YUM overview
YUM
Software Update Mechanism Based on RPM Package Construction
Automatically resolving dependencies
All packages are provided by a centralized YUM software repository
The Way of Providing Software Warehouse
FTP service: ftp://...
HTTP service: http://...
Local directory: file://...
Sources of RPM Packages
Collection of RPM Packets Published by CentOS
RPM Packet Collection Published by Third Party Organizations
User-defined RPM package set
Building CentOS 7 Software Warehouse
RPM package from CentOS 7 CD
Provide to clients via FTP, HTTP, or local directories
FTP service name: vsftpd
FTP site: / var/ftp/centos7
Add unofficial RPM package groups to the software repository
Including all RPM packages with dependencies
Using createrepo Tool to Build Warehouse Data Files
View the YUM package
- yum info [software name] view service information
- yum list [software name] view yum repository
- Yum search & lt; keyword & gt; find out if there is software
Update YUM package
- yum update updates software packages, software and system kernels
- yun upgrade updates software packages, only updates software
Demo
Building remote YUM warehouse
1. Open two CentOS 7 virtual machines in VMware 15. One serves as a server to build local YUM warehouse and FTP service. The other serves as a client to use server remote service. The server is renamed demo01 and the client is renamed demo02.
[root@localhost ~]# hostnamectl set-hostname demo01 [root@localhost ~]# su [root@demo01 ~]#
[root@localhost ~]# hostnamectl set-hostname demo02 [root@localhost ~]# su [root@demo02 ~]#
2. Mount the CentOS 7 Mirror File into the mnt directory in demo01
[root@demo01 ~]# Df-hT// View disk information to see if mirror files are added to CD-ROM //File System Type Capacity Used Available% Mount Points /dev/sda2 xfs 20G 3.3G 17G 17% / devtmpfs devtmpfs 898M 0 898M 0% /dev tmpfs tmpfs 912M 0 912M 0% /dev/shm tmpfs tmpfs 912M 9.0M 903M 1% /run tmpfs tmpfs 912M 0 912M 0% /sys/fs/cgroup /dev/sda5 xfs 10G 37M 10G 1% /home /dev/sda1 xfs 6.0G 174M 5.9G 3% /boot tmpfs tmpfs 183M 12K 183M 1% /run/user/42 tmpfs tmpfs 183M 24K 183M 1% /run/user/0 /dev/sr0 iso9660 4.3G 4.3G 0 100% /run/media/root/CentOS 7 x86_64 //Read mirror files [root@demo01 ~]# Mount/dev/sr0/mnt// Mount the mirror file to the MNT directory mount: /dev/sr0 Write protection will be mounted as read-only [root@demo01 ~]# Ls/mnt//Successful mounting CentOS_BuildTag EULA images LiveOS repodata RPM-GPG-KEY-CentOS-Testing-7 EFI GPL isolinux Packages RPM-GPG-KEY-CentOS-7 TRANS.TBL
3. Install FTP service in demo01, and often see if the FTP site is successfully created.
[root@demo01 ~]# yum install vsftpd -y //Loaded plug-ins: fastest mirror, langpacks Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile * base: mirrors.zju.edu.cn * extras: mirrors.zju.edu.cn * updates: mirrors.zju.edu.cn //Resolving dependencies --> Inspection of affairs under way ---> software package vsftpd.x86_64.0.3.0.2-25.el7 Will be installed ...//Eliminate part of the content. //Installation in progress: vsftpd-3.0.2-25.el7.x86_64 1/1 //Verification: vsftpd-3.0.2-25.el7.x86_64 1/1 //Installed: vsftpd.x86_64 0:3.0.2-25.el7 //Complete! [root@demo01 ~]# Ls/var//View directory information account cache db ftp gopher lib lock mail opt run target yp adm crash empty games kerberos local log nis preserve spool tmp //Successful creation of FTP site
4. Create a directory in the FTP site as the source of YUM warehouse, copy the mounted mirror file into the source directory of YUM warehouse, then create a directory, and use the createrepo tool to create an extended directory.
