148. Remove linked list elements
Difficulty: simple
Collection
Give you a head node of the linked list and an integer val. please delete all nodes in the linked list that meet the requirements Val = = Val node and returns a new header node.
Example 1:
Input: head = [1,2,6,3,4,5,6], val = 6
Output: [1,2,3,4,5]
Example 2:
Input: head = [], val = 1
Output: []
Example 3:
Input: head = [7,7,7,7], val = 7
Output: []
Tips:
The number of nodes in the list is in the range [0, 104]
1 <= Node.val <= 50
0 <= val <= 50
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def removeElements(self, head: ListNode, val: int) -> ListNode:
head=ListNode(next=head)
pre=head
while pre.next:
if pre.next.val == val:
pre.next=pre.next.next
else:
pre=pre.next
return head.next
53. Rotating linked list
Difficulty: medium
Collection
Give you a head node of the linked list. Rotate the linked list and move each node of the linked list k positions to the right.
Example 1:
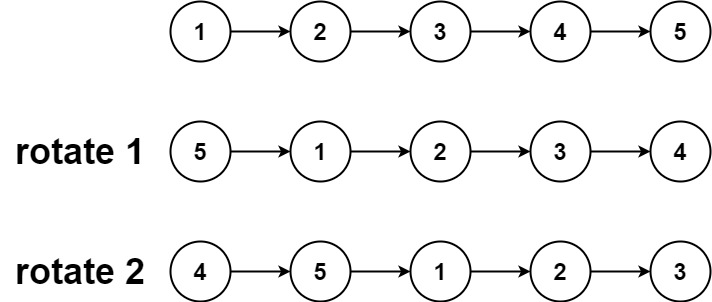
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 2 Output:[4,5,1,2,3]
Example 2:
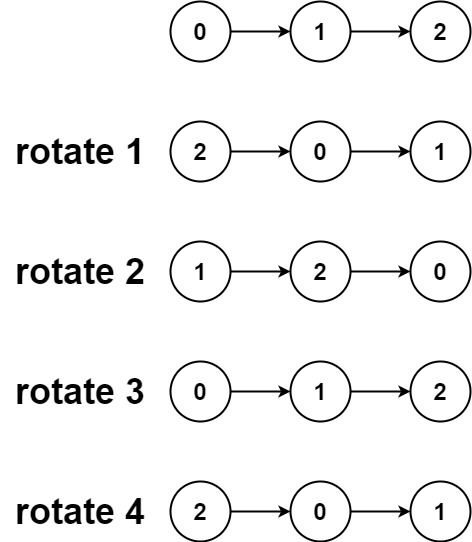
Input: head = [0,1,2], k = 4 Output:[2,0,1]
Tips:
- The number of nodes in the linked list is within the range [0, 500]
- -100 <= Node.val <= 100
- 0 <= k <= 2 * 10^9
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def rotateRight(self, head: Optional[ListNode], k: int) -> Optional[ListNode]:
if not head:
return None
length=0
temp=head
while temp.next:
length+=1
temp=temp.next
temp.next=head
k=k%(length+1)
temp=head
for i in range(length-k):
temp=temp.next
head=temp.next
temp.next=None
return head
20. Merge two ordered linked lists
Difficulty: simple
Collection
Merge the two ascending linked lists into a new ascending linked list and return. The new linked list is composed of all nodes of a given two linked lists.
