Variables and data types
1. Variables
1. Memory is the data space in the computer. Different data are stored in the space with different memory addresses. Independent of each other.
2. How to find the stored data?
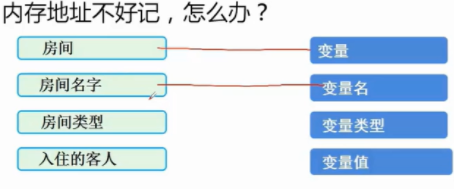
Variable name not found
3. Variable naming rules
Word, down, beauty, man, number, camel
Words: Letters
Bottom: underline
US dollar sign $
Person: RMB symbol ¥
Must start above
The follow-up can only be words, words, beauty, people and numbers
Number: number
Camel: Camel nomenclature or hump nomenclature. Capitalize the first letter of each word after the beginning.
When a variable name consists of multiple words, the first word is capitalized, and then the first letter of each word is capitalized.
Variable names should be meaningful
Do not use Chinese for variable names
Keywords cannot be used

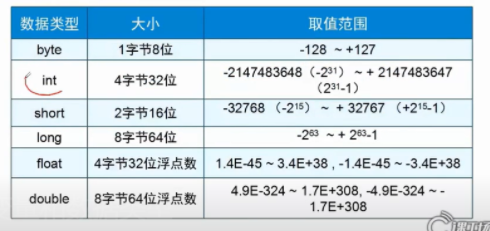
2.java common data types
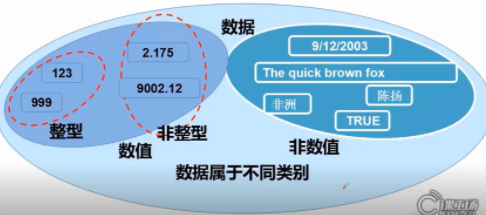
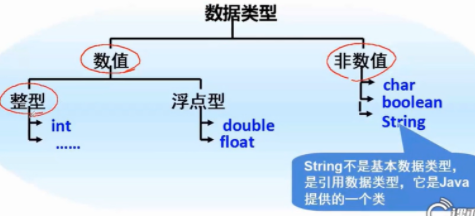
1. Data types are divided into numeric and non numeric
The values are divided into
Integer (int)
Non integer (double double precision floating point number, folat single precision floating point number)
Non numerical
char single character
boolean (true or false)
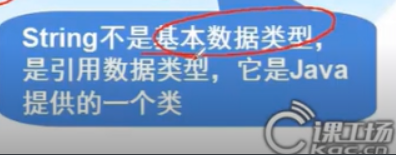
String string
3. Variable declaration and use

1. Declare variable: give the variable a name int money
2. Assignment: money=1000;
=Assign the following to the front for
It can be combined into one sentence int money=1000
4. Constant

1. Constants that do not change should be capitalized.
2. Add final before the variable to become a constant.
final double PAI=3.14
In double PAI=3.14; Add final to make it a constant
3. The two characters are separated by an underscore
final double GOOD_UP=100;
5. Use of scanner
1. It is necessary to open an entry for the user to enter the program through the keyboard
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); //a key
The program keyboard needs to enter the opening: Scanner
Entry name input (variable name can be changed freely)
But now it is in the state of error reporting.
You need to write in front of class 👇
import java.util.*;
This sentence means that the Scanner above is located in the java.util package. It is equivalent to importing the java.util. The following * means importing everything in the package.
Then write below
String name =input.next();
Next is next. This sentence means next. The next input is what needs to be output
//Import a package
import java.util.*;
// You need to open an entry input for the user to enter the program through the keyboard
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
//Get string using input
System.out.println("Please enter your name:");
String name =input.next();Scanner can only output strings, not characters.
nextInt can output integers. When outputting integers, change next to nextInt.
The age entered is an integer
System.out.println("Please enter age:");
int age =input.nextInt();Change String to int and next to nextInt.
The input score is small floating point
System.out.println("Please enter your grade:");
double score = input.nextDouble();Change String to double and next to nextDouble.
Input steps using user keyboard:
1. Import the package import java.util. *;
-
//You need to open an entry for the user to enter the program through the keyboard. input Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
3. Use iinput to obtain the data entered by the user's keyboard
character string
System.out.println("Please enter your name:");
String name =input.next();integer
System.out.println("Please enter age:");
int age =input.nextInt();Floating point number
System.out.println("Please enter your grade:");
double score = input.nextDouble();No nextChar.
6. Use of data types