[root@demo01 ~]# Cd/var/ftp//Enter FTP Site Directory [root@demo01 ftp]# ls // / View directory information pub [root@demo01 ftp]# mkdir centos7 // Create a directory as the source of YUM warehouse [root@demo01 ftp]# ls // / Check to see if the creation was successful centos7 pub [root@demo01 ftp]# Cp-rf/mnt/* centos7/&// Copy all mounted mirror files into YUM warehouse source directory and execute in the background [1] 2997 [root@demo01 ftp]# mkdir other// Create directories as extended directories [root@demo01 ftp]# ls // / Check to see if the creation was successful centos7 other pub [root@demo01 ftp]# Createrepo-g/mnt/repodata/repomd.xml other///Create extended data files using createrepo Saving Primary metadata Saving file lists metadata Saving other metadata Generating sqlite DBs Sqlite DBs complete [1]+ complete cp -i -rf /mnt/* centos7/ //Copy Mirror File Task Completion [root@demo01 ftp]# ls centos7 / // Check whether the file was successfully copied into the directory CentOS_BuildTag EULA images LiveOS repodata RPM-GPG-KEY-CentOS-Testing-7 EFI GPL isolinux Packages RPM-GPG-KEY-CentOS-7 TRANS.TBL [root@demo01 ftp]# cd other/repodata/// Enter the Extended Data File Directory [root@demo01 repodata]# ls // / Check whether the data file was successfully created 01a3b489a465bcac22a43492163df43451dc6ce47d27f66de289756b91635523-filelists.sqlite.bz2 401dc19bda88c82c403423fb835844d64345f7e95f5b9835888189c03834cc93-filelists.xml.gz 5dc1e6e73c84803f059bb3065e684e56adfc289a7e398946574d79dac6643945-primary.sqlite.bz2 5f62201963ee83e178738d9f88078560377cc06f972a4c0094ab3be00cae515f-repomd.xml 6bf9672d0862e8ef8b8ff05a2fd0208a922b1f5978e6589d87944c88259cb670-other.xml.gz 7c36572015e075add2b38b900837bcdbb8a504130ddff49b2351a7fc0affa3d4-other.sqlite.bz2 c48538ac0f65ece36eb71d41b76f1eb1f98c58cc26777348490feaed8f38ab56-repomd.xml.gz dabe2ce5481d23de1f4f52bdcfee0f9af98316c9e0de2ce8123adeefa0dd08b9-primary.xml.gz repomd.xml
5. Open FTP service and check whether the port is successfully opened. Then close the firewall and enhanced security function to facilitate client access to the server.
[root@demo01 repodata]# cd ~// Home Directory [root@demo01 ~]# System CTL start vsftpd // Open FTP service [root@demo01 ~]# Netstat-ntap | grep 21 // / Check whether port 21 is open tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:6010 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1621/sshd: root@pts tcp 0 0 192.168.144.133:22 192.168.144.1:49340 ESTABLISHED 1621/sshd: root@pts tcp6 0 0 :::21 :::* LISTEN 3183/vsftpd //Successfully opened tcp6 0 0 ::1:6010 :::* LISTEN 1621/sshd: root@pts [root@demo01 ~]# System CTL stop firewalld. service // / close firewall function [root@demo01 ~]# setenforce 0//Turn off Enhanced Security Function
