1. jdbcTemplate
1.1 basic concepts
-
JdbcTemplate is a template object provided in the spring framework. It is a simple encapsulation of the original cumbersome Jdbc API object
-
Core object
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = new JdbcTemplate(DataSource dataSource);
-
Core method
Execute addition, deletion and modification statements int update(); // //Query multiple List<T> query(); // Query one T queryForObject(); // Implement ORM mapping encapsulation new BeanPropertyRowMapper<>();
1.2 Spring integration
1.2.1 Maven configuration
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.25</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>1.2.8</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.3.15</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId>
<version>1.9.7</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>5.3.15</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-tx</artifactId>
<version>5.3.15</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.13.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-test</artifactId>
<version>5.3.15</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
1.2.2 entity class
-
Account
public class Account { private Integer id; private String name; private Double money; }
1.2.3 Dao layer interface
-
AccountDao
package cn.knightzz.dao; import cn.knightzz.entity.Account; import java.util.List; public interface AccountDao { /** * Query all accounts * @return */ public List<Account> findAll(); /** * Query account by id * @param id * @return */ public Account findById(Integer id); /** * Add account information * @param account */ public void save(Account account); /** * Update account information * @param account */ public void update(Account account); /** * Delete account information * @param id */ public void delete(Integer id); } -
AccountDaoImpl
package cn.knightzz.dao.impl; import cn.knightzz.dao.AccountDao; import cn.knightzz.entity.Account; import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory; import org.springframework.jdbc.core.BeanPropertyRowMapper; import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate; import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository; import javax.annotation.Resource; import java.util.List; /** * @author Wang Tianci * @title: AccountDaoImpl * @projectName mybatis-apply-06 * @description: * @website http://knightzz.cn/ * @github https://github.com/knightzz1998 * @date 2022/1/27 14:07 */ @Repository("accountDao") public class AccountDaoImpl implements AccountDao { @Resource JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate; @Override public List<Account> findAll() { String sql = "select * from account"; List<Account> accountList = jdbcTemplate.query(sql, new BeanPropertyRowMapper<>(Account.class)); return accountList; } @Override public Account findById(Integer id) { String sql = "select * from account where id = ?"; Account account = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, new BeanPropertyRowMapper<>(Account.class), id); return account; } @Override public void save(Account account) { String sql = "insert into account(id, name ,money) values(null , ?, ?)"; jdbcTemplate.update(sql, account.getName(), account.getMoney()); } @Override public void update(Account account) { String sql = "update account set name = ?, money = ? where id = ?"; jdbcTemplate.update(sql, account.getName(), account.getMoney(), account.getId()); } @Override public void delete(Integer id) { String sql = "delete from account where id = ?"; jdbcTemplate.update(sql, id); } }
1.3.4 Service layer interface
-
AccountService interface
package cn.knightzz.service; import cn.knightzz.entity.Account; import java.util.List; public interface AccountService { /** * Query all accounts * @return */ public List<Account> findAll(); /** * Query account by id * @param id * @return */ public Account findById(Integer id); /** * Add account information * @param account */ public void save(Account account); /** * Update account information * @param account */ public void update(Account account); /** * Delete account information * @param id */ public void delete(Integer id); } -
AccountServiceImpl
package cn.knightzz.service.impl; import cn.knightzz.dao.AccountDao; import cn.knightzz.entity.Account; import cn.knightzz.service.AccountService; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; import javax.annotation.Resource; import java.util.List; @Service("accountService") public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService { @Resource AccountDao accountDao; @Override public List<Account> findAll() { return accountDao.findAll(); } @Override public Account findById(Integer id) { return accountDao.findById(id); } @Override public void save(Account account) { accountDao.save(account); } @Override public void update(Account account) { accountDao.update(account); } @Override public void delete(Integer id) { accountDao.delete(id); } }
1.3.5 test code
-
AccountServiceTest
package cn.knightzz.service; import cn.knightzz.config.SpringConfig; import cn.knightzz.entity.Account; import junit.framework.TestCase; import org.junit.Test; import org.junit.runner.RunWith; import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration; import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner; import javax.annotation.Resource; import java.util.List; @RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class) @ContextConfiguration(classes = {SpringConfig.class}) public class AccountServiceTest extends TestCase { @Resource AccountService accountService; @Test public void testFindAll() { List<Account> accountList = accountService.findAll(); for (Account account : accountList) { System.out.println(account); } } @Test public void testFindById() { Account account = accountService.findById(1); System.out.println(account); } @Test public void testSave() { Account accout = new Account(); accout.setId(3); accout.setName("kiss"); accout.setMoney(300d); accountService.save(accout); } @Test public void testUpdate() { Account accout = new Account(); accout.setId(3); accout.setName("knightzz"); accout.setMoney(400d); accountService.update(accout); } public void testDelete() { } }
2. Spring transaction
2.1 Spring transaction control mode
- Spring's transaction control can be divided into programmatic transaction control and declarative transaction control.
