Introduction to DNS
DNS (Domain Name System) Domain Name System:
It is a system that uses client/server mechanism to translate computer name to IP address.As an important network service, DNS is not only the basis of the work of the international Internet, but also widely used in the internal network of enterprises.
Role of DNS Server
Forward Resolution: Find the corresponding IP address based on the host name (domain name)
Reverse Resolution: Find the corresponding host domain name based on the IP address
Distributed Data Structure for DNS System
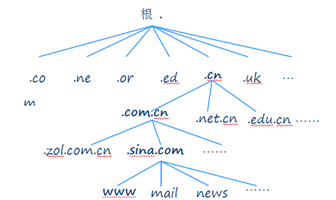
DNS Query Mode
Recursive Query: How most clients resolve domain names to DNS servers Iterative Query: How most DNS servers resolve domain names to other DNS servers
Type of DNS Server
Cache Domain Name Server
Cached Domain Name Server: Also known as Cache-only server, caches domain name query results locally by querying other domain name servers for domain name->IP address records, which improves the speed of repeated queries.
Primary Domain Name Server
Primary Domain Name Server: The official server for a specific DNS zone that is unique and responsible for maintaining mapped records of all domain names - > IP addresses in that zone.
From Domain Name Server
From a Domain Name Server: Also known as a secondary domain name server, it maintains domain name - >IP address records from the primary domain name server.
BIND Domain Name Service Base
BIND (Berkeley Internet Name Daemon) Berkeley Internet Domain Name Service. Official site: https://www.isc.org/ BIND Server-side Program Main Executor: /usr/sbin/named Service script: /etc/init.d/named Default listening port: 53 Main profile: /etc/named.conf The data file where the DNS parsing record is saved is located: /var/named/chroot/var/named/
Profile Analysis
/etc/named.conf
options { #option
listen-on port 53 { 127.0.0.1; }; #Service listening port 53
listen-on-v6 port 53 { ::1; }; #Service listening port 53 (ipv6)
directory "/var/named"; #Directory where profile is stored
dump-file "/var/named/data/cache_dump.db"; #Cache of parsed content
statistics-file "/var/named/data/named_stats.txt"; #Static caching (not commonly used)
memstatistics-file "/var/named/data/named_mem_stats.txt"; #Static caching (in-memory, not commonly used)
allow-query { localhost; }; #Clients Allowed to Connect
recursion yes; #recursive lookup
dnssec-enable yes; #DNS Encryption
dnssec-validation yes; #Advanced algorithm for DNS encryption
dnssec-lookaside auto; #What about DNS encryption
/* Path to ISC DLV key */
bindkeys-file "/etc/named.iscdlv.key"; #Key for encryption (private key public key encryption, very strong)
};
logging { #Journal
channel default_debug {
file "data/named.run"; #Run State File
severity dynamic; #Static server address (root domain)
};
};
zone "." IN { #Root Domain Resolution
type hint; master slave
file "named.ca"; #Root Domain Profile
};
include "/etc/named.rfc1912.zones"; #Extended Profile (New Domain Name)
/etc/named.rfc1912.zones
zone "localhost.localdomain" IN { #Local Host Full Name Resolution
type master; #Type as Domain
file "named.localhost"; #Domain Profiles (files stored in the / var / name directory)
allow-update { none; }; #Client updates are not allowed
};
zone "localhost" IN { #Local Host Name Resolution
type master;
file "named.localhost";
allow-update { none; };
};
zone ".0.ip4.arpa" IN { #ipv6 local address reverse resolution
type master;
file "named.loopback";
allow-update { none; };
};
zone "1.0.0.127.in-addr.arpa" IN { #Local Address Reverse Resolution
type master;
file "named.loopback";
allow-update { none; };
};
zone "0.in-addr.arpa" IN { #Local Full Network Address Reverse Resolution (and/or Domain Update)
type master;
file "named.empty";
allow-update { none; };
};/var/named/named.localhost
$TTL 1D #Update to a maximum of 1 day
@(Use domain name of domain) IN SOA(authority DNS Server) @(authority DNS Name of the server) rname.invalid.(rname@invalid Mail of) (
0 ; serial #(Change Number) Ten-digit serial number
1D ; update frequency
1H ; Failed Retry Time
1W ; Failure Time
3H ) ; Cache time
NS(Domain Name Server) @(Domain Name Server Name)
A(Forward Parsing Record) 127.0.0.1(Forward Resolving ip)
AAAA(ipv6 Forward Resolution) ::1(ipv6 Forward Resolving ip)Set up DNS server
Install DNS Server
Install the bind package
yum install bind
Start Services
systemctl start named.service
Set self-start state
systemctl enable named.service
configuration file
Configure Main Profile
vim /etc/named.conf
//Change to
listen-on-v6 port 53 { any; };
allow-query { any; };Configure zones file
Forward Resolution Configuration
Add Forward Resolution
zone "lzy.com." IN {
type master;
file "lzy.com.zone";
allow-update { none; };
};Reverse Resolution Configuration
Add Reverse Resolution
zone "134.168.192.in-addr.arpa" IN {
tpye master;
file "134.168.192.zone";
allow-update { none; };
};Configuration Zone Profile
Copy Files
cp /var/named/named.empty /var/named/lzy.com.zone cp /var/named/named.empty /var/named/134.192.168.zone
Modify permissions
chown :named zlt.com.zone
Forward Resolution Configuration
Designing forward resolution for the excesoft.com domain name, rename the/var/named/named.empty copy to excesoft.com.zone,
Modify the file group named and modify its contents
$TTL 3H
@ IN SOA lzy.com. root.lzy.com. (
0 ; serial
1D ; refresh
1H ; retry
1W ; expire
3H) ; minimum
NS dns.lzy.com.
dns A 192.168.134.139
www A 192.168.134.139Reverse Resolution Configuration
Designing reverse resolution for excesoft.com domain name, rename/var/named/named.empty copy to 137.168.192.zone, repair Change the file group to named and modify its contents.
Configure Network Card
vim /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-ens33 BOOTPROTO=static IPADDR1=192.168.134.139 NETMASK=255.255.255.0 GATEWAY=192.168.134.2 DNS1=192.168.134.139
Start DNS Server
systemctl start named.service
Check Profile
named-checkconf
Configure Client
Modify Profile
Modify the configuration file: #vim/etc/resolv.conf.
Write the following:
excesoft.
nameserver 192.168.137.22Test DNS Server
Test DNS Server Test on the client computer using the command nslookup.