summary
The adjacency matrix is constructed from the given matrix
List<List<Integer>> graph = new ArrayList<>(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) graph.add(new ArrayList<>(3));
for (int[] path : paths) {
graph.get(path[0] - 1).add(path[1] - 1);
graph.get(path[1] - 1).add(path[0] - 1);
}
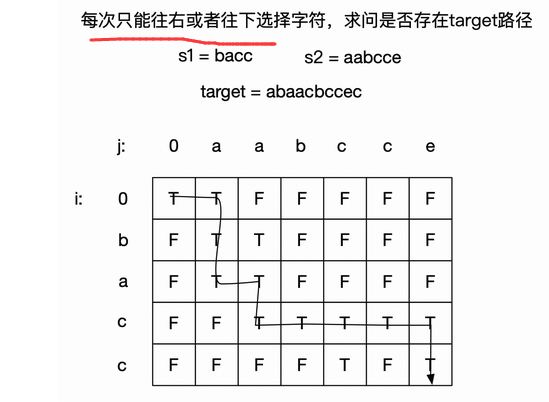
In a matrix that can go in four directions, it is usually wrong to use memo [] [because memo [] [] can only represent the results obtained by going in three directions at the current point, and it cannot go back. Therefore, for example, in question 79, in word search, we can judge in advance whether it is possible to search the target string, which is also a kind of pruning.
2021.08.11 day 1 summation problem
Sum of two numbers
Given an integer array nums and an integer target value target, please find the two integers with and as the target value target in the array and return their array subscripts.
Idea: traverse the array, put the traversed elements into the map, and then compare there to see if there is target num [i] in the map
class Solution {
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
Map<Integer,Integer>map=new HashMap();
for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){
if(map.containsKey(target-nums[i]))
return new int[]{i,map.get(target-nums[i])};
map.put(nums[i],i);
}
return null;
}
}
2 167. Sum of two numbers II - input ordered array
class Solution {
public int[] twoSum(int[] numbers, int target) {
int i=0;int j=numbers.length-1;
while(i<j){
if(numbers[i]+numbers[j]<target) i++;
else if(numbers[i]+numbers[j]>target) j--;
else return new int[]{i+1,j+1};
}
return null;
}
}
2021.08.12 day 2 summation problem
3.15 sum of three
Give you an array nums containing n integers. Judge whether there are three elements a, b and c in nums, so that a + b + c = 0? Please find all triples with a sum of 0 and no repetition.
Note: the answer cannot contain duplicate triples.
Solution ideas: fix the first number, and then use the double pointer to find the remaining two numbers. Remember to de duplicate each time. In order to avoid repetition, sort the array first to reduce the weight
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> threeSum(int[] nums) {
Arrays.sort(nums);
List<List<Integer>>list=new ArrayList();
for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){
if(i>0&&nums[i]==nums[i-1])
continue;//duplicate removal
int L=i+1;int R=nums.length-1;
while(L<R){
if(nums[L]+nums[R]>0-nums[i])
R--;
else if(nums[L]+nums[R]<0-nums[i])
L++;
else {
list.add(Arrays.asList(nums[i],nums[L],nums[R]));
int temp=nums[L];
int temp2=nums[R];
while(L<R&&nums[++L]==temp);//L remove the weight and pay attention to avoid crossing the boundary
while(L<R&&nums[--R]==temp2);//R remove the weight and pay attention to avoid crossing the boundary
}
}
}
return list;
}
}
4.18 sum of four numbers

First look at the violence solution, quadruple for loop enumeration, then sort by using Collections.sort(ans), and then reduce the weight
class Solution {
public static List<List<Integer>> fourSum(int[] nums, int target) {
List<List<Integer>> resp = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){
for(int j=i+1;j<nums.length;j++){
for(int k=j+1;k<nums.length;k++){
for(int l=k+1;l<nums.length;l++){
if(nums[i]+nums[j]+nums[k]+nums[l] == target){
List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();
ans.add(nums[i]);
ans.add(nums[j]);
ans.add(nums[k]);
ans.add(nums[l]);
Collections.sort(ans);
if(!resp.contains(ans)){
resp.add(ans);
}
}
}
}
}
}
return resp;
}
}
Then add a for loop to the sum of three numbers
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> fourSum(int[] nums, int target) {
Arrays.sort(nums);
List<List<Integer>>list=new ArrayList();
for(int k=0;k<nums.length;k++){
if(k>0&&nums[k]==nums[k-1])
continue;//duplicate removal
for(int i=k+1;i<nums.length;i++){
if(i>k+1&&nums[i]==nums[i-1])
continue;//duplicate removal
int L=i+1;int R=nums.length-1;
while(L<R){
if(nums[L]+nums[R]>target-nums[k]-nums[i])
R--;
else if(nums[L]+nums[R]<target-nums[k]-nums[i])
L++;
else {
list.add(Arrays.asList(nums[k],nums[i],nums[L],nums[R]));
int temp=nums[L];
int temp2=nums[R];
while(L<R&&nums[++L]==temp);//L remove the weight and pay attention to avoid crossing the boundary
while(L<R&&nums[--R]==temp2);//R remove the weight and pay attention to avoid crossing the boundary
}
}
}
}
return list;
}
}
The effect of pruning is still immediate
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> fourSum(int[] nums, int target) {
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
if (nums == null || nums.length < 4) {
return result;
}
Arrays.sort(nums);
int length = nums.length;
// ergodic
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length - 3; i++) {
// prune
if (nums[i] + nums[i + 1] + nums[i + 2] + nums[i + 3] > target) break;
if (nums[i] + nums[length - 3] + nums[length - 2] + nums[length - 1] < target) continue;
// duplicate removal
if (i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1]) continue;
// Cycle the second number
for (int j = i + 1; j < nums.length - 2; j++) {
// prune
if (nums[i] + nums[j] + nums[j + 1] + nums[j + 2] > target) break;
if (nums[i] + nums[j] + nums[length - 2] + nums[length - 1] < target) continue;
// duplicate removal
if (j > i + 1 && nums[j] == nums[j - 1]) continue;
// Define pointer
int left = j + 1, right = nums.length - 1;
while (left < right) {
int sum = nums[i] + nums[j] + nums[left] + nums[right];
if (sum > target) {
right--;
} else if (sum < target) {
left++;
} else if (sum == target) {
result.add(Arrays.asList(nums[i], nums[j], nums[left], nums[right]));
// De duplication after finding an array
while (left < right && nums[right] == nums[right - 1]) right--;
while (left < right && nums[left] == nums[left + 1]) left++;
// Move pointer
right--;
left++;
}
}
}
}
return result;
}
}
2021.08.13 fiboracci series on the third day
5 509. Fibonacci number