6. Install FTP tools in client demo02 and use FTP tools to access server FTP sites.
[root@demo02 ~]# Yum install ftp-y//install FTP tools //Loaded plug-ins: fastest mirror, langpacks base | 3.6 kB 00:00:00 extras | 3.4 kB 00:00:00 updates | 3.4 kB 00:00:00 (1/4): base/7/x86_64/group_gz | 166 kB 00:00:25 ...//Eliminate part of the content. //Installation in progress: ftp-0.17-67.el7.x86_64 1/1 //Verification: ftp-0.17-67.el7.x86_641/1 //Installed: ftp.x86_64 0:0.17-67.el7 //Complete! [root@demo02 ~]# ftp 192.168.144.133//Access server FTP site Connected to 192.168.144.133 (192.168.144.133). 220 (vsFTPd 3.0.2) Name (192.168.144.133:root): ftp //Prompt for user name and use anonymous user access 331 Please specify the password. Password: //Input password prompt, anonymous user without password, just return directly. 230 Login successful. Remote system type is UNIX. Using binary mode to transfer files. //Successful visit ftp> ls //View server FTP site information 227 Entering Passive Mode (192,168,144,133,94,209). 150 Here comes the directory listing. drwxr-xr-x 8 0 0 220 Sep 17 09:00 centos7 //Established YUM Source Point Directory drwxr-xr-x 3 0 0 22 Sep 17 09:00 other //Extended data information drwxr-xr-x 2 0 0 6 Oct 30 2018 pub 226 Directory send OK. ftp> bye //Exit visit 221 Goodbye.
7. Enter the local YUM directory in the client, create a new directory in the directory, move the files from the source directory to the new directory, and then clear the YUM cache. Experiments are made to see if YUM can be used to install the software at this time.
[root@demo02 ~]# Cd/etc/yum.repos.d///Enter local Yum warehouse
[root@demo02 yum.repos.d]# ls // View
CentOS-Base.repo CentOS-Debuginfo.repo CentOS-Media.repo CentOS-Vault.repo
CentOS-CR.repo CentOS-fasttrack.repo CentOS-Sources.repo
[root@demo02 yum.repos.d]# mkdir bak // Create a new directory
[root@demo02 yum.repos.d]# mv *.repo bak / // / Move all suffix repo files to the BAK directory
[root@demo02 yum.repos.d]# ls // / View directory information
bak
[root@demo02 yum.repos.d]# ls bak / see bak directory information
CentOS-Base.repo CentOS-Debuginfo.repo CentOS-Media.repo CentOS-Vault.repo
CentOS-CR.repo CentOS-fasttrack.repo CentOS-Sources.repo //Successful migration to bak directory
[root@demo02 yum.repos.d]# yum clean all // clear yum cache
//Loaded plug-ins: fastest mirror, langpacks
Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile
There are no enabled repos.
Run "yum repolist all" to see the repos you have.
To enable Red Hat Subscription Management repositories:
subscription-manager repos --enable <repo>
To enable custom repositories:
yum-config-manager --enable <repo>
[root@demo02 yum.repos.d]# yum install httpd // install http services using yum
//Loaded plug-ins: fastest mirror, langpacks
Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile
There are no enabled repos.
Run "yum repolist all" to see the repos you have.
To enable Red Hat Subscription Management repositories:
subscription-manager repos --enable <repo>
To enable custom repositories:
yum-config-manager --enable <repo> //could not be installed8. Recreate the yum configuration file in the client Yum repository directory
[root@demo02 yum.repos.d]# vim centos7.repo//edit yum configuration file [base] name=centos7.Packages baseurl=ftp://192.168.144.133/centos7//Write the location of yum warehouse software enabled=1 gpgcheck=1 //Turn on key authentication gpgkey=ftp://192.168.144.133/centos7/RPM-GPG-KEY-CentOS-7//Input Key Location [other] name=other.Packages baseurl=ftp://192.168.144.133/other// Write an extended data file location for yum warehouse enabled=1 gpgcheck=0 ~ ~ ~ ~ :wq //Save and exit after completion
9. Reload the software information of Yum warehouse with the yum list command and install HTTP service with Yum to see if the yum warehouse is recreated
[root@demo02 yum.repos.d]# yum list//reload Yum repository Loaded plug-ins: fastest mirror, langpacks Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile ... [root@demo02 yum.repos.d]# Yum install httpd-y// install http services using yum Loaded plug-ins: fastest mirror, langpacks Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile Resolving dependencies --> Inspecting business The package httpd.x86_64.0.2.4.6-67.el7.centos will be installed ... Installed: httpd.x86_64 0:2.4.6-67.el7.centos Installed as a dependency: apr.x86_64 0:1.4.8-3.el7 apr-util.x86_64 0:1.5.2-6.el7 httpd-tools.x86_64 0:2.4.6-67.el7.centos mailcap.noarch 0:2.1.41-2.el7 Complete! // Successful installation
NFS Sharing Service
Network File System Network File System
Dependent on RPC (remote procedure call)
nsf-utils, rpcbind packages need to be installed
System Services nfs, rpcbind
Shared Profile: / etc/exports
Publishing shared resources using NFS
Install nfs-utils, rpcbind packages
yum install nfs-utils rpccbind
systemctl enable nfs
systemctl enable rpcbind
View service commands
Showmount-e to see if shared services are available
Demo
Building NFS Service
1. Open two CentOS 7 virtual machines in VMware 15. One serves as a server and the other serves as a client. The server provides storage space for the client to use. The server is renamed tast01 and the client is renamed tast02.