2.1.1 programmatic transactions
- Developers directly couple the transaction code and business code, which is not needed in actual development
2.1.2 declarative transactions
- Developers use configuration to realize transaction control, decouple business code and transaction code, and use AOP idea.
2.2 programmable transaction control object
2.2.1 different Dao layer implementation objects
- PlatformTransactionManager is an interface type, and different Dao layer technologies have different implementation classes.
- When Dao layer technology is JDBC template or mybatis: DataSourceTransactionManager
- When Dao layer technology is hibernate: hibernate transaction manager
- When Dao layer technology is JPA: JPA transaction manager
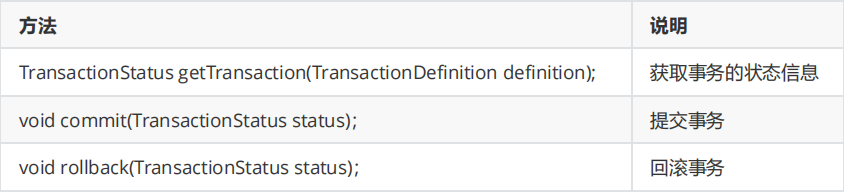
2.2.2 PlatformTransactionManager
-
The PlatformTransactionManager interface is the transaction manager of spring,
-
It provides our common methods of operating transactions
-
common method
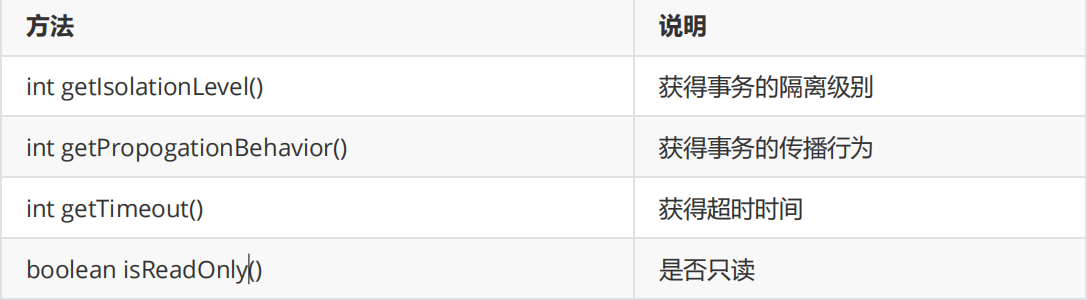
2.2.3 TransactionDefinition
-
The TransactionDefinition interface provides transaction definition information (transaction isolation level, transaction propagation behavior, etc.)
-
common method
2.2.4 transaction isolation level
-
Setting the isolation level can solve the problems caused by transaction concurrency, such as dirty reading, non repeatable reading and virtual reading (phantom reading).
-
ISOLATION_DEFAULT uses the database default level
-
ISOLATION_READ_UNCOMMITTED read uncommitted
-
ISOLATION_READ_COMMITTED read committed
-
ISOLATION_REPEATABLE_READ repeatable
-
ISOLATION_SERIALIZABLE serialization
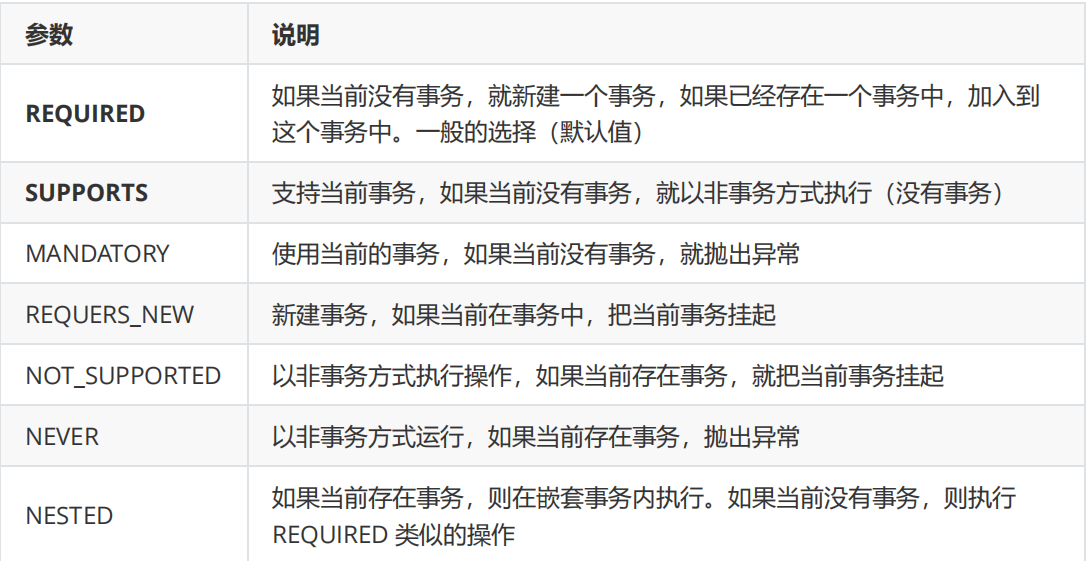
2.2.5 transaction communication behavior
-
Transaction propagation behavior refers to how to control transactions when a business method is called by another business method
-
Read only: it is recommended to set it as read-only when querying
-
Timeout: the default value is - 1. There is no timeout limit. If yes, set in seconds
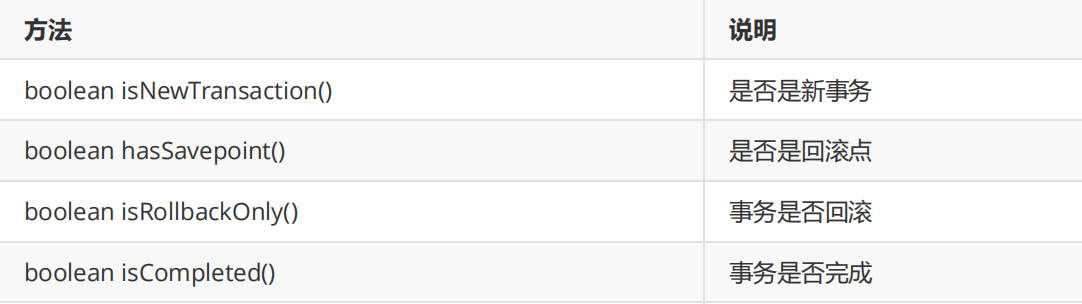
2.2.6 TransactionStatus
-
The TransactionStatus interface provides the specific running status of a transaction.