Example 1:
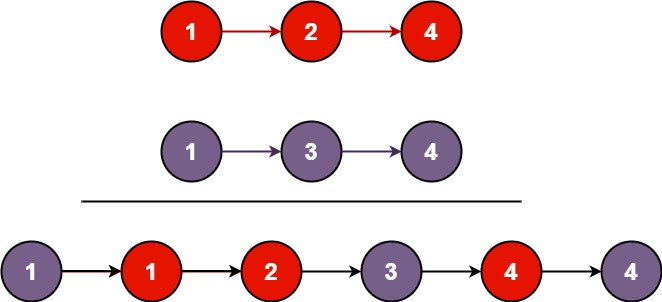
Input: l1 = [1,2,4], l2 = [1,3,4] Output:[1,1,2,3,4,4]
Example 2:
Input: l1 = [], l2 = [] Output:[]
Example 3:
Input: l1 = [], l2 = [0] Output:[0]
Tips:
- The number of nodes in the two linked lists ranges from [0, 50]
- -100 <= Node.val <= 100
- l1 and l2 are arranged in non decreasing order
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def mergeTwoLists(self, list1: Optional[ListNode], list2: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
if not list1:
return list2
if not list2:
return list1
ls = ListNode()
tail = ls
while list1 and list2:
if list1.val < list2.val:
ls.next = list1
ls = ls.next
list1=list1.next
else:
ls.next = list2
ls = ls.next
list2=list2.next
if list1:
ls.next=list1
if list2:
ls.next=list2
return tail.next
131. Cross linked list
Difficulty: simple
Collection
Here are the head nodes headA and headB of the two single linked lists. Please find and return the starting node where the two single linked lists intersect. If there is no intersecting node between the two linked lists, null is returned.
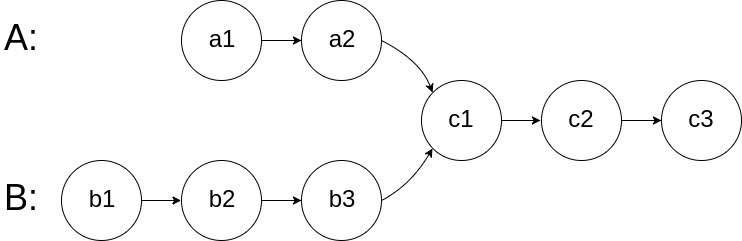
As shown in the figure, two linked lists intersect at node c1 * *:**
The title data ensures that there are no links in the whole chain structure.
Note that after the function returns the result, the linked list must maintain its original structure.
Custom profiling:
The input of the evaluation system is as follows (the program you designed does not apply to this input):
- intersectVal - the value of the starting node of the intersection. If there are no intersecting nodes, this value is 0
- listA - the first linked list
- listB - second linked list
- Skippa - the number of nodes that jump to the cross node in listA (starting from the head node)
- skipB - the number of nodes that jump to the cross node in listB (starting from the head node)
The evaluation system will create a linked data structure based on these inputs and pass the two head nodes headA and headB to your program. If the program can correctly return the intersection node, your solution will be regarded as the correct answer.
Example 1:
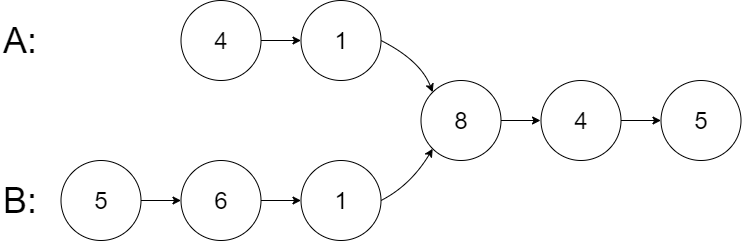
Input: intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,6,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2, skipB = 3 Output: Intersected at '8' Explanation: the value of intersection node is 8 (note that if two linked lists intersect, it cannot be 0). The linked list starts from the respective header A by [4,1,8,4,5],Linked list B by [5,6,1,8,4,5]. stay A In, there are 2 nodes before the intersecting node; stay B In, there are 3 nodes before the intersection node.