class Solution {
public int fib(int n) {
if(n<=1)
return n;
int a=0,b=1,c=0;
for(int i=1;i<n;i++){
c=a+b;
a=b;
b=c;
}
return c;
}
}
6.70. Climbing stairs
Suppose you are climbing stairs. You need n steps to reach the roof.
You can climb one or two steps at a time. How many different ways can you climb to the roof?
Note: given n is a positive integer.
The idea of solving the problem is that the nth stairs can be obtained by jumping one step of the Nth-1 stairs or two steps of the nth-2 stairs. Therefore, f(n) = f(n-1+f(n-2)
class Solution {
public int climbStairs(int n) {
if(n<3)
return n;
int a=1,b=2,c=0;
for(int i=3;i<=n;i++){
c=a+b;
a=b;
b=c;
}
return c;
}
}
2021.08.14 day 4 dynamic programming method
7 53. Maximum subsequence sum
Given an integer array nums, find a continuous sub array with the largest sum (the sub array contains at least one element) and return its maximum sum.
Idea: dp[i] represents the maximum suborder sum at the end of each element,
If the maximum suborder sum at the end of the previous element is greater than 0, the maximum suborder sum at the end of the current element is the sum of the current element plus the maximum suborder sum at the end of the previous element
Otherwise, the maximum sub order sum at the end of the current element is the current element
class Solution {
public int maxSubArray(int[] nums) {
int dp[]=new int [nums.length];
dp[0]=nums[0];
int max=dp[0];
for(int i=1;i<nums.length;i++){
dp[i]=dp[i-1]>0?nums[i]+dp[i-1]:nums[i];
max=Math.max(dp[i],max);
}
return max;
}
}
class Solution {
public int maxSubArray(int[] nums) {
//The solution idea is to discard the sequence before the current pointer if it is less than 0, that is, do not participate in the subsequent calculation if it is less than 0, and add it to num [i] if it is greater than 0
int curSum=nums[0];
int max=nums[0];
for(int i=1;i<nums.length;i++)
{
if(nums[i-1]>0) nums[i]=nums[i-1]+nums[i];
max=Math.max(nums[i],max);
}
return max;
}
}
class Solution {
public int maxSubArray(int[] nums) {
int result=Integer.MIN_VALUE;
int sum=0;
for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++)
{
sum+=nums[i];
if(sum>result) result=sum;
if(sum<0) sum=0;
}
return result;
}
}
8 416. Segmentation and subsets
Give you a non empty array num containing only positive integers. Please judge whether you can divide this array into two subsets so that the sum of the elements of the two subsets is equal.
Train of thought 1 memorization and regression search,
The last one
return memo[i][target] = dfs(nums, target - nums[i], i + 1, memo) || dfs(nums, target, i + 1, memo);
It means that num [i] can be taken or not taken. If it is not taken, it is necessary to search for target in the next element. If it is taken, it is necessary to search for target - num [i] in the next element.
class Solution {
public boolean canPartition(int[] nums) {
int sum = Arrays.stream(nums).sum();
if (sum % 2 != 0) return false;
Arrays.sort(nums);
return dfs(nums, sum / 2, 0, new Boolean[nums.length][sum / 2 + 1]);
}
private boolean dfs(int[] nums, int target, int i, Boolean[][] memo) {
if (i >= nums.length || nums[i] > target)
return false;
if (nums[i] == target)
return true;
if (memo[i][target] != null)
return memo[i][target];
return memo[i][target] = dfs(nums, target - nums[i], i + 1, memo) || dfs(nums, target, i + 1, memo);
}
}