//Data type: / / numeric value (integer int float\double)
//Non numeric value (String double quotation mark character char single quotation mark boolean value: true, false)
//All data types except String are called basic data types
//String is called a reference data type
//Floating point numbers are double by default
double num2=1.0; float num3=1.0f;
double is more widely used than float. If you want to use float to represent floating point numbers, you need to add f after it.
int num1 = 10; double num2 = 9.8; float num3 = 1.8f; //When one of the expressions is double, the whole result is promoted to double //Force type conversion, report the error reason, and assign double to int int num4=num1-num2
When one of the expressions is double, the whole result is promoted to double
int num4=num1-num2 error
Error reason, assign double to int
To change double into int, add (int) before it to complete a cast
int num4=num1-(int)num2
After the cast, double becomes int, and all after the decimal point is erased.
Forced conversion is to change a data type with a large range (double) into a data type with a small range (int)
Automatic conversion
//The automatic type conversion int is directly assigned to double //The assignment with a large range itself is directly converted to a small range num2 = 100;
Those with a large range can be directly assigned to those with a small range
num2 = 100;
7. Conversion rules
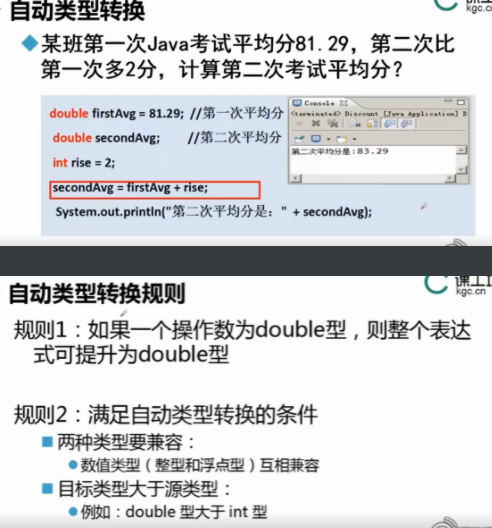
double firstAvg=81.29;//First average score
double secondAvg: //Second average score
int rise=2;
secoundAvg=firstAvg+rise;
System.out.println("The average score for the second time is"+secondAvg)
double firstAvg=81.29; Assign a value of 81.29 to firstavg, because it is a decimal, so use double.
double secondAvg: the final required formula.
System.out.println("the average score of the second time is" + secondAvg) the final output is secondavg+ secondAvg
int rise=2; It's an integer
secoundAvg=firstAvg+rise; The following int integer automatically becomes double.
8. Assignment operator

=The value or expression on the right of the action assignment is assigned to the left in the order from right to left.
int rise=2, 2 is assigned to rise

public static void main(String[] args) {
int num1=8;
int num2=9;
System.out.println("Before exchange:");
System.out.println("num1:"+num1);
System.out.println("num2:"+num2);System.out.println("num1:"+num1);
The string itself is output in "double quotation marks", and the value of assignment is output in num1 linked with + outside.
int num3=num1;
num1=num2;
num2=num3;
System.out.println("After exchange:");
System.out.println("num1:"+num1);
System.out.println("num2:"+num2);Find an intermediate temporary variable num3 and store the value of num1 first
Then exchange
9. Arithmetic operator
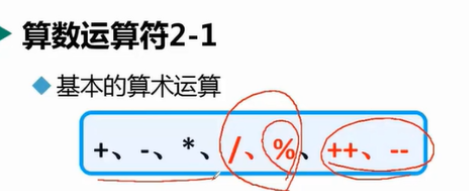
int num1 =9;
int num2=2;
int num3=num1/num2;
int num4=num1%num2;
System.out.println("num1/num2:"+num3);
System.out.println("num1%num2:"+num4);/As long as the quotient is used for division, the% remainder takes the remainder.
int num1 =9; System.out.println(++num1); //num1=num1+1 Result 10
++For self addition, the original value is + 1.
int num2=2; System.out.println(--num2); //num1=num1-1 result 1
--It is self subtraction, and the original value is - 1.
System.out.println(num1++);//num1=num1+1 System.out.println(num2--);//num1=num1-1
++And -- can be written after variables or expressions.
System.out.println(num1++);//num1=num1+1 result 9 System.out.println(num2--);//num1=num1-1 result 2
There is a difference between before and after writing
++Or --, self addition or self subtraction before operation
++Or --, after, first calculate, then add or subtract, and then output first, and then add or subtract, so the output is the original value.
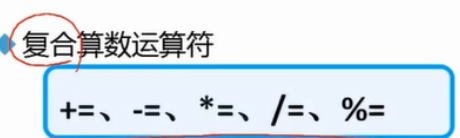
+=, - = are all operators
int num1 =9;
num1 += 2; // After + 2 on its own basis, it is assigned to num1
System.out.println(num1);