Example 2:
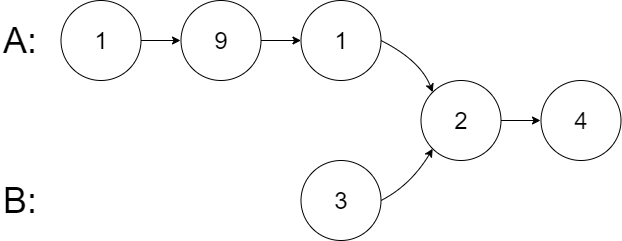
Input: intersectVal = 2, listA = [1,9,1,2,4], listB = [3,2,4], skipA = 3, skipB = 1 Output: Intersected at '2' Explanation: the value of intersection node is 2 (note that if two linked lists intersect, it cannot be 0). The linked list starts from the respective header A by [1,9,1,2,4],Linked list B by [3,2,4]. stay A In, there are 3 nodes before the intersection node; stay B In, there is 1 node before the intersection node.
Example 3:
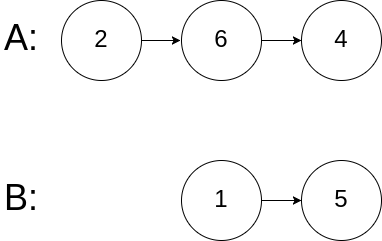
Input: intersectVal = 0, listA = [2,6,4], listB = [1,5], skipA = 3, skipB = 2 Output: null Explanation: the linked list starts from the respective header A by [2,6,4],Linked list B by [1,5]. Because the two linked lists do not intersect, so intersectVal Must be 0, and skipA and skipB Can be any value. The two linked lists do not intersect, so they return null .
Tips:
- The number of nodes in listA is m
- The number of nodes in listB is n
- 1 <= m, n <= 3 * 104
- 1 <= Node.val <= 105
- 0 <= skipA <= m
- 0 <= skipB <= n
- If listA and listB have no intersection, intersectVal is 0
- If listA and listB have an intersection, intersectVal == listA[skipA] == listB[skipB]
**Advanced: * * can you design a solution with time complexity O(m + n) and only O(1) memory?
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution:
def getIntersectionNode(self, headA: ListNode, headB: ListNode) -> ListNode:
p=headA
q=headB
while p!=q:
if p:
p=p.next
else:
p=headB
if q:
q=q.next
else:
q=headA
return p
70. Delete the duplicate Element II in the sorting linked list
Difficulty: medium
Collection
Given the head of a sorted linked list, delete all nodes with duplicate numbers in the original linked list, leaving only different numbers. Returns the sorted linked list.
Example 1:
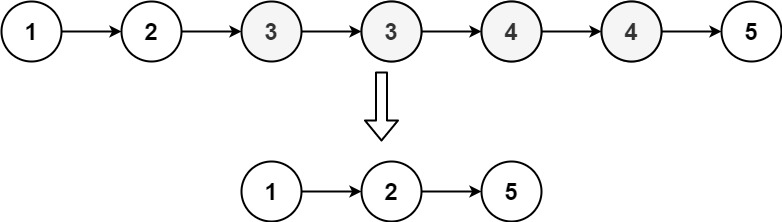
Input: head = [1,2,3,3,4,4,5] Output:[1,2,5]
Example 2:
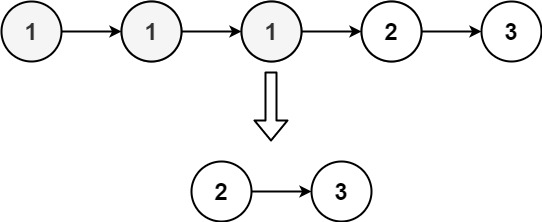
Input: head = [1,1,1,2,3] Output:[2,3]
Tips:
- The number of nodes in the linked list is within the range [0, 300]
- -100 <= Node.val <= 100
- The title data ensures that the linked list has been arranged in ascending order
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def deleteDuplicates(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
dummy=ListNode()
dummy.next=head
p=dummy
while p.next:
q=p.next
while q and q.val==p.next.val:
q=q.next
if p.next.next==q:
p=p.next
else:
p.next=q
return dummy.next