1.SNAT
1.1 SNAT application environment
- LAN hosts share a single public IP address to access the Internet (private IP cannot be routed normally in the Internet)
1.2 SNAT principle
- Modify the source address of the packet
1.3 preconditions for SNAT conversion
- 1. Each host of LAN has correctly set IP address, subnet mask and default gateway address
- 2.Linux gateway turns on IP routing forwarding
There are two ways to turn on the IP forwarding function
- Temporary open:
echo 1 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_ forward or sysctl -w net.ipv4. ip_ forward=1
- Permanently open:
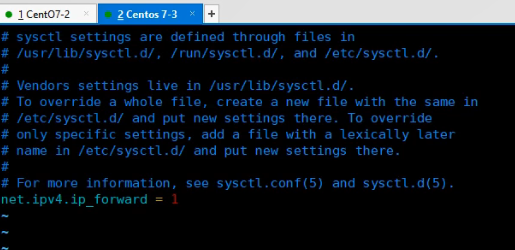
vim /etc/sysctl.conf net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1 #Write this line to the configuration file sysctl -P #Read the modified configuration
1.4 SNAT conversion
- Fixed public IP address
iptables -t nat -A POSTRORTING -s 192.168.148.0/24 -o ens33 -j SNAT --to 12.0.0.1
or
iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -s 192.168.148.0/24 -o ens33 -j SNAT --to-source 12.0.0.1-12.0.0.10
Intranet IP Outbound extranet card Extranet IP Or address pool
1.5 examples
-
Install the httpd service and turn it on
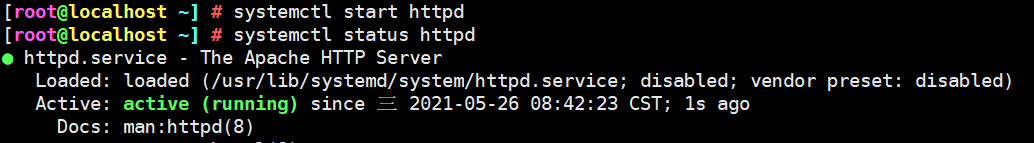
-
Set different networks. The server uses VMne0, the gateway uses two network cards, and the client uses network VMnet1
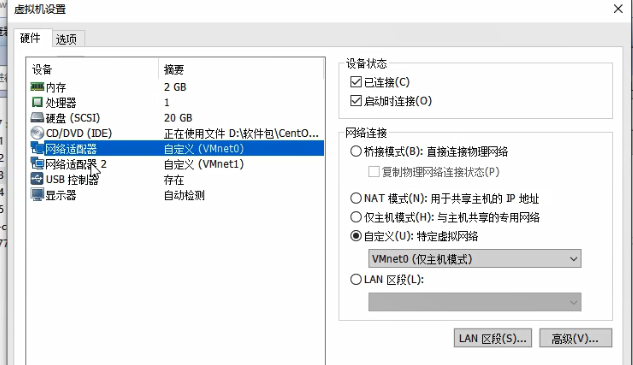
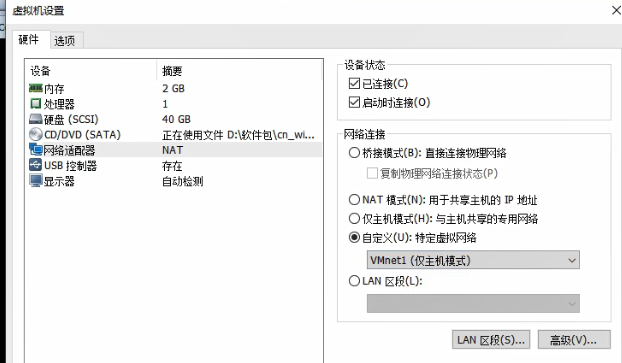
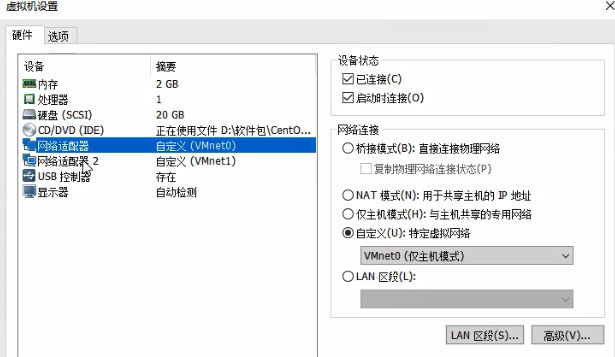
Remember to turn off the firewall on the server side
