In database terminology, PostgreSQL uses a client / server model. A PostgreSQL session consists of the following related processes (programs):
1. A server process that manages database files, accepts connections from client applications to the database, and performs operations on the database on behalf of the client. The database server program is called postgres.
2. Client applications of users who need to perform database operations.
The PostgreSQL server can handle multiple concurrent requests from clients. Therefore, it starts ("forks") a new process for each connection
1.psql installation
Ubuntu installation:
Install the PostgreSQL client.
sudo apt-get install postgresql-client
Install PostgreSQL server
sudo apt-get install postgresql
Normally, after the installation is completed, the PostgreSQL server will be automatically opened on port 5432 of this machine.
Centos installation:
PostgreSQL: Linux downloads (Red Hat family)
Linux user and database accounts and database names named "postgres" will be created by default
2.1 basic command line
2.1.1 login database
The commands to log in to the database using the psql command are:
psql -U dbuser -d exampledb -h 127.0.0.1 -p 5432
The parameters of the above command have the following meanings: - U specifies the user, - d specifies the database, - h specifies the server, and - p specifies the port.
After entering the above command, the system will prompt for the password of the dbuser user.
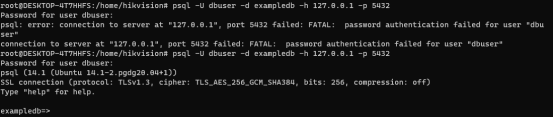
Account: psql - U postgres - d} postgres

2.1.2 add new users and new databases
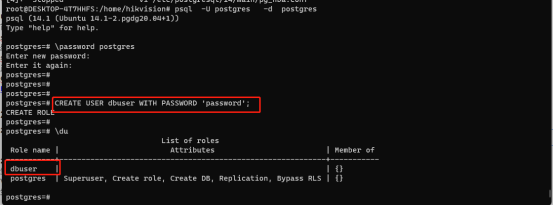
Step 1: set the password postgres password
\password postgres
Step 2: create the database user dbuser (the Linux system user just created) and set the password
CREATE USER dbuser WITH PASSWORD 'password';
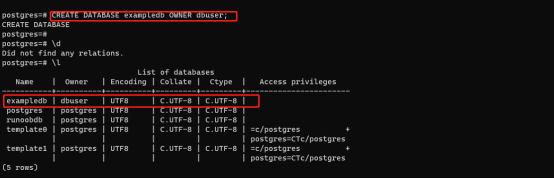
Step 3: create a user database, here exampledb, and specify the owner as dbuser.
CREATE DATABASE exampledb OWNER dbuser;
Step 4: give all permissions of the exampledb database to dbuser, otherwise dbuser can only log in to the console without any database operation permissions.
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON DATABASE exampledb to dbuser;
Step 5: exit
\q
2.3 console commands
| command line | meaning | remarks |
| \h | View the explanation of the SQL command | For example, \ h select. |
| \? | View psql command list | \? |
| \l | List all databases | \l |
| \c | Connect to other databases | \c [database_name] |
| \d | Lists all tables in the current database | \d |
| \d | List the structure of a table | \d [table_name] |
| \du | List all users | \du |
| \e | Open the text editor | \e |
| \conninfo | Lists information about the current database and connection | \conninfo |
2.4 database operation
| command line | meaning | remarks |
| CREATE | Create a new table | CREATE TABLE user_tbl(name VARCHAR(20), signup_date DATE); |
| INSERT | insert data | INSERT INTO user_tbl(name, signup_date) VALUES('zhang San ',' 2013-12-22 '); |
| SELECT | Select record | SELECT * FROM user_tbl; |
| UPDATE | Update data | UPDATE user_tbl set name = 'Li Si' WHERE name = 'Zhang San'; |
| DELETE | Delete record | DELETE FROM user_tbl WHERE name = 'Li Si'; |
| ALTER | Add field | ALTER TABLE user_tbl ADD email VARCHAR(40); |
| Update structure | ALTER TABLE user_tbl ALTER COLUMN signup_date SET NOT NULL; | |
| Rename field | ALTER TABLE user_tbl RENAME COLUMN signup_date TO signup; | |