-
We can simply understand the relationship between the three: the transaction manager manages the transaction by reading the transaction definition parameters, and then a series of events will occur
Business status.
2.2.7 code implementation
-
SpringConfig
@Bean("transactionManager") public DataSourceTransactionManager getDataSourceTransactionManager(@Autowired DataSource dataSource){ return new DataSourceTransactionManager(dataSource); } -
Service
@Resource private PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager; /** * Transfer operation * * @param outUser * @param inUser * @param money */ @Override public void transfer(String outUser, String inUser, Double money) { // Create transaction definition object DefaultTransactionDefinition def = new DefaultTransactionDefinition(); // Set whether it is read-only. false supports transactions def.setReadOnly(false); // Set the transaction isolation level. You can repeatedly read the default level of mysql def.setIsolationLevel(TransactionDefinition.ISOLATION_REPEATABLE_READ); // Transaction propagation behavior must be set def.setPropagationBehavior(TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRED); // Configure transaction manager TransactionStatus status = transactionManager.getTransaction(def); try { // transfer accounts accountDao.out(outUser, money); accountDao.in(inUser, money); // Commit transaction transactionManager.commit(status); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); // Rollback transaction transactionManager.rollback(status); } }
2.3 declarative transaction control based on XML
2.3.1 development steps
- Introduce tx namespace
- Transaction manager notification configuration
- Transaction manager AOP configuration
- Test transaction control transfer business code
2.3.2 introducing tx namespace
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w2.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/s chema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd">
</beans>
2.3.3 transaction manager notification configuration
<!--Transaction manager-->
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean> <!--Notification enhancement-->
<tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager">
<!--Define the properties of the transaction-->
<tx:attributes>
<tx:method name="*"/>
</tx:attributes>
</tx:advice>
2.3.4 transaction manager AOP configuration
<!--aop to configure-->
<aop:config> <!--Section configuration-->
<aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut="execution(* com.lagou.serivce..*.*(..))"> </aop:advisor>
</aop:config>
2.3.5 configuration of transaction parameters
<tx:method name="transfer" isolation="REPEATABLE_READ" propagation="REQUIRED" timeout="-1" read-only="false"/>
-
Name: tangent point method name
-
Isolation: isolation level of transaction
-
Propagation: propagation behavior of transactions
-
Timeout: timeout
-
Read only: read only
2.3.6 common configuration of crud transaction
<tx:attributes>
<tx:method name="save*" propagation="REQUIRED"/>
<tx:method name="delete*" propagation="REQUIRED"/>
<tx:method name="update*" propagation="REQUIRED"/>
<tx:method name="find*" read-only="true"/>
<tx:method name="*"/>
</tx:attributes>
2.4 annotation based declarative transaction control
2.4.1 basic steps
- Modify the service layer and add transaction annotation
- Modify the spring core configuration file and enable transaction annotation support
2.4.2 enable transaction configuration
-
Springconfig: @ enabletransactionmanagement start transaction
@Configuration @ComponentScan("cn.knightzz") @EnableAspectJAutoProxy @EnableTransactionManagement @Import(DataSourceConfig.class) public class SpringConfig {
2.4.3 adding notes to service
-
Note: the code of transaction annotation should not be wrapped with try catch, otherwise the exception cannot be caught and rolled back
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED, isolation = Isolation.REPEATABLE_READ, timeout = -1, readOnly = false) @Override public void transfer(String outUser, String inUser, Double money) { accountDao.out(outUser, money); int i = 1 / 0; accountDao.in(inUser, money); }