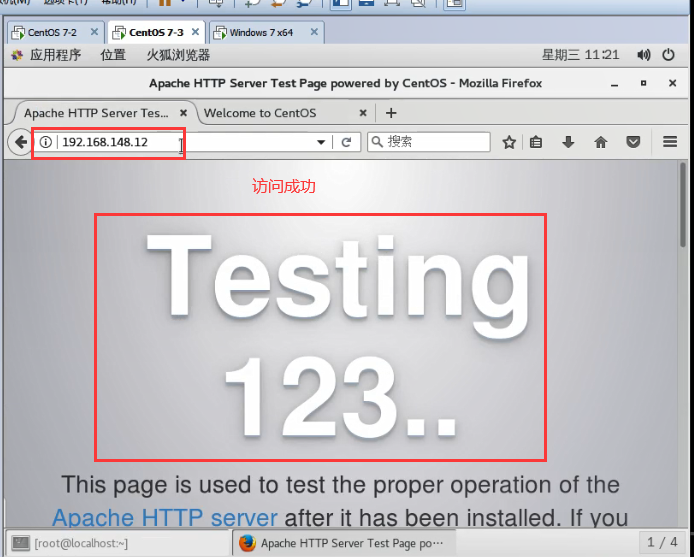
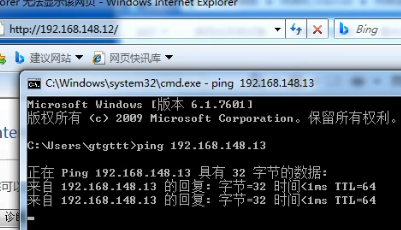
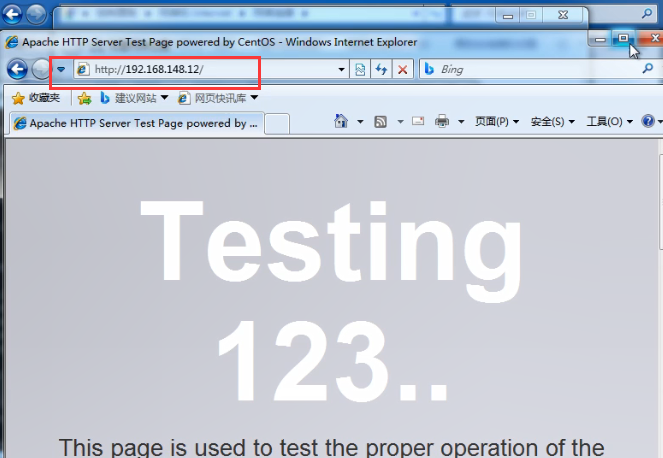
- Test whether the server can access itself
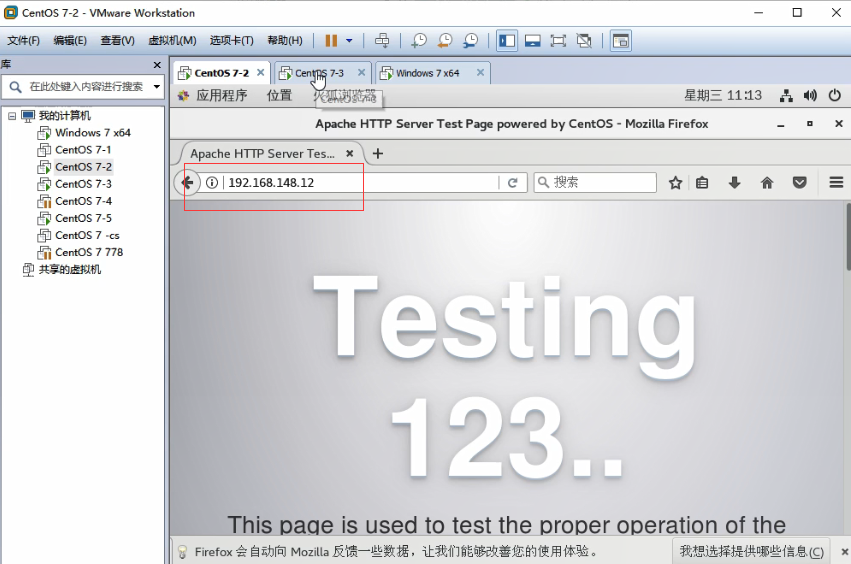
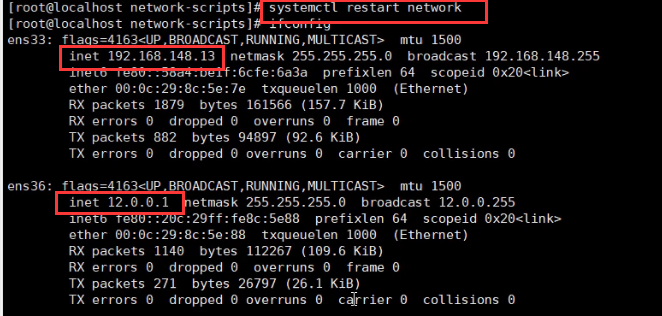
Configure gateway server
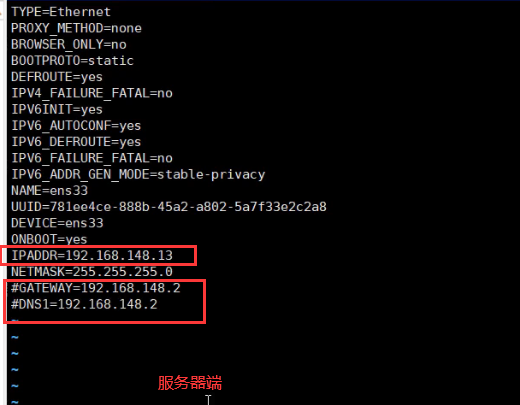
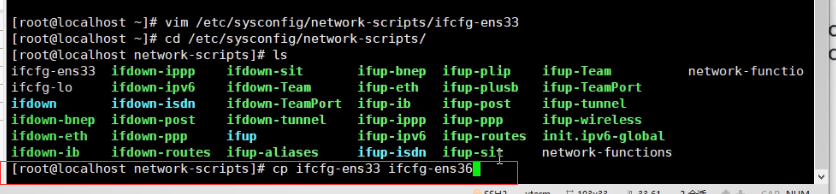
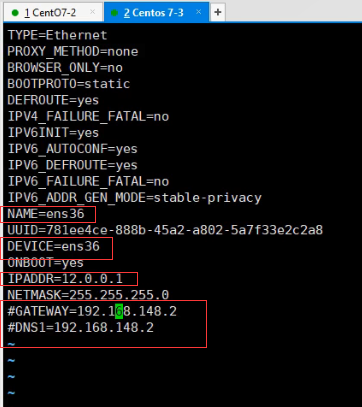
Restart the network card and you can see that the IP address has been configured
Modify the gateway address of the server
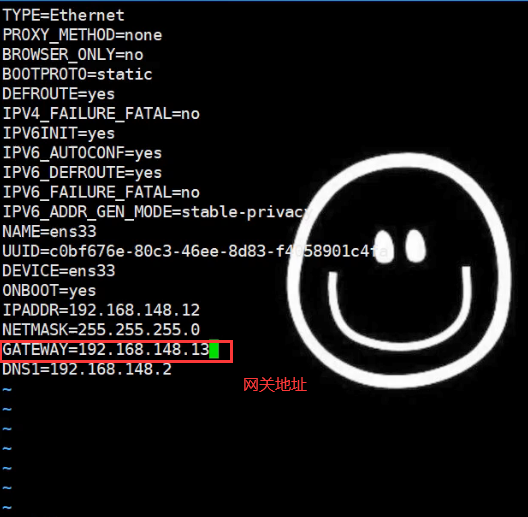
Gateway server access server IP
Configure client and set IP
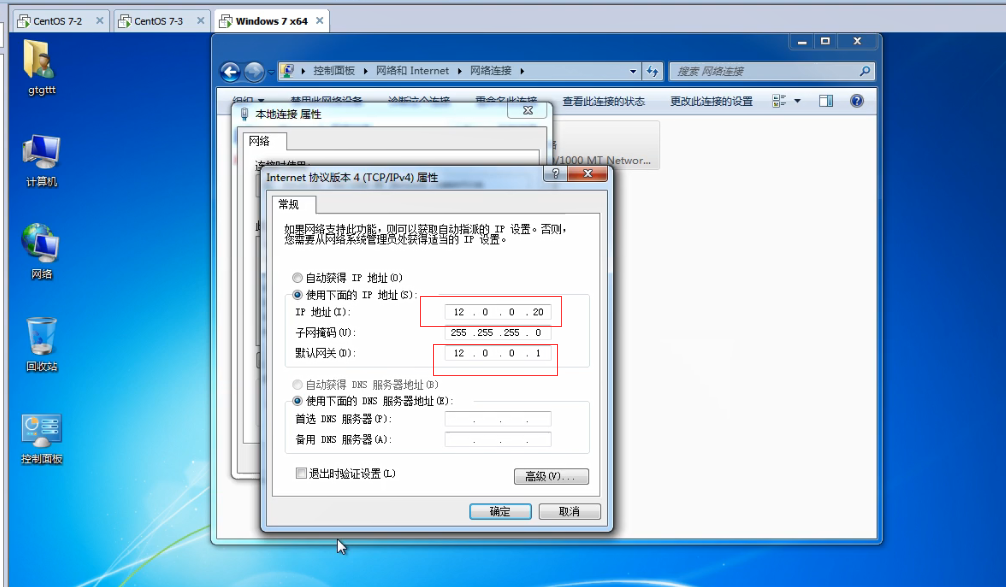
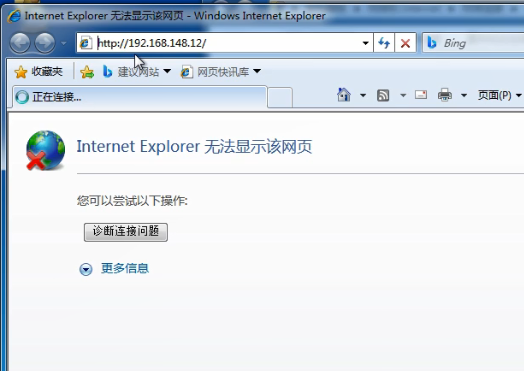
ping the gateway server, but the server cannot be accessed
Turn on IP routing forwarding

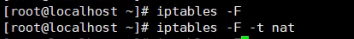
SNAT conversion, check the rules and kill all the rules
Perform SNAT conversion

Test access
Non fixed public IP address (shared dynamic IP address)
iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -s 192.168.148.0/24 -0 ens33 -j MASQUERADE
.
be careful! SNAT conversion of an IP address can generally enable 100 to 200 hosts in the intranet to access the Internet.
2.DNAT
2.1 DNAT application environment
Publish servers located in a local area network on the Internet
1.2 DNAT principle
Modify the destination address of the packet.
1.3 prerequisites for DNAT conversion
-
1. LAN servers can access the Internet
-
