Lesson 4 Basic _ constraint
1. Summary
1. Concepts
Rules that act on fields in a table to restrict data stored in the table.
2. Purpose
Ensure that the data is correct, valid and complete.
3. Classification
| constraint | describe | Keyword |
|---|---|---|
| Non-empty constraint | Restrict the field to data that cannot be null | NOT NULL |
| Unique Constraint | Ensure that all data in this field is unique and not duplicated | UNIQUE |
| Primary Key Constraint | Primary keys are the only representation of a row of data, requiring non-empty and unique | PRIMARY KEY |
| Default Constraints | When saving data, if no value is set for the field, the default value is used | DEFAULT |
| Check constraints (after version 8.0.16) | Ensure that a field meets a condition | CHECK |
| Foreign Key Constraints | Used to connect data between two tables to ensure data consistency and integrity | FOREIGN KEY |
Note: Constraints are used for fields in tables and can be added when creating/modifying tables.
2. case
1. Create tables on demand
| Field name | Field Meaning | Field type | constraint condition | Constraint Keys |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| id | ID Unique Identification | int | Primary key and self-growing | PRIMARY KEY,AUTO_INCREMENT |
| name | Full name | varchar(10) | Not empty and unique | NOT NULL,UNIQUE |
| age | Age | int | Greater than 0 and less than or equal to 120 | CHECK |
| status | state | char(1) | Default 1 if no value is specified | DEFAULT |
| gender | Gender | char(1) | nothing |
2. Functional implementation
--Constraint table creation
create table user(
id int primary key auto_increment comment 'Primary key',
name varchar(10) not null unique comment 'Full name',
age int check (age>0 && age<=120) comment 'Age',
status char(1) default '1' comment 'state',
gender char(1) comment 'Gender'
)comment 'User table';
--insert data
insert into user(name,age,status,gender) value ('Tom1',19,'1','male'),('Tom2',25,'0','male')
3. Graphical Interface Creation Table
Right-click tables_New_Table under test database
3. Foreign Key Constraints
1. Concepts
Connect data between two tables to ensure data consistency and integrity.
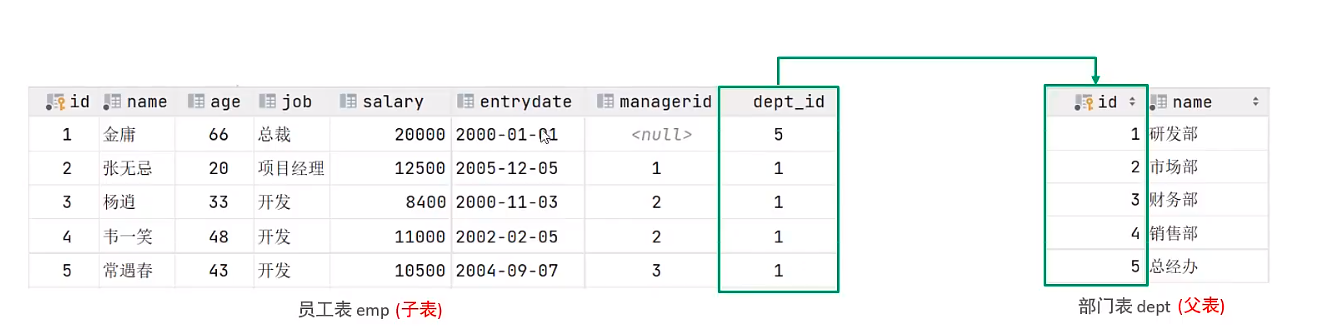
Note: At the database level, these two tables do not have foreign key associations, so data consistency and integrity cannot be guaranteed.
2. Grammar
1. Create foreign keys directly
CREATE TABLE table name
Field name data type,
...
[CONSTRAINT] [Foreign Key Name] FOREIGN KEY (Foreign Key Field Name) REFERENCES main table (Primary Table Column Name)
);
(2) Add foreign keys
ALTER TABLE table name ADD CONSTRAINT foreign key name FOREIGN KEY (foreign key field name) REFERENCES main table (main table column name);
--Data preparation
--1.Create Department Table
create table dept(
id int auto_increment comment 'ID' primary key ,
name varchar(50) not null comment 'Department Name'
)comment 'Department table'
--2.Enter departmental data
insert into dept(id,name) values (1,'R&D Department'),(2,'Marketing Department'),(3,'Finance Department'),(4,'Sales Department'),(5,'Chief Executive');
--3.Create employee table
create table emp(
id int auto_increment comment 'ID' primary key,
name varchar(50) not null comment 'Full name',
age int comment 'Age',
job varchar(20) comment 'position',
salary int comment 'salary',
entrydate date comment 'Enrollment Time',
managerid int comment 'Direct Leadership ID',
dept_id int comment 'department ID'
)comment 'Employee Sheet';
--4.Enter employee data
insert into emp(id,name,age,job,salary,entrydate,managerid,dept_id) values
(1,'Jin Yong',66,'CEO',20000,'2000-01-01',null,5),
(2,'Zhang Wuji',20,'project manager',12500,'2005-12-05',1,1),
(3,'Yang Xiao',33,'Development',8400,'2000-11-03',2,1),
(4,'Xiangr',48,'Development',11500,'2002-02-05',2,1),
(5,'Zhao Min',22,'Development',10500,'2004-09-07',3,1),
(6,'Xiao Zhao',19,'Trainee',6600,'2004-10-12',2,1);
--Add Foreign Key
alter table emp add constraint fk_emp_dept_id foreign key (dept_id) references dept(id);
(3) Delete foreign keys
ALTER TABLE table name DROP FOREIGN KEY foreign key name;
--Delete foreign keys alter table emp drop foreign key fk_emp_dept_id;
3. Delete/update behavior of foreign key constraints
1 Behavior
| behavior | Explain |
|---|---|
| NO ACTION | When deleting/updating a corresponding record in the parent table, first check if the record has a corresponding foreign key, if deletion/updating is not allowed. (same as RESTRICT) |
| RESTRICT | When deleting/updating a corresponding record in the parent table, first check if the record has a corresponding foreign key, if deletion/updating is not allowed. (consistent with NO ACTION) |
| CASCADE | When deleting/updating a corresponding record in the parent table, first check if the record has a corresponding foreign key, and if so delete/update the record in the child table |
| SET NULL | When deleting/updating a corresponding record in the parent table, check to see if the record has a corresponding foreign key. If so, set the value of the foreign key to null in the wordtable (which requires that the foreign key allow null) |
| SET DEFAULT | When the parent table changes, the wordtable sets the foreign key column to a default value (innodb does not support it) |
(2) Grammar
ALTER TABLE table name ADD CONSTRAINT foreign key name FOREIGN KEY (foreign key field name) REFERENCES main table (main table column name) ON UPDATE CASCADE ONDELETE CASCADE;