First, complete sub task 3: configure and install nginx. It's smooth and successful at one time
Step 1: installation environment
Note: before installing these environments, you can check whether you have installed them. If you have, you don't need to install them again
rpm -qa | grep gcc

We can find that we have it now
If not:
1, gcc installation. To install nginx, you need to compile the source code downloaded from the official website. The compilation depends on the gcc environment. If there is no gcc environment, you need to install:
yum install -y gcc-c++
2, PCRE devel installation
PCRE(Perl Compatible Regular Expressions) is a perl library, including perl compatible regular expression libraries. The http module of nginx uses pcre to parse regular expressions, so it is necessary to install pcre library on linux. pcre devel is a secondary development library developed using pcre. Nginx also needs this library. Command:
yum install -y pcre pcre-devel
3, zlib installation
Zlib library provides many ways of compression and decompression. nginx uses zlib to gzip the contents of http package, so you need to install zlib library on Centos.
yum install -y zlib zlib-devel
4, OpenSSL installation
OpenSSL is a powerful secure socket layer cryptographic library, including the main cryptographic algorithms, common key and certificate encapsulation management functions and SSL protocol, and provides rich applications for testing or other purposes.
nginx supports not only http protocol, but also https (that is, http is transmitted over ssl Protocol), so you need to install OpenSSL Library in Centos.
yum install -y openssl openssl-devel
Although we have the first gcc here, I still need to implement the following three:

Step 2: Download and unzip
1. Download nginx link: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1Wxvle1ZhWoLeyDddsccNlw
Extraction code: p9d5
– sharing from Baidu online disk super member V3
2. Unzip: tar -zxvf nginx-1.18.0.tar.gz -C /usr/local (unzip to C/user/local directory)
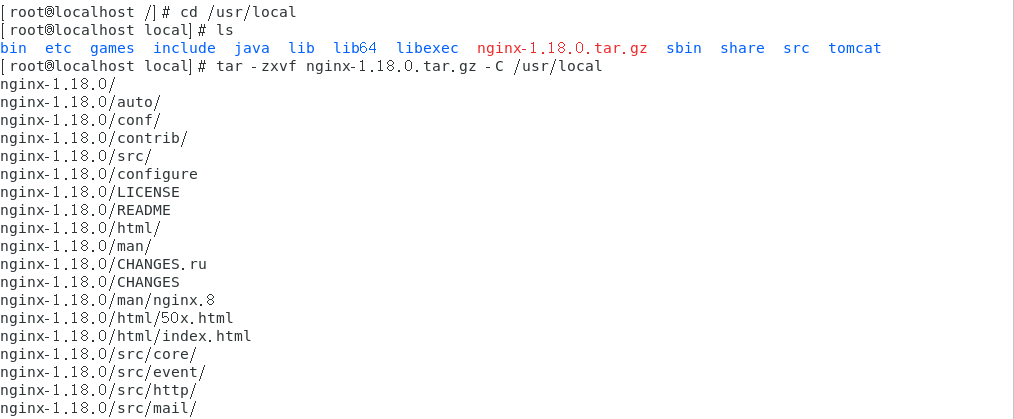
3. Rename
tar -zxvf nginx-1.18.0.tar.gz -C /usr/local
Step 3: Configure
cd /usr/local/nginx Enter into nginx folder ./configure Use default configuration
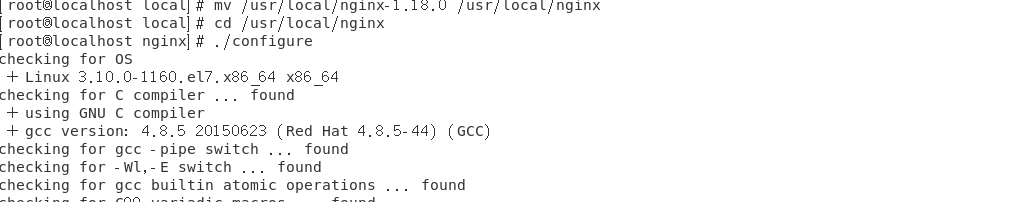
Step 4: compile and install
make && make install
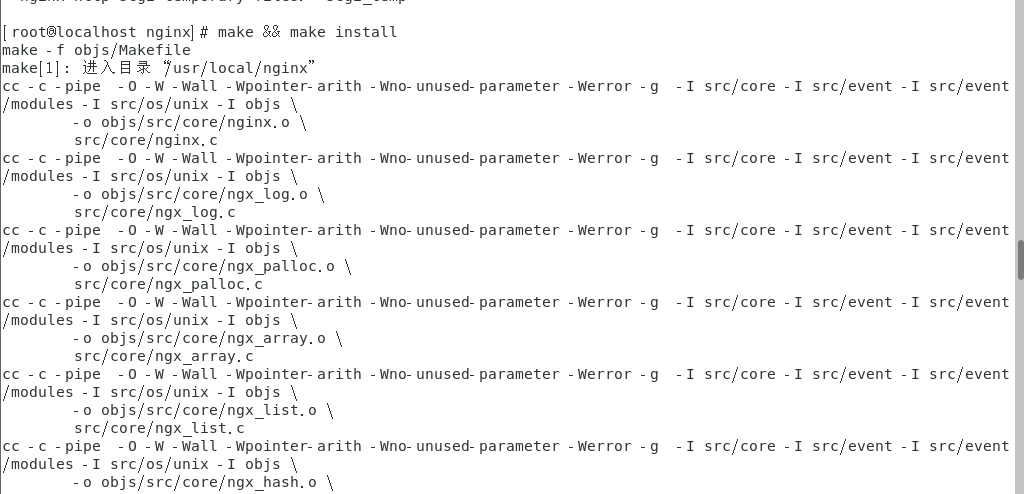
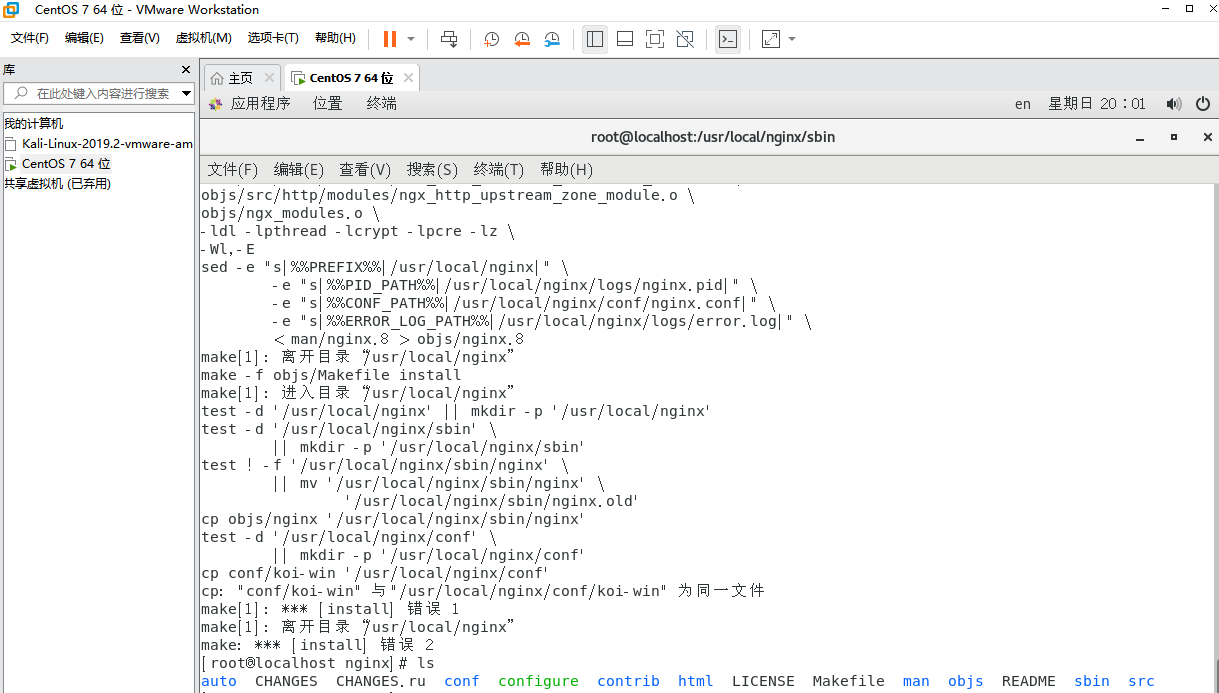
Step 5: start nginx (an error will be reported here)
cd /usr/local/nginx/sbin/ Enter into nginx of sbin catalogue ./nginx start-up nginx

