1. Introduction to rsync
rsync is a tool for synchronous backup of full and incremental local or remote data mirrors
Common command parameters for rsync
Description of command parameter parameters
- a (- archive) archive mode, which means that files are transmitted recursively and all file attributes are preserved, equal to rtopgDl
- V (- verbose) displays information about the output process, the progress of transmission, etc.
- Z (- compress) transmission is compressed to improve transmission efficiency
-- exclude=/etc/hosts specifies that file information that does not need to be transferred is excluded (as is the tar parameter)
- exclude-from=file file file name in the directory file, you can exclude multiple files (and
The tar parameter is the same.
--bwlimit=PATE limit I/O bandwidth;KBytes per second
limit socket I/O bandwidth speed limit function
- delete keeps the target directory and source directory data identical and synchronizes the data indiscriminately
2. rsync characteristics
Supporting copying special files such as soft links, devices, etc.
(2) Excluding synchronization of specified files or directories is equivalent to tar exclusion of packaging commands.
(3) Keep the permissions, time, hard links, ownership and group attributes of the original file or directory unchanged.
4. Achieve incremental synchronization, only synchronize the changed data, and the transmission efficiency is high.
rcp,rsh,ssh can be used to cooperate with the transmission of files.
Files and data can be transmitted through socket (process mode)
_Supporting anonymous authentication process mode transmission to facilitate secure data backup
3. rsync application work scenario
(1) Timing synchronization data is realized by using timing task + rsync. The main synchronization data information is used by the staff inside the website.
(2) Using real-time synchronization software + rsync to realize real-time synchronization of data. The main synchronization data information is the data information uploaded by website users.
4. rsync data transmission mode
(1) Data transmission between hosts locally (at this time similar to the function of the cp command)
