (bootstrap.kubeconfig,kubelet.kubeconfig)
cd /opt/kubernetes/cfg/ #Change the profile to VIP vim /opt/kubernetes/cfg/bootstrap.kubeconfig server: https://192.168.142.20:6443 #Change line 5 to the address of Vip vim /opt/kubernetes/cfg/kubelet.kubeconfig server: https://192.168.142.20:6443 #Change line 5 to the address of Vip vim /opt/kubernetes/cfg/kube-proxy.kubeconfig server: https://192.168.142.20:6443 #Change line 5 to the address of Vip
- Self test after replacement
grep 20 *
bootstrap.kubeconfig: server: https://192.168.142.20:6443 kubelet.kubeconfig: server: https://192.168.142.20:6443 kube-proxy.kubeconfig: server: https://192.168.142.20:6443
- View the k8s log of nginx on lb01
tail /var/log/nginx/k8s-access.log
192.168.142.140 192.168.142.129:6443 - [08/Feb/2020:19:20:40 +0800] 200 1119 192.168.142.140 192.168.142.120:6443 - [08/Feb/2020:19:20:40 +0800] 200 1119 192.168.142.150 192.168.142.129:6443 - [08/Feb/2020:19:20:44 +0800] 200 1120 192.168.142.150 192.168.142.120:6443 - [08/Feb/2020:19:20:44 +0800] 200 1120
4, Create Pod
- Test create Pod
kubectl run nginx --image=nginx
- View state
kubectl get pods
- Bind anonymous users in the cluster to give administrator permission (to solve the problem that the logs cannot be viewed)
kubectl create clusterrolebinding cluster-system-anonymous --clusterrole=cluster-admin --user=system:anonymous
- View Pod network
kubectl get pods -o wid
5, Create UI display interface
- Create dashborad working directory on master1
mkdir /k8s/dashboard cd /k8s/dashboard #Upload official documents to the directory
- Create page, pay attention to order
#Authorized access api kubectl create -f dashboard-rbac.yaml #Encrypt kubectl create -f dashboard-secret.yaml #Configuration application kubectl create -f dashboard-configmap.yaml #Controller kubectl create -f dashboard-controller.yaml #Publish for access kubectl create -f dashboard-service.yaml
- After completion, check that the creation is under the specified Kube system namespace
kubectl get pods -n kube-system
- See how to access
kubectl get pods,svc -n kube-system
- Enter the nodeIP address in the browser to access (Google browser can't access the solution)
1. Operate on the master side, write a certificate for self signing
vim dashboard-cert.sh cat > dashboard-csr.json <<EOF { "CN": "Dashboard", "hosts": [], "key": { "algo": "rsa", "size": 2048 }, "names": [ { "C": "CN", "L": "NanJing", "ST": "NanJing" } ] } EOF K8S_CA=$1 cfssl gencert -ca=$K8S_CA/ca.pem -ca-key=$K8S_CA/ca-key.pem -config=$K8S_CA/ca-config.json -profile=kubernetes dashboard-csr.json | cfssljson -bare dashboard kubectl delete secret kubernetes-dashboard-certs -n kube-system kubectl create secret generic kubernetes-dashboard-certs --from-file=./ -n kube-system
2. Reapply the new self signed certificate
bash dashboard-cert.sh /root/k8s/apiserver/
3. Modify yaml file
vim dashboard-controller.yaml #Add the following under line 47 - --tls-key-file=dashboard-key.pem - --tls-cert-file=dashboard.pem
4. Redeployment
kubectl apply -f dashboard-controller.yaml
5. Generate login token
- Generate token
kubectl create -f k8s-admin.yaml
- Save token
kubectl get secret -n kube-system
NAME TYPE DATA AGE dashboard-admin-token-drs7c kubernetes.io/service-account-token 3 60s default-token-mmvcg kubernetes.io/service-account-token 3 55m kubernetes-dashboard-certs Opaque 10 10m kubernetes-dashboard-key-holder Opaque 2 23m kubernetes-dashboard-token-crqvs kubernetes.io/service-account-token 3 23m
- View token
kubectl describe secret dashboard-admin-token-drs7c -n kube-system
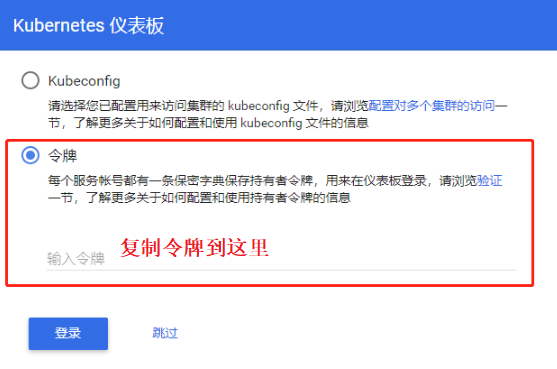
6. After copying and pasting the token, log in to the UI interface