Idea 2: dynamic programming

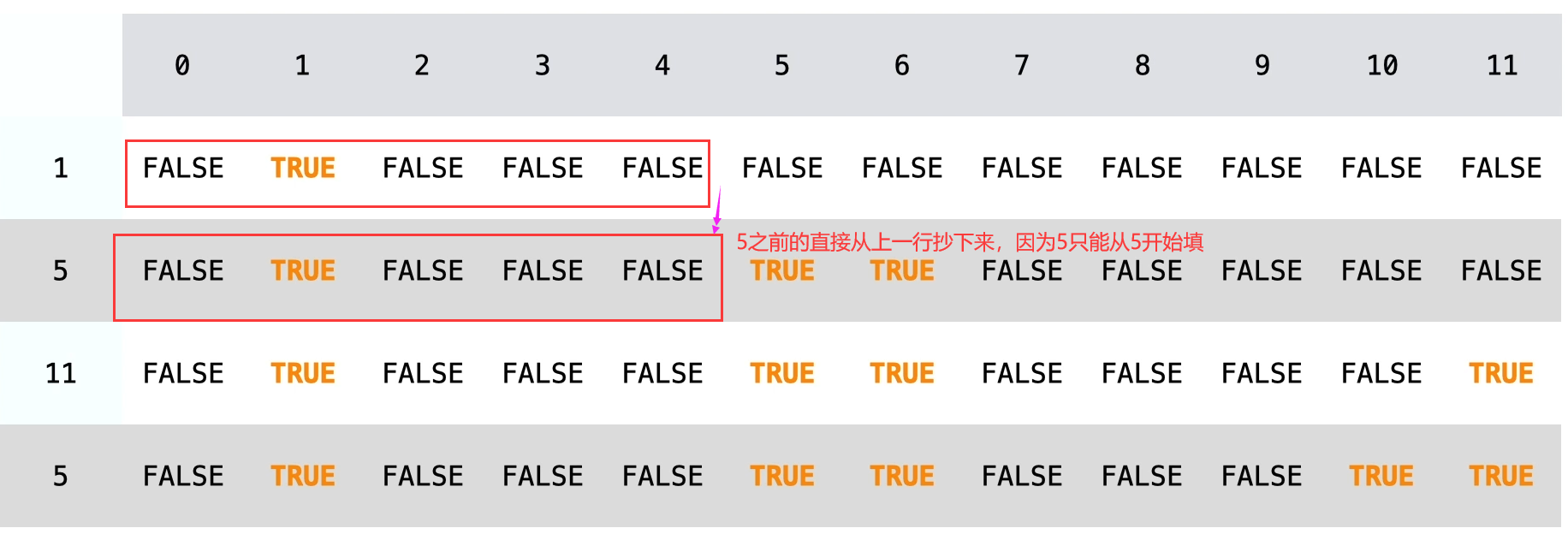
Considering the current element, dp will be transferred from a number on the left of the previous line. For example, the current num [i] is equal to 5 and target=9. When we go to 5, we need to consider whether the previous num elements can be rounded up to 4
Regardless of the current element, the state is directly copied from the previous grid. What can be composed originally and what can be composed now
class Solution {
public boolean canPartition(int[] nums) {
//In essence, it is a 0,1 knapsack problem to find whether the sum of several numbers in the array can reach half of the sum of all elements of the array, and each element can only be used once
int sum=0;
int max=0;
for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){
sum+=nums[i];
max=Math.max(nums[i],max);
}
if(sum%2!=0||max>sum/2)
return false;
int target=sum/2;
boolean dp[][]=new boolean[nums.length+1][target+1];
for(int i=1;i<=nums.length;i++) {
for(int j=0;j<=target;j++){
if(nums[i-1]>j)//You can't use nums[i-1] to form j, you can only use the result of the previous line
dp[i][j]=dp[i-1][j];//Copy the result of the previous line directly
else if(nums[i-1]<j)//You can use the current num [I-1] to form J. it also depends on whether the previous elements can form j-num [I-1], or you can directly copy the previous results without the current num [I-1], and the two are the same
dp[i][j]=dp[i-1][j]||dp[i-1][j-nums[i-1]];
else
dp[i][j]=true;//j can be formed because nums[i-1]=j
}
}
return dp[nums.length][target];
}
}
???
9 322. Change
public class Solution {
public int coinChange(int[] coins, int amount) {
int max = amount + 1;
int[] dp = new int[amount + 1];
Arrays.fill(dp, max);
dp[0] = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= amount; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < coins.length; j++) {
if (coins[j] <= i) {
dp[i] = Math.min(dp[i], dp[i - coins[j]] + 1);
}
}
}
return dp[amount] > amount ? -1 : dp[amount];
}
}
I used hashSet to write timeout before
public class Solution {
public int coinChange(int[] coins, int amount) {
if(amount==0) return 0;
int dp[]=new int [amount+1];
dp[0]=0;
Set<Integer>set=new HashSet();
for(int i=0;i<coins.length;i++) set.add(coins[i]);
for(int i=1;i<=amount;i++)
{
dp[i]=Integer.MAX_VALUE;
if(set.contains(i)) dp[i]=1;
else {
for(int j=1;j<=i/2;j++)
{
if(dp[j]!=-1&&dp[i-j]!=-1)
dp[i]=Math.min(dp[i],dp[j]+dp[i-j]);
}
if(dp[i]==Integer.MAX_VALUE) dp[i]=-1;
}
}
return dp[amount];
}
}
2021.08.15 day 5 stack
10 20. Valid brackets
Given a string s that only includes' (',') ',' {','} ',' [','] ', judge whether the string is valid.
Valid strings must meet:
The left parenthesis must be closed with the same type of right parenthesis. The left parentheses must be closed in the correct order.
class Solution {
public boolean isValid(String s) {
Stack<Character>stack=new Stack();
for(int i=0;i<s.length();i++){
if(s.charAt(i)==')'){
if(!stack.isEmpty()&&stack.peek()=='(') stack.pop();
else return false;
}
else if(s.charAt(i)=='}'){
if(!stack.isEmpty()&&stack.peek()=='{') stack.pop();
else return false;
}
else if(s.charAt(i)==']'){
if(!stack.isEmpty()&&stack.peek()=='[') stack.pop();
else return false;
}
else
stack.push(s.charAt(i));
}
return stack.isEmpty();
}
}
11 496. Next larger element I
Give you two arrays nums1 and nums2 without duplicate elements, where nums1 is a subset of nums2.
Please find out the next larger value of each element in nums1 in nums2.
The next larger element of the number x in nums1 refers to the first element larger than x to the right of the corresponding position in nums2. If it does not exist, the corresponding position outputs - 1.
Idea 1: where is the violence ratio? Now find the corresponding element in array 1 in array 2, and then find the next element larger than the element from this position
class Solution {
public int[] nextGreaterElement(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {
int arr[]=new int [nums1.length];
for(int i=0;i<nums1.length;i++){
int j=0;
while(j<nums2.length&&nums2[j]!=nums1[i])
j++;
j++;//Move back one bit
while(j<nums2.length&&nums2[j]<nums1[i])
j++;
arr[i]=j>=nums2.length?-1:nums2[j];
}
return arr;
}
}
I'm also stupid. I can modify the original array nums1 without additional space
class Solution {
public int[] nextGreaterElement(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {
for(int i=0;i<nums1.length;i++){
int j=0;
while(j<nums2.length&&nums2[j++]!=nums1[i]);
while(j<nums2.length&&nums2[j]<nums1[i])
j++;
nums1[i]=j>=nums2.length?-1:nums2[j];
}
return nums1;
}
}
In fact, finding the first number on the right that is greater than yourself is a typical "stack" application (also known as "monotone stack"), which puts each element into and out of the stack once. In this process, you can find the first number on the right that is greater than yourself.
Idea 2: monotone stack
After traversing nums2, if no smaller element is found from front to back, put the element on the stack, and then find one larger than the top of the stack, store the top of the stack element and the corresponding larger element in the map, pop up the top of the stack, and pay attention to the cyclic comparison of the top of the stack
Finally, for elements that cannot be found in the map, the corresponding value is set to - 1;
public class Solution {
public int[] nextGreaterElement(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {
int len1 = nums1.length;
int len2 = nums2.length;
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
// First process nums2 and store the corresponding relationship in the hash table
for (int i = 0; i < len2; i++) {
while (!stack.isEmpty() && stack.peek() < nums2[i]) {
map.put(stack.pop(), nums2[i]);
}
stack.add(nums2[i]);
}
// Traverse nums1 to get the result set
for (int i = 0; i < len1; i++) {
nums1[i] = map.getOrDefault(nums1[i], -1);
}
return nums1;
}
}
503. Next larger element II
Given a circular array (the next element of the last element is the first element of the array) , output the next larger element of each element. The next larger element of the number x is in the order of array traversal, and the first larger number after this number means that you should search for its next larger number cyclically. If it does not exist, output - 1.
Problem solving ideas, straighten the circular array
class Solution {
public int[] nextGreaterElements(int[] nums) {
int n=nums.length;
int ret[]=new int[n];
Arrays.fill(ret, -1);
Stack<Integer>stack=new Stack();
// Map<Integer,Integer>map=new HashMap();// There are duplicate elements in the array, so it's not easy to use map
for(int i=0;i<n*2-1;i++){
while(!stack.isEmpty()&&nums[stack.peek()]<nums[i%n]){
ret[stack.pop()]=nums[i%n];
}
//stack.push(nums[i%n]);
stack.push(i%n);//Save the index, absolutely
}
return ret;
}
}
Improved version, otherwise there will be repeated judgment
class Solution {
public int[] nextGreaterElements(int[] nums) {
int n=nums.length;
int ret[]=new int[n];
Arrays.fill(ret, -1);
Stack<Integer>stack=new Stack();
for(int i=0;i<n*2-1;i++){
while(!stack.isEmpty()&&nums[stack.peek()]<nums[i%n]){
ret[stack.pop()]=nums[i%n];
}
if(ret[i%n]==-1)
stack.push(i%n);//Save the index, absolutely
}
return ret;
}
}
Static array
class Solution {
public int[] nextGreaterElements(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
int[] ans = new int[n];
Arrays.fill(ans, -1);
// Use the array to simulate the stack. hh represents the bottom of the stack and tt represents the top of the stack
int[] d = new int[n * 2];
int hh = 0, tt = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < n * 2; i++) {
while (hh <= tt && nums[i % n] > nums[d[tt]]) {
int u = d[tt--];
ans[u] = nums[i % n];
}
d[++tt] = i % n;
}
return ans;
}
}
12 456.132 mode
Give you an integer array nums. There are n integers in the array. The subsequence of 132 mode is composed of three integers nums[i], nums[j] and nums[k], and satisfies I < J < K and nums[i] < nums[k] < nums[j].
If there is a subsequence of 132 mode in nums, return true; Otherwise, false is returned.

reference resources: Graphical monotone stack
class Solution {
public boolean find132pattern(int[] nums) {
int len=nums.length;
if(len<3) return false;
Stack<Integer> st=new Stack<>();
int K=-1;
for(int I=len-1;I>=0;I--){
if(K>-1&&nums[K]>nums[I]) return true;
while(!st.isEmpty()&&nums[st.peek()]<nums[I]){
K=st.pop();
}
st.push(I);
}
return false;
}
}
2021.08.16 day 6 figures
13 119. Yanghui triangle II
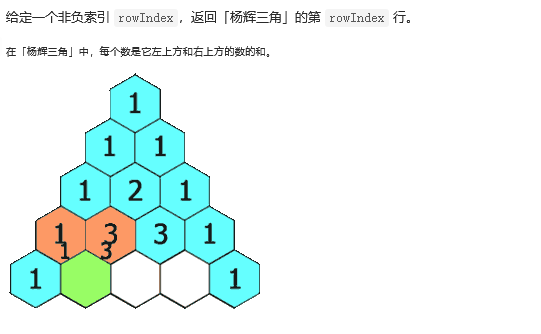
class Solution {
public List<Integer> getRow(int rowIndex) {
List<List<Integer>>list=new ArrayList();
for(int i=0;i<=rowIndex;i++){
List list2=new ArrayList();
for(int j=0;j<=i;j++){
if(j==0||j==i){
list2.add(1);
}else{
list2.add(list.get(i-1).get(j-1)+list.get(i-1).get(j));
}
}
list.add(list2);
}
return list.get(rowIndex);
}
}
class Solution {
public List<Integer> getRow(int rowIndex) {
List<Integer> pre = new ArrayList<Integer>();
for (int i = 0; i <= rowIndex; ++i) {
List<Integer> cur = new ArrayList<Integer>();
for (int j = 0; j <= i; ++j) {
if (j == 0 || j == i) {
cur.add(1);
} else {
cur.add(pre.get(j - 1) + pre.get(j));
}
}
pre = cur;
}
return pre;
}
}
14 279. Complete square