| Delete field | ALTER TABLE user_tbl DROP COLUMN email; | |
| Table renaming | ALTER TABLE user_tbl RENAME TO backup_tbl; | |
| DROP | Delete table | TABLE IF EXISTS backup_tbl; |
2.5 database import and export
Display not used
2.6 problem solving

solve:
Step 1: # change the peer in the Database administrative file to trust
vi /etc/postgresql/14/main/pg_hba.conf
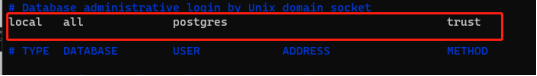
Step 2: sudo service postgresql restart
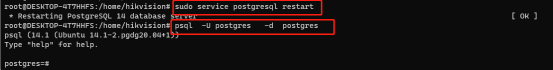
3.API usage
You can refer to the boss blog:
C/C + + connecting to PostgreSQL database - PostgreSQL tutorial ™
PostgreSQL connection C/C + + interface instance
3.0 libpqxx compilation
wget http://pqxx.org/download/software/libpqxx/libpqxx-4.0.1.tar.gz tar -xzf libpqxx-4.0.1.tar.gz cd libpqxx-4.0.1 ./configure --prefix=/usr/local --enable-shared make && make install
Centos compilation problem:
PostgreSQL - pg_config -bash: pg_config: command not found
solve:
yum install postgresql-devel
3.1 common API operations
| S.N. | API & Description |
| 1 | pqxx::connection C( const std::string & dbstring ) yiibai.com This is a type definition that will be used to connect to the database. Here, dbstring provides the required parameters, such as dbname=postgres user=postgres password=Hik123456 hostaddr=127.0.0.1 port=7017 If the connection setting is successful, it creates C and connection objects to provide various useful public functions. |
| 2 | C.is_open() is_open() is a public method that connects objects and returns a Boolean value. If the connection is active, this method returns true; otherwise, it returns false. |
| 3 | C.disconnect() The database opened using this method is disconnected. |
| 4 | pqxx::work W( C ) This is a type definition that will be used to create a transaction object, use C connection mode, and finally be used to execute the transaction mode of SQL statements. If the transaction object is created successfully, it is assigned to the variable W, which will be used to access the public methods of the related transactional objects. |
| 5 | W.exec(const std::string & sql) This public method from the transaction object will be used to execute SQL statements. |
| 6 | W.commit() This public method from the transaction object will be used to commit the transaction. |
| 7 | W.abort() This public method from the transaction object will be used to roll back the transaction. |
| 8 | pqxx::nontransaction N( C ) This is a type definition used to create non transactional objects that use C connection mode and will eventually be used to execute SQL statements in non transactional mode. If the transaction object is created successfully, it is assigned to the public method that variable N will be used to access the related non transactional object. |
| 9 | N.exec(const std::string & sql) Public methods from non transactional objects will be used to execute SQL statements and return a result object, which is actually a record returned by an iterator. |
3.2 connection examples
Connect to database
Example:
#include <iostream>
#include <pqxx/pqxx>
using namespace std;
using namespace pqxx;
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
try{
connection C("dbname=postgres user=postgres password=Hik123456 \
hostaddr=127.0.0.1 port=7017");
if (C.is_open()) {
cout << "Opened database successfully: " << C.dbname() << endl;
} else {
cout << "Can't open database" << endl;
return 1;
}
C.disconnect ();
}catch (const std::exception &e){
cerr << e.what() << std::endl;