2. The gateway's Internet address has the correct DNS resolution record
-
3.Linux gateway turns on IP routing forwarding
vim /etc/ sysctl.conf net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1 sysctl -P
1.4 DNAT conversion of Web Services publishing Intranet
#The destination address of the packet coming in from ens33 to access the web service is converted to 192 168.80.11
iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -i ens33 -d 12.0.0.1 -p tcp --dport 80 -j DNAT --to 192.168.80.11
or
iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -i ens33 -d 12.0.0.1 -p tcp --dport 80 -j DNAT --to-destination 192.168.148.11
Inbound external network card Extranet IP Intranet server IP
iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -i ens33 -p tcp --dport 80 -j DNAT --to 192.168.80.11-192.168.148.20
1.5 modify DNAT conversion of target port during Publishing
#Publish the OpenSSH server inside the LAN, and the external network host needs to use port 250 for connection iptables one t nat -A PREROUTING -i ens33 -d 12.0.0.1 -p tcp --dport 250 -j DNAT --to 192.168.80.11:22 #Using SSH test in extranet environment ssh -p 250 root@12.0.0.1 yum -y install net-tools #If there is no ifconfig command, you can use yum to install it in advance ifconfig ens33
Note: when DNAT is used, it can be used together with SNAT to realize the correct return of response data packets
1.6 expansion
Host firewalls mainly use INPUT and OUTPUT chains. When setting rules, it is generally necessary to specify the ports in detail