[root@localhost ~]# hostnamectl set-hostname tast01 [root@localhost ~]# su [root@tast01 ~]#
[root@localhost ~]# hostnamectl set-hostname tast02 [root@localhost ~]# su [root@tast02 ~]#
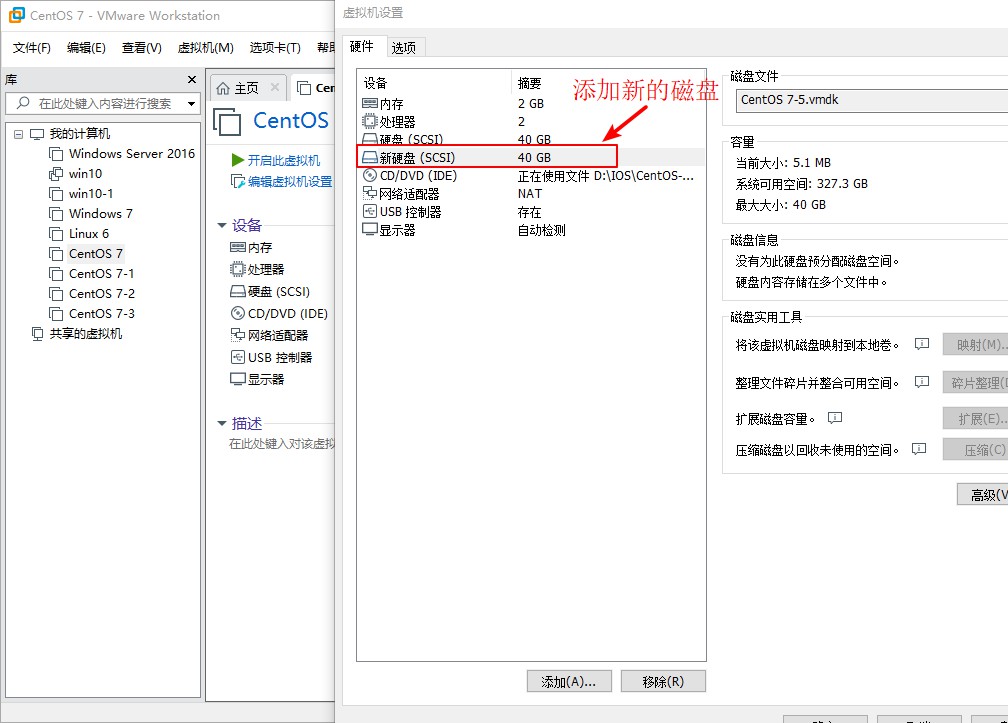
2. The newly added disk in the server is partitioned, formatted, and then automatically mounted in the mnt directory.
[root@tast01 ~]# Ls/dev/// Check the device directory to see if you can read the newly added hard disk
agpgart hugepages port sr0 tty23 tty42 tty61 vcs5
autofs hwrng ppp stderr tty24 tty43 tty62 vcs6
block initctl ptmx stdin tty25 tty44 tty63 vcsa
bsg input pts stdout tty26 tty45 tty7 vcsa1
btrfs-control kmsg random tty tty27 tty46 tty8 vcsa2
bus log raw tty0 tty28 tty47 tty9 vcsa3
cdrom loop-control rtc tty1 tty29 tty48 ttyS0 vcsa4
char lp0 rtc0 tty10 tty3 tty49 ttyS1 vcsa5
console lp1 sda tty11 tty30 tty5 ttyS2 vcsa6
core lp2 sda1 tty12 tty31 tty50 ttyS3 vfio
cpu lp3 sda2 tty13 tty32 tty51 uhid vga_arbiter
cpu_dma_latency mapper sda3 tty14 tty33 tty52 uinput vhci
crash mcelog sda4 tty15 tty34 tty53 urandom vhost-net
disk mem sda5 tty16 tty35 tty54 usbmon0 vmci
dri mqueue sdb tty17 tty36 tty55 usbmon1 vsock
fb0 net sg0 tty18 tty37 tty56 usbmon2 zero
fd network_latency sg1 tty19 tty38 tty57 vcs
full network_throughput sg2 tty2 tty39 tty58 vcs1
fuse null shm tty20 tty4 tty59 vcs2
hidraw0 nvram snapshot tty21 tty40 tty6 vcs3
hpet oldmem snd tty22 tty41 tty60 vcs4
[root@tast01 ~]# Fdisk/dev/sdb//Create disk partitions
//Welcome to fdisk (util-linux 2.23.2).
//Changes will stay in memory until you decide to write them to disk.
//Think twice before using write commands.
Device does not contain a recognized partition table
//Create a new DOS disk label using disk identifier 0xa928f95d.
//Command (Enter m for help):n
Partition type:
p primary (0 primary, 0 extended, 4 free)
e extended
Select (default p):
Using default response p
//Partition number (1-4, default 1):
//Start sector (2048-83886079, default 2048):
//The default value 2048 will be used
Last A sector, +A sector or +size{K,M,G} (2048-83886079,The default is 83886079):
//The default value 83886079 will be used
//Partition 1 has been set to the Linux type with a size of 40 GiB
//Command (Enter m for help):w
The partition table has been altered!
Calling ioctl() to re-read partition table.
//Synchronizing disks.
[root@tast01 ~]# Mkfs.xfs/dev/sdb1//formatted disk information
