1, Class notes:
-
su - meaning and home directory meaning?
When switching users, the configuration information of the user's home directory will be called / loaded. For example, if a command is configured for the user alone, only the user will recognize the command, and other users cannot.
-
Relative path and absolute path
Start with /, not with /
-
What is the difference between cd /home and cd /home /?
The difference is whether home is a directory or a file. The last / is the directory separator
-
Alias alias
Enter alias on the command line to view all aliases in the system
Note: the alias defined on the command line is only valid for the current shell process. If you want to be valid permanently, you should define it in the configuration file only for the current user: ~ / Bashrc is valid for all users: / etc/bashrc
-
File + file name / / you can view the file type
Do not look at the extension under Linux,
2, View files more, less, cat, head, tail
-
Small files can be viewed with cat, and long files can be viewed with more and less, or head and tail
-
cat -n: displays the line number
-
tail -f /var/log/messages dynamic monitoring log files
-
more: used when browsing longer files
Enter: next line
Space: next page
b: Previous page
q: Exit
-
less: used when browsing long documents and turning pages up and down
Up key: previous line
Down key: next line
pageup: Previous page
pagedown: next page
q: Exit
3, Create file touch
<span style="background-color:#282c34"><span style="color:#282c34"> <span style="color:#abb2bf">touch a.txt </span>
<span style="color:#abb2bf">touch a.txt b.txt</span>
<span style="color:#Abb2bf "> touch a {1.. 6}. TXT / / use wildcard {}</span>
<span style="color:#abb2bf">touch {a,b,c}{1..3}.txt</span>
<span style="color:#abb2bf">a1.txt a2.txt a3.txt b1.txt b2.txt b3.txt c1.txt c2.txt c3.txt</span></span></span>4, Create directory mkdir
<span style="background-color:#282c34"><span style="color:#282c34"> <span style="color:#abb2bf">mkdir aa</span>
<span style="color:#Abb2bf "> MKDIR - P - v A / B / C / / - P recursively creates directories, - v displays the creation process</span>
<span style="color:#abb2bf">mkdir abc{1..3}</span></span></span>5, Delete rm
<span style="background-color:#282c34"><span style="color:#282c34"> <span style="color:#Abb2bf "> RM - R / / deleting directories also plays a recursive role</span> <span style="color:#Abb2bf "> RM - F / / delete files and force deletion</span> <span style="color:#Abb2bf "> RM - RF / / can be deleted</span></span></span>
6, Copy cp
<span style="background-color:#282c34"><span style="color:#282c34"> <span style="color:#abb2bf">touch a1 a2</span> <span style="color:#abb2bf">mkdir D1 D2</span> <span style="color:#Abb2bf "> CP - P A1 A2 / TMP / / keep the attributes and permissions of the original file</span> <span style="color:#Abb2bf "> CP - R D1 / TMP / D3 / / adding - r when copying a directory indicates recursive copying, otherwise an error will be reported</span> <span style="color:#abb2bf">[root@localhost opt]# cp /opt/D1/ /tmp/D3</span> <span style="color:#abb2bf">cp: omitting directory '/opt/D1/'</span></span></span>
7, Mobile mv
mv file1 /tmp/;ls /tmp/file //; Is a command separator that allows you to enter multiple commands
<span style="background-color:#282c34"><span style="color:#282c34"> <span style="color:#abb2bf">vim test.config.simple</span>
<span style="color:#abb2bf">[root@localhost opt]# ll</span>
<span style="color:#abb2bf">total 4</span>
<span style="color:#abb2bf">drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 6 Dec 15 20:50 D1</span>
<span style="color:#abb2bf">drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 6 Dec 15 20:49 D2</span>
<span style="color:#abb2bf">drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 6 Dec 15 20:50 D3</span>
<span style="color:#abb2bf">-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 10 Dec 15 20:57 test.config</span>
<span style="color:#abb2bf">[root@localhost opt]# mv test.config{.simple,}</span>
<span style="color:#abb2bf">[root@localhost opt]# ls</span>
<span style="color:#abb2bf">D1 D2 D3 test.config</span></span></span>8, Text editor vim
1. Basic grammar
-
vi is a text editor, and vi tools are installed by default in most distributions
-
vim is an upgraded version of vi
-
vim features:
-
Different colors are displayed in the text, and the administrator can identify the errors in the text by color
-
Support block diagram mode
-
Many software also use vi editing methods by default, such as crontab (scheduled task)
-
<span style="background-color:#282c34"><span style="color:#282c34"> <span style="color:#abb2bf">vim file1</span> <span style="color:#Abb2bf "> A / / input mode</span> <span style="color:#Abb2bf ">: WQ / / save push</span></span></span>
2. Working mode of VI editor
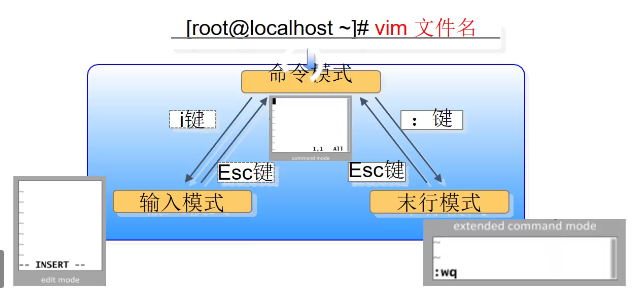
Command mode (general mode): used to move the cursor, copy and delete lines
Input mode (edit mode): edit text
Last line mode (command line mode): used to set environment, line number, tab and indentation.