The network firewall mainly uses the FORWARD chain. When setting rules, it is rarely specified to the port. Generally, it can be specified to the IP address or to the network segment
1.6.1 backup and restore of firewall rules
export(backups)Rules for all tables iptables-save > /opt/ ipt.txt
Import(reduction)rule iptables-restore < /opt/ ipt.txt
Rule quick restore take iptables The rule file is saved in/etc/sysconfig/iptables In, iptables The rules are automatically restored when the service starts iptables-save > /etc/sysconfig/ iptables systemctl stop iptables #Stopping iptables service will clear the rules of all tables systemctl start iptables #Starting iptables service will automatically restore the rules in / etc/ sysconfig/ iptables
tcpdump tcp -i ens33 -t -s 0 -C 100 and dst port ! 22 and src net 192.168.148.0/24 -w . /target. cap
tcp:ip, icmp, arp, rarp, tcp, udp, icmp and other options should be placed in the position of the first parameter to filter the type of datagram
-i ens33: only the packets passing through the interface ens33 are caught
-t: Do not show timestamp
-s 0: when fetching packets, the default fetching length is 68 bytes. After adding - s0, you can catch the complete packet
-c 100: grab only 100 packets
dst port ! 22: do not grab packets whose target port is 22
src net 192.168.148.0/24: the source network address of the packet is 192.168.148.0/24
-W . /target.cap: save as a cap file for easy analysis with ethereal (wireshark)