5%2=1 5/2=2
num1=6 num2=1
10. Comprehensive application of arithmetic operators
import java.util.*;
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Enter a four digit membership card number, and the console calculates each digit of the membership card number and the sum of the numbers.
//Scanner usage: make a cut first
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
//Please enter a four digit membership card number for the output statement
System.out.println("Please enter a four digit membership card number:");
//The input card number is an integer. Use int and nextInt input to obtain the input card number and output
int no =input.nextInt();
//Output card number
System.out.println("The membership card number is:"+no);
//8369 take out ten thousand values
int num1=no%10;
int num2=no/10%10;
int num3=no/100%10;
int num4=no/1000;
int num5=num1+num2+num3+num4;
//Use the remaining 10 methods to get a bit
System.out.println("Single digits of card number:"+num1);
//Divide by 10 and then take the remainder to get ten
System.out.println("Ten digits of card number:"+num2);
//Divide by 100 and then take the remainder to get the hundred
System.out.println("Hundred digits of card number"+num3);
//Get the thousands by dividing by 1000
System.out.println("Thousand digits of card number"+num4);
System.out.println("Number of members:"+num1+"Ten digits:"+num2+"Hundreds:"+num3+"thousands :"+num4);
System.out.println("Total number of four digits of card number:"+num5);
11. Relational operators
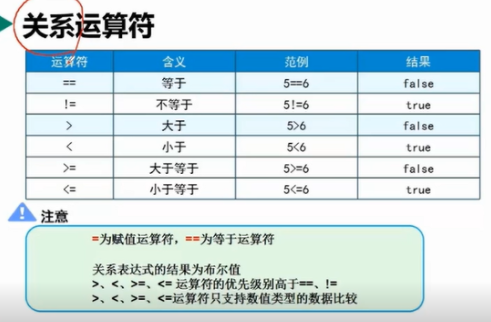
The result of the relational expression is a Boolean value
==Is the equal operator
12. Logical operators
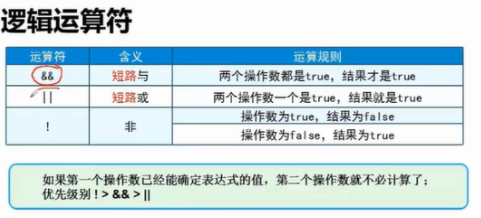
Logical operators are used to connect two expressions or operands
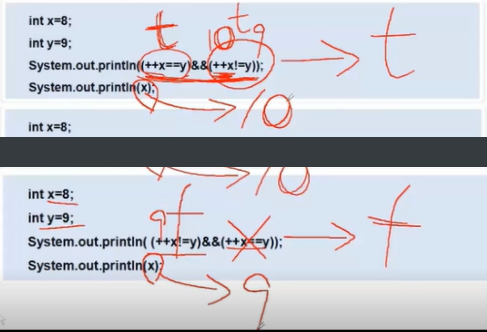
Do not continue after short circuit, and the second + + X will not operate, so x in the second formula is 8 + 1 = 9
12. Conditional operator
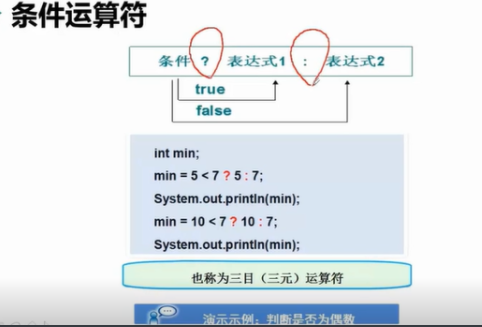
Conditions? Expression 1: expression
If the condition is true, the first expression is output; if it is wrong, the second expression is output.
import java.util.*;
//Judge whether a genus is even (a number divisible by 2)
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Please enter a number other than 0:");
int num = input.nextInt();
String result =(num%2==0)?"even numbers":"Odd number";
System.out.println(num+"yes"+result);
}
}

import java.util.*;
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Enter a four digit membership card number, the console calculates the digits of the membership card number, and calculates the sum of the numbers, and then calculates whether there is a winner according to the size of the sum
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Please enter a four digit membership card number:");
int no =input.nextInt();
//Output card number
System.out.println("The membership card number is:"+no);
int num1=no%10;
int num2=no/10%10;
int num3=no/100%10;
int num4=no/1000;
int num5=num1+num2+num3+num4;
System.out.println("Single digits of card number:"+num1);
System.out.println("Ten digits of card number:"+num2);
System.out.println("Hundred digits of card number"+num3);
System.out.println("Thousand digits of card number"+num4);
System.out.println("Number of members:"+num1+"Ten digits:"+num2+"Hundreds:"+num3+"thousands :"+num4);
System.out.println("Total number of four digits of card number:"+num5);
String result=(num5>10)?"You won the prize":"You didn't win the prize";
System.out.println("Card number is"+no+"Member of"+result);
}