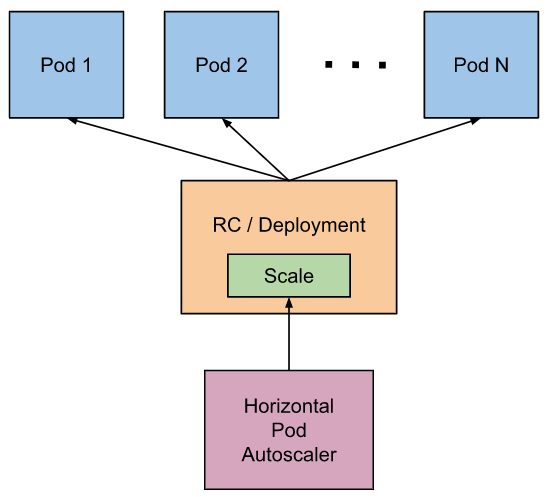
Horizontal Pod Autoscaler (HPA) can automatically scale the number of pods in ReplicationController, Deployment, ReplicaSet and StatefulSet based on CPU utilization. In addition to CPU utilization, automatic scaling can also be performed based on custom metrics provided by other applications. Pod auto scaling is not applicable to objects that cannot be scaled, such as DaemonSet.
The Pod horizontal automatic scaling feature is implemented by Kubernetes API resources and controllers. The controller periodically adjusts the number of replicas in the replica controller or Deployment so that the observed metrics such as Pod average CPU utilization and average memory utilization match the target values set by the user.
Illustration of Pod horizontal automatic expansion and contraction mechanism
Kubernetes V1.19 and metrics server are used in this paper v0.5.1 demonstrate the automatic expansion and contraction of pod horizontally.
Install metrics server v0.5.1
Metrics Server is the source of Kubernetes built-in auto scaling container resource metrics. The Metrics Server collects resource metrics from Kubelets and exposes them to Kubernetes apiserver through the Metrics API for use by Horizontal Pod Autoscaler.
1. Download the metrics server v0.5.1 deployment file. Note that metrics server requires the version of Kubernetes. See GitHub description of metrics server
wget https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/metrics-server/releases/download/v0.5.1/components.yaml
2. The image used by metrics server is in Google's warehouse, which cannot be downloaded in the mainland. You can change the warehouse to Alibaba cloud warehouse. If the cluster is built locally and there is no certificate, you need to add -- kubelet secure TLS configuration.
Modify components.yaml
Change k8s.gcr.io/metrics-server/metrics-server:v0.5.1 to registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/google_containers/metrics-server:v0.5.1
Add -- kubelet secure TLS configuration
spec:
containers:
- args:
- --cert-dir=/tmp
- --secure-port=443
- --kubelet-preferred-address-types=InternalIP,ExternalIP,Hostname
- --kubelet-use-node-status-port
- --metric-resolution=15s
# Add -- kubelet secure TLS configuration
- --kubelet-insecure-tls
3. Deploying metrics server
Deployment command: kubectl apply -f components.yaml
Check whether the deployment is successful: kubectl get Pods - n Kube system

Horizontal Pod Autoscaler horizontal autoscaler demonstration
Automatic scaling based on CPU utilization
Use the official HPA example image walkthrough, which defines a index.php page to perform CPU intensive computing
<?php
$x = 0.0001;
for ($i = 0; $i <= 1000000; $i++) {
$x += sqrt($x);
}
echo "OK!";
?>1. Write the HPA example declaration file php-apache.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: php-apache
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
run: php-apache
replicas: 1
template:
metadata:
labels:
run: php-apache
spec:
containers:
- name: php-apache
# Use mirrrogoglecontainers / HPA example to avoid being blocked by walls
image: mirrorgooglecontainers/hpa-example
ports:
- containerPort: 80
resources:
limits:
cpu: 500m
requests:
cpu: 200m
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: php-apache
labels:
run: php-apache
spec:
ports:
- port: 80
selector:
run: php-apacheDeploy PHP Apache: kubectl apply -f php-apache.yaml
Check whether PHP Apache is successfully deployed: kubectl get pods
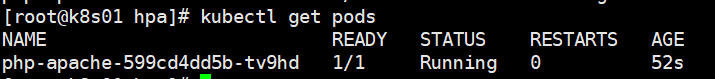
2. Create Horizontal Pod Autoscaler. Available kubectl autoscale deployment XXX creates HPA.
kubectl autoscale deployment php-apache --cpu-percent=50 --min=1 --max=10
The above command will create a Horizontal Pod Autoscaler to control PHP Apache and keep the number of copies of Pod between 1 and 10. Generally speaking, HPA keeps the average CPU utilization of all pods at about 50% by increasing or decreasing the number of Pod copies.
View HPA status
kubectl get hpa

3. Send a large number of requests to PHP Apache to increase the load of PHP Apache.
Open a new Linux client window, start a container, and send a request to the PHP Apache server through a loop.
kubectl run -i --tty load-generator --image=busybox --restart=Never -- /bin/sh -c "while sleep 0.01; do wget -q -O- http://php-apache; done"
Use another Linux client window to check the status of HPA. After waiting for more than ten seconds, the CPU utilization of PHP Apache pod gradually increases and the number of pods gradually increases until the CPU utilization of pod stabilizes at about 50% and the expansion stops.
kubectl get hpa

