JavaScript basic syntax 07
catalogue
• traversal of objects
• built in objects
• comprehensive cases
I Traversal object
Syntax:

Generally, it is not used to traverse arrays in this way. It is mainly used to traverse objects
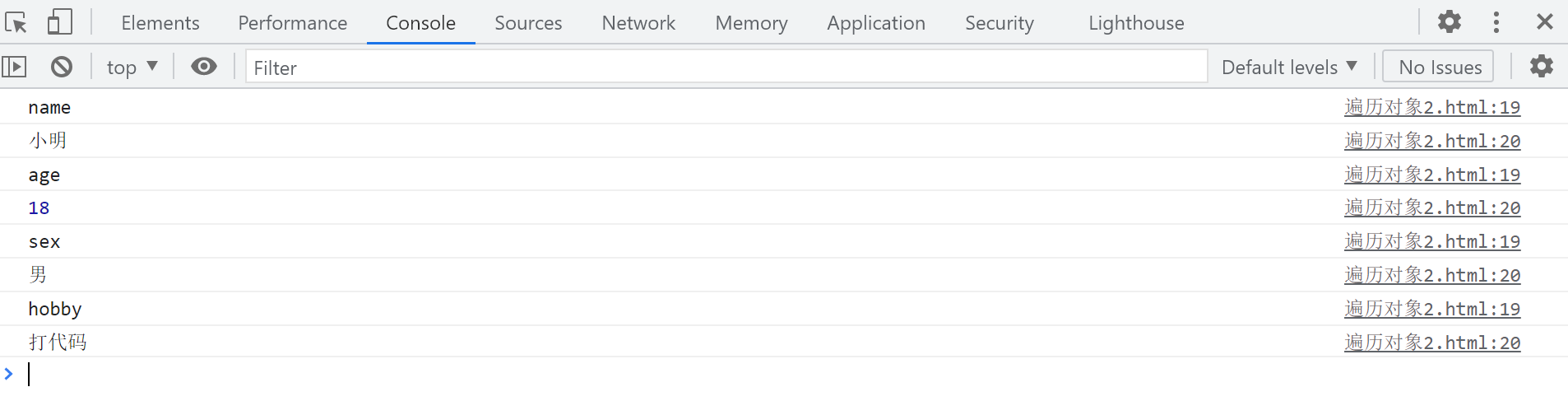
Remember: K is the attribute name of the object, and the object name [k] is the attribute value
For example
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
let person = {
name : 'Xiao Ming',
age : 18,
sex : 'male',
hobby : 'Type code'
}
//Traversal object
for (let k in person){
console.log(k) // Print attribute name
console.log(person[k]) //Print attribute values
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
Console output results
Traverse array objects:
Print out the objects in the following data:
//Define an array that stores several student information
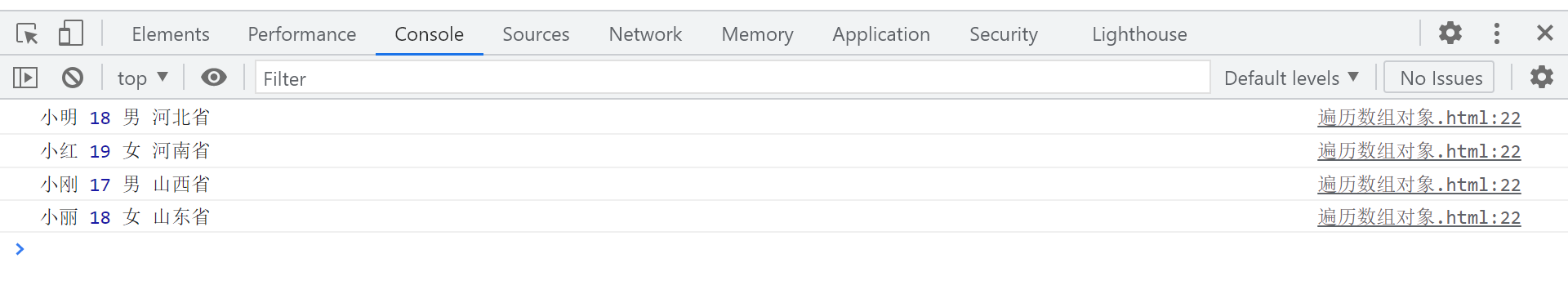
let students = [
{name: 'Xiaoming', age: 18, gender: 'male', hometown: 'Hebei Province'},
{name: 'Xiaohong', age: 19, gender: 'female', hometown: 'Henan Province'},
{name: 'Xiaogang', age: 17, gender: 'male', hometown: 'Shanxi Province'},
{name: 'Xiaoli', age: 18, gender: 'female', hometown: 'Shandong Province'}
]
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
// Define an array that stores several student information
let students = [
{name: 'Xiao Ming', age: 18, gender: 'male', hometown: 'Hebei Province'},
{name: 'Xiao Hong', age: 19, gender: 'female', hometown: 'Henan Province'},
{name: 'Xiao Gang', age: 17, gender: 'male', hometown: 'Shanxi Province'},
{name: 'Xiao Li', age: 18, gender: 'female', hometown: 'Shandong Province'}
]
// Traversal array
for (let i = 0; i < students.length; i++) {
// The console prints the elements of the array
// Object name Property name or object name ['property name']
console.log(students[i].name, students[i].age,students[i].gender,students[i].hometown)
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
Console output results
II Built in object
Master the built-in objects and call the functions prepared by JavaScript for us
What are built-in objects?