return 1;
}
}Operation results:

3.3 creating an example
Create a table in the created database
Running example:
#include <iostream>
#include <pqxx/pqxx>
using namespace std;
using namespace pqxx;
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
char * sql;
try{
connection C("dbname=postgres user=postgres password=Hik123456 \
hostaddr=127.0.0.1 port=7017");
if (C.is_open()) {
cout << "Opened database successfully: " << C.dbname() << endl;
} else {
cout << "Can't open database" << endl;
return 1;
}
/* Create SQL statement */
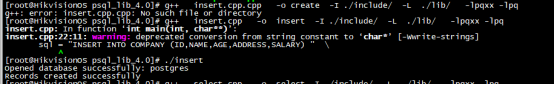
sql = "CREATE TABLE COMPANY(" \
"ID INT PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL," \
"NAME TEXT NOT NULL," \
"AGE INT NOT NULL," \
"ADDRESS CHAR(50)," \
"SALARY REAL );";
/* Create a transactional object. */
work W(C);
/* Execute SQL query */
W.exec( sql );
W.commit();
cout << "Table created successfully" << endl;
C.disconnect ();
}catch (const std::exception &e){
cerr << e.what() << std::endl;
return 1;
}
return 0;
}Operation results:
Server:
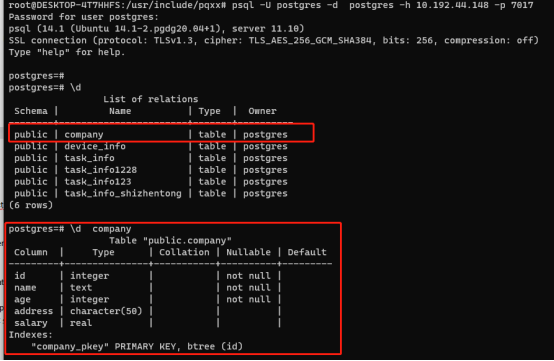
3.4 add examples
Insert entries into the company table in the created database
Example:
#include <iostream>
#include <pqxx/pqxx>
using namespace std;
using namespace pqxx;
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
char * sql;
try{
connection C("dbname=postgres user=postgres password=Hik123456 \
hostaddr=127.0.0.1 port=7017");
if (C.is_open()) {
cout << "Opened database successfully: " << C.dbname() << endl;
} else {
cout << "Can't open database" << endl;
return 1;
}
/* Create SQL statement */
sql = "INSERT INTO COMPANY (ID,NAME,AGE,ADDRESS,SALARY) " \
"VALUES (1, 'Paul', 32, 'California', 20000.00 ); " \
"INSERT INTO COMPANY (ID,NAME,AGE,ADDRESS,SALARY) " \
"VALUES (2, 'Allen', 25, 'Texas', 15000.00 ); " \
"INSERT INTO COMPANY (ID,NAME,AGE,ADDRESS,SALARY)" \
"VALUES (3, 'Teddy', 23, 'Norway', 20000.00 );" \
"INSERT INTO COMPANY (ID,NAME,AGE,ADDRESS,SALARY)" \
"VALUES (4, 'Mark', 25, 'Rich-Mond ', 65000.00 );";
/* Create a transactional object. */
work W(C);
/* Execute SQL query */
W.exec( sql );
W.commit();
cout << "Records created successfully" << endl;
C.disconnect ();
}catch (const std::exception &e){
cerr << e.what() << std::endl;
return 1;
}
return 0;
}Operation results:
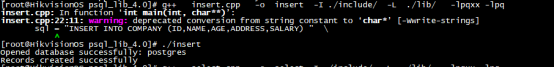
Database:
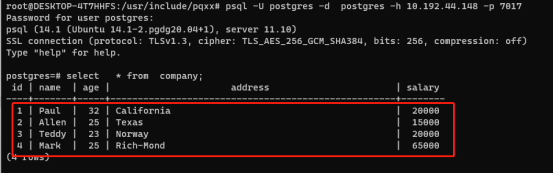
3.5 selection examples
Query the contents of tables in the created database
Example:
#include <iostream>
#include <pqxx/pqxx>
using namespace std;
using namespace pqxx;
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
char * sql;
try{
connection C("dbname=postgres user=postgres password=Hik123456 \
hostaddr=127.0.0.1 port=7017");
if (C.is_open()) {
cout << "Opened database successfully: " << C.dbname() << endl;
} else {
cout << "Can't open database" << endl;
return 1;
}
/* Create SQL statement */
sql = "SELECT * from COMPANY";
/* Create a non-transactional object. */
nontransaction N(C);
/* Execute SQL query */
result R( N.exec( sql ));
/* List down all the records */
for (result::const_iterator c = R.begin(); c != R.end(); ++c) {
cout << "ID = " << c[0].as<int>() << endl;
cout << "Name = " << c[1].as<string>() << endl;
cout << "Age = " << c[2].as<int>() << endl;
cout << "Address = " << c[3].as<string>() << endl;
cout << "Salary = " << c[4].as<float>() << endl;
}
cout << "Operation done successfully" << endl;
C.disconnect ();
}catch (const std::exception &e){
cerr << e.what() << std::endl;