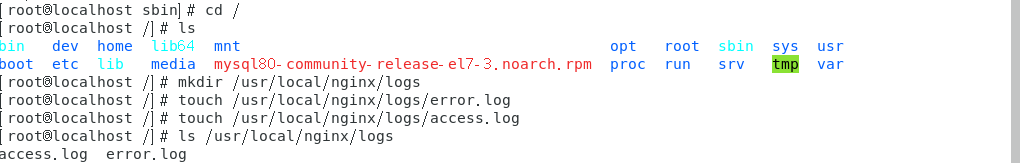
According to the error message, we can see that we do not have folders and files. Create new folders and files
mkdir /usr/local/nginx/logs create folder touch /usr/local/nginx/logs/error.log create a file touch /usr/local/nginx/logs/access.log create a file ls /usr/local/nginx/logs see
Step 6: 1. Start nginx
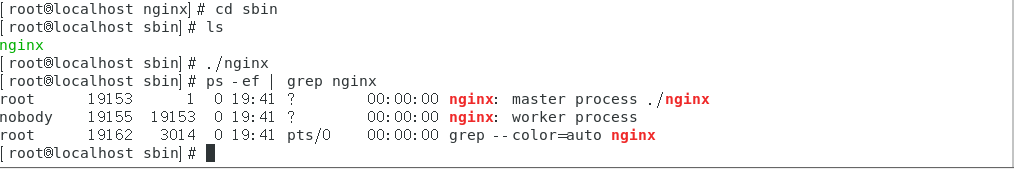
View nginx process
ps -ef | grep nginx
3. Stop nginx
./nginx -s quit: The stop step in this way is to wait nginx The process finished processing the task and stopped. ./nginx -s stop: This method is equivalent to finding out first nginx process id Reuse kill The command forces the process to be killed. ./nginx -s reload restart nginx(This method is not recommended. It is recommended to stop before starting)
Reload profile
After the configuration file nginx.conf of ngin x is modified, you need to restart nginx to make the configuration effective. Use. / nginx -s reload to make the configuration information effective in nginx without stopping nginx and then starting nginx
Step 7: open port 80 (the last article was written in detail here)
Last ip+80 access:
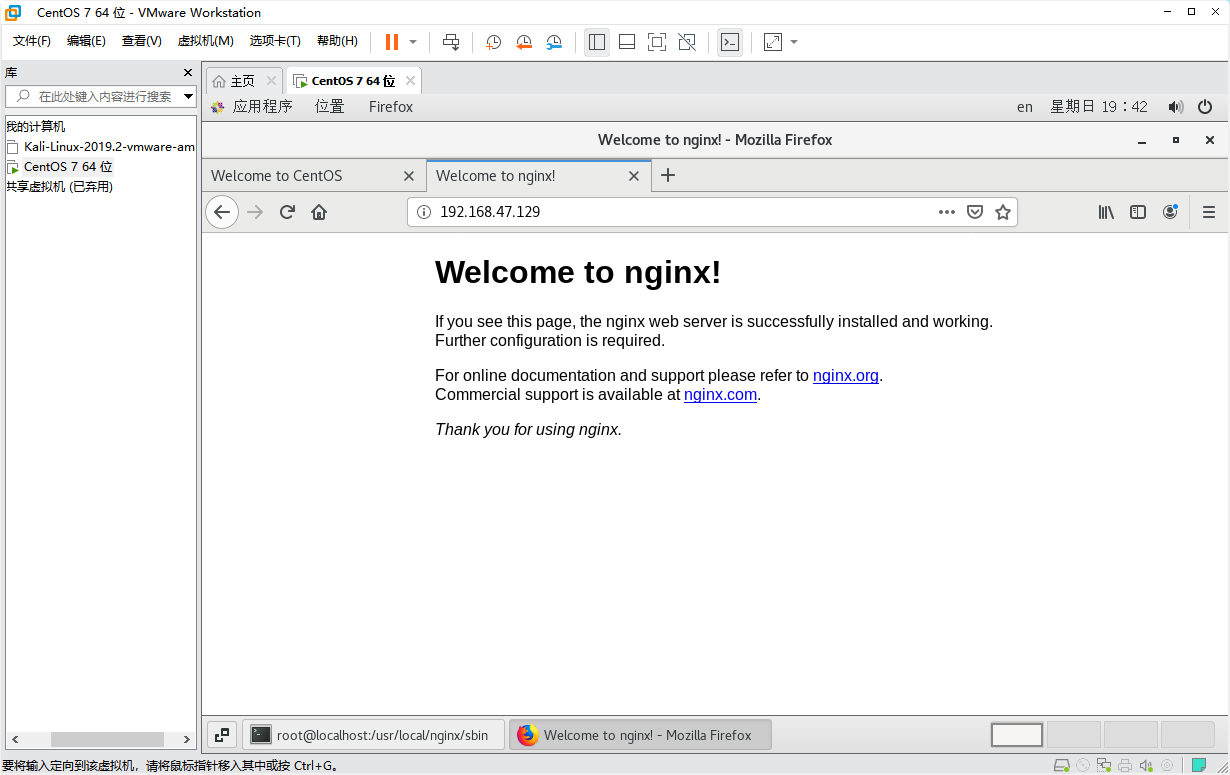
success!
