introduce
Vue resource is a plug-in of vue.js, which initiates requests and processes responses through XMLHttpRequest or JSONP
Vue resource is recommended by vue 1, while axios is recommended by vue 2.0. In fact, both of them can send requests to the backend to get responses.
install
Since vue-resource.js is a plug-in of Vue, it needs to be installed.
For local installation, please refer to: https://blog.csdn.net/cnds123321/article/details/103988468
CDN can also be used to introduce:
<script src="https://cdn.staticfile.org/vue-resource/1.5.1/vue-resource.min.js"></script>
grammar
Using Vue resource in a Vue instance requires $http.
The syntax is as follows:
// Using http based on global Vue objects
Vue.http.get('/someUrl', [options]).then(successCallback, errorCallback);
Vue.http.post('/someUrl', [body], [options]).then(successCallback, errorCallback);
// Using $http in a Vue instance
this.$http.get('/someUrl', [options]).then(successCallback, errorCallback);
this.$http.post('/someUrl', [body], [options]).then(successCallback, errorCallback);After sending the request, use the then method to process the response results. The then method has two parameters. The first parameter is the callback function returned when the response succeeds, and the second parameter is the callback function when the response fails.
The specific writing method of callback function:
this.$http.get("/url",[options]).then(function(response){
// Response success callback function
},function(response){
// Response failure callback function
});GET request
Here is the Java used as the back-end language, using servlet s to respond to front-end requests.
You need to pass parameters here, using the
this.$http.get("url", {
params: {
parm1: value1,
parm2: value2
}
}).then(function(res) {
document.write(res.body);
}, function(res) {
console.log(res.status);
});index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"/>
<title>Vue Study</title>
<!-- Introduce vue.js -->
<script src="js/vue.min.js"></script>
<!--Introduce vue-resource.js Plug-in unit-->
<script src="js/vue-resource.min.js"></script>
<!-- Use CDN Introduce Vue.js -->
<!--<script type="text/javascript" src=" https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/vue/2.1.8/vue.min.js"></script>-->
<!-- Use CDN Introduce vue-resource.js -->
<!--<script type="text/javascript" src="https://cdn.staticfile.org/vue-resource/1.5.1/vue-resource.min.js"></script>-->
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<p>Login successful user (user name: admin;Password: admin)</p>
//User name: < input type = "text" V-model = "user" > < br >
//Password: < input type = "password" V-model = "password" > < br >
<input type="button" value="Sign in" @click="login()">
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
user: '',
password: ''
},
methods: {
login: function () {
this.$http.get('http://localhost:8080/loginServlet', {
params: {
user: this.user,
password: this.password
}
}).then(function (res) {
if (res.data.ok != 1) {
alert(res.data.msg);
} else {
alert(res.data.msg);
}
}, function (res) {
console.log('Transmission failure');
});
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>Browser display:
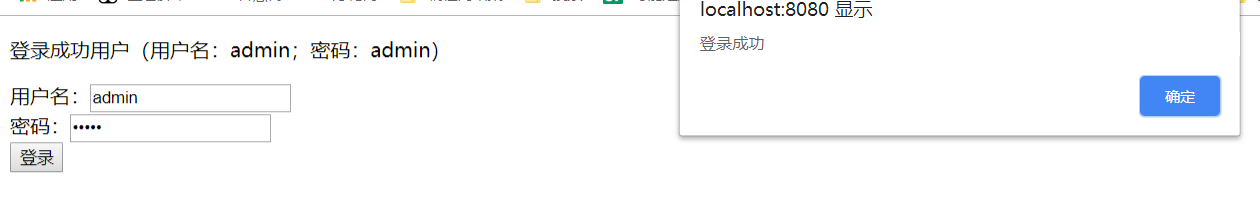
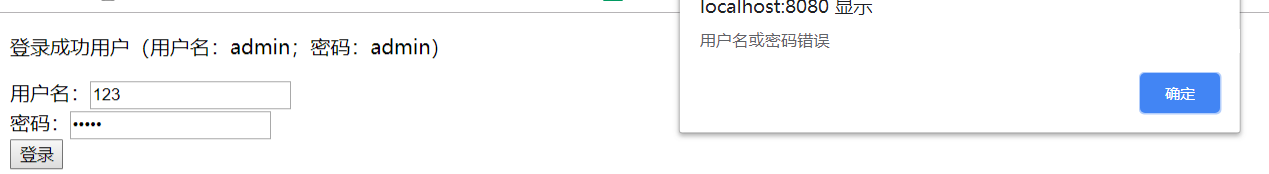
View with Google browser

The response is:

POST request
The third parameter {emulateJSON:true} is required for post to send data to the backend.
The function of emulateJSON: if the Web server cannot process the request encoded as application/json, you can enable the emulateJSON option.
Syntax to send a POST request:
// Send POST request
this.$http.post(
'url',
data,
{emulateJSON: true}
).then(function (res) {
// Callback function responding successfully
}, function (res) {
// Callback function with failed response
});index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"/>
<title>Vue Study</title>
<!-- Introduce vue.js -->
<script src="js/vue.min.js"></script>
<!--Introduce vue-resource.js Plug-in unit-->
<script src="js/vue-resource.min.js"></script>
<!-- Use CDN Introduce Vue.js -->
<!--<script type="text/javascript" src=" https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/vue/2.1.8/vue.min.js"></script>-->
<!-- Use CDN Introduce vue-resource.js -->
<!--<script type="text/javascript" src="https://cdn.staticfile.org/vue-resource/1.5.1/vue-resource.min.js"></script>-->
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<p>Login successful user (user name: admin;Password: admin)</p>
//User name: < input type = "text" V-model = "user" > < br >
//Password: < input type = "password" V-model = "password" > < br >
<input type="button" value="Sign in" @click="login()">
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
user: '',
password: ''
},
methods: {
login: function () {
// Send POST request
this.$http.post('http://localhost:8080/loginServlet',
{
user: this.user,
password: this.password
},
{emulateJSON: true}
).then(function (res) {
if (res.data.ok != 1) {
alert(res.data.msg);
} else {
alert(res.data.msg);
}
}, function (res) {
console.log('Transmission failure');
});
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>Browser submission:
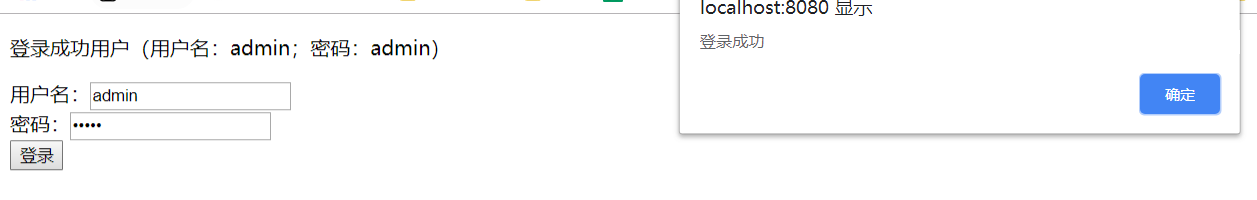
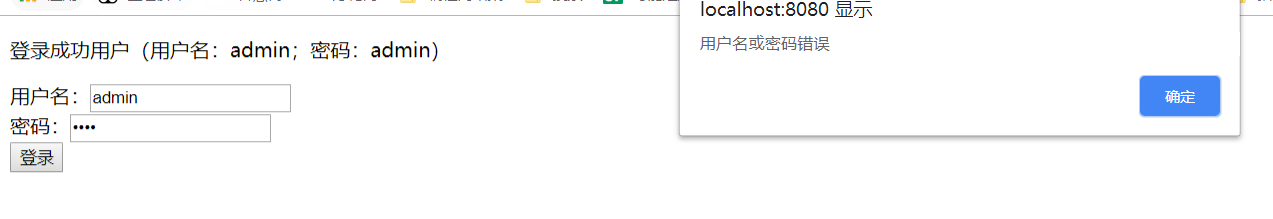
To view browser requests:

Response data:

API
Use Vue.http as a global object or this.$http within a Vue instance to initiate HTTP requests.
// Using http based on global Vue objects
Vue.http.get('/someUrl', [options]).then(successCallback, errorCallback);
Vue.http.post('/someUrl', [body], [options]).then(successCallback, errorCallback);
// Using $http in a Vue instance
this.$http.get('/someUrl', [options]).then(successCallback, errorCallback);
this.$http.post('/someUrl', [body], [options]).then(successCallback, errorCallback);
Vue resource provides seven request APIs (rest style):
get(url, [options]) head(url, [options]) delete(url, [options]) jsonp(url, [options]) post(url, [body], [options]) put(url, [body], [options]) patch(url, [body], [options])
In addition to jsonp, six other API names are standard HTTP methods.
options parameter description:
| parameter | type | describe |
|---|---|---|
| url | string | Requested destination URL |
| body | Object, FormData, string | Data sent as request body |
| headers | Object | Header object sent as request header |
| params | Object | Parameter object as URL parameter |
| method | string | HTTP methods (such as GET, POST,...) |
| timeout | number | Request timeout in milliseconds (0 means never timeout) |
| before | function(request) | Modify the callback function of the request before it is sent |
| progress | function(event) | The callback function ProgressEvent used to process the upload progress |
| credentials | boolean | Need to present credentials for cross site requests |
| emulateHTTP | boolean | Whether you need to set the X-HTTP-Method-Override header and send PUT, PATCH and DELETE requests in the traditional POST mode. |
| emulateJSON | boolean | Set the type of request body to application/x-www-form-urlencoded |
The response object obtained from a request is processed by the following properties and methods:
| attribute | type | describe |
|---|---|---|
| url | string | URL source for response |
| body | Object, Blob, string | Response data |
| headers | Header | Request header object |
| ok | boolean | true when the HTTP response code is a value between 200 and 299 |
| status | number | HTTP response code |
| statusText | string | HTTP response status |
| Method | type | describe |
| text() | Agreed value | Returns the response body as a string |
| json() | Agreed value | Return the response body as a formatted json object |
| blob() | Agreed value | Return the response body as a binary Blob object |
Complete code
Project structure:

If you are interested in full source code.
You can search the WeChat public number [Java instance program] or scan the underlying two-dimensional code to pay more attention to the public number.
Note: the source code can be obtained in the background of CSDN202001181642.