Solution idea: first judge whether the current I is a complete square number. If so, dp[i]=1; If not, traverse the previous dp in turn to find the smallest one in dp[j]+dp[i-j], that is, the least square number of components j plus the least square number of components i-j, and add it to 1 / 2, because it will be repeated later
class Solution {
public int numSquares(int n) {
int dp[]=new int[n+1];
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
if((int)Math.sqrt(i)*(int)Math.sqrt(i)==i){
dp[i]=1;
}
else{
dp[i]=Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for(int j=1;j<=i/2;j++){
dp[i]=Math.min(dp[j]+dp[i-j],dp[i]);
}
}
}
return dp[n];
}
}

Problem solving ideas 2

class Solution {
public int numSquares(int n) {
int[] f = new int[n + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
int minn = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int j = 1; j * j <= i; j++) {
minn = Math.min(minn, f[i - j * j]);
}
f[i] = minn + 1;
}
return f[n];
}
}
Problem solving thinking 3 BFS
The value of each node is the accumulation from the root node to the current node. The number of squares is actually the cumulative sum equal to target when traversing to which layer. We only need to traverse layer by layer, that is, BFS. When the cumulative sum is equal to target, we can directly return the current number of layers.
Reference: [data structure and algorithm] BFS, dynamic programming, Lagrange's square sum theorem, etc
class Solution{
public int numSquares(int n) {
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
//Record the accessed node values
Set<Integer> visited = new HashSet<>();
queue.offer(0);
visited.add(0);
//Which layer of the tree
int level = 0;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
//Number of nodes per layer
int size = queue.size();
level++;
//Traverse all nodes of the current layer
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
//The value of the node
int digit = queue.poll();
//Accessing the child nodes of the current node is similar to the left and right child nodes of a binary tree
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
//Values of child nodes
int nodeValue = digit + j * j;
//nodeValue is always the sum of perfect squares when it is equal to n
//When to return directly
if (nodeValue == n)
return level;
//If greater than n, terminate the inner loop
if (nodeValue > n)
break;
if (!visited.contains(nodeValue)) {
queue.offer(nodeValue);
visited.add(nodeValue);
}
}
}
}
return level;
}
}
15 483. Minimum good base

August 17, 2021 day 7 tree
16 112. Path sum
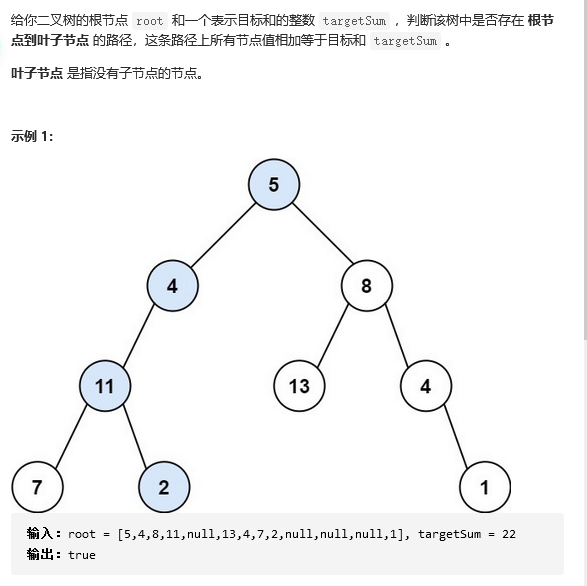
class Solution {
public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int sum) {
if(root==null)
return false;
if(root.left==null&&root.right==null)
return root.val==sum;
return hasPathSum(root.right, sum-root.val)|| hasPathSum(root.left, sum-root.val);
}
}
Idea 2: sequence traversal: one queue stores the node, and the other queue stores the sum value when adding the current node val
17 230. The K-th smallest element in the binary search tree
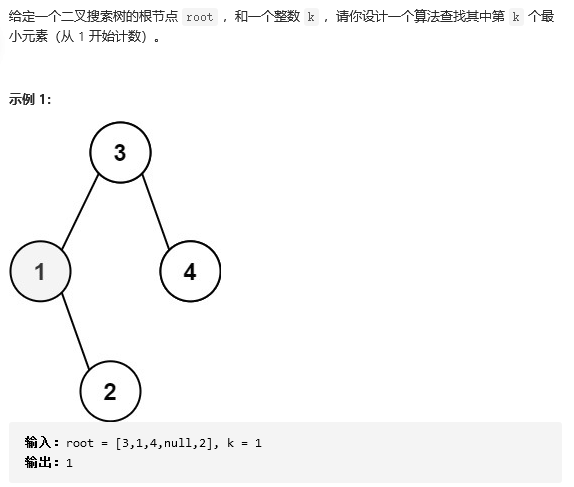
Since it is a binary search tree, then the middle order traversal is an ordered ascending sequence. Let's just go through the middle order traversal directly. 2
class Solution {
int count=0;
int val=-1;
public int kthSmallest(TreeNode root, int k) {
inOrder(root,k);
return val;
}
public void inOrder(TreeNode root, int k){
if(root==null)
return ;
inOrder(root.left, k);
count++;
if(count==k){
val= root.val;
return;
}
inOrder(root.right, k);
}
}
Train of thought 2;: Order traversal in iteration
18 968. Monitoring binary tree
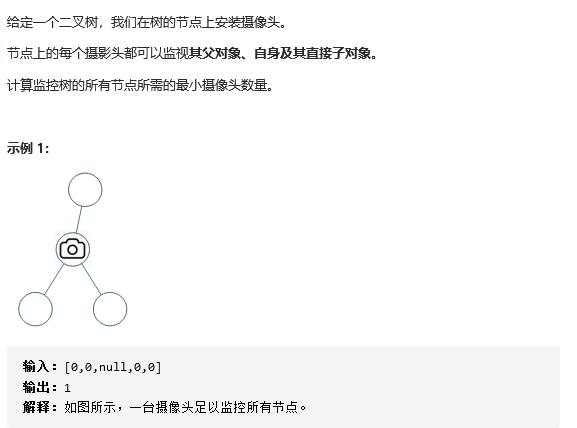
Reference for problem solving ideas: 968. Monitoring binary tree: [state transition on recursion] detailed explanation
class Solution {
int res=0;
public int minCameraCover(TreeNode root) {
return dfs(root)==0?res+1:res;//If the parent node is in an uncovered state, you need to add a camera to the parent node
}
public int dfs(TreeNode root){
if(root==null)
return 2;//Node has coverage
int left=dfs(root.left);
int right=dfs(root.right);
//0 means no coverage, 1 means there is a camera, 2 means there is coverage, and the left and right nodes can form 9 states
//(00,01,02,10,11,12,20,21,22)
//As long as there is no coverage, the parent node needs a camera to cover the child node 00,01,10,20,02
if(left==0||right==0){
res++;
return 1;
}
//As long as one of the child nodes has a camera, the parent node will be covered 11,21,12
if(left==1||right==1){
return 2;
}
//Another is 22. The two child nodes are covered. The parent node can have no camera and can use its own parent node
return 0;
}
}
2021.08.18 day 8 string
(19) 720. The longest word in the dictionary