meta-data=/dev/sdb1 isize=512 agcount=4, agsize=2621376 blks
= sectsz=512 attr=2, projid32bit=1
= crc=1 finobt=0, sparse=0
data = bsize=4096 blocks=10485504, imaxpct=25
= sunit=0 swidth=0 blks
naming =version 2 bsize=4096 ascii-ci=0 ftype=1
log =internal log bsize=4096 blocks=5119, version=2
= sectsz=512 sunit=0 blks, lazy-count=1
realtime =none extsz=4096 blocks=0, rtextents=0
[root@tast01 ~]# Vim/etc/fstab//Enter Edit Automount Profile
#
# /etc/fstab
# Created by anaconda on Sat Aug 10 03:42:29 2019
#
# Accessible filesystems, by reference, are maintained under '/dev/disk'
# See man pages fstab(5), findfs(8), mount(8) and/or blkid(8) for more info
#
UUID=729c9a26-dfdc-40f9-ae91-1ade55be51bb / xfs defaults 0 0
UUID=9559d8d9-8f6a-4adb-a41f-02862b167946 /boot xfs defaults 0 0
UUID=5ed35562-b598-43e0-8f8a-db788aa06d40 /home xfs defaults 0 0
UUID=bcc2cc5c-4f4e-4e1d-b4e1-245cfed5cf9d swap swap defaults 0 0
/dev/sdb1/ /mnt xfs defaults 0 0 //Setting up automatic mounting of sdb1 disk
~
~
~
~
:wq //Save exit
[root@tast01 ~]# Mount-a//Load Automount Files
[root@tast01 ~]# Df-h//View Disk Information
//File system capacity used Available% mount point
/dev/sda2 20G 3.3G 17G 17% /
devtmpfs 898M 0 898M 0% /dev
tmpfs 912M 0 912M 0% /dev/shm
tmpfs 912M 9.0M 903M 1% /run
tmpfs 912M 0 912M 0% /sys/fs/cgroup
/dev/sda5 10G 37M 10G 1% /home
/dev/sda1 6.0G 174M 5.9G 3% /boot
tmpfs 183M 12K 183M 1% /run/user/42
tmpfs 183M 0 183M 0% /run/user/0
/dev/sdb1 40G 33M 40G 1% /mnt //Successful mount3. Install the NFS package in the server and set the service as boot-up and self-start
[root@tast01 ~]# Yum install nfs-utlis rpcbind-y//install software //Loaded plug-ins: fastest mirror, langpacks base | 3.6 kB 00:00:00 extras | 3.4 kB 00:00:00 updates | 3.4 kB 00:00:00 (1/4): base/7/x86_64/group_gz | 166 kB 00:00:25 ...//Eliminate part of the content. //Verification: rpcbind-0.2.0-47.el7.x86_641/2 //Verification: rpcbind-0.2.0-42.el7.x86_64 2/2 //Updated: rpcbind.x86_64 0:0.2.0-47.el7 //Complete! [root@tast01 ~]# System CTL enable NFS // / Set up boot-up self-startup Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/nfs-server.service to /usr/lib/systemd/system/nfs-server.service. [root@tast01 ~]# System CTL enable rpcbind // / Settings Open Self-Start Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/rpcbind.service to /usr/lib/systemd/system/rpcbind.service.