The object provided inside JavaScript contains various properties and methods for developers to call
For example; Built in object Math
The Math object is a "math master" object provided by JavaScript
It provides a series of methods to do mathematical operations
Methods include:
Random: generate random numbers between 0 and 1 (including 0 and excluding 1)
ceil: round up
floor: round down
max: find the maximum number
min: find the lowest decimal point
pow: power operation
abs: absolute value
You can query Math object online documents online
Generate random numbers using the random of the built-in object Math

Random roll call with random
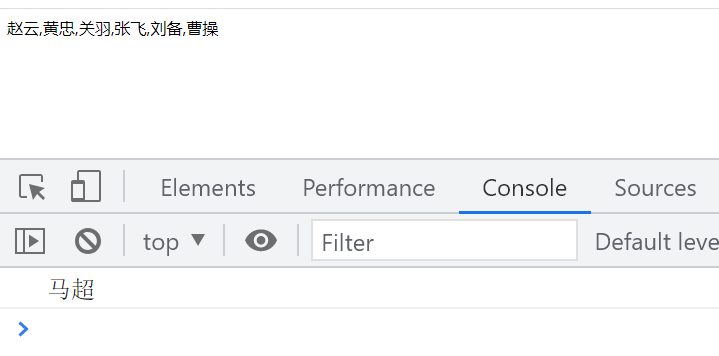
Randomly display a name ['Zhao Yun', 'Huang Zhong', 'Guan Yu', 'Zhang Fei', 'Ma Chao', 'Liu Bei', 'Cao Cao'] on the page, but not
Allow repeated display
analysis:
① : use a random function to randomly generate a number as an index number
② : array [random number] printout
③ : delete the index number from the array
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- adopt src Attribute introduction js file -->
<script src="./random.js" ></script>
<script>
//Prepare array
let arr = ['Zhao Yun','Huang Zhong','Guan Yu','Fei Zhang','ma chao','Liu Bei','Cao Cao']
//Through the random function, a random number is obtained
//Maximum subscript of array = array length - 1
let random = getRandom(0,arr.length - 1)
//Take the random number as the array subscript, and the console outputs the named
console.log(arr[random])
//The previously mentioned delete array element: array name Splice (starting position, number of deleted)
arr.splice(random,1)
//Browser to see if the named ones have been deleted
document.write(arr)
</script>
</body>
</html>
Result diagram
III Comprehensive case
Randomly generate numbers and guess numbers
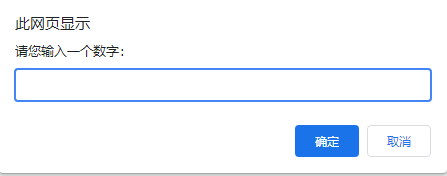
Requirements: the program randomly generates a number between 1 and 10, and the user inputs a number
① : if it is greater than this number, you will be prompted. If the number is larger, continue to guess
② : if it is less than this number, you will be prompted. If the number is small, continue to guess
③ : if you guess correctly, you will be prompted to guess correctly, and the program ends
analysis:
① : use random numbers to generate a number
② : you need to guess all the time, so you need to keep cycling
③ : because the condition is the result. If you guess correctly, you can judge the condition to exit. It is appropriate to use the while loop
④ : multiple branch statements can be used for internal judgment
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
// random number
function getRandom(min, max) {
return Math.floor(Math.random() * (max - min + 1)) + min
}
// Generate random numbers between 1 and 10
let random = getRandom(1, 10)
// console.log(random)
// 3. The user inputs the pop-up box continuously until the input is correct
while (true) {
let num = +prompt('Please enter a number:')
// If the input is greater than the random number, you will be prompted to guess big
if (random < num) {
alert('Guess big')
// If the input is less than the random number, you will be prompted to guess smaller
} else if (random > num) {
alert('Guess it's small')
// If the input is just right, the prompt is correct
} else {
alert('correct')
break // break exit loop return exit function
}
}
</script>
</body>
</html>