Problem solving ideas
20 3. Longest substring without repeated characters
Given a string s, please find the length of the longest substring that does not contain duplicate characters.
Problem solving idea: traverse the character array. If there is no such character in the map, directly put the character into the container, and define a left pointer and a max
If the current character already exists in the container, record a current max value max=Math.max(i-left,max);
At this time, the left pointer should also judge whether it needs to move to the next repeated character. For abba, b repeats first, and left points to 2. Now a repeats, and left cannot point to 1, but continues to point to 2. Therefore, left = math.max (left, map.get (arr [I]) + 1; That is, the left pointer cannot move back
Finally, it is also necessary to judge whether the last character is a non repeated number. max=Math.max(arr.length-left,max);
class Solution {
public int lengthOfLongestSubstring(String s) {
if(s.length()<=1)
return s.length();
int left=0;int max=0;
Map<Character,Integer>map=new HashMap();
char arr[]=s.toCharArray();
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){
if(!map.containsKey(arr[i])){
map.put(arr[i],i);
}
else{
max=Math.max(i-left,max);
left=Math.max(left,map.get(arr[i])+1);
map.put(arr[i],i);
}
}
max=Math.max(arr.length-left,max);
return max;
}
}
Modify the code of the second edition as follows
class Solution {
public int lengthOfLongestSubstring(String s) {
int left=0;int max=0;
Map<Character,Integer>map=new HashMap();
char arr[]=s.toCharArray();
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){
if(map.containsKey(arr[i])){
max=Math.max(i-left,max);
left=Math.max(left,map.get(arr[i])+1);
}
map.put(arr[i],i);
}
max=Math.max(arr.length-left,max);
return max;
}
}
Problem solving idea 2, map each character to the array
Check whether the number of characters in the sliding window is greater than 1. If it is greater than 1, make a max judgment, and move the left pointer until the number of characters is greater than 1
class Solution {
public int lengthOfLongestSubstring(String s) {
int arr[]=new int[128];
char arr1[]=s.toCharArray();
int left=0;int max=0;
for(int i=0;i<arr1.length;i++){
arr[arr1[i]-32]++;
if(arr[arr1[i]-32]>1){
max=Math.max(max,i-left);
while(arr[arr1[i]-32]>1){
arr[arr1[left]-32]--;
left++;
}
}
}
return max=Math.max(max,s.length()-left);
}
}
21 97. Interleaved string
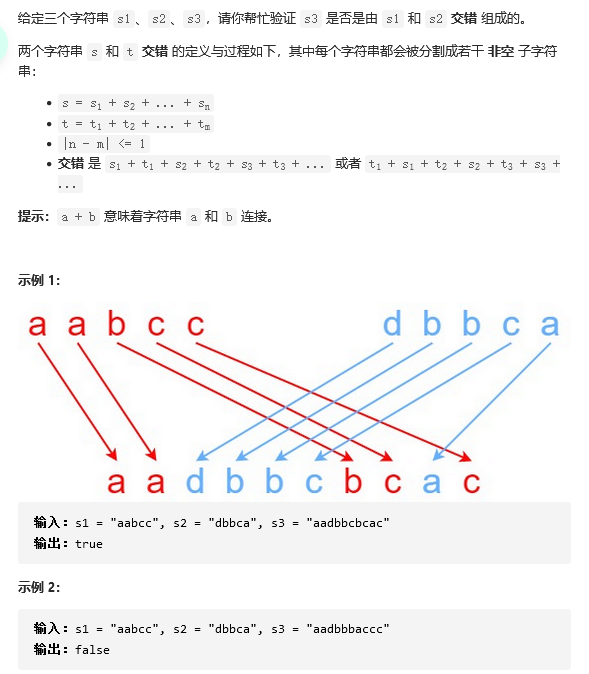
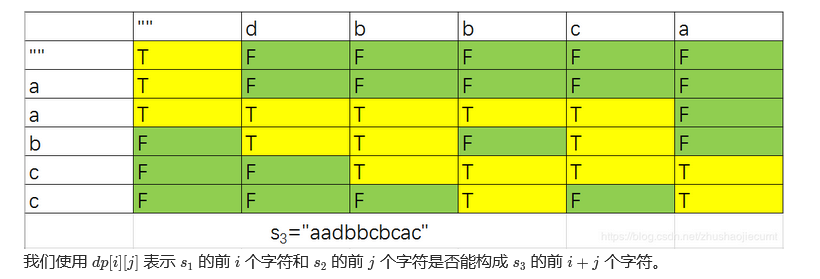
Solution idea: dynamic programming, see if the first j characters of s1 and s2 can form the first i+j characters of s3
reference resources: Dynamic programming explains Python 3 line by line
class Solution {
public boolean isInterleave(String s1, String s2, String s3) {
int m=s1.length();
int n=s2.length();
int p=s3.length();
if(m+n!=p)
return false;
boolean dp[][]=new boolean[m+1][n+1];
//dp[i][j] indicates whether the I characters of s1 and the first j characters of s2 can form the first i+j characters of s3
dp[0][0]=true;
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++)//Fill in the first column
dp[i][0]=dp[i-1][0]&&s1.charAt(i-1)==s3.charAt(i-1);
for(int j=1;j<=n;j++)//Fill in the first line
dp[0][j]=dp[0][j-1]&&s2.charAt(j-1)==s3.charAt(j-1);
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){
for(int j=1;j<=n;j++){
//dp[i][j] can be changed from dp[i-1][j] and dp[i][j-1]
dp[i][j]=(dp[i-1][j]&&s1.charAt(i-1)==s3.charAt(i+j-1))||
(dp[i][j-1]&&s2.charAt(j-1)==s3.charAt(i+j-1));
}
}
return dp[m][n];
}
}
Problem solving idea 2, depth first traversal, search each character of s3 in s1 and s2, which is essentially a path search
reference resources:
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/interleaving-string/solution/lei-si-lu-jing-wen-ti-zhao-zhun-zhuang-tai-fang-ch/
class Solution {
private boolean[][] visited;
public boolean isInterleave(String s1, String s2, String s3) {
if (s1.length() + s2.length() != s3.length())
return false;
visited = new boolean[s1.length() + 1][s2.length() + 1];
return backtrack(s1, s2, s3, 0, 0, 0);
}
private boolean backtrack(String s1, String s2, String s3, int i, int j, int k) {
if (k == s3.length())//All characters of description s3 are matched
return true;
if (visited[i][j])//If the current node has been accessed, it means that the previous path cannot go through it. Even if you go through the same node in another way, it still cannot go through
return false;//In the two-dimensional matrix, this element has been accessed, which means that its right and lower sides have been accessed, but it doesn't work. If we go through this point another way, it must still not work
visited[i][j] = true;
if (i < s1.length() && s1.charAt(i) == s3.charAt(k)
&& backtrack(s1, s2, s3, i + 1, j, k + 1)
|| j < s2.length() && s2.charAt(j) == s3.charAt(k)
&& backtrack(s1, s2, s3, i, j + 1, k + 1))
return true;
return false;
}
}
August 19, 2021 day 9
(22) 28. Implement str ()
23 524. Match the longest word in the dictionary by deleting letters
Give you a string s and a string array dictionary as a dictionary, find and return the longest string in the dictionary, which can be obtained by deleting some characters in S.
If there is more than one answer, the string with the longest length and the smallest dictionary order is returned. If the answer does not exist, an empty string is returned.
Example 1:
Input: s = "abpcplea", dictionary = ["ale", "apple", "monkey", "plea"]
Output: "apple"
Example 2:
Input: s = "abpcplea", dictionary = ["a", "b", "c"]
Output: "a"
Problem solving ideas

public class Solution {
public boolean isSubsequence(String x, String y) {
int j = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < y.length() && j < x.length(); i++)
if (x.charAt(j) == y.charAt(i))
j++;
return j == x.length();
}
public String findLongestWord(String s, List < String > d) {
String max_str = "";
for (String str: d) {
if (isSubsequence(str, s)) {
if (str.length() > max_str.length() || (str.length() == max_str.length() && str.compareTo(max_str) < 0))
max_str = str;
}
}
return max_str;
}
}
(24) 1392. Longest prefix