Command mode to enter input mode:
| letter | meaning |
|---|---|
| o | Enter the next line of the current character |
| i | Enter before current character |
| a | Enter after current character |
| I | Input at the beginning of the current line |
| A | Current line end input |
| O | Input on the previous line of the current line |
| s | Enter after deleting the current character |
| S | Enter after deleting the current line |
| Home key | Line beginning |
| End key | End of line |
Command mode cursor control:
| letter | Cursor movement |
|---|---|
| ↑↓←→ | Up, down, left and right |
| 0 or ^ | Position the cursor at the beginning of the line |
| $ | Position the cursor at the end of the line |
| gg | Position the cursor at the beginning of the article |
| G | Position the cursor at the end of the article |
| nG | N stands for number, that is, move the cursor to line n |
| yy | copy |
| nyy | N stands for number, copy n lines |
| shift+v+↑↓←→+yy+p | Select the row you want to copy in the visual interface |
| v | Visualization mode |
| ctrl+v | Visualization mode block |
Tips: how to add #?
ctrl+v select shift+i and enter #ESC
Copy paste delete
| letter | meaning |
|---|---|
| y | copy |
| yy | Copy a row |
| p | paste |
| u | revoke |
| dd+p | shear |
| d^ | Deletes the current character to the beginning of the line |
| d$ | Delete current character to end of line |
| dgg | Delete current row to first row |
| dG | Delete current line to last line |
Last line mode
| character | meaning |
|---|---|
| shift+; | : |
| :w | Save exit |
| :q | sign out |
| :wq | Save exit |
| :w! | Force save |
| :q! | forced return |
| :wq! | Force save exit |
| :w /tmp/cc.txt | Save as |
| :! commend | Temporarily enter linux commands |
| :e /root/aa.txt | Open a file |
| :e! | Reopen this file (refresh) |
| :set | View all environment settings |
| :set nu/:set nonu | View line number / cancel line number |
| :set tabstop=16 | Set the tab to 16 bytes in length |
| :set autoindent | Auto indent |
| /Keywords, N, n | Search from top to bottom, n next, n previous |
| ? keyword | Search from bottom to top, n previous, n next |
| :noh | Cancel highlight mode |
3. vim profile:
<span style="background-color:#282c34"><span style="color:#282c34"> <span style="color:#Abb2bf "> VIM ~ /. Vimrc / / permanently add a line number for an individual. Enable the line number function</span> <span style="color:#Abb2bf "> VIM / etc / vimrc / / permanently added for everyone, in the last line</span></span></span>
4. Substitution syntax:
/old/new/
s: OK
g: To the end of the line
%: Global
| Last line mode | meaning |
|---|---|
| :s/ab/xx/ | Replace the first matching string on the current line |
| :s/ab/xx/g | Replace all matching strings in the current line |
| :%s/ab/xx/g | Replace matching strings in all rows |
| :3,5s/ab/xx/g | Replace lines 3 to 5 |
5. vim exchange file:
Premise: if two terminals open the same file, they will be prompted
If the machine goes down, the file exchange will record the operation of the file and prompt for reply, deletion and other operations
Window 1:
<span style="background-color:#282c34"><span style="color:#282c34"> <span style="color:#abb2bf">cd ~</span> <span style="color:#abb2bf">vim 1.txt</span> <span style="color:#Abb2bf "> Ctrl + Z / / put vim applications in the background</span></span></span>
Window 2
<span style="background-color:#282c34"><span style="color:#282c34"> <span style="color:#abb2bf">[root@localhost /]# cd ~;vim 1.txt / / the swap file appears</span></span></span>
resolvent:
Delete duplicate open file processes and delete swap files
<span style="background-color:#282c34"><span style="color:#282c34"> <span style="color:#Abb2bf "> jobs - L / / view the daemon directory for details</span> <span style="color:#Abb2bf "> PS - EF / / view the process</span> <span style="color:#abb2bf">kill -9 24234</span></span></span>
Open any window again, delete the exchange file, save and exit.
9, Script bash
<span style="background-color:#282c34"><span style="color:#282c34"> <span style="color:#Abb2bf "> VIM a2.sh / / the script must be given permission and the first line</span> <span style="color:#abb2bf">chmod +x a2.sh</span> <span style="color:#abb2bf">#!/ bin/bash / / the first line of the script</span> <span style="color:#Abb2bf "> date / / content</span> <span style="color:#Abb2bf ">. / a2.sh / / running</span> <span style="color:#abb2bf">Thu 16 Dec 09:43:39 CST 2021</span></span></span>