return 1;
}
return 0;
}Operation results:
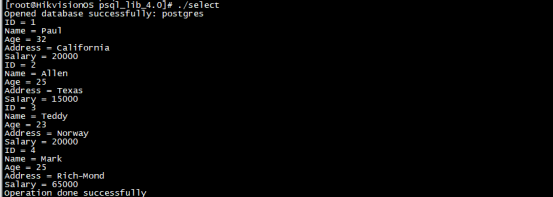
3.6 modification example
Modify a table in the created database
Example:
#include <iostream>
#include <pqxx/pqxx>
using namespace std;
using namespace pqxx;
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
char * sql;
try{
connection C("dbname=postgres user=postgres password=Hik123456 \
hostaddr=127.0.0.1 port=7017");
if (C.is_open()) {
cout << "Opened database successfully: " << C.dbname() << endl;
} else {
cout << "Can't open database" << endl;
return 1;
}
/* Create a transactional object. */
work W(C);
/* Create SQL UPDATE statement */
sql = "UPDATE COMPANY set SALARY = 25000.00 where ID=1";
/* Execute SQL query */
W.exec( sql );
W.commit();
cout << "Records updated successfully" << endl;
/* Create SQL SELECT statement */
sql = "SELECT * from COMPANY";
/* Create a non-transactional object. */
nontransaction N(C);
/* Execute SQL query */
result R( N.exec( sql ));
/* List down all the records */
for (result::const_iterator c = R.begin(); c != R.end(); ++c) {
cout << "ID = " << c[0].as<int>() << endl;
cout << "Name = " << c[1].as<string>() << endl;
cout << "Age = " << c[2].as<int>() << endl;
cout << "Address = " << c[3].as<string>() << endl;
cout << "Salary = " << c[4].as<float>() << endl;
}
cout << "Operation done successfully" << endl;
C.disconnect ();
}catch (const std::exception &e){
cerr << e.what() << std::endl;
return 1;
}
return 0;
}Operation results:
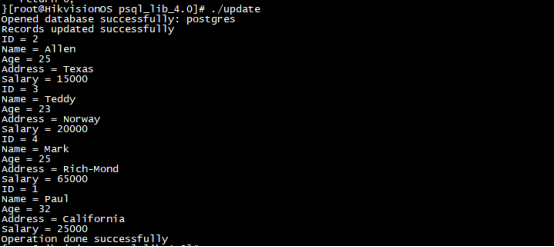
Database:
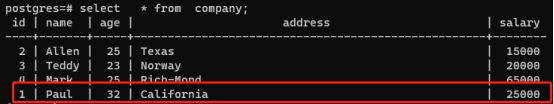
3.7 delete example
Delete entries in a table from the created database
Example:
#include <iostream>
#include <pqxx/pqxx>
using namespace std;
using namespace pqxx;
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
char * sql;
try{
connection C("dbname=postgres user=postgres password=Hik123456 \
hostaddr=127.0.0.1 port=7017");
if (C.is_open()) {
cout << "Opened database successfully: " << C.dbname() << endl;
} else {
cout << "Can't open database" << endl;
return 1;
}
/* Create a transactional object. */
work W(C);
/* Create SQL DELETE statement */
sql = "DELETE from COMPANY where ID = 2";
/* Execute SQL query */
W.exec( sql );
W.commit();
cout << "Records deleted successfully" << endl;
/* Create SQL SELECT statement */
sql = "SELECT * from COMPANY";
/* Create a non-transactional object. */
nontransaction N(C);
/* Execute SQL query */
result R( N.exec( sql ));
/* List down all the records */
for (result::const_iterator c = R.begin(); c != R.end(); ++c) {
cout << "ID = " << c[0].as<int>() << endl;
cout << "Name = " << c[1].as<string>() << endl;
cout << "Age = " << c[2].as<int>() << endl;
cout << "Address = " << c[3].as<string>() << endl;
cout << "Salary = " << c[4].as<float>() << endl;
}
cout << "Operation done successfully" << endl;
C.disconnect ();
}catch (const std::exception &e){
cerr << e.what() << std::endl;
return 1;
}
return 0;
}Operation results:
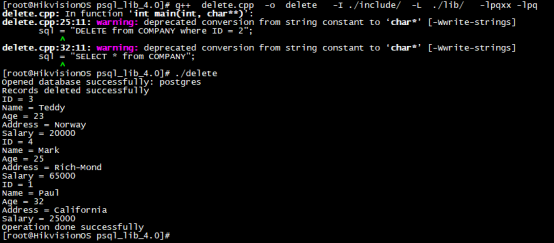
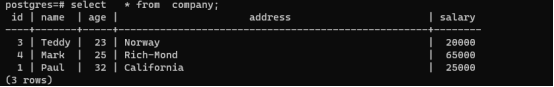
Database:
4. Client display
HeidiSQL_ Heidis QL is a graphical interface for simplifying Mini MySQL server and database management
Use steps:
Step 1: open the software, enter the host and port, as well as their user name and password
Step 2: select a data table and view it
5. Reference:
PostgreSQL: The world's most advanced open source database
postgresql common commands and operations - single nettle ring - blog Garden
http://www.postgres.cn/docs/10/intro-whatis.html