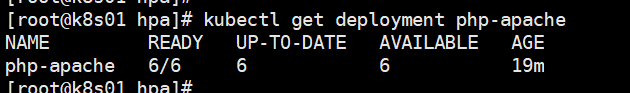
Check the number of pod s in PHP Apache
kubectl get deployment php-apache
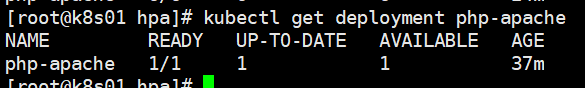
4. Stop sending requests and reduce the load of PHP Apache. HPA will reduce the number of pod s in PHP Apache.
Use Ctrl+C to stop another client's busybox.
After a period of time, the number of PHP apace pods is reduced to 1
Auto scale based on memory usage
To clean up, first delete the load generator and PHP Apache hpa,php-apache
kubectl delete pod load-generator
kubectl delete hpa php-apache
kubectl delete -f php-apache.yaml
The blogger's docker hub provides an image of the test memory, codingsoldier / image test: v3
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/hpa")
public class HpaController {
public Map map = new HashMap();
@RequestMapping("/mem")
public String mem(@RequestParam("value") Integer value) {
for (int i = 0; i < value; i++) {
MemObj memObj = new MemObj(UUID.randomUUID().toString(), new Random().nextInt(Integer.MAX_VALUE));
map.put(UUID.randomUUID().toString(), memObj);
}
return "ok";
}
}1. Create a new hpa-mem-test.yaml and use the image codingsoldier/image-test:v3
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: hpa-mem-test
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
run: hpa-mem-test
replicas: 1
template:
metadata:
labels:
run: hpa-mem-test
spec:
containers:
- name: hpa-mem-test
# This is the image submitted by the blogger to the docker hub for testing memory
image: codingsoldier/image-test:v3
ports:
- containerPort: 80
resources:
limits:
memory: 400Mi
requests:
memory: 200Mi
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: hpa-mem-test
labels:
run: hpa-mem-test
spec:
ports:
- port: 80
selector:
run: hpa-mem-test
2. Only the autoscaling/v2beta2 API version supports memory indicator monitoring. If the Kubernetes version is too old, autoscaling/v2beta2 API cannot be used.
Create HPA using the declaration file and create hpa-mem.yaml
apiVersion: autoscaling/v2beta2
kind: HorizontalPodAutoscaler
metadata:
name: hpa-mem-test
spec:
# The object specified for scaling is HPA MEM test deployment
scaleTargetRef:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
name: hpa-mem-test
minReplicas: 1
maxReplicas: 10
metrics:
# The memory utilization of each Pod is within 60%
- type: Resource
resource:
name: memory
target:
type: Utilization
averageUtilization: 60
3. Deploy hpa-mem-test.yaml and hpa-mem.yaml
kubectl apply -f hpa-mem-test.yaml
kubectl apply -f hpa-mem.yaml
4. Open a new Linux client window to run busybox in an interactive Shell
kubectl run -i --tty busybox --image=busybox -- sh
Send a request to HPA MEM test in busybox to increase memory usage
wget -q -O- http://hpa-mem-test/hpa/mem?value=99999
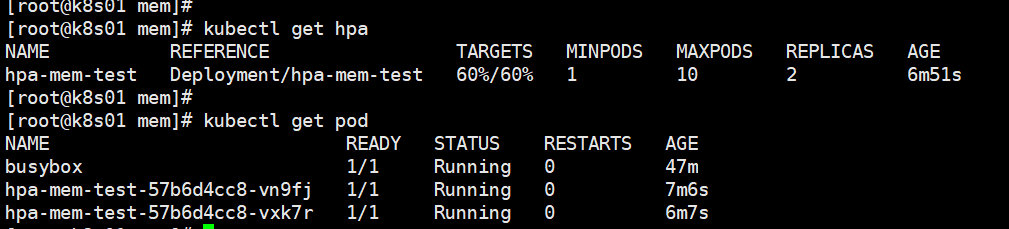
5. View HPA status
kubectl get hpa
Wait for more than ten seconds to see if HPA changes

The memory usage of pod has increased to 80% (if the memory usage does not exceed 60%), you can execute WGet - Q - O again- http://hpa-mem-test/hpa/mem?value=99999 , increase pod memory usage.
The HPA MEM test is increased to two pods, the application memory usage in the pod is stable at 60%, and the capacity expansion is stopped.
Expand and shrink according to other indicators
Using the autoscaling/v2beta2 API version, you can use other metrics when automatically scaling the Deployment of PHP Apache.
apiVersion: autoscaling/v2beta2
kind: HorizontalPodAutoscaler
metadata:
name: php-apache
spec:
# The object specified for scaling is PHP Apache deployment
scaleTargetRef:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
name: php-apache
minReplicas: 1
maxReplicas: 10
metrics:
# CPU utilization of each Pod is within 50%
- type: Resource
resource:
name: cpu
target:
type: Utilization
averageUtilization: 50
# The memory utilization of each Pod is within 60%
- type: Resource
resource:
name: memory
target:
type: Utilization
averageUtilization: 60
# Each Pod can serve 1000 packet requests per second
- type: Pods
pods:
metric:
name: packets-per-second
target:
type: AverageValue
averageValue: 1k
# The total number of requests that can be served by Pod after progress reaches 10000 per second
- type: Object
object:
metric:
name: requests-per-second
describedObject:
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
name: main-route
target:
type: Value
value: 10k