(2) Transfer data by means of rcp,ssh and other channels (at this time similar to the function of scp command)
(3) Transfer data in the form of a socket (this is an important function of rsync itself), with emphasis on mastering
5. rsync daemon - server configuration
1. Check whether rsync software is installed in the system
rpm -qa rsync rsync-3.0.6-12.el6.x86_64
2. rsync multi-module master configuration file
cat >/etc/rsyncd.conf<<EOF #rsync server# #created by yanxinjiang 2017-8-1 ##rsyncd.conf start## uid = rsync gid = rsync use chroot = no max connections = 200 timeout = 300 pid file = /var/run/rsyncd.pid lock file = /var/run/rsync.lock log file = /var/log/rsyncd.log ignore errors read only = false list = false hosts allow = 172.16.1.0/24 hosts deny = 0.0.0.0/32 auth users = rsync_backup secrets file = /etc/rsync.password [backup] path = /backup [nfsbackup] path = /nfsbackup EOF
3. Creating Backup Directory and Authorizing Management Users
mkdir /backup -p chown -R rsync.rsync /backup/ useradd rsync -s /sbin/nologin -M
4. Create rsync Server and Client Identity Authentication Files
echo "rsync_backup:123456" >/etc/rsync.password chmod 600 /etc/rsync.password
5. Start rsync service
[root@backup ~]# rsync --daemon [root@backup ~]# lsof -i:873 COMMAND PID USER FD TYPE DEVICE SIZE/OFF NODE NAME rsync 31209 root 3u IPv4 7505812 0t0 TCP *:rsync (LISTEN) rsync 31209 root 5u IPv6 7505813 0t0 TCP *:rsync (LISTEN)
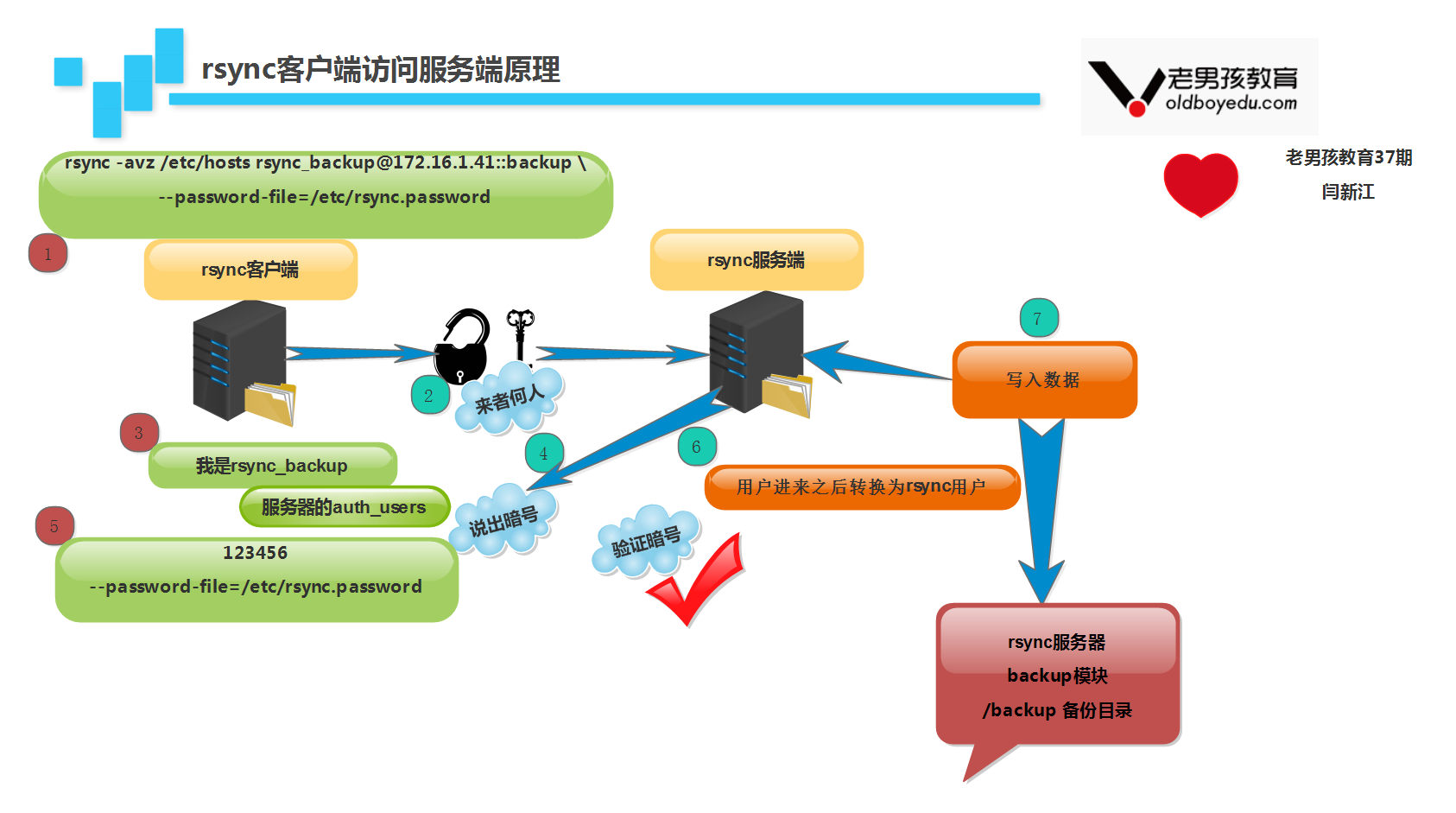
6. rsync daemon - client configuration
1. Create client identity file and authorize
[root@nfs01 ~]# echo "123456" >/etc/rsync.password [root@nfs01 ~]# chmod 600 /etc/rsync.password
2. client testing rsync service
[root@nfs01 ~]# rsync -avz /etc/hosts rsync_backup@172.16.1.41::backup --password-file=/etc/rsync.password sending incremental file list sent 26 bytes received 8 bytes 3.24 bytes/sec total size is 314 speedup is 9.24
3. rsync undifferentiated data synchronization
Client Push
[root@nfs01 data]# ls /data/ a b c d e f g pull.txt [root@nfs01 data]# rsync -avz /data --delete rsync_backup@172.16.1.41::backup --password-file=/etc/rsync.password sending incremental file list data/ data/a data/b data/cServer-side inspection
[root@backup backup]# ls /backup/data/
a b c d e f g pull.txt