2021.08.20 day 10
25 1042. Non contiguous flower planting

Problem solving idea: build an adjacency matrix, and then compare each node there to see what flowers are used in its adjacency nodes. It will just put another kind of flowers. Since there are up to 3 paths in each garden and 4 kinds of flowers, we can certainly find a matching answer.
reference resources: The idea is very simple and difficult to implement (coloring problem)
class Solution {
public int[] gardenNoAdj(int n, int[][] paths) {
Map<Integer,Set<Integer>>graph=new HashMap();
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
graph.put(i,new HashSet());
for(int []path:paths){
graph.get(path[0]).add(path[1]);
graph.get(path[1]).add(path[0]);
}
int res[]=new int[n];
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
boolean[]used=new boolean[5];
for(int adj:graph.get(i))
used[res[adj-1]]=true;//Find the unused 1-4 parts of adjacent points// For example, adj=1,res[0]=0 description
//Res was originally 0. If it is not 0, it means that a flower has been put into res
for(int j=1;j<=4;j++){
if(!used[j])
res[i-1]=j;
}
}
return res;
}
}

class Solution {
public int[] gardenNoAdj(int n, int[][] paths) {
List<List<Integer>> graph = new ArrayList<>(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) graph.add(new ArrayList<>(3));
for (int[] path : paths) {
graph.get(path[0] - 1).add(path[1] - 1);
graph.get(path[1] - 1).add(path[0] - 1);
}
int[] ans = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
boolean[] used = new boolean[5];
for (int j : graph.get(i)) used[ans[j]] = true;
int t = 1;
while (used[t]) ++t;
ans[i] = t;
}
return ans;
}
}
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Solution {
public int[] gardenNoAdj(int n, int[][] paths) {
int[] res = new int[n];
if(paths.length == 0){
Arrays.fill(res,1);
return res;
}
int[][] adjoinGarden = new int[n + 1][3];
int[] gardenSize = new int[n + 1];
for (int[] p : paths) {
int v1 = p[0];
int v2 = p[1];
adjoinGarden[v1][gardenSize[v1]++] = v2;
adjoinGarden[v2][gardenSize[v2]++] = v1;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
boolean[] color = new boolean[4];
for (int j : adjoinGarden[i]) {
if (j != 0 && res[j - 1] != 0) {
color[res[j - 1] - 1] = true;
}
}
if (!color[0]) {
res[i - 1] = 1;
} else if (!color[1]) {
res[i - 1] = 2;
} else if (!color[2]) {
res[i - 1] = 3;
} else {
res[i - 1] = 4;
}
}
return res;
}
}
26 787. The cheapest flight in the transfer station K

Problem solving ideas, summarize and constantly change src in the process of backtracking, and record cost at the same time
Timeout. If I search memo [] [] by memory, I will still make an error, because memo [] [] can only represent the minimum value of memo when the last point passes here, not the minimum value from memo [] [] to dst
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>>graph=new ArrayList();
int[][]costs;
// Integer[][]memo;
boolean visited[];
int max;
//
public int findCheapestPrice(int n, int[][] flights, int src, int dst, int k) {
costs=new int[n][n];
// memo=new Integer[n][n];
visited=new boolean[n];
max=n;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
graph.add(new ArrayList());//Add n critical tables
for(int[] flight:flights){
costs[flight[0]][flight[1]]=flight[2];//Initialization cost
// costs[flight[1]][flight[0]]=flight[2];// Initialization cost / / note that it is a directed graph
graph.get(flight[0]).add(flight[1]);//Initialize adjacency table
// graph.get(flight[1]).add(flight[0]);// Initialize adjacency table
}
int result=dfs(src,dst,k+2,0);
return (result ==max*10000) ?-1:result;
}
public int dfs(int src,int dst,int k, int cost){
if((src==dst)&&k>0){
//The destination has been reached. Record the current cost
// return memo[src][dst]=cost;
return cost;
}
if(k<=0)//There are more than k transfer stations, which do not meet the requirements. A larger value is returned
return max*10000;
// if(memo[src][dst]!=null)
// return memo[src][dst];
if(visited[src])
return max*10000 ; //Cannot reverse access
visited[src]=true;
int result= max*10000 ;
for(int i=0;i<graph.get(src).size();i++){
if(costs[src][graph.get(src).get(i)]>0){//Note that it is a directed graph. If it is not greater than 0, it indicates that there is no connection before two points and cannot take off
int temp1= dfs(graph.get(src).get(i),dst,k-1,cost+costs[src][graph.get(src).get(i)]);
result=Math.min(result,temp1);
}
}
visited[src]=false;
return result;
// return memo[src][dst]=result;
}
}
Although the official deep search also timed out, there are more examples that can pass because there are more pruning bars, and the minimum value of res is reflected here
public class Solution {
private int[][] graph;
private boolean[] visited;
private int res = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
public int findCheapestPrice(int n, int[][] flights, int src, int dst, int K) {
K = Math.min(K, n - 2);
this.graph = new int[n][n];
for (int[] flight : flights) {
graph[flight[0]][flight[1]] = flight[2];
}
this.visited = new boolean[n];
// Start depth first traversal. Note: K + 1 is transmitted here because there are k stops, a total of K + 1 stations
dfs(src, dst, K + 1, 0);
if (res == Integer.MAX_VALUE) {
return -1;
}
return res;
}
/**
* Starting from src to dst, you can pass station k at most (here k includes src)
*
* @param src starting station
* @param dst Terminus
* @param k Number of sites passed
* @param cost Price spent
*/
private void dfs(int src, int dst, int k, int cost) {
if (src == dst) {
res = cost;
return;
}
if (k == 0) {
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < graph[src].length; i++) {
if (graph[src][i] > 0) {
if (visited[i]) {
continue;
}
// Pruning: skip paths that may incur higher costs to select the least price
if (cost + graph[src][i] > res) {
continue;
}
visited[i] = true;
dfs(i, dst, k - 1, cost + graph[src][i]);
visited[i] = false;
}
}
}
}
Author: LeetCode
Link: https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/cheapest-flights-within-k-stops/solution/k-zhan-zhong-zhuan-nei-zui-bian-yi-de-hang-ban-b-2/
Source: force buckle( LeetCode)
The copyright belongs to the author. For commercial reprint, please contact the author for authorization. For non-commercial reprint, please indicate the source.
A brother's memory search
class Solution {
// See DAG
// dp[i][j][k], the minimum cost of the most transfer K stations from station I to station j! Look at the title description and naturally think of this state
public int findCheapestPrice(int n, int[][] flights, int src, int dst, int K) {
int[][] cost = new int[n][n];
for(int i = 0; i < flights.length; i++){
int st = flights[i][0];
int en = flights[i][1];
int price = flights[i][2];
cost[st][en] = price;
}
int[][][] dp = new int[n][n][K+2];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++){
Arrays.fill(dp[i][j], -1);
}
}
int res = f(cost, src, dst, K+1, dp);
return res >= 1000000 ? -1 : res;
}
private int f(int[][] cost, int src, int dst, int K, int[][][] dp){
if(K < 0){
return 1000000;
}
if(dp[src][dst][K] != -1){
return dp[src][dst][K];
}
if(src == dst){
return dp[src][dst][K] = 0;
}
int ans = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for(int i = 0; i < cost.length; i++){
if(cost[src][i] != 0){
ans = Math.min(ans, cost[src][i] + f(cost, i, dst, K-1, dp));
}
}
return dp[src][dst][K] = (ans == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? 1000000 : ans);
}
}

dynamic programming
class Solution {
public int findCheapestPrice(int n, int[][] flights, int src, int dst, int K) {
// dp[i][k] is the minimum cost of arriving at station I after passing through K transfer stations
int[][] dp = new int[n][K + 1];
// Loop initializes the entire two-dimensional array.
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) Arrays.fill(dp[i], Integer.MAX_VALUE);
// Use the information in flights to initialize the direct shift of src
for(int[] flight : flights) {
if(flight[0] == src){
dp[flight[1]][0] = flight[2];
}
}
// Loop initializes the row with dst == src in the array
for(int i = 0; i <= K; i++){
dp[src][i] = 0;
}
//Dynamic programming state transition equation, start filling in the form
//The direct has been initialized (i.e. in the case of k = 0). Now it starts from k = 1, that is, there is only one transfer station
for(int k = 1; k <= K; k++){
for(int[] flight : flights){
//Combined with topic understanding
if(dp[flight[0]][k - 1] != Integer.MAX_VALUE){
dp[flight[1]][k] = Math.min(dp[flight[1]][k], dp[flight[0]][k - 1] + flight[2]);
}
}
}
return dp[dst][K] == Integer.MAX_VALUE? -1: dp[dst][K];
}
}