Nginx configuration file nginx.conf description
#user nobody;
worker_processes 1; #Work process: number. According to the hardware adjustment, it is usually equal to the number of CPUs or twice the number of CPUs.
#Error log storage path
#error_log logs/error.log;
#error_log logs/error.log notice;
#error_log logs/error.log info;
#pid logs/nginx.pid; # pid storage path of nginx process
events {
worker_connections 1024; # Maximum number of connections for worker processes
}
http {
include mime.types; #Specifies the MIME type, which is defined by mime.type
default_type application/octet-stream;
# Log format settings
#log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
# '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
# '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
#access_log logs/access.log main; #Use log_ After the format instruction sets the log format, you need to use access_log to specify the storage path of log files
sendfile on; #Specify whether nginx calls the sendfile function to output the file. For normal applications, on must be set.
If the disk is used for downloading and other applications io Heavy load application, can be set off,To balance disk and network io Processing speed, reduce system uptime.
#tcp_nopush on; #This option allows or disables TCP using socket s_ The option of cork, which is only used when sendfile
#keepalive_timeout 0; #keepalive timeout
keepalive_timeout 65;
#gzip on; #Open gzip compression service
#Virtual host
server {
listen 80; #Configure listening port number
server_name localhost; #Configure the access domain name. There can be multiple domain names separated by spaces
#charset koi8-r; #Character set settings
#access_log logs/host.access.log main;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
#Error jump page
#error_page 404 /404.html;
# redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html
#
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
# proxy the PHP scripts to Apache listening on 127.0.0.1:80
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1;
#}
# pass the PHP scripts to FastCGI server listening on 127.0.0.1:9000
#
#location ~ \.php$ { #Request url filtering, regular matching, ~ is case sensitive, ~ * is case insensitive.
# root html; #root directory
# fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000; #Request to turn to the defined list of servers
# fastcgi_index index.php; # If the requested fastcgi_ The index URI ends with /, and the file set by the instruction will be appended to the URI and saved in the variable $fastcig_ script_ In name
# fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /scripts$fastcgi_script_name;
# include fastcgi_params;
#}
# deny access to .htaccess files, if Apache's document root
# concurs with nginx's one
#
#location ~ /\.ht {
# deny all;
#}
}
# another virtual host using mix of IP-, name-, and port-based configuration
#
#server {
# listen 8000;
# listen somename:8080;
# server_name somename alias another.alias;
# location / {
# root html;
# index index.html index.htm;
# }
#}
# HTTPS server
#
#server {
# listen 443 ssl; #Listening port
# server_name localhost; #domain name
# ssl_certificate cert.pem; #Certificate location
# ssl_certificate_key cert.key; #Private key location
# ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:1m;
# ssl_session_timeout 5m;
# ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5; #Password encryption method
# ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on; # ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on; #
# location / {
# root html;
# index index.html index.htm;
# }
#}
Remember to take a snapshot!!!!