4. Edit the NFS service profile and start the service to see if the service is enabled; close the firewall and enhanced security functions; and then use the command to see if the service is available.
[root@tast01 ~]# Vim/etc/exports//edit shared service configuration file /mnt 192.168.144.0/24(rw,sync,no_root_squash) //Configuration of shared disks, usable segment information, readable and writable permissions, synchronization information, without degrading processing ~ ~ ~ :wq //Save exit [root@tast01 ~]# System CTL start NFS // start service [root@tast01 ~]# System CTL start rpcbind // start service [root@tast01 ~]# Netstat-ntap | grep RPC // / Check if the service is started tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:20048 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 3774/rpc.mountd tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:37286 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 3773/rpc.statd tcp6 0 0 :::20048 :::* LISTEN 3774/rpc.mountd tcp6 0 0 :::52041 :::* LISTEN 3773/rpc.statd //Successful startup [root@tast01 ~]# System CTL stop firewalld. service // / close firewall [root@tast01 ~]# setenforce 0//Turn off Enhanced Safety Function [root@tast01 ~]# Showmount-e//Check if the service is available Export list for tast01: /mnt 192.168.144.0/24 //Successful service delivery
5. Turn off the firewall function and enhanced security function in the client, because we need to use the client to provide website services to facilitate our access to the website, and then install http services.
[root@tast02 ~]# systemctl stop firewalld.service [root@tast02 ~]# setenforce 0 [root@tast02 ~]# yum install httpd -y Loaded plug-ins: fastest mirror, langpacks Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile * base: mirrors.163.com * extras: mirrors.163.com * updates: mirrors.cn99.com Resolving dependencies --> Inspecting business The package httpd.x86_64.0.2.4.6-89.el7.centos.1 will be installed ... Installed: httpd.x86_64 0:2.4.6-89.el7.centos.1 Installed as a dependency: apr.x86_64 0:1.4.8-3.el7_4.1 apr-util.x86_64 0:1.5.2-6.el7 httpd-tools.x86_64 0:2.4.6-89.el7.centos.1 mailcap.noarch 0:2.1.41-2.el7 Complete!
6. The client http service site uses the disk added in the server to store the website information, and automatically mounts the disk settings added by the server to the http service site in the client.