Breadth first search, also timeout?
I also want to mark the searched nodes. It doesn't seem to work
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>>graph=new ArrayList();
int[][]costs;
public int findCheapestPrice(int n, int[][] flights, int src, int dst, int k) {
costs=new int[n][n];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
graph.add(new ArrayList());//Add n critical tables
for(int[] flight:flights){
costs[flight[0]][flight[1]]=flight[2];//Initialization cost
graph.get(flight[0]).add(flight[1]);//Initialize adjacency table
}
boolean visited[]=new boolean[n];
Queue<Integer>queue=new LinkedList();
Queue<Integer>cost=new LinkedList();
int result=Integer.MAX_VALUE;
queue.offer(src);
visited[src]=true;
cost.offer(0);
int count=0;
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
int size=queue.size();
count++;
if(count>k+2){
break;
}
for(int j=0;j<size;j++){
int temp=queue.poll();
int tempCost=cost.poll();
if(temp==dst){
result=Math.min(result,tempCost);
}
for(int i=0;i<graph.get(temp).size();i++){
if(!visited[graph.get(temp).get(i)]){
queue.offer(graph.get(temp).get(i));
cost.offer(tempCost+costs[temp][graph.get(temp).get(i)]);
}
}
}
}
return result==Integer.MAX_VALUE?-1:result;
}
}
After pruning, more examples can be passed
There is an 8ms, which can be passed
class Solution {
public int findCheapestPrice(int n, int[][] flights, int src, int dst, int K) {
// Used to record (current city, information list of cities that can fly to (each item includes [city coordinates, cost]))
Map<Integer, List<int[]>> map = new HashMap<>();
// Create map information
for(int[] flight: flights) {
List<int[]> list = map.getOrDefault(flight[0], new ArrayList<>());
list.add(new int[]{flight[1], flight[2]});
map.put(flight[0], list);
}
// It is used to record the minimum cost when flying to the city
int[] minValues = new int[n];
Arrays.fill(minValues, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
// The starting point fee is 0
minValues[src] = 0;
// Two queues: record city coordinates and current accumulated expenses
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
Queue<Integer> queueValue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(src);
queueValue.offer(0);
// Record the current number of stations. If it is greater than K, it will jump out directly
int count = 0;
int ans = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
while(!queue.isEmpty()) {
if(count > K) break;
int size = queue.size();
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
int f = queue.poll();
int v = queueValue.poll();
List<int[]> list = map.getOrDefault(f, new ArrayList<>());
// Traverse the next city you can fly to
for(int[] nextF: list) {
// If the next city is the destination, the minimum cost of updating
if(nextF[0] == dst) {
ans = Math.min(ans, v+nextF[1]);
continue;
}
// If the cost of flying to the next city is less than the current minimum value, it will be updated; if it is greater than the current minimum value, it will not be put in the queue
if(minValues[nextF[0]] > v + nextF[1]) {
minValues[nextF[0]] = v + nextF[1];
queue.offer(nextF[0]);
queueValue.offer(v+nextF[1]);
}
}
}
count++;
}
// It means that after transferring through station K, you can't fly to the destination and return to - 1
if(ans == Integer.MAX_VALUE) return -1;
return ans;
}
}
Figure 11 on August 21, 2021
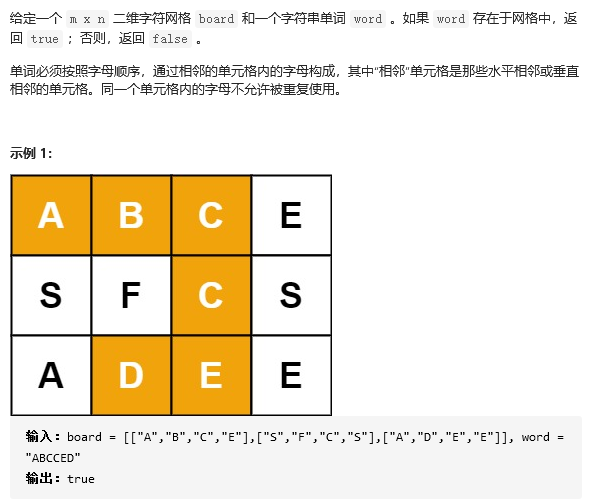
27 79. Word search
class Solution {
int m;
int n;
boolean[][]visited;
public boolean exist(char[][] board, String word) {
m=board.length;
n=board[0].length;
for(int i=0;i<m;i++){
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){
if(board[i][j]==word.charAt(0)){//Search from the first letter
visited=new boolean[m][n];
if(dfs(board,i,j,1,word)){
return true;
}
}
}
}
return false;
}
public boolean dfs(char[][]board,int i,int j,int curLen,String word){
if(i>=m||i<0||j>=n||j<0||curLen>word.length()||board[i][j]!=word.charAt(curLen-1))
return false;
if((curLen==word.length())&&board[i][j]==word.charAt(curLen-1))
return true;
if(visited[i][j])
return false;
// visited[i][j]=true;
char temp=board[i][j];
board[i][j]='*';
// boolean b1,b2,b3,b4;
boolean b1= dfs(board, i+1, j,curLen+1, word)||
dfs(board, i-1, j,curLen+1, word)||
dfs(board, i, j+1,curLen+1, word)||
dfs(board, i, j-1,curLen+1, word);
// visited[i][j]=false;
board[i][j]=temp;
return b1;
// Return B1 | B2 | B3 | B4; / / more calculations will be returned here
}
}
I tried to mark it with the visited array before, but the two pieces of code in the following figure are written backwards, resulting in an error. The following figure is right now
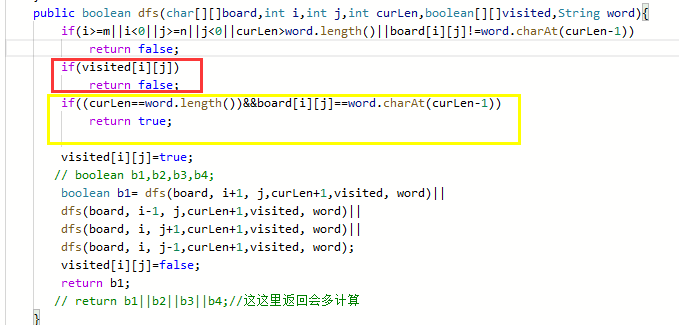
If it is written backwards, it will lead to the backtracking shown in the figure below. One character is used twice
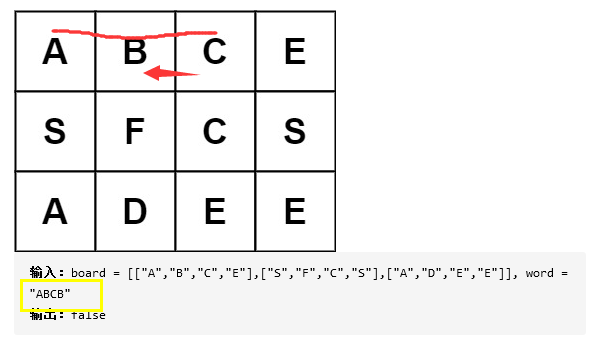
There is a 17ms, which is to compare the number of characters in each of the two strings
public class Solution {
private char[][] board;
private char[] word;
private int m;
private int n;
private int targetLen;
public boolean exist(char[][] board, String str) {
this.board = board;
this.m = board.length;
this.n = board[0].length;
this.word = str.toCharArray();
this.targetLen = word.length;
if(targetLen > m*n){
return false;
}
int[] f1 = new int[133];
int[] f2 = new int[133];
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
++f1[board[i][j]];
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < targetLen; i++) {
++f2[word[i]] ;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 133; i++) {
if(f1[i] < f2[i]) {
return false;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (board[i][j] == word[0]) {
boolean[][] visit = new boolean[m][n];
boolean res = dfs(i, j, 0,visit);
if (res) {
return true;
}
}
}
}
return false;
}
private boolean dfs(int i, int j, int index,boolean [][]visit) {
if (index == targetLen) {
return true;
}
if (i < 0 || i >= m || j < 0 || j >= n) {
return false;
}
if(visit[i][j]){
return false;
}
if (board[i][j] == word[index]) {
visit[i][j] = true;
boolean res = dfs(i - 1, j, index + 1,visit)
||
dfs(i + 1, j, index + 1,visit)
||
dfs(i, j - 1, index + 1,visit)
||
dfs(i, j + 1, index + 1,visit);
visit[i][j] = false;
return res;
}
return false;
}
}
28 329. Longest incremental path in matrix
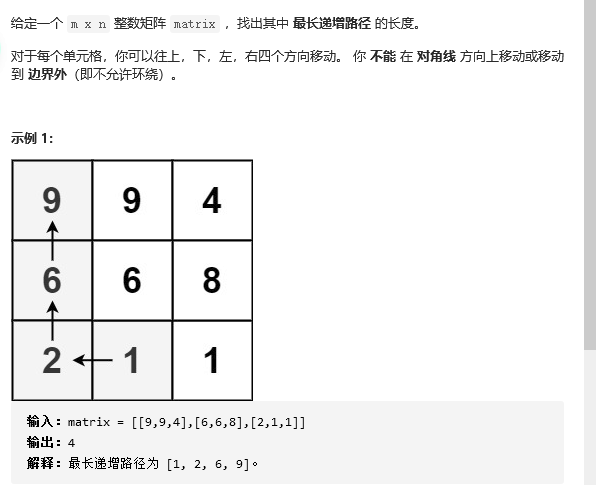
Problem solving idea: enumerate each point and find out the longest increasing path of each point
The code of the first edition is as follows
class Solution {
int m;
int n;
boolean [][]visited;
int dr[]={0,1,0,-1};
public int longestIncreasingPath(int[][] matrix) {
m=matrix.length;
n=matrix[0].length;
visited=new boolean[m][n];
int max=0;
for(int i=0;i<m;i++){
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){
max=Math.max(max,dfs(matrix,i,j,0,-1));
}
}
return max;
}
public int dfs(int [][]matrix,int i,int j,int curLen,int last){
if(i<0||i>=m||j<0||j>=n||matrix[i][j]<=last)
return curLen;
if(visited[i][j])
return 0;
visited[i][j]=true;
int cur=0;
for(int p=0;p<4;p++){
int newX=i+dr[p];int newY=j+dr[(p+1)%4];
int a=dfs(matrix,newX, newY, curLen+1, matrix[i][j]);
cur=Math.max(cur,a);
}
visited[i][j]=false;
return cur;
}
}
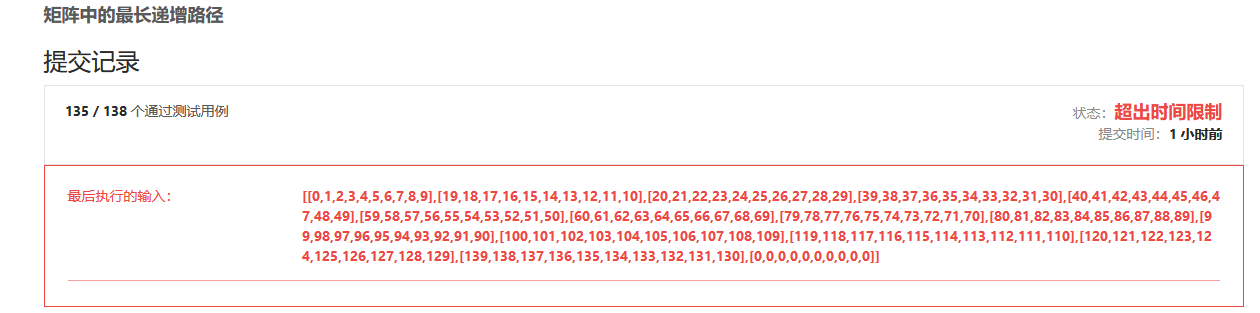
The code timed out because there are a lot of repeated calculations, but the memo [] [] cannot be used directly. The memo I calculated is directional. It is the maximum length returned by the current element to the previous element when the path of the previous point passes through here, rather than the maximum length that can be obtained from the current point
In fact, the visited array can not be used for this problem. It should be that the problem requires an incremental path. Our judgment conditions will give this conditional condition. If it is not satisfied, it will not be accessed in reverse.
Starting from the current point, we can find the longest increasing path of its adjacent elements smaller than it, and take the largest one
class Solution {
int m;
int n;
int dr[]={0,1,0,-1};
int maxValue;
public int longestIncreasingPath(int[][] matrix) {
m=matrix.length;
n=matrix[0].length;
int memo[][]=new int[m][n];
int max=0;
for(int i=0;i<m;i++){
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){
max=Math.max(max,dfs(matrix,i,j,memo));
}
}
return max;
}
public int dfs(int [][]matrix,int i,int j,int memo[][]){
if(memo[i][j]!=0)
return memo[i][j];
memo[i][j]=1;
int cur=0;
for(int p=0;p<4;p++){
int newX=i+dr[p];int newY=j+dr[(p+1)%4];
if(newX>=0&&newX<m&&newY>=0&&newY<n&&matrix[newX][newY]>matrix[i][j]){
memo[i][j]=Math.max(memo[i][j],dfs(matrix,newX, newY,memo)+1);
}
}
return memo[i][j];
}
}
reference resources: Longest increasing path in matrix