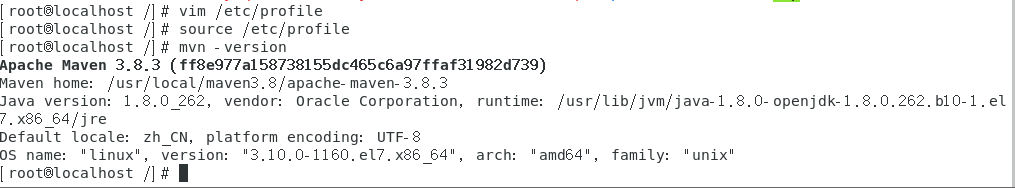
Install and configure the Maven/Gradle running environment in the virtual machine. After the configuration is completed, run the "mvn -v" command in the terminal console to test whether the configuration is correct (this is also a one-time success)
1: First, import the Maven compressed package: Apache Maven official download address: https://maven.apache.org/download.cgi
Link: https://pan.baidu.com/s/11XPAjjbmtf0kw-_Nw4iRpA Extraction code: csuc --From Baidu online disk super member V3 Sharing
2: . unzip the downloaded Maven installation package (the location is arranged by yourself)
3. Set Maven's domestic image address (Alibaba cloud is used here)
Find the conf folder under the Maven folder (switch to the conf file directory: cd conf), open the settings.xml configuration file (open the settings.xml file: vim settings.xml), and add the following code (if there is no comment on the original image address, comment it out first): ), press [ESC] after adding, and then enter [: x] to save and exit editing:
<mirror>
<id>alimaven</id>
<name>aliyun maven</name>
<url>https://maven.aliyun.com/nexus/content/groups/public/</url>
<mirrorOf>central</mirrorOf>
</mirror>
4. Set Maven local warehouse file directory (mainly used to save downloaded jar files)
First, determine where the jar is saved (here I save it in the / opt/apache-maven-3.6.3/LocalJAR directory, you can create a file directory through the mkdir command, and it is recommended to save it in the Maven directory), find the conf folder under the Maven folder (switch to the conf file directory: cd conf), open the settings.xml configuration file, and open the settings.xml file: vim settings.xml), Add the following code, press [ESC] after adding, and then enter [: x] to save and exit editing:
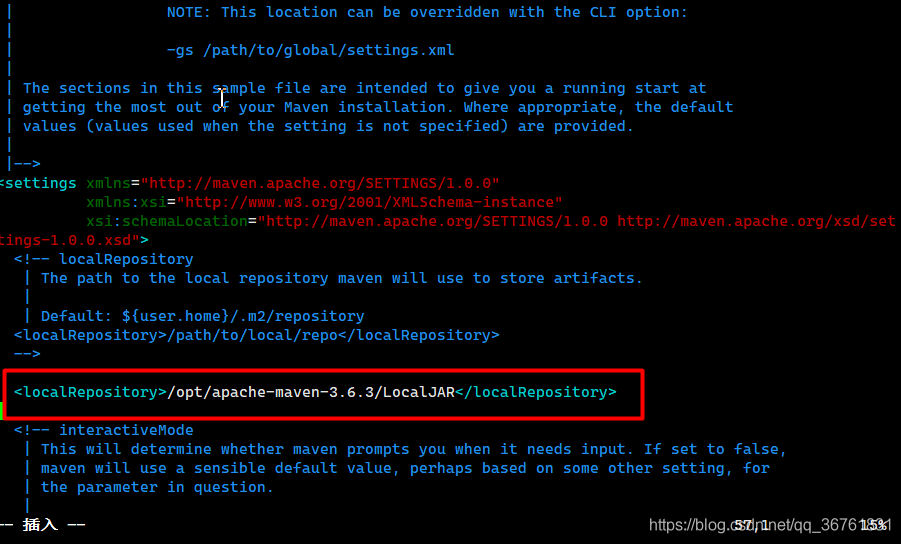
5. Specify the JDK Version (set the JDK version of the project created by Maven)
Add the following code:
<profile>
<id>jdk-1.8</id>
<activation>
<activeByDefault>true</activeByDefault>
<jdk>1.8</jdk>
</activation>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>1.8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>1.8</maven.compiler.target>
<maven.compiler.compilerVersion>1.8</maven.compiler.compilerVersion>
</properties>
</profile>
6. Configure Maven environment variables
Open environment variable configuration file command: vim /etc/profile
Add the following configuration at the end of the file
#Your maven path
MAVEN_HOME=/usr/local/maven/apache-maven-3.6.1
export PATH=${MAVEN_HOME}/bin:${PATH}
Reload environment variables: source /etc/profile
7. View results: mvn -version