[root@tast02 ~]# Vim/etc/fstab//edit automount configuration file # # /etc/fstab # Created by anaconda on Sat Aug 10 03:42:29 2019 # # Accessible filesystems, by reference, are maintained under '/dev/disk' # See man pages fstab(5), findfs(8), mount(8) and/or blkid(8) for more info # UUID=729c9a26-dfdc-40f9-ae91-1ade55be51bb / xfs defaults 0 0 UUID=9559d8d9-8f6a-4adb-a41f-02862b167946 /boot xfs defaults 0 0 UUID=5ed35562-b598-43e0-8f8a-db788aa06d40 /home xfs defaults 0 0 UUID=bcc2cc5c-4f4e-4e1d-b4e1-245cfed5cf9d swap swap defaults 0 0 192.168.144.133:/mnt /var/www/html nfs defaults,_netdev 0 0 //Add automount entries ~ ~ ~ :wq //Save exit [root@tast02 ~]# Mount-a//reload mount information [root@tast02 ~]# df -hT //File System Type Capacity Used Available% Mount Points /dev/sda2 xfs 20G 3.4G 17G 17% / devtmpfs devtmpfs 898M 0 898M 0% /dev tmpfs tmpfs 912M 0 912M 0% /dev/shm tmpfs tmpfs 912M 9.0M 903M 1% /run tmpfs tmpfs 912M 0 912M 0% /sys/fs/cgroup /dev/sda5 xfs 10G 37M 10G 1% /home /dev/sda1 xfs 6.0G 174M 5.9G 3% /boot tmpfs tmpfs 183M 12K 183M 1% /run/user/42 tmpfs tmpfs 183M 0 183M 0% /run/user/0 192.168.144.133:/mnt nfs4 40G 33M 40G 1% /var/www/html //Successful mount
7. Edit the index.html file in the http service site, and then enable the http service.
[root@tast02 ~]# Cd/var/www/html///Enter the site [root@tast02 html]# ls // / See if there are any files [root@tast02 html]# vim index.html//edit index.html file <h1>this is nfs web </h1> //Editorial content ~ ~ ~ :wq //Save exit [root@tast02 html]# cat index.html // View index.html content <h1>this is nfs web </h1> //Display content information [root@tast02 html]# System CTL start httpd // enable http services
8. Visit the http website built by the client in the host to see if the service is successfully built.
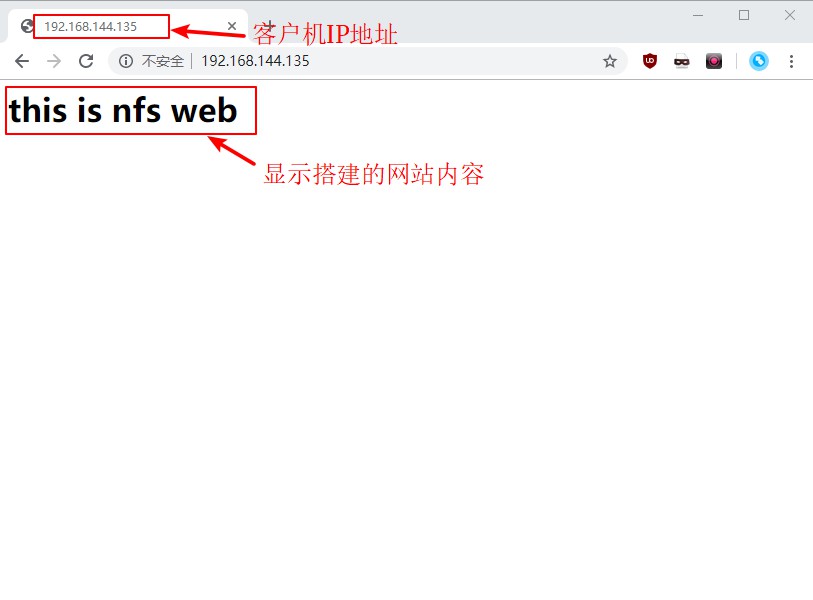
9. Go back to the server to see if there is an index.html file we edited in the mnt directory, and then check whether the content of the file is our edited content.
[root@tast01 ~]# Cd/mnt//Enter MNT directory [root@tast01 mnt]# ls // / View directory content index.html //Display the files we created [root@tast01 mnt]# cat index.html // / View file content <h1>this is nfs web </h1> //Show what we wrote