backtracking in matrix depth first search is often necessary. Because such problems usually require that each element can only be used once, we need to maintain a see matrix (record the accessed elements and repeatedly set the state when dfs presses and returns the stack) However, the state of see is different every time the starting position is selected, resulting in the non reusability of the calculation results (because the calculation results only represent the results in a certain state of see, we can't cache them).
Finally, we can only use backtracking to solve the problem, and the time complexity is exponential. For example, in the classic Word Search II, whether we use a dictionary tree or not, backtracking is inevitable.
The condition that each element of this question can only be used once is implicit - because the (strict) incremental path is required, it is impossible for elements at the same position to appear twice in the effective path. However, the buff brought by the incremental path is more than the previous implicit condition. Because in the inner loop, mat [II] [JJ] > mat [i] [J] It ensures that the previously accessed elements will not appear in the subsequent path at all, so see has no meaning. You can even directly cache the calculation results of each sub call, because no matter where you start the iteration, because there is no state (no see), the calculation results become unique - so they can be cached.
2021.08.22 the 12th natural interesting question
29 121. The best time to buy and sell stocks
Given an array of prices, its ith element prices[i] represents the price of a given stock on day I.
You can only choose to buy this stock one day and sell it on a different day in the future. Design an algorithm to calculate the maximum profit you can make.
Returns the maximum profit you can make from this transaction. If you can't make any profit, return 0.
Solution: to enumerate the profits sold every day, we must find the minimum value before each day
class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
int min=Integer.MAX_VALUE;int max=0;
for(int i=0;i<prices.length;i++){
min=Math.min(min,prices[i]);
max=Math.max(max,prices[i]-min);
}
return max;
}
}
30 122. The best time to buy and sell stocks II

class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
int max=0;
for(int i=1;i<prices.length;i++){
if(prices[i]-prices[i-1]>0){
max=max+prices[i]-prices[i-1];
}